Home>Instruments>Brass Instruments>What Does The Trombone Have That The Other Brass Instruments Do Not?


Brass Instruments
What Does The Trombone Have That The Other Brass Instruments Do Not?
Modified: January 22, 2024
Discover the unique qualities of the trombone and its distinct features among brass instruments. Explore the versatility and rich sound of this beloved instrument.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
The trombone, with its distinctive slide and powerful sound, holds a special place in the world of brass instruments. Its unique design gives it a range of capabilities that set it apart from other members of the brass family, such as the trumpet or French horn. With its rich history, versatile playing techniques, and wide range of musical applications, the trombone has earned a well-deserved reputation as a fascinating and essential instrument.
Originating from ancient times, the trombone has undergone numerous changes and developments during its evolution. Its distinctive slide allows for smooth and precise pitch control, offering a flexibility that is unmatched by valves. This versatility allows the trombone to perform a wide array of musical genres, from the powerful and majestic sound in orchestras to the lively improvisations in jazz ensembles.
In this article, we will delve into the world of trombones, exploring the instrument’s history, anatomy, unique features, and playing techniques. We will also compare the trombone to other brass instruments and explore the trombone’s role in different musical genres. Whether you’re a music enthusiast, a beginner player, or simply curious about the trombone, this article will take you on an informative and captivating journey through the world of this fascinating instrument.
History of the Trombone
The trombone has a rich and fascinating history that dates back centuries. Its origins can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where early versions of brass instruments were used for ceremonial purposes and in military bands. However, it was during the Renaissance period in the 15th century that the trombone, as we know it today, first emerged.
During this time, the trombone underwent significant developments in both design and functionality. The addition of a slide allowed for greater control over pitch and extended the instrument’s range. This innovation led to the instrument being used in various ensembles, including the orchestra, where it played a vital role in providing harmonic support and adding depth to the sound.
In the 18th and 19th centuries, the trombone underwent further advancements, with improvements to the slide mechanism and refinements to the instrument’s overall design. Composers such as Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart and Ludwig van Beethoven began including specific parts for the trombone in their compositions, recognizing its unique capabilities and its ability to add grandeur and expressiveness to their music.
During the 20th century, the trombone experienced a surge in popularity, thanks to the rise of jazz music. Jazz trombonists, such as J.J. Johnson and Tommy Dorsey, showcased the instrument’s versatility and expressive potential, pushing its boundaries and establishing it as a prominent solo instrument in the genre.
Today, the trombone remains an integral part of various musical genres, including classical, jazz, and even popular music. Its distinct sound, range, and ability to play both melody and harmony make it a standout amongst other brass instruments. The trombone’s rich history and continued evolution have shaped it into a versatile and indispensable instrument that continues to captivate audiences worldwide.
The Anatomy of the Trombone
The trombone is a brass instrument that consists of several key components, each playing a vital role in producing its unique sound. Understanding the anatomy of the trombone is crucial for players to develop a deep understanding of the instrument and maximize their performance capabilities.
The main parts of the trombone include the bell, slide, mouthpiece, and the various tubing sections. The bell is the flared end of the instrument, responsible for projecting the sound. The slide, consisting of two inner tubes, allows the player to change the pitch by extending or contracting it. This distinguishing feature sets the trombone apart from other brass instruments, which utilize valves to achieve the same effect.
The mouthpiece is a small, cup-shaped component that the player blows air into to create sound. It is an essential element that greatly influences the timbre and tone quality of the trombone. Different shapes and sizes of mouthpieces can produce variations in sound, allowing players to customize their playing experience.
Another crucial aspect of the trombone’s anatomy is the tubing sections. The trombone typically consists of a large, cylindrical section called the leadpipe, followed by the main tubing portion, and culminating in the bell. The length and diameter of the tubing determine the fundamental pitch of the instrument and play a significant role in its overall timbre and projection.
Within the tubing sections, players will find various tuning slides that help adjust the instrument’s pitch and intonation. These slides can be adjusted for precise tuning and are crucial for maintaining accurate pitch during performances.
Lastly, the trombone also features various braces and braces that provide structural support and strength to the instrument. These components ensure that the trombone remains stable and durable under the pressure of playing.
Understanding the anatomy of the trombone is not only important for players but also for anyone who appreciates the instrument and its unique sound. Each component works harmoniously together, allowing the trombone to produce its characteristic rich and resonant tones. The combination of the bell, slide, mouthpiece, and tubing creates a beautiful and versatile instrument that has captivated audiences for centuries.
Unique Features of the Trombone
The trombone possesses a set of distinctive features that set it apart from other brass instruments, contributing to its unique sound and versatility. These features play a significant role in shaping the character and capabilities of the trombone.
