Home>Production & Technology>Music Theory>What Is A N 6-4 In Music Theory

Music Theory
What Is A N 6-4 In Music Theory
Published: January 31, 2024
Learn the concept of N 6-4 in music theory and understand its significance in chord progressions. Explore more about music theory with our comprehensive guide.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the fascinating world of music theory! Music theory plays a crucial role in understanding and analyzing the complex structure and composition of music. It provides a foundation for musicians to create, perform, and appreciate music more deeply.
In this article, we will delve into the intriguing concept of the N6-4 chord in music theory. The N6-4, also known as the Neapolitan Sixth chord, is a chromatic chord that adds color and tension to musical compositions. Understanding its definition, function, and implementation can significantly enhance your understanding and appreciation of music.
As we explore the N6-4, we will discover its unique role in harmonic progressions and its effect on the resolution of musical phrases. Along the way, we will also delve into voice leading principles and examine real-life examples to solidify our understanding.
So, whether you are a musician, music student, or simply a curious music lover, get ready to unlock the secrets of the N6-4 chord and deepen your understanding of music theory!
Definition of N6-4
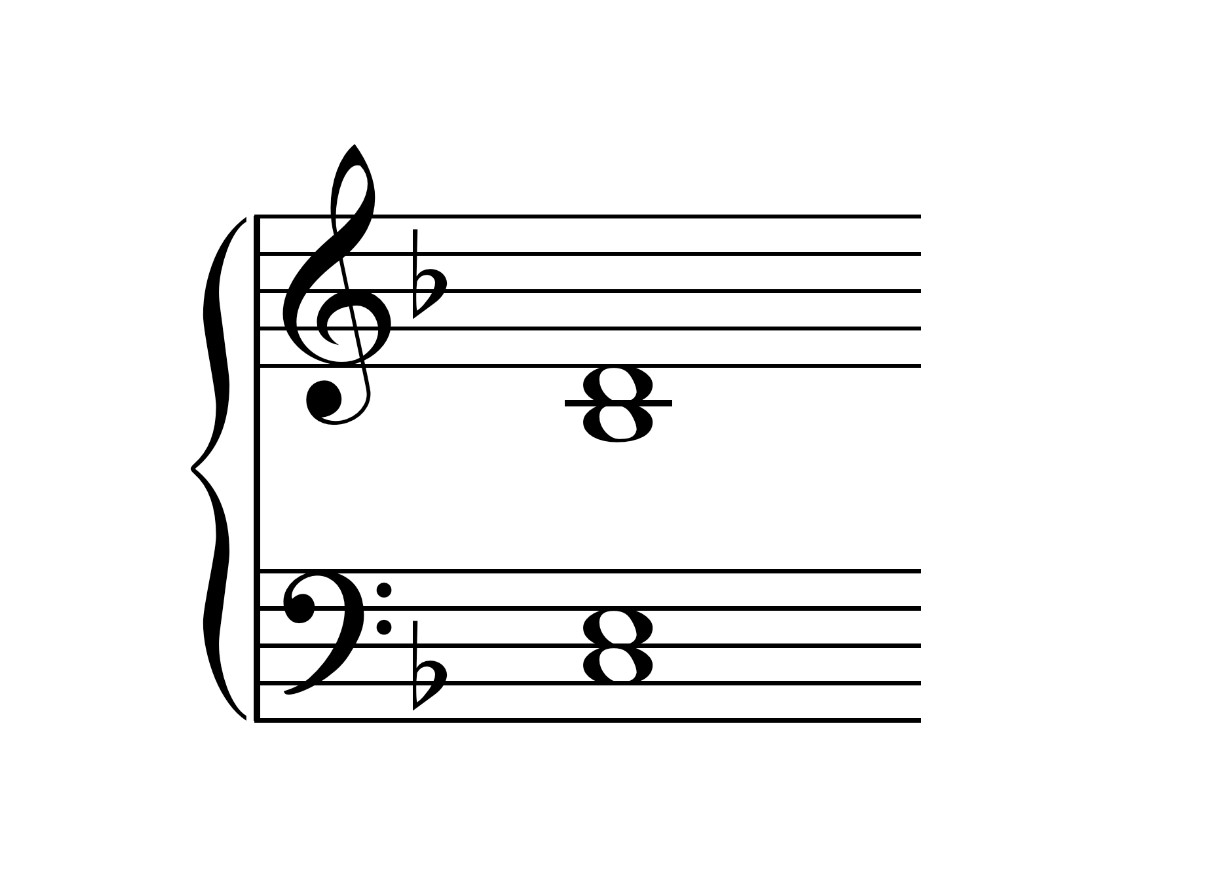
The N6-4 chord, also known as the Neapolitan Sixth chord, is a chromatic chord that originates from the Neapolitan region of Italy. It is characterized by its unique root position voicing, consisting of a major triad built on the lowered second scale degree of the key.
