Home>Production & Technology>Treble>What Is The Fourth Space In The Treble Clef

Treble
What Is The Fourth Space In The Treble Clef
Published: November 27, 2023
Discover the role of the fourth space in the treble clef and its significance in music notation. Learn how it relates to the treble staff and note placement.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Music is a universal language that speaks to the soul and evokes emotions. It is a powerful means of expression that has been embraced by cultures around the world for centuries. To properly understand and appreciate music, one must have a basic knowledge of music notation. Among the various symbols used in music notation, the treble clef plays a vital role in determining the pitch of notes.
In this article, we will explore the treble clef and specifically focus on the fourth space within it. The treble clef, also known as the G clef, is commonly used for notating higher-pitched instruments such as the piano, violin, flute, and voice.
Understanding the treble clef and its components is essential for musicians and music enthusiasts alike, as it forms the foundation of reading and interpreting sheet music. The fourth space within the treble clef holds significant importance, as it represents a specific pitch in the musical scale.
Join us as we delve into the world of music notation and unlock the mystery of the fourth space in the treble clef. Gain insights into the potential notes that can be found in this space, discover commonly used notes, and comprehend the significance of the fourth space in musical compositions.
Whether you are a novice musician or a seasoned player, this article will provide you with valuable knowledge, deepen your understanding of music notation, and open up new possibilities for musical exploration.
The Basics of Music Notation
