Jazz
How To Listen To Jazz Ted Gioia
Modified: January 22, 2024
Learn how to listen to jazz and appreciate its intricacies with Ted Gioia's comprehensive guide. Discover the history, styles, and key players of this iconic genre.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding the Origins of Jazz
- The Evolution of Jazz Styles
- Key Elements of Jazz Music
- Appreciating Jazz Improvisation
- Exploring Different Jazz Instruments
- Notable Jazz Artists and Their Contributions
- Building a Jazz Music Collection
- Attending Live Jazz Performances
- Engaging in Active Listening Techniques
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to the fascinating world of jazz music. With its rich history, diverse styles, and unique improvisation, jazz has captivated listeners for over a century. Whether you’re a seasoned jazz enthusiast or someone curious to explore this genre, this comprehensive guide will provide you with a deeper understanding and appreciation of jazz.
Jazz emerged in the early 20th century in the United States, born out of the African-American communities in New Orleans. It quickly gained popularity and spread throughout the country, eventually making its way to the rest of the world. What sets jazz apart from other genres is its emphasis on improvisation and individual expression. It creates a space for musicians to showcase their creativity and interact with one another in a live setting.
Understanding the origins of jazz is crucial to appreciating its significance. It was heavily influenced by African musical traditions, European classical music, and the blues. This unique blend created a distinctive sound that continues to evolve and push musical boundaries to this day.
In this guide, we will take a journey through the evolution of jazz styles, exploring key elements of jazz music, and delving into the art of jazz improvisation. We will also discuss the different instruments commonly used in jazz and highlight some notable jazz artists and their contributions to the genre. Additionally, we will provide tips on building your jazz music collection, attending live jazz performances, and engaging in active listening techniques.
So, whether you’re looking to expand your musical horizons or simply want to deepen your knowledge of jazz, join us as we dive into this incredible genre and immerse ourselves in the soul-stirring melodies, swinging rhythms, and spontaneous creativity of jazz music.
Understanding the Origins of Jazz
To truly appreciate jazz, it is essential to understand its roots and the cultural influences that gave birth to this vibrant genre. Jazz originated in the early 20th century in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana. It was deeply influenced by the melodic and rhythmic traditions brought to the United States by enslaved Africans.
One of the key elements that shaped jazz was the blending of African musical traditions with European classical music. African musicians utilized complex rhythmic patterns and improvisation in their music, while European classical music provided the framework of harmony and structure. The fusion of these two styles gave birth to a unique sound that set jazz apart.
Another important influence on jazz came from the blues, a genre that has its roots in African-American communities. Blues music expresses deep emotions and tells personal stories through soulful vocals and heartfelt melodies. Jazz incorporated elements of blues, such as the use of blue notes and call-and-response patterns, to create a distinct and expressive sound.
New Orleans, often called the birthplace of jazz, was a melting pot of diverse cultures and musical traditions. The city’s vibrant and multicultural atmosphere played a significant role in the development of jazz. Musicians from different backgrounds would come together in jam sessions, trading musical ideas and creating a musical dialogue.
Jazz initially gained popularity in the speakeasies and dance halls of New Orleans. It then spread to other cities, such as Chicago and New York, where it continued to evolve and garner a larger audience. The advent of recording technology in the 1920s allowed jazz to reach a wider audience, making it one of the first truly popular music genres.
Notable early jazz pioneers like Louis Armstrong, Jelly Roll Morton, and Duke Ellington played a crucial role in defining and popularizing the genre. Their innovative techniques, intricate arrangements, and charismatic performances brought jazz to the forefront of American music.
Today, jazz has evolved into a global phenomenon, with various subgenres and styles that continue to push artistic boundaries. From the traditional sounds of New Orleans jazz to the complex harmonies of bebop and the experimental nature of free jazz, there is a vast world of jazz waiting to be explored.
By understanding the origins of jazz and the cultural contexts in which it developed, we can develop a deeper appreciation for the beauty and significance of this incredible genre.
The Evolution of Jazz Styles
Jazz is a genre that has undergone continuous evolution and transformation over the years. From its early roots in New Orleans, it has branched out into numerous styles, each with its own distinctive characteristics and influential figures.