In terms of music notation, the N6-4 chord is often notated as ♭II6 or ♭II64, indicating the lowered second scale degree (♭II) in relation to the tonic and the chord’s root position voicing (6 or 64).
For example, in the key of C major, the N6-4 chord would be based on the note Db (the lowered second scale degree) and would consist of the pitches Db-F-Ab. This creates a distinctively rich and colorful sound due to the chromatic alteration.
The N6-4 chord is called the “Neapolitan” due to its prevalence in Neapolitan opera during the 18th and 19th centuries. Its unique sound became an important feature of the classical and romantic musical styles of that time.
It is worth noting that the N6-4 chord is typically used in major keys, although it is occasionally found in minor keys as well. In minor keys, the second scale degree is already a lowered note, so the Neapolitan chord retains its unique character even without further chromatic alteration.
The N6-4 chord is often employed as a predominant chord, meaning it usually appears before a dominant chord in a harmonic progression. Its primary function is to create tension and establish a temporary tonal center that leads to the dominant chord, thereby enhancing the sense of resolution and musical tension-release.
Function of N6-4
The N6-4 chord serves an important function in the harmonic progression of a piece of music. Its primary role is to create tension and prepare the listener for the eventual resolution to the dominant chord.
One of the key functions of the N6-4 chord is its ability to create a sense of harmonic instability. By introducing a chromatic alteration in the harmonic progression, the N6-4 chord adds a layer of tension and unexpectedness to the music. This momentary departure from the diatonic harmony catches the listener’s attention and creates a sense of anticipation for the upcoming resolution.
Another function of the N6-4 chord is its role as a predominant chord. Predominant chords are responsible for building tension and leading to the dominant chord, which is essential for establishing tonal stability. The N6-4 chord acts as a stepping stone between the tonic and the dominant, bridging the gap and creating a smooth harmonic transition.
In addition to its role as a predominant chord, the N6-4 chord can also function as a passing chord. In this context, it acts as a brief embellishment within a larger harmonic progression. By briefly interrupting the harmonic flow and adding an unexpected chromatic touch, the N6-4 chord adds color and interest to the music.
Furthermore, the N6-4 chord can function as a tonic substitute in certain musical contexts. By temporarily shifting the tonal center to the Neapolitan chord, the listener experiences a momentary departure from the home key, adding harmonic variety and creating a sense of musical surprise.
It is important to note that the function of the N6-4 chord can vary based on its specific context within a piece of music. Its function can be influenced by factors such as the surrounding chords, the musical style, and the composer’s intention. Therefore, understanding the harmonic context and analyzing the role of the N6-4 chord in a specific musical passage is vital to fully grasp its function and significance.
Resolutions and Progressions
The N6-4 chord introduces a distinct chromatic color to a musical composition and plays a crucial role in harmonic progressions. Understanding its resolutions and progressions is essential in comprehending its function within a piece of music.
One of the primary resolutions of the N6-4 chord is its progression to the dominant chord. The tension created by the N6-4 chord is resolved by moving to the dominant chord, usually in root position. This resolution creates a sense of stability and closure in the harmonic progression and is a common progression found in many musical genres.
Another common resolution involves the N6-4 chord progressing to the tonic chord. The N6-4 serves as a temporary departure from the diatonic harmony, and its resolution to the tonic chord brings a sense of resolution and tonal stability. This resolution can be particularly effective in creating a strong cadence, marking the end of a musical phrase or section.
Furthermore, the N6-4 chord can also be involved in passing progressions. As a passing chord, the N6-4 chord may occur between two diatonic chords to create smooth voice leading and add color to the progression. This passing function allows the N6-4 chord to smoothly connect two chords and create harmonic interest along the way.
It is important to note that the resolution and progression of the N6-4 chord can be influenced by various factors, such as the key, the surrounding chords, and the desired musical effect. Different composers and musical styles may employ distinct resolutions and progressions, showcasing the versatility and creative potential of the N6-4 chord.
Overall, understanding the resolutions and progressions of the N6-4 chord allows musicians and composers to harness its unique potential, create harmonic tension and release, and add depth and complexity to their musical compositions.