Music notation is the system of writing and representing music through symbols, allowing musicians to read and perform musical compositions accurately. It serves as a visual representation of the sounds and rhythms produced by musical instruments and voices.
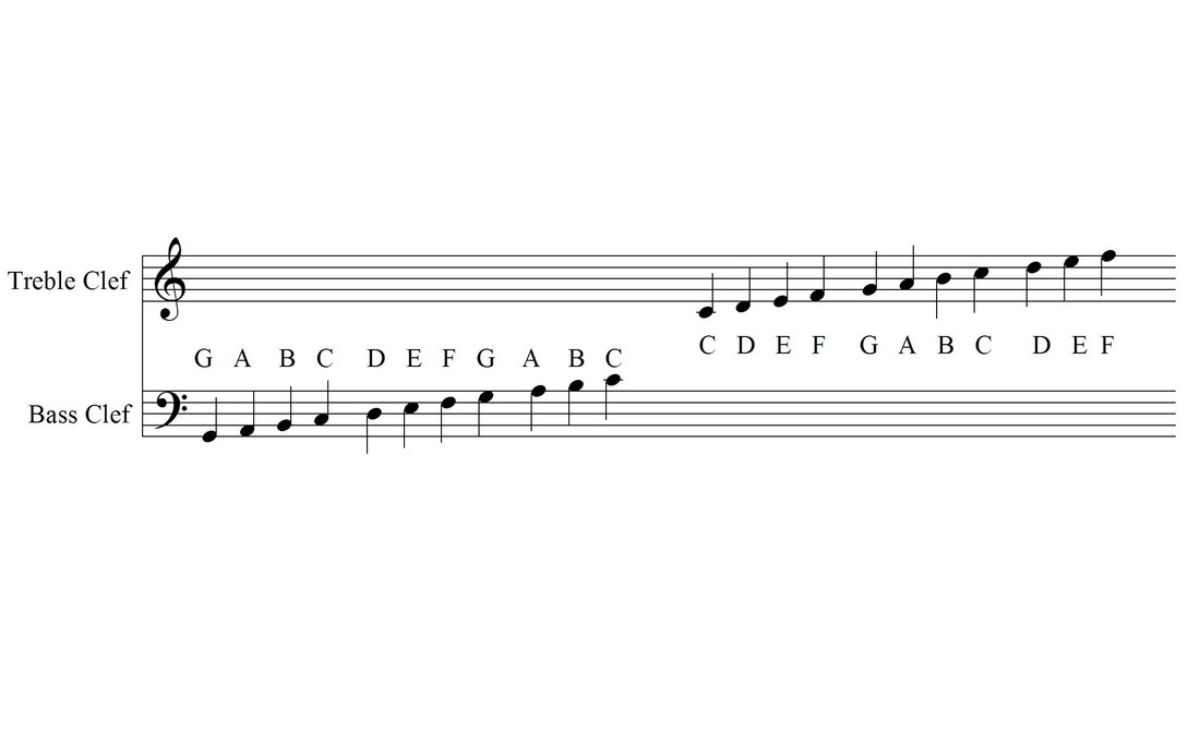
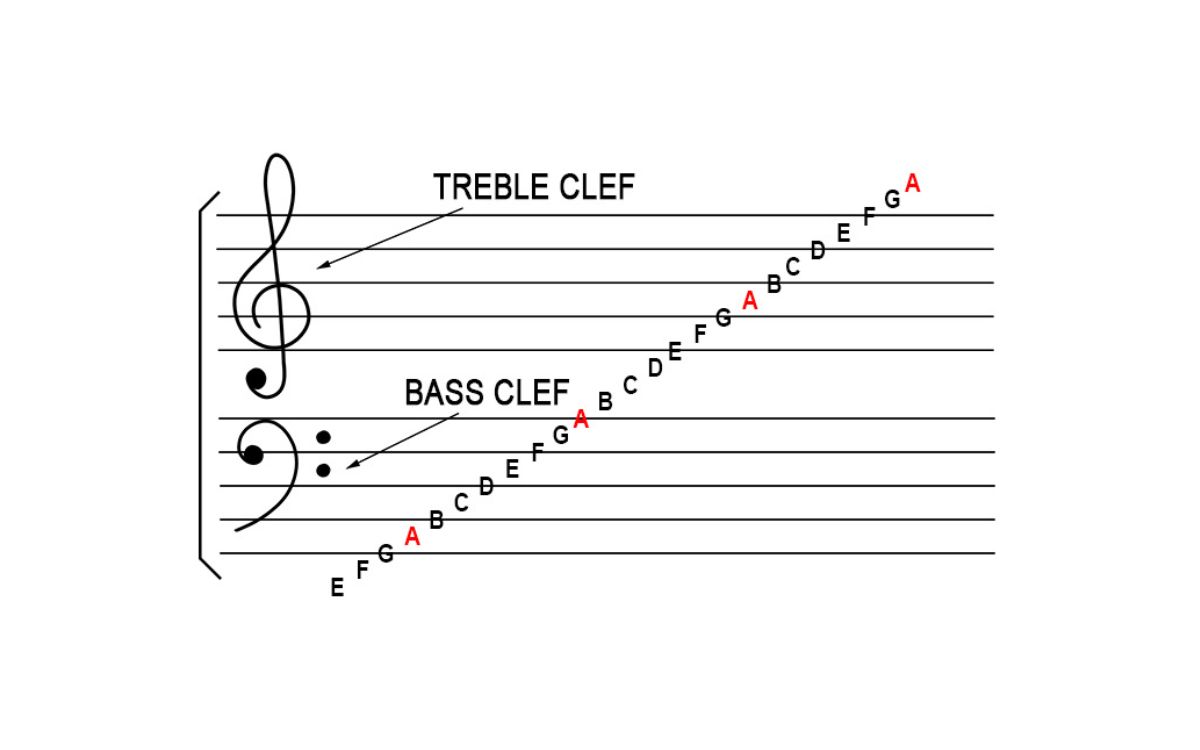
The foundation of music notation lies in a set of five horizontal lines called the staff. Each line and space on the staff corresponds to a particular pitch, indicating the note that needs to be played or sung. Different clefs, such as the treble clef, bass clef, and alto clef, are used to indicate the specific range of notes that each instrument or voice type should play.
Notes are represented by oval-shaped figures placed on or between the lines and spaces of the staff. The position of the note on the staff determines its pitch, while the shape of the notehead indicates its duration. Additional symbols, such as accidentals, rests, and dynamics markings, provide further information about pitch alterations, timing, and volume.
Understanding music notation is crucial for musicians, as it enables them to communicate and reproduce music accurately. It allows performers to decipher the composer’s intentions and faithfully interpret the piece, while also facilitating collaboration among musicians in ensemble settings.
Having a solid grasp of the basics of music notation is fundamental for anyone interested in learning or appreciating music. It provides a universal language through which musical ideas can be communicated and preserved for future generations.
Now that we have established the fundamentals of music notation, let’s explore one of the most widely used clefs in music—the treble clef—and its significance in determining pitch for higher-pitched instruments and voices.