One of the earliest styles of jazz is New Orleans or Dixieland jazz. This style emerged in the early 20th century and is characterized by its ensemble playing, with multiple musicians improvising and creating intricate polyphonic melodies. It features lively rhythms and incorporates elements of ragtime and blues. Notable musicians associated with this style include Louis Armstrong, Jelly Roll Morton, and King Oliver.
In the 1930s and 1940s, a new style called swing became popular. Swing music, often performed by large orchestras, features a strong rhythm section and emphasizes a steady, propulsive beat that encourages dancing. Big band leaders like Duke Ellington, Count Basie, and Benny Goodman were instrumental in popularizing swing and creating iconic recordings.
Another significant development in jazz was the rise of bebop in the 1940s. Bebop pushed the boundaries of harmony and improvisation, featuring faster tempos and complex chord progressions. It was characterized by intricate melodies, advanced harmonies, and virtuosic solos. Musicians such as Charlie Parker, Dizzy Gillespie, and Thelonious Monk were at the forefront of this groundbreaking movement.
In the 1950s and 1960s, jazz continued to evolve with the advent of cool jazz and hard bop. Cool jazz, pioneered by musicians like Miles Davis and Chet Baker, had a more relaxed and laid-back sound, incorporating elements of classical music and a focus on improvisation. Hard bop, on the other hand, was characterized by a more aggressive and intense approach, with a strong emphasis on blues and soul influences. Art Blakey, Horace Silver, and Lee Morgan were key figures in the hard bop movement.
In the 1960s, jazz further expanded with the emergence of free jazz. Free jazz is characterized by its avant-garde and experimental nature, with musicians improvising without the constraints of traditional harmonies and structures. Artists such as Ornette Coleman, John Coltrane, and Sun Ra pushed the boundaries of jazz, exploring new forms of expression and pushing the limits of improvisation.
In the late 20th century and into the 21st century, jazz continued to diversify and incorporate influences from other genres such as rock, funk, and world music. Fusion jazz emerged, blending jazz with elements of rock and electronic music. Artists like Herbie Hancock, Chick Corea, and Weather Report brought a fresh and innovative approach to the genre.
Contemporary jazz features a wide range of styles, from smooth jazz and Latin jazz to contemporary fusion and experimental jazz. This genre continues to evolve and adapt to the changing musical landscape, with artists like Kamasi Washington, Robert Glasper, and Esperanza Spalding pushing the boundaries and taking jazz in exciting new directions.
As you explore the evolution of jazz styles, you will discover a vast and dynamic landscape that showcases the incredible versatility and adaptability of this genre. Whether you prefer the traditional sounds of Dixieland or the avant-garde experiments of free jazz, there is a style of jazz that will resonate with your musical preferences.
Key Elements of Jazz Music
Jazz music is known for its unique characteristics and expressive qualities. To fully appreciate and understand jazz, it is important to familiarize yourself with its key elements. These elements are what give jazz its distinctive sound and make it such a beloved genre.
One of the fundamental elements of jazz is improvisation. Unlike other genres where the music is strictly composed, jazz allows for spontaneous creativity and individual expression. Improvisation is the art of creating music on the spot, where musicians create melodies, harmonies, and rhythms in real-time. This element of improvisation is what gives jazz its dynamic and ever-changing nature, making each performance unique and exciting.
Rhythm is another essential element in jazz music. Jazz rhythms are often syncopated, meaning that the emphasis falls on offbeats or unexpected accents. This rhythmic complexity gives jazz its distinct swing and groove and creates a sense of energy and propulsion. The rhythmic interplay between the different instruments, such as the drums, bass, and piano, is a key factor in the overall feel of a jazz composition or improvisation.
Harmony plays a significant role in jazz as well. Jazz harmony often incorporates complex and extended chords, such as seventh chords and altered chords. These harmonic choices add color and depth to the music and provide a rich palette for improvisation. Jazz musicians are known for their advanced knowledge of harmony and their ability to navigate complex chord progressions with ease.