One of the most distinct aspects of the trombone is its sliding mechanism. Unlike other brass instruments that utilize valves to change pitch, the trombone’s slide allows for smooth and precise adjustments. This sliding action provides players with unparalleled control over intonation, allowing for seamless glissandos, expressive phrasing, and subtle microtonal shifts. The slide also enables the trombone to produce smooth legato lines and rapid articulations, adding to its expressive range.
Another unique attribute of the trombone is its wide range. The trombone can produce rich and sonorous low notes, filling the role of the bass voice in ensembles. Simultaneously, it can also reach impressive heights, soaring above the orchestra or jazz band. The trombone’s extensive range allows for melodic and expressive playing across different musical genres and styles.
The trombone’s larger bore size compared to other brass instruments contributes to its powerful and resonant sound. The wide bore accentuates the trombone’s rich harmonic spectrum, giving it a warm and vibrant tone. This tonal quality makes the trombone well-suited for lyrical passages, blending in with other brass instruments, or taking center stage as a solo instrument.
In addition to its tonal qualities, the trombone’s wide range of playing techniques adds to its unique features. Techniques such as growling, flutter tonguing, and multiphonics can be achieved on the trombone, enhancing its expressiveness and expanding its tonal palette. Moreover, the use of mutes, such as the wah-wah mute or plunger, further extends the instrument’s versatility, allowing for a range of muted and distinctive effects.
Lastly, the trombone’s role in the brass section of an ensemble gives it a unique position. It often serves as the backbone of the brass section, providing a solid foundation and harmonic support. At the same time, the trombone is capable of taking on melodic roles, showcasing its agility and versatility.
The unique combination of the sliding mechanism, wide range, tonal qualities, playing techniques, and ensemble role make the trombone a truly remarkable instrument. Its versatility and expressive capabilities have earned it a place in various musical genres, from orchestral and chamber music to jazz and contemporary styles, ensuring its continued prominence and fascination among musicians and audiences alike.
Versatility of the Trombone
The trombone is renowned for its versatility, making it a versatile and adaptable instrument across various musical genres. Its wide range of pitch, expressive capabilities, and unique tonal qualities allow it to seamlessly transition between different musical styles and settings.
In the classical music realm, the trombone plays a crucial role in orchestras and wind ensembles. Its robust and resonant sound enables it to blend well with other brass instruments, providing a solid foundation for the ensemble. From the powerful harmonies of a symphony to the delicate melodies of a chamber music piece, the trombone adds depth, richness, and grandeur to classical compositions.
Moreover, the trombone is an essential part of jazz music, where its versatility truly shines. In jazz ensembles, trombonists often take on both supporting and solo roles. The trombone’s slide allows for expressive techniques such as glissandos, smears, and flutter tonguing, ideal for improvisation and creating unique tonal colors. Jazz trombonists have the freedom to explore various styles and playing techniques, showcasing the instrument’s adaptability in blues, swing, bebop, and more.
Besides classical and jazz, the trombone has found its place in other genres as well. In Latin music, the trombone contributes to the energetic and rhythmic sections, adding a vibrant and soulful sound to salsa, merengue, and other Latin styles. In contemporary genres like rock, pop, and funk, trombone players infuse their distinct sound into horn sections, lending a dynamic and punchy element to the music.
Furthermore, the trombone’s versatility extends beyond traditional music genres. It has been embraced in experimental and avant-garde compositions, where its wide pitch range and unique timbre contribute to innovative and unconventional soundscapes. From contemporary classical to film scores, the trombone’s versatility allows it to adapt to even the most eclectic and boundary-pushing musical expressions.
Whether interpreting classical masterpieces, taking center stage in a jazz solo, contributing to the infectious rhythms of Latin music, or exploring experimental soundscapes, the trombone effortlessly adapts to diverse musical contexts. Its ability to convey a wide range of emotions, from sublime and majestic to raw and gritty, makes it a versatile and captivating instrument that continues to inspire musicians across genres and generations.
Playing Techniques on the Trombone
The trombone offers a wide range of playing techniques that allow musicians to explore different tonal colors, expressiveness, and musical effects. From traditional techniques to modern innovations, these techniques contribute to the instrument’s versatility and artistic capabilities.
One of the fundamental techniques on the trombone is the lip buzzing or embouchure control. By manipulating the position of their lips and controlling the airflow, players can produce a variety of tones and pitches. Adjusting the tightness or looseness of the embouchure, trombonists can achieve different timbres and dynamic variations.