Understanding the Treble Clef
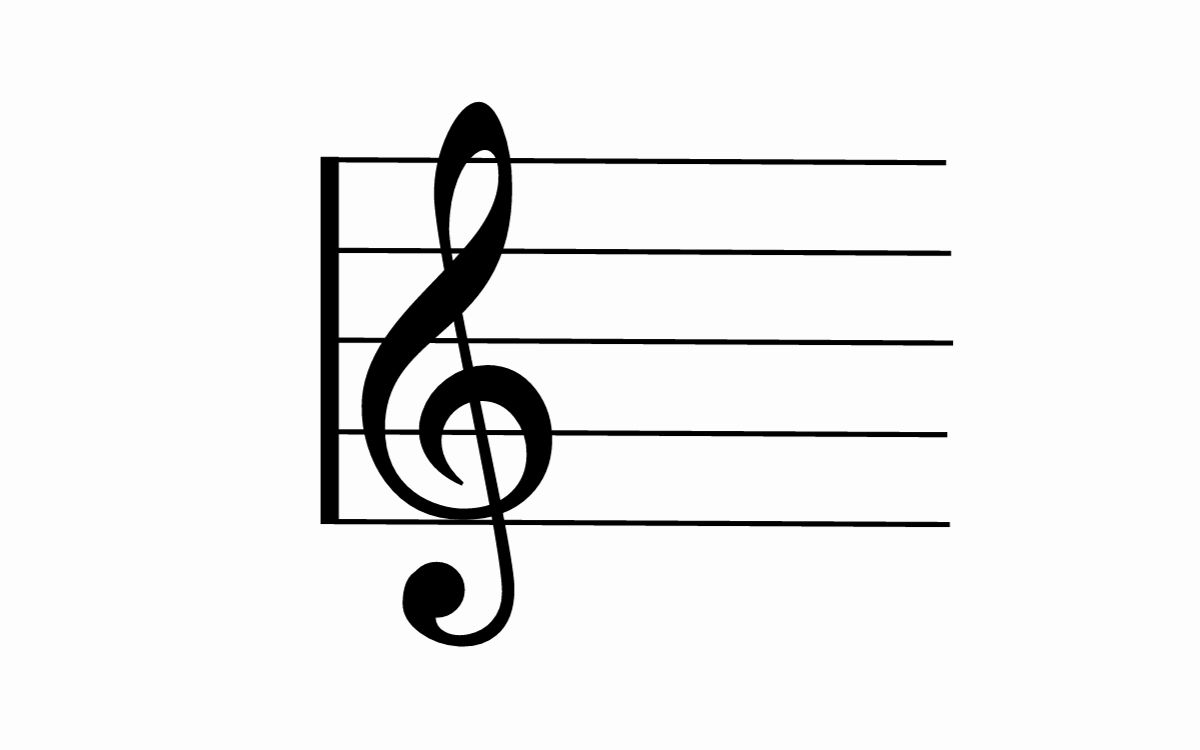
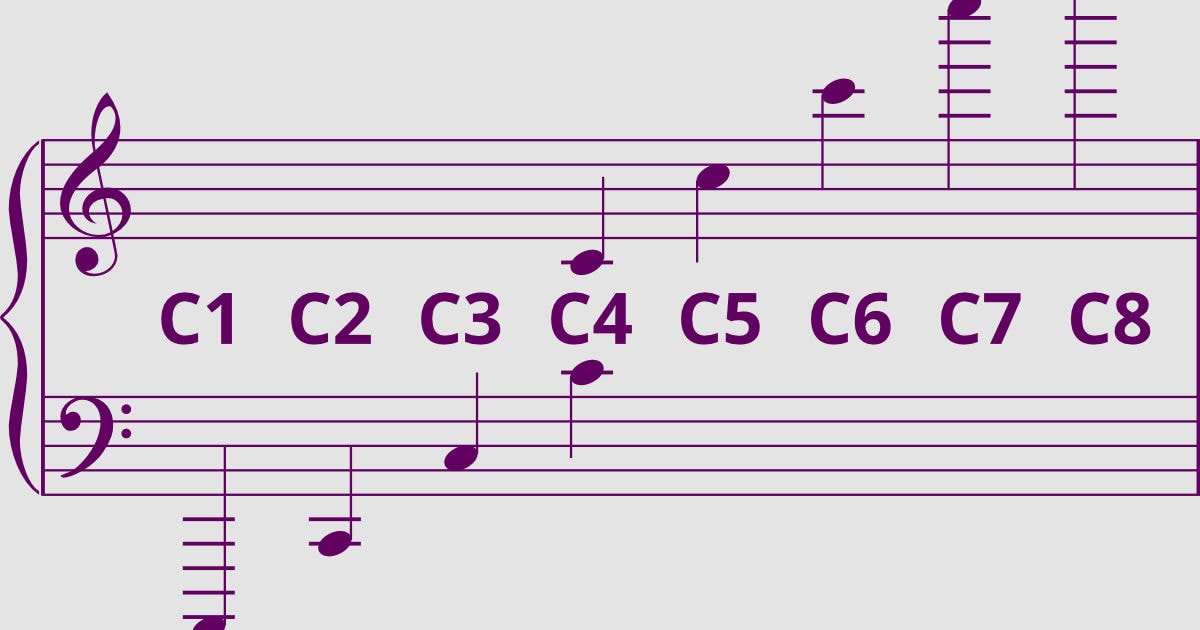
The treble clef, also known as the G clef, is one of the most commonly used clefs in music notation. It is easily recognizable by its spiral-shaped symbol that curls around the second line of the staff. The treble clef is primarily used to notate higher-pitched instruments such as the piano, violin, flute, and female vocal ranges.