Melody is another crucial element in jazz music. Jazz melodies are often characterized by their improvisational nature and intricate phrasing. The melody is typically delivered by a soloist, such as a trumpet or saxophone player, who adds their own personal touch and interpretation to the composition. The ability to create compelling and memorable melodies is a hallmark of jazz musicianship.
Swing is a defining characteristic of jazz music. It refers to the rhythmic feel and groove that is inherent in jazz. Swing often involves playing eighth notes with a slight emphasis on the second and fourth beats, creating a sense of forward motion and momentum. This swing feel is what makes jazz music so infectious and enjoyable to listen to.
Call-and-response is a technique commonly used in jazz music. It involves a musical conversation between musicians, where one musician plays a phrase or melody, and another musician responds with their own variation or improvisation. Call-and-response adds an interactive and conversational element to jazz performances, allowing musicians to interact and play off each other’s ideas.
Dynamics and expression are also key elements in jazz. Jazz musicians are skilled at using dynamics, such as playing soft (pianissimo) or loud (fortissimo), to enhance their musical expression. They can also manipulate tone and subtleties in their playing to convey emotion and mood, adding depth and nuance to their performances.
Understanding and appreciating these key elements of jazz music will help you develop a deeper connection with the genre. As you listen to jazz, pay attention to the improvisation, rhythm, harmony, melody, swing, call-and-response, dynamics, and expression that are at the heart of this captivating musical style.
Appreciating Jazz Improvisation
One of the defining characteristics of jazz music is its emphasis on improvisation. Jazz musicians have the freedom to create and explore new musical ideas in the moment, adding a unique and personal touch to their performances. Appreciating jazz improvisation involves understanding the process, techniques, and creative decisions that musicians make on the spot.
The foundation of jazz improvisation lies in a deep understanding of music theory and harmony. Jazz musicians have a solid grasp of chord progressions, scales, and patterns, allowing them to navigate complex harmonic structures with ease. They use this knowledge as a springboard for their improvisations, creating melodic lines and improvisational ideas that fit within the underlying chord progression.
Rhythm is another important aspect of jazz improvisation. Jazz musicians play with a sense of swing, syncopation, and rhythmic variation, adding excitement and groove to their solos. They experiment with different rhythmic patterns and accents, creating an engaging and dynamic performance.
Melodic development is key in jazz improvisation. Musicians start with a simple melodic idea and then expand upon it, exploring different variations and embellishments. They use techniques such as motivic development, where a short musical motif is repeated and transformed throughout the improvisation, creating cohesion and unity in their playing.
Jazz musicians also utilize a wide range of techniques to add depth and expression to their improvisations. They use bending and gliding notes, vibrato, and different articulations to infuse their playing with emotion and personality. Dynamics, such as playing softly and loudly, are used to create contrast and shape the overall phrasing of the improvisation.
Listening and interacting with other musicians is a crucial aspect of jazz improvisation. Jazz musicians often engage in call-and-response interactions, where they respond to each other’s musical phrases and ideas. This creates a musical dialogue and allows for spontaneous and collaborative improvisation.
Appreciating jazz improvisation involves actively listening and engaging with the performer’s creative choices. Pay attention to the melodic patterns, rhythmic variations, and harmonic ideas that the musician explores. Take note of how they develop their improvisation over the course of a performance, building tension and releasing it in a satisfying manner.
It’s also important to appreciate the element of risk-taking in jazz improvisation. Improvising requires musicians to step outside their comfort zones and take chances, embracing the unknown. It’s this element of spontaneity and unpredictability that makes jazz improvisation so thrilling and captivating.
To enhance your appreciation of jazz improvisation, explore recordings by legendary jazz improvisers such as Louis Armstrong, Charlie Parker, John Coltrane, and Miles Davis. Attend live jazz performances to witness the magic of improvisation happening in real-time, and consider taking up an instrument yourself to experience the joy and challenge of improvising firsthand.
By understanding the techniques, creative decisions, and risks involved in jazz improvisation, you can deepen your appreciation for this integral aspect of jazz music and gain a greater understanding of the immense talent and skill of jazz musicians.