Another key technique on the trombone is the use of the slide. The slide allows players to change the pitch smoothly and precisely. Sliding outward lowers the pitch, while sliding inward raises it. Mastering the slide technique is crucial for playing accurate intonation, executing glissandos (smooth slides between pitches), and producing expressive musical phrases.
Articulation is another essential aspect of trombone playing. By using the tongue to start notes with crisp attacks, players can articulate different rhythmic patterns and create accents. Techniques such as legato (smooth and connected notes) and staccato (short and detached notes) add further depth and expression to musical performances.
The trombone also offers the ability to perform vibrato, a technique that introduces subtle variations in pitch to add expressiveness and warmth to the sound. Vibrato on the trombone is achieved by subtly moving the slide in a rhythmic and controlled manner while sustaining a note.
Various extended techniques have been developed for the trombone to expand its sonic possibilities. These techniques include growling, a vocal-like effect produced by simultaneously humming or singing while playing the trombone, resulting in a gritty or distorted sound. Flutter tonguing, achieved by rolling the tongue to create a fluttering sound, adds a fluttering or buzzing effect to the notes.
Mutes are another playing technique that trombone players utilize to alter the instrument’s sound. Mutes, such as the straight mute or cup mute, are inserted into the bell to change the timbre, volume, and character of the trombone’s sound, adding a unique color to the music.
Lastly, the trombone offers the opportunity for advanced techniques such as multiphonics, where players produce more than one pitch simultaneously, and microtonal playing, which involves adjusting the slide to achieve pitches that fall between the traditional half steps.
Mastering these playing techniques on the trombone requires practice, dedication, and a deep understanding of the instrument. Trombonists who can skillfully employ these techniques can unlock a world of expressive possibilities, bringing their musical performances to life with nuance, emotion, and a personal artistic touch.
Comparison of the Trombone with Other Brass Instruments
When comparing the trombone to other brass instruments, such as the trumpet, French horn, and tuba, several key differences stand out. These differences in design, playing technique, and sound production contribute to the distinct characteristics and roles of each instrument within the brass family.
The most striking difference between the trombone and other brass instruments is the slide mechanism. While the trumpet, French horn, and tuba utilize valves to change pitch, the trombone relies on the slide, allowing for smooth and precise adjustments. This sliding action provides trombonists with unparalleled control over intonation and enables seamless glissandos and expressive phrasing not easily achieved on valve-based instruments.
Another notable difference is the mouthpiece size and shape. The trombone’s mouthpiece is larger and deeper compared to the trumpet and French horn mouthpieces, allowing for a broader, more resonant sound. The tuba, on the other hand, has the largest mouthpiece among brass instruments, producing a deep and rich bass sound.
In terms of range, the trombone falls between the trumpet and French horn. The trumpet has the highest range, capable of playing piercing high notes, while the French horn’s range extends deeper into the lower register. The trombone, with its wider bore and larger size, offers a wider range than the French horn and produces rich and sonorous low notes, making it suitable for bass and tenor parts.
When it comes to their roles in ensembles, each instrument assumes a specific role. The trumpet often takes on melodic parts and stands out as a prominent solo instrument. The French horn is known for its characteristic mellow and rich sound, often playing lyrical melodies and adding depth to harmonies. The trombone is versatile, excelling in harmonic support, basslines, and its ability to blend with other brass instruments or stand out as a soloist.
Sound production also differs among these brass instruments. The trumpet produces a bright and piercing sound, while the French horn’s sound is warmer and more rounded. The trombone’s wide bore contributes to its rich and resonant sound, capable of producing both powerful and expressive tones. The tuba, with its large size and deep cup mouthpiece, creates a deep and majestic sound, providing a solid foundation in brass sections.