The position of the treble clef on the staff indicates the pitch range that should be played or sung. The lines and spaces on the staff represent specific notes, with the placement of the note on the staff indicating its pitch. The treble clef is specifically designed to indicate the location of the note G above middle C, hence its alternative name, G clef.
The treble clef encompasses a wide range of notes, extending from A below middle C to the highest registers of many instruments. Its purpose is to clearly define the higher-pitched register of a musical composition, providing clarity and ease of reading for musicians.
Learning to read and interpret the treble clef is essential for musicians who play higher-pitched instruments or have a higher vocal range. Being able to identify and locate notes within the treble clef allows musicians to read and perform music accurately, ensuring that the intended melodies and harmonies are conveyed in their playing or singing.
Throughout musical history, the treble clef has played a significant role in shaping compositions and performances. Its use in notating music for higher-pitched instruments and voices has allowed for the creation of intricate melodies and soaring melodies that captivate listeners.
Now that we have gained a deeper understanding of the treble clef and its purpose, let’s focus on a specific space within the treble clef—the fourth space—and explore its significance in music notation.
The Fourth Space in the Treble Clef
Within the treble clef, each line and space represents a specific pitch. The fourth space in the treble clef holds particular significance as it represents a specific note in the musical scale. Understanding the notes that can be found in the fourth space is essential for musicians reading and interpreting sheet music.
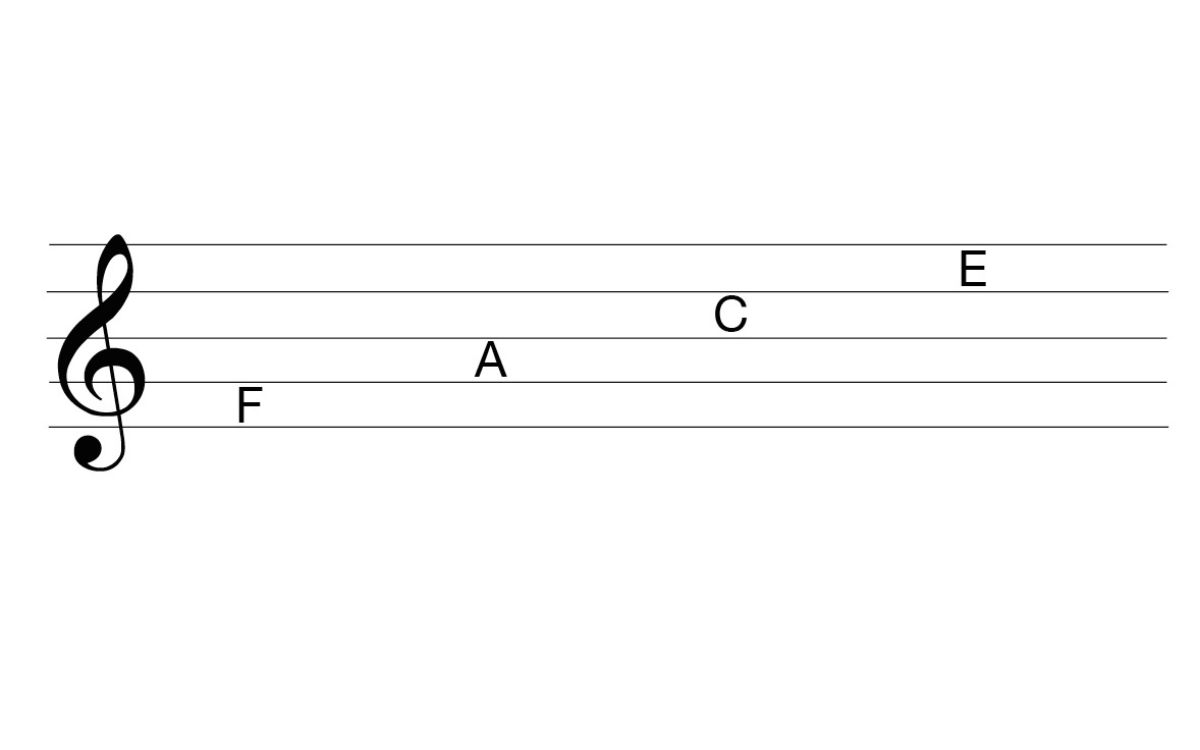
To identify the note in the fourth space, it is helpful to remember the mnemonic device used by many musicians: “FACE.” Each letter in the word corresponds to a note found in the spaces of the treble clef. Starting from the bottom space, F is found in the first space, A is found in the second space, C is found in the third space, and E is found in the fourth space.