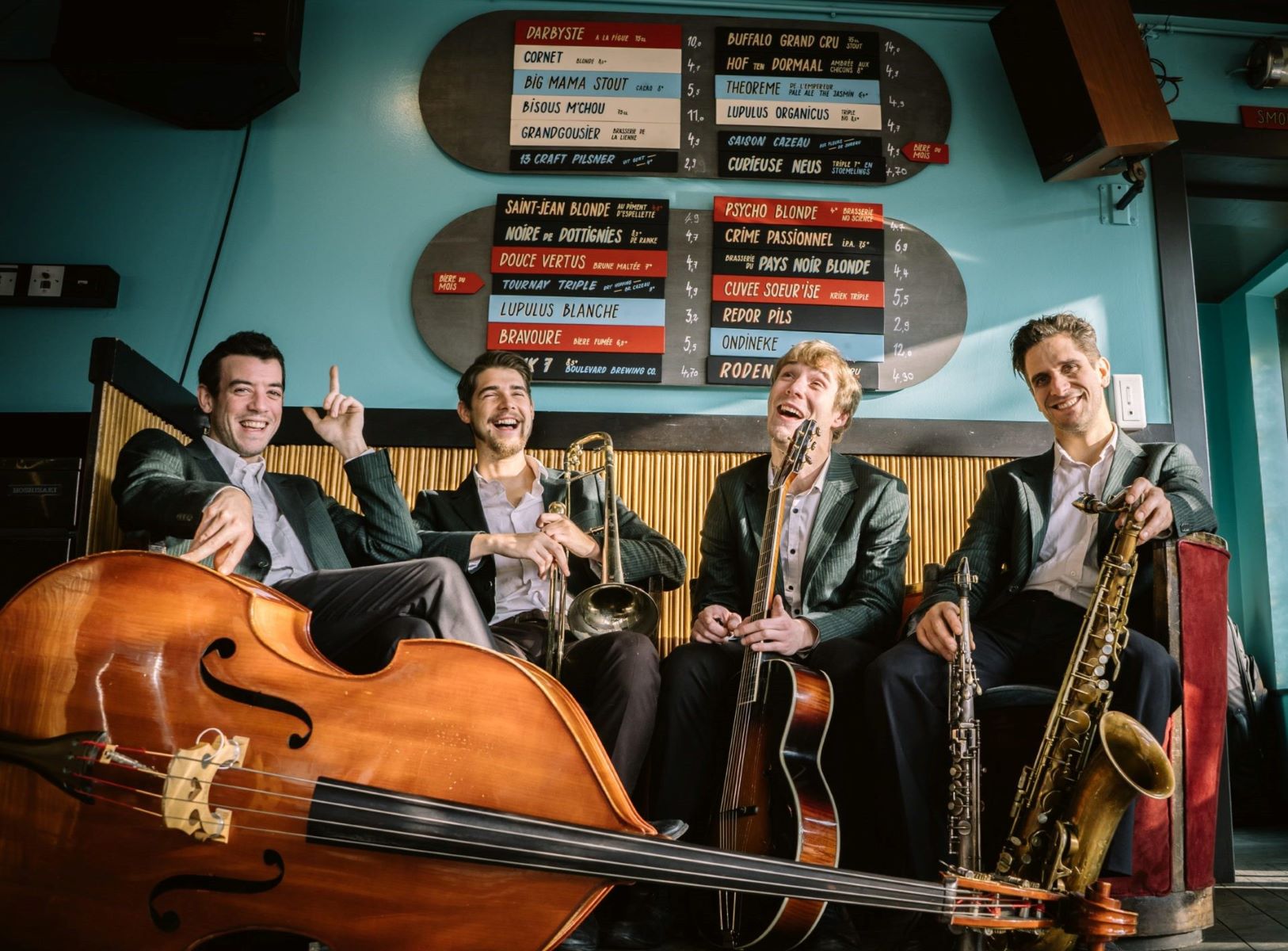
Exploring Different Jazz Instruments
Jazz music showcases a diverse array of instruments, each contributing its unique sound and character to the genre. From the smooth melodies of the saxophone to the rhythmic grooves of the drums, exploring the various jazz instruments allows us to appreciate the breadth of musical possibilities within the genre.