Voice Leading
When incorporating the N6-4 chord into a musical composition, it is essential to pay attention to voice leading principles. Voice leading refers to the smooth and logical movement of individual melodic lines within a harmonic progression.
When voice leading with the N6-4 chord, one must consider the resolution of the chord and how it interacts with the surrounding chords. Maintaining smooth voice leading ensures that the musical lines flow seamlessly and creates a pleasing and cohesive sound.
First and foremost, it is crucial to avoid awkward leaps or large intervals between the voices when transitioning to and from the N6-4 chord. By keeping the voice leading smooth and stepwise, the overall sound remains balanced and natural.
Additionally, attention should be paid to the resolution of the N6-4 chord. As mentioned earlier, the N6-4 chord often resolves to the dominant or tonic chord. In these resolutions, it is important to ensure that the individual voices move in a logical and predictable manner. This allows for smooth voice leading and a seamless transition from the N6-4 to the resolving chord.
Furthermore, consideration should be given to the dissonances and consonances created by the harmonic progression involving the N6-4 chord. Dissonant intervals, such as augmented seconds or tritones, can be used for expressive purposes but should be resolved appropriately to achieve a pleasing resolution. Consonant intervals, on the other hand, can provide stability and contribute to a sense of resolution.
Applying the principles of voice leading to the N6-4 chord ensures that the musical lines interact harmoniously and create a coherent and aesthetically pleasing composition. By paying attention to the smoothness of voice leading, composers and musicians can optimize the expressive potential of the N6-4 chord and create a rich and captivating musical experience.
Examples
To solidify our understanding of the N6-4 chord, let’s explore some examples of its usage in different musical contexts.
In Beethoven’s Symphony No. 3, also known as the “Eroica Symphony,” the N6-4 chord is used in the first movement during a transition from the dominant to the tonic. The N6-4 chord creates a momentary harmonic tension before resolving to the tonic, adding depth and drama to the composition.
In Johann Sebastian Bach’s Prelude in C Major from The Well-Tempered Clavier, Book 1, the N6-4 chord appears as a passing chord in bars 11 and 12. This passing progression (I-V6/N6-4-I) allows for smooth voice leading and creates a pleasing harmonic flow throughout the piece.
In Franz Schubert’s song “Gretchen am Spinnrade,” the N6-4 chord is used to highlight a significant moment in the text. As Gretchen sings about her longing and inner turmoil, the N6-4 chord is employed to intensify the emotional impact and emphasize her emotional struggle.
These examples showcase the versatility of the N6-4 chord in various musical genres and styles. Whether it’s in symphonies, solo piano works, or art songs, the N6-4 chord adds a unique flavor to the harmonic progressions, elevating the emotional impact of the music.
By studying and analyzing these examples, we can gain a deeper appreciation for how the N6-4 chord is used in real musical compositions. It allows us to see how composers throughout history have utilized this chord to evoke specific emotions, enhance tension and resolution, and create compelling musical narratives.
Exploring examples from different genres and time periods provides a comprehensive understanding of the N6-4 chord’s versatility and the creative opportunities it presents for composers and musicians.
Conclusion
The N6-4 chord, also known as the Neapolitan Sixth chord, is a captivating and versatile chromatic chord that adds color, tension, and expressive possibilities to musical compositions. Understanding its definition, function, and role in harmonic progressions is essential for musicians and music enthusiasts alike.
Throughout this article, we have explored the definition of the N6-4 chord, its unique characteristics, and its function within a musical context. We have seen how the N6-4 chord creates tension and leads to resolutions, whether to the dominant or tonic chord, and how it can function as a predominant or passing chord.
We also discussed the importance of voice leading principles when incorporating the N6-4 chord into a composition. Smooth and logical movement of individual melodic lines ensures a satisfying and harmonious sound.
Moreover, we examined real-life examples that demonstrated the application of the N6-4 chord in various musical genres, from classical symphonies to solo piano works and art songs. These examples showcased the versatility and expressive potential of the N6-4 chord.
Overall, understanding the N6-4 chord provides musicians with a broader palette of harmonic possibilities, allowing for greater musical depth and artistic expression. By incorporating the N6-4 chord into compositions, musicians can create moments of tension and resolution, surprise and anticipation, and evoke a range of emotions within the listener.
So, whether you’re a composer, performer, or music lover, continue exploring the rich world of music theory, and embrace the power of the N6-4 chord in your musical journey. As you unravel its secrets and incorporate it into your compositions, the N6-4 chord will become an invaluable tool for creating captivating and memorable musical experiences.