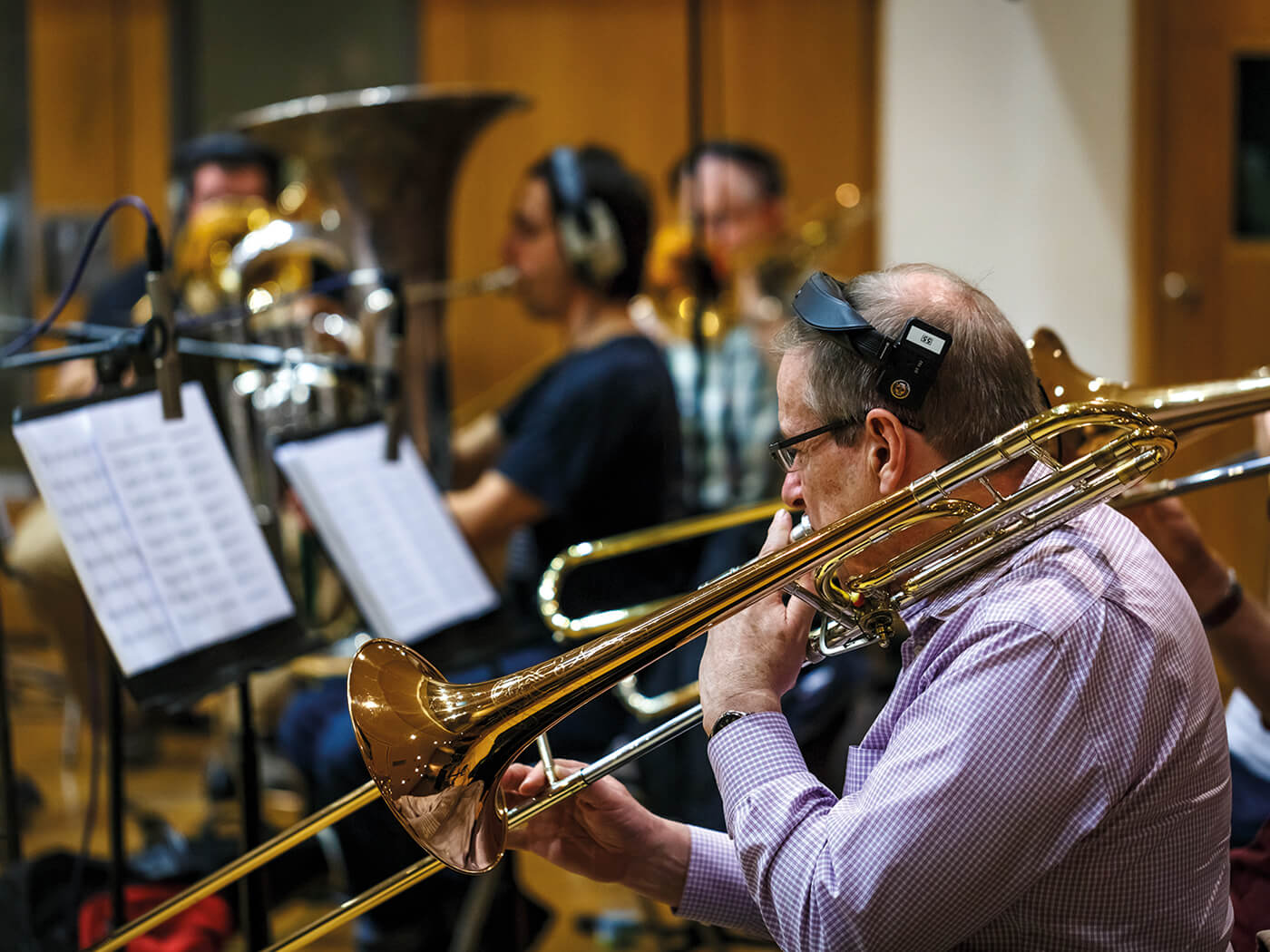
While each brass instrument possesses its own unique characteristics and playing techniques, they can also complement and harmonize with one another in ensemble settings. The combination of their individual sounds creates a rich and vibrant brass section, demonstrating the versatility and beauty of the brass family as a whole.
Role of Trombone in Different Musical Genres
The trombone plays a crucial role in various musical genres, contributing to the unique sound and character of each style. Its versatility and distinctive sound allow it to adapt seamlessly to different genres, enhancing the overall musical experience.
In classical music, the trombone shines in symphony orchestras, where it forms an essential part of the brass section. Its rich and resonant sound adds depth and power to orchestral compositions, providing a solid harmonic foundation. The trombone frequently plays both supporting and solo roles, contributing to the grandeur of symphonies, concertos, and chamber music pieces.
Jazz music is another genre where the trombone occupies a prominent position. In big bands and jazz ensembles, the trombone often takes on both supporting and improvisational roles. Its slide allows for fluid glissandos and smears, making it ideal for expressive solos and adding a unique flavor to jazz improvisation. Trombonists in jazz bands often perform intricate harmonies, punctuating the music with their distinctive sound.
In Latin music, especially salsa and merengue, the trombone is a cornerstone of the brass section. Known for its power and energy, the trombone adds a vibrant and dynamic element to the rhythmic foundations of Latin music. Its bold sound provides rhythmic accents and supports the driving percussion, contributing to the infectious energy that characterizes Latin genres.
Contemporary genres like pop, rock, and funk also make use of the trombone’s versatility. In these genres, trombone players often form part of horn sections, providing a punchy and vibrant sound that adds depth and excitement to the music. The trombone’s distinctive tonal quality and ability to play both high and low ranges make it well-suited for creating catchy hooks, powerful harmonies, and energetic fills.