The saxophone is often considered the quintessential jazz instrument. Its versatile tone and expressive capabilities make it a staple in many jazz ensembles. Saxophonists like Charlie Parker, John Coltrane, and Sonny Rollins have pushed the boundaries of the instrument, showcasing its range and technical prowess across different jazz styles.
Another essential instrument in jazz is the trumpet. With its bright and piercing sound, the trumpet takes center stage, often delivering thrilling solos and melodic lines. Legends like Louis Armstrong, Miles Davis, and Dizzy Gillespie have left an indelible mark on jazz music with their innovative trumpet playing.
The piano is a foundational instrument in jazz, providing harmonies, melodies, and rhythmic support. Pianists like Duke Ellington, Thelonious Monk, and Herbie Hancock have not only shaped the genre with their unique playing styles but have also been influential composers and bandleaders in their own right.
The double bass, or simply bass, forms the backbone of the jazz rhythm section. It provides the foundation with its deep and resonant tones and interacts closely with the drums to create a solid groove. Bassists like Charles Mingus, Ray Brown, and Ron Carter have contributed heavily to the development of jazz through their innovative and influential playing.
The drums are integral to jazz, driving the rhythm and setting the mood for performances. Drummers like Art Blakey, Max Roach, and Tony Williams have pushed the boundaries of rhythm, showcasing their technical prowess and improvisational skills. Their rhythmic innovations have revolutionized jazz drumming and continue to inspire drummers today.
The guitar has also found its place in jazz, providing melodic lines, harmonic accompaniment, and even virtuosic solos. Jazz guitarists like Django Reinhardt, Wes Montgomery, and Pat Metheny have developed unique and influential styles, blending elements of swing, blues, and bebop with their innovative use of chords and phrasing.
Other instruments that play a significant role in jazz include the trombone, clarinet, vibraphone, and flute. Each instrument brings its distinct timbre and style to jazz music, adding to the richness and variety of the genre.
Exploring different jazz instruments allows us to appreciate the individual artistry and contributions of the musicians who play them. It also deepens our understanding of the complex interplay between instruments and the collaborative nature of jazz performance.
As you listen to jazz recordings or attend live performances, pay attention to the unique qualities and techniques displayed by each instrument. Notice how they interact with one another, complementing and responding to each other’s musical ideas. This will enhance your enjoyment and appreciation of the intricate and dynamic world of jazz music.
Notable Jazz Artists and Their Contributions
Jazz has been blessed with countless exceptional artists who have left an indelible mark on the genre. These musicians have pushed boundaries, revolutionized playing styles, and created groundbreaking compositions, shaping the course of jazz history. Exploring the contributions of these notable jazz artists allows us to appreciate the immense talent and innovation that has defined the genre.
Louis Armstrong, often referred to as the “Father of Jazz,” was a trumpet player and vocalist who had a profound influence on jazz and popular music. His virtuosic trumpet playing, distinctive gravelly voice, and infectious stage presence propelled him to stardom. Armstrong’s contributions include his pioneering improvisation, scat singing, and his role in popularizing jazz as a soloist, paving the way for future generations of jazz musicians.
Duke Ellington, a pivotal composer, bandleader, and pianist, was a masterful orchestrator who brought sophistication and elegance to jazz. As a prolific composer, he composed numerous jazz standards, including “Take the ‘A’ Train” and “It Don’t Mean a Thing (If It Ain’t Got That Swing).” Ellington’s contributions include his visionary approach to jazz composition, his innovative use of harmony and arrangement, and his ability to seamlessly blend different styles within the jazz idiom.
Charlie Parker, known as “Bird,” was an alto saxophonist and composer who played a crucial role in the development of bebop. Parker’s extraordinary technique, rapid-fire improvisation, and innovative harmonic ideas revolutionized jazz. His contributions include his virtuosic saxophone playing, his use of complex chord progressions and substitutions, and his influence in shaping the vocabulary of modern jazz improvisation.