With E being the note found in the fourth space, it serves as a reference point for reading and locating other notes within the treble clef. Musicians can use this knowledge to quickly identify and play or sing notes that are positioned higher or lower than E on the staff.
The fourth space in the treble clef is vital in determining the melodic contour of a musical composition. It acts as a reference point for successive notes and helps musicians maintain the correct pitch relationships while playing or singing. Additionally, notes in the fourth space often serve as pivotal points for melodic phrases and musical motifs.
Throughout various musical genres and compositions, you will find numerous instances where the fourth space in the treble clef is utilized to enhance melodies and create memorable musical moments. It is a key component in building melodic phrases and sequences that captivate listeners and evoke emotional responses.
As musicians continue to develop their skills and knowledge of music notation, understanding the significance of the fourth space in the treble clef becomes invaluable. It allows for a deeper appreciation and comprehension of the musical elements at play, enhancing the performance and interpretation of a wide range of musical compositions.
Now that we have explored the importance of the fourth space in the treble clef, let’s delve into the potential notes that can be found in this space.
Potential Notes in the Fourth Space
In the treble clef, the fourth space corresponds to the note E. This means that whenever a note is placed in the fourth space of the treble clef, it will be an E. However, it’s important to note that the pitch of the note can vary depending on additional musical notations such as accidentals or key signatures.
In its natural state, without any accompanying accidentals, the E in the fourth space of the treble clef is considered to be an E-natural. This means it is neither raised nor lowered and is played or sung at its standard pitch.
However, when accidentals such as sharps or flats are added to the music, the pitch of the note in the fourth space can be altered. For example, if there is a sharp symbol before the note, it becomes E-sharp (E♯) – a note that is one semitone higher than E. On the other hand, if there is a flat symbol, the note becomes E-flat (E♭) – a note that is one semitone lower than E.
These alterations can occur within a piece of music to create different tonal colors, modulate to different keys, or add chromaticism and tension to the composition. The potential for different notes in the fourth space allows composers and arrangers to craft intricate melodies and harmonies.
It’s worth noting that the most common occurrence in the fourth space of the treble clef is the natural note E. The altered versions, E-sharp and E-flat, are not as commonly found but can appear in various musical contexts.
Understanding the potential notes in the fourth space allows musicians to accurately read and perform sheet music. It provides clarity in interpreting the composer’s intentions and ensures that the correct pitch is played or sung at the designated point in the musical composition.
Now that we’ve explored the potential notes in the fourth space of the treble clef, let’s uncover some commonly used notes found in this space.
Commonly Used Notes in the Fourth Space
The fourth space in the treble clef, which represents the note E, is frequently utilized in musical compositions across various genres and styles. While the potential notes in this space can be altered with accidentals, the most commonly encountered note is E-natural.
E-natural in the fourth space of the treble clef serves as a foundational note for melodies, harmonies, and chords. Its bright and resonant sound lends itself to creating uplifting and vibrant musical moments. Composers and arrangers often incorporate E specifically in sequences and motifs to add depth and complexity.
Examples of commonly used notes in the fourth space of the treble clef include:
- E-natural (E)
- E-sharp (E♯)
- E-flat (E♭)
These notes, both natural and altered, can be integrated into melodies, harmonies, and chords to provide different tonal colors and evoke specific emotions in the listener. The context of the musical piece and the compositional intent determine which notes are used and how they interact with other elements in the composition.