Furthermore, the trombone is not limited to these traditional genres. It frequently finds its place in experimental and avant-garde music, where its unique sound and extended techniques can add texture and intrigue to unconventional compositions. From contemporary classical music to film scores, the trombone’s versatility allows it to adapt and contribute to innovative and boundary-pushing musical expressions.
The role of the trombone in different musical genres highlights its adaptability and wide-ranging capabilities. Whether it’s adding power and grandeur to classical compositions, infusing soulful melodies into jazz improvisations, driving the rhythmic energy in Latin music, or enhancing the dynamic presence in contemporary genres, the trombone adds a distinctive and captivating voice to the music it touches.
Notable Trombone Players
Throughout history, numerous talented trombone players have made significant contributions to the world of music, showcasing the versatility and expressive potential of the instrument. These notable trombonists have left a lasting impact on their respective genres and have inspired countless musicians with their remarkable skills and artistry.
J.J. Johnson, often referred to as the “king of bebop trombone,” revolutionized jazz trombone playing. His virtuosic technique and melodic improvisations pushed the boundaries of what was thought possible on the instrument. Johnson’s recordings and collaborations with jazz greats like Charlie Parker and Miles Davis have become legendary and continue to inspire aspiring trombonists today.
Tommy Dorsey is another name that stands out in the world of jazz and big band music. Known for his distinctive smooth and lyrical playing style, Dorsey became one of the most influential trombonists of the swing era. His beautiful and expressive solos, such as “I’m Getting Sentimental Over You,” have become timeless classics.
In classical music, Christian Lindberg has made a significant impact as a contemporary trombone virtuoso. Known for his dazzling technique and innovative approach to the instrument, Lindberg has performed and premiered numerous compositions written specifically for him. His performances showcase the trombone’s capabilities as a solo instrument in the classical realm.
In the world of Latin music, Juan Pablo Torres is celebrated as a master of the trombone. His contributions to the Cuban music scene, particularly in the genre of timba, have been instrumental in shaping the sound of modern Cuban music. Torres’s powerful and rhythmic playing brings a distinctive flavor to the brass sections of Latin ensembles.
Jack Teagarden, a pioneer of jazz trombone, left an indelible mark on the music world. His soulful and bluesy playing style, combined with his warm and expressive voice, earned him great acclaim. Teagarden’s recordings, such as “Stars Fell on Alabama” and “Basin Street Blues,” continue to be revered for their timeless appeal.
Other notable trombonists include Wycliffe Gordon, a versatile jazz trombonist known for his technical prowess and soulful playing, and Bill Watrous, admired for his remarkable range and ability to seamlessly transition between genres.
These are just a few of the many notable trombone players who have made significant contributions to the world of music. Their exceptional talents, innovative techniques, and artistic interpretations have helped elevate the trombone to new heights and have inspired generations of musicians to explore the instrument’s full potential.
Conclusion
The trombone stands as a remarkable instrument within the brass family, with its unique qualities and versatility captivating musicians and audiences alike. From its rich history to its distinct slide mechanism, the trombone offers a range of capabilities that set it apart from other brass instruments.
Throughout the centuries, the trombone has evolved and adapted, leaving its mark on various musical genres. Its role in classical music, jazz, Latin, and contemporary genres highlights its ability to blend harmoniously or take center stage, adding depth, power, and expressiveness to any ensemble.
The trombone’s sliding mechanism allows for seamless glissandos, precise intonation control, and expressive playing techniques that enable trombonists to create captivating performances. This, alongside its wide range, unique tonal qualities, and ability to adapt to different styles, solidifies its position as an instrument of unparalleled versatility.
Notable trombone players, from J.J. Johnson to Tommy Dorsey and beyond, have left lasting legacies, pushing the boundaries of the instrument and inspiring others to explore its potential. Their contributions have paved the way for contemporary trombonists, who continue to explore new territories and expand the instrument’s horizons.
Whether in orchestras, jazz ensembles, Latin bands, or other musical settings, the trombone’s distinct sound has the power to evoke a wide range of emotions, creating powerful moments of beauty and excitement. Its ability to both support and solo, blend and stand out, make it an essential component of any brass section.
In conclusion, the trombone’s rich history, unique features, and versatile capabilities make it a beloved instrument in the world of music. Its unmistakable sound and expressive potential continue to captivate audiences across all genres. As trombonists explore new techniques, push boundaries, and embrace innovation, the future of the trombone remains bright and ensures its enduring presence in the world of music for generations to come.