Ella Fitzgerald, often referred to as the “First Lady of Song,” was a legendary vocalist renowned for her impeccable phrasing, extraordinary range, and flawless interpretive skills. Fitzgerald’s contributions include her exquisite vocal improvisation and scat singing, her ability to create a deep emotional connection with her audience, and her influence on generations of jazz vocalists.
Miles Davis, a trumpeter, bandleader, and composer, played a pivotal role in shaping jazz from the 1940s until his death in 1991. Davis was an innovator who constantly reinvented himself and the jazz genre. His contributions include his role in the development of cool jazz, modal jazz, and jazz fusion, his use of space and silence in his playing, and his ability to assemble talented and influential ensembles.
John Coltrane, an iconic saxophonist and composer, is known for his soaring and exploratory improvisations. Coltrane’s contributions include his groundbreaking use of extended saxophone techniques, his exploration of complex harmonic structures, and his spiritually-infused compositions that pushed the boundaries of jazz into new territories.
These are just a few examples of the many notable jazz artists and their significant contributions to the genre. Countless others, such as Billie Holiday, Thelonious Monk, Sarah Vaughan, and Herbie Hancock, have made lasting impacts on jazz through their innovative playing, captivating vocals, and pioneering compositions. Each artist has added their unique voice and perspective, shaping the rich tapestry of jazz music as we know it today.
Exploring the recordings and performances of these influential jazz artists allows us to deepen our appreciation of their contributions and provides a gateway into the vast world of jazz music. Their dedication, creativity, and artistry continue to inspire and influence generations of musicians, ensuring that the jazz legacy lives on.
Building a Jazz Music Collection
Building a jazz music collection is an exciting journey that allows you to explore the rich history and diverse styles within the genre. As you start or expand your collection, consider the following tips to help you curate a well-rounded and enjoyable selection of jazz recordings.
1. Research and Discover: Begin by researching different jazz artists, styles, and eras. Take advantage of online streaming platforms, jazz forums, and music magazines to discover new artists and albums that resonate with your musical tastes. Listen to a variety of jazz subgenres, from classic swing and bebop to modal jazz and fusion, to get a feel for the breadth of jazz music.
2. Iconic Recordings: Identify key recordings that have shaped the jazz genre. Look for landmark albums by legendary artists like Miles Davis’ “Kind of Blue,” John Coltrane’s “A Love Supreme,” and Louis Armstrong’s “Hot Fives and Sevens.” These albums not only provide a glimpse into the evolution of jazz but also showcase the groundbreaking techniques and innovative approaches of the artists.
3. Explore Different Eras: Jazz has gone through various distinct eras, each with its own defining characteristics. From the early swing of the 1920s and 1930s to the avant-garde experiments of the 1960s, exploring different eras allows you to appreciate the evolution and progression of jazz music. Include recordings from influential artists of each era to capture the essence of their respective periods.
4. Dig Deeper: Once you have a foundation of well-known artists and albums, go further by exploring lesser-known and underappreciated musicians. Delve into the catalogues of artists like Sun Ra, Eric Dolphy, and Mary Lou Williams, who may not have received as much mainstream recognition but have made significant contributions to jazz.
5. Live Recordings: Jazz is known for its dynamic and spontaneous live performances. Seek out live recordings, such as those from the Newport Jazz Festival or concerts by artists like Ella Fitzgerald or Thelonious Monk. These recordings capture the raw energy and improvisation that make jazz performances so captivating.
6. Support Local Artists: Keep an eye out for talented emerging jazz artists in your local music scene. Attend live performances at jazz clubs or festivals and purchase albums directly from the musicians themselves. Not only will you discover fresh and innovative sounds, but you will also support the growth and sustainability of the jazz community.
7. Embrace Different Instruments and Vocalists: Jazz is not limited to one instrument or style. Make sure to include a variety of instrumentalists and vocalists in your collection to experience the full breadth of jazz expression. Explore recordings by influential jazz vocalists like Billie Holiday, Sarah Vaughan, and Ella Fitzgerald, as well as instrumentalists on instruments such as trumpet, saxophone, piano, and bass.