Moreover, the fourth space can act as a transition point or passing note in melodic lines, connecting lower and higher pitches within the treble clef. Musicians often use the fourth space note as a springboard for melodic exploration, leading to subsequent musical phrases and patterns.
It’s important for musicians to become familiar with these commonly encountered notes in the fourth space of the treble clef, as they frequently appear in musical compositions. Understanding their role and significance contributes to a more nuanced and nuanced interpretation of the music, allowing performers to bring out the intended musicality and expression.
As one delves further into the realm of music and explores compositions from different eras and genres, it becomes apparent how these notes are skillfully employed to create unique and memorable musical experiences.
Now, with an understanding of the commonly used notes in the fourth space of the treble clef, let’s explore the broader significance and importance of the fourth space in music.
Importance of the Fourth Space in Music
The fourth space in the treble clef holds considerable importance in the realm of music, playing a vital role in musical compositions and performances. Understanding the significance of the fourth space enhances musicians’ ability to read, interpret, and bring music to life.
One of the primary reasons why the fourth space is significant is its position within the treble clef staff. It acts as a reference point for musicians, providing a key landmark when reading and navigating notes in the higher range. The fourth space, representing the note E, serves as a touchstone for identifying and relating other notes within the treble clef.
Furthermore, the fourth space often serves as a pivotal note within melodic phrases. Composers and arrangers strategically place important melodic gestures in the fourth space to create memorable musical moments. This can be seen in countless musical compositions, where the fourth space note acts as a climactic point or transition to propel the melody forward.
The fourth space’s importance extends beyond individual notes. Its utilization in harmonies and chords contributes to the overall harmonic progression and tonal palette of a composition. In combination with other notes and intervals, the fourth space note adds complexity and depth to the musical texture, providing richness to melodies and harmonies alike.
Additionally, the fourth space note can convey specific emotions and moods depending on the context of the composition. Whether it is played softly with delicacy or emphasized with vigor, the fourth space note can evoke different feelings in the listener and contribute to the overall expressive character of the music.
Moreover, an understanding of the significance of the fourth space in music allows musicians to better communicate and collaborate with one another. When performers are well-versed in the role of the fourth space, they can follow musical cues, anticipate melodic developments, and synchronize their playing or singing with precision.
Overall, the fourth space in the treble clef carries immense importance in music notation and performance. It serves as a fundamental reference point, a catalyst for melodic expression, and a contributor to harmonic richness. Musicians who appreciate and harness the significance of the fourth space can bring a heightened level of nuance, emotion, and artistic interpretation to their musical endeavors.
As we conclude this exploration of the importance of the fourth space in music, let’s reflect on the knowledge gained and celebrate the deep connection between musicians, their instruments, and the intricate world of musical expression.
Conclusion
Understanding the treble clef and its components is essential for musicians seeking to read and interpret sheet music accurately. Within the treble clef, the fourth space holds significant importance as it represents a specific note in the musical scale. The fourth space, with its potential for different notes and its role as a reference point, contributes to the depth and expressiveness of musical compositions.
By familiarizing ourselves with the basics of music notation, we gain a universal language through which musical ideas can be communicated and preserved. The treble clef, with its iconic spiral-shaped symbol, serves as a guide for higher-pitched instruments and voices, allowing for the clear representation of musical pitches.
The fourth space in the treble clef, most commonly associated with the note E, acts as a pivotal point for melodies, harmonies, and chords. It serves as a springboard for musical exploration, a touchstone for pitch relationships, and a reference point for musicians as they navigate the higher registers of their instruments or voices.
Through our exploration of the potential notes and commonly used notes in the fourth space, we have discovered the versatility and significance of this musical element. The fourth space contributes to the melodic contour, harmony, and emotional impact of a composition, enriching the musical experience for both performers and listeners.
Whether we are playing a musical instrument or singing, recognizing the importance of the fourth space allows us to accurately read and perform sheet music. It enables us to convey the intended melodies, harmonies, and expressions with precision and authenticity.
As we continue to delve into the world of music, let us embrace the artistry and beauty that the treble clef and its components bring into our lives. By understanding and appreciating the fourth space in the treble clef, we can unlock new depths of musical understanding, enrich our performances, and connect with the profound emotional power that music holds.
So, let us embrace the treble clef, explore the potential of the fourth space, and continue to immerse ourselves in the awe-inspiring world of music.