8. Seek Recommendations: Don’t be afraid to seek recommendations from fellow jazz enthusiasts, friends, or music store employees. They may introduce you to artists or albums you may not have discovered otherwise. Join jazz forums or online communities where you can engage in discussions and exchange recommendations with like-minded individuals.
Remember, building a jazz music collection is a personal journey, and there are no strict rules. Let your own musical tastes and interests guide you as you explore the vast world of jazz. Enjoy the process of discovering new artists, albums, and styles, and let your collection be a reflection of your appreciation for the rich and diverse landscape of jazz music.
Attending Live Jazz Performances
Attending live jazz performances is an exhilarating and immersive experience that allows you to fully appreciate the energy, spontaneity, and creative expression of this vibrant genre. Whether you’re a seasoned jazz enthusiast or new to the world of jazz, here are some reasons why attending live jazz performances should be on your agenda.
1. Feel the Energy: Live jazz performances offer a unique energy and atmosphere that cannot be replicated through recordings alone. Being in the same space as the musicians and feeling the rhythm, groove, and improvisation in real-time creates an electric atmosphere that is both captivating and inspiring.
2. Witness the Art of Improvisation: Jazz is renowned for its improvisational nature, and witnessing musicians create music on the spot is a thrilling experience. Live performances offer a front-row seat to the art of spontaneous creation, where musicians interact, respond to each other, and take risks, crafting unique and unforgettable moments.
3. Connect with the Performers: Attending live jazz performances allows you to connect with the musicians on a more personal level. After the show, you may have the opportunity to meet and talk with the performers, gaining insights into their creative process, influences, and experiences. Building a personal connection with the artists can deepen your appreciation for their music and provide a unique perspective on their craft.
4. Experience Musical Collaboration: Jazz performances often involve a high level of musical collaboration and interaction among the musicians. Witnessing the camaraderie and interplay between band members as they communicate through eye contact, musical cues, and improvisational dialogues is a privilege that brings the music to life.
5. Discover New Talent: Live jazz performances are a great platform to discover emerging talent and local artists. Many jazz clubs and festivals showcase up-and-coming musicians who may become future jazz legends. By attending these performances, you can be at the forefront of discovering fresh and innovative sounds, supporting the growth of the jazz community.
6. Immerse Yourself in Jazz Culture: Live jazz performances provide an immersion into the broader jazz culture. Jazz venues often have a unique ambiance and history associated with the genre. From iconic clubs like the Blue Note in New York to intimate jazz bars in small towns, attending these performances allows you to embrace the rich heritage and traditions of jazz.
7. Enhance Your Listening Skills: Active listening is key to fully experiencing and appreciating jazz music. Attending live performances provides an opportunity to train your ears to discern different improvisational techniques, musical motifs, and interact with the nuances of ensemble playing.
8. Support the Jazz Community: By attending live jazz performances, you are supporting the musicians, venues, and organizers who contribute to the vitality and sustainability of the jazz community. Your presence helps ensure that jazz continues to thrive and provides opportunities for future generations of jazz musicians.
Whether it’s a small intimate club, a large concert hall, or an outdoor jazz festival, make it a priority to experience live jazz performances whenever possible. Soak in the atmosphere, connect with the music, and let yourself be transported by the incredible talents and spontaneous creativity that jazz musicians bring to the stage.
Engaging in Active Listening Techniques
When it comes to jazz music, active listening is key to fully appreciating the intricacies and nuances of this dynamic genre. Engaging in active listening techniques not only enhances your enjoyment but also deepens your understanding of the music and allows you to connect with the emotions and intentions of the performers. Here are some techniques to help you actively listen and get the most out of your jazz listening experiences.
1. Focus and Concentration: Find a quiet and comfortable space where you can give your full attention to the music. Minimize distractions and engage your mind in the music, allowing yourself to be fully present and immersed in the listening experience.
2. Pay Attention to the Ensemble: Jazz is often a collaborative and interactive art form, with musicians responding to each other’s cues and improvising in real-time. Pay attention to how the ensemble interacts and communicates, playing off one another’s ideas and creating a musical dialogue.
3. Follow the Melodic and Rhythmic Development: Listen closely to the melodic and rhythmic lines within the music. Pay attention to how the melodies evolve and develop, and notice the rhythmic variations and syncopations that give jazz its distinctiveness.
4. Identify Different Instruments and Their Roles: Train your ear to identify different instruments and their specific roles within the ensemble. Notice how each instrument contributes to the overall sound and texture of the music, and how they interact and complement one another.
5. Analyze the Harmony and Chord Progressions: Jazz harmony often features complex chord progressions and substitutions, adding depth and complexity to the music. Listen for the changes in chords and analyze how they create tension and resolution throughout the performance.
6. Engage with the Improvisation: Improvisation is a central element of jazz. As you listen to solos, pay attention to how the musicians develop their improvisations, build motifs, and craft their narratives. Notice the melodic choices, rhythmic variations, and harmonic explorations that make each solo unique.
7. Observe the Dynamics and Artistic Expression: Jazz musicians use dynamics, such as playing softly or loudly, to shape the phrasing and emotional impact of their performances. Take note of the subtle changes in volume and artistic expression, and how they contribute to the overall storytelling of the music.
8. Connect with the Emotion and Mood: Allow yourself to be moved by the emotions portrayed in the music. Jazz encompasses a wide range of moods, from joy and playfulness to introspection and melancholy. Let the music evoke and resonate with your own emotions, creating a deeper connection to the performance.
9. Take Notes and Reflect: After listening to jazz recordings or attending live performances, take some time to reflect on your experience. Write down your observations, emotions, and any questions or thoughts that arise. This practice helps solidify your understanding and allows you to revisit and explore different aspects of the music in more depth.
Engaging in active listening techniques allows you to develop a deeper connection and appreciation for jazz music. By focusing on the ensemble interaction, melodic and rhythmic development, harmony, improvisation, dynamics, and emotional expression, you’ll gain a richer understanding of the artistry, creativity, and mastery that jazz musicians bring to their performances.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve embarked on a journey into the captivating world of jazz music. With its rich history, diverse styles, and unique improvisation, jazz offers a truly extraordinary musical experience. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored the origins of jazz, the evolution of its styles, key elements of the music, the art of improvisation, the diverse range of jazz instruments, notable jazz artists, and the importance of attending live performances and engaging in active listening.
By understanding the cultural and historical influences that shaped jazz, you gain a deeper appreciation for the genre’s significance and impact. From the early New Orleans jazz to the avant-garde experiments of free jazz, each era and style of jazz music brings something special to the table.
Key elements such as improvisation, rhythm, harmony, melody, swing, and call-and-response contribute to jazz’s unmistakable sound and style. Jazz instruments, from the saxophone and trumpet to the piano and drums, each bring their own unique flavors to the genre.
We’ve explored the contributions of notable jazz artists who have pushed boundaries, redefined playing styles, and left a lasting legacy. From Louis Armstrong and Duke Ellington to Charlie Parker and Miles Davis, these artists have shaped the course of jazz history through their groundbreaking techniques and innovative compositions.
Building a jazz music collection allows you to explore the vast and diverse world of jazz. From iconic recordings to discovering new talent, your collection reflects your personal appreciation for this remarkable genre.
Attending live jazz performances offers an immersive and thrilling experience. The energy, improvisation, collaboration, and connection between performers and audience create a unique and electrifying atmosphere that cannot be replicated elsewhere.
Lastly, through active listening techniques, you can fully engage with the music, analyze its elements, and connect with the emotions and intentions of the performers. By focusing on the ensemble, following melodic and rhythmic development, identifying instruments, embracing improvisation, and connecting with the artistry, you deepen your understanding and enjoyment of jazz music.
So, whether you’re exploring jazz for the first time or delving deeper into the genre, continue to embrace the magic and versatility of jazz. Immerse yourself in its rhythms, melodies, and improvisations. Engage in active listening, attend live performances, and connect with the vibrant jazz community. Let jazz transport you to new musical heights, and may its soul-stirring melodies continue to inspire and captivate you on your ongoing jazz journey.