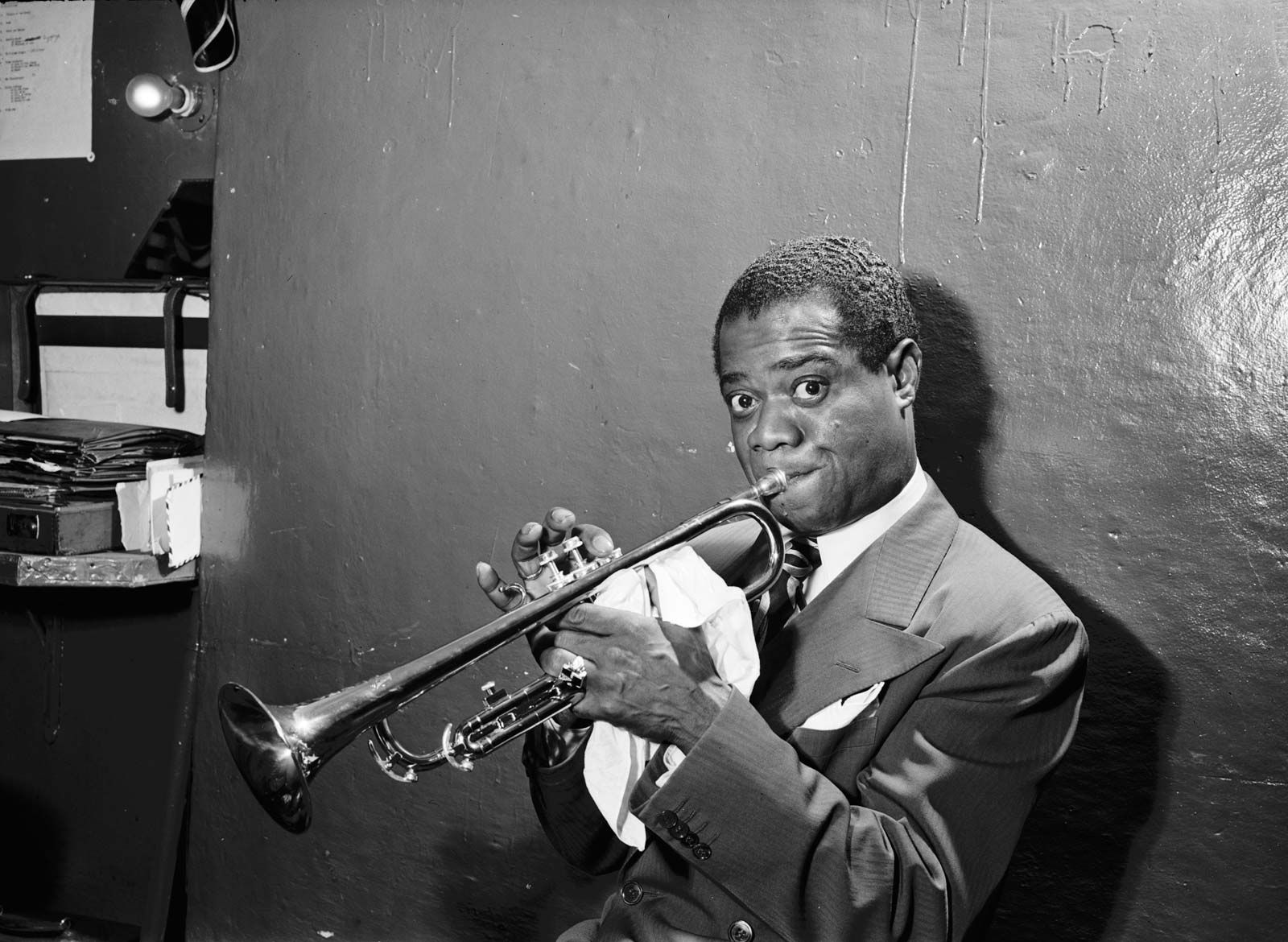
Home>Genres>Jazz>What Did Louis Armstrong Contribute To Jazz


Jazz
What Did Louis Armstrong Contribute To Jazz
Modified: January 28, 2024
Louis Armstrong's monumental contributions to jazz revolutionized the genre, pioneering innovations in improvisation, trumpet playing, and vocal style. Discover how this legendary musician shaped the world of jazz.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Jazz, often referred to as America’s classical music, is a genre deeply rooted in the African American cultural experience. It emerged in the early 20th century and has since become a symbol of creativity, improvisation, and individual expression. At the forefront of this incredible musical journey stands Louis Armstrong, a true jazz legend.
Born on August 4, 1901, in New Orleans, Louisiana, Louis Armstrong grew up in a world filled with vibrant rhythms and soulful melodies. His love for music became evident at a young age, and he honed his skills as a cornet and trumpet player in local marching bands.
Armstrong’s musical journey was heavily influenced by the rich musical heritage of New Orleans, which encompassed a blend of African rhythms, European classical music, and the blues. It was in this melting pot of musical styles and influences that the foundations of jazz were laid, and Armstrong was there to witness its birth.
As Armstrong’s talent grew, so too did his reputation within the jazz community. His unique style of playing, characterized by his distinctive embouchure and impeccable technique, captivated audiences and fellow musicians alike. Armstrong had an innate ability to infuse life into melodies, effortlessly combining sophisticated techniques with raw emotion.
In the early 1920s, Armstrong’s musical career began to skyrocket. He joined King Oliver’s Creole Jazz Band, where he had the opportunity to showcase his skills as a soloist. It was during this time that Armstrong developed his signature improvisational style, also known as “scat singing.” Through vocalizing syllables and nonsensical sounds, Armstrong transformed his voice into an instrument, taking melodies to new heights of expression.
Armstrong’s impact on jazz music cannot be overstated. He revolutionized the concept of solo performance, taking jazz beyond mere ensemble playing. His virtuosic trumpet playing and captivating stage presence brought him international acclaim and opened doors for other jazz musicians.
With his infectious energy and sheer musical genius, Armstrong became a cultural ambassador for jazz. He toured extensively, spreading the joy of jazz to audiences worldwide. His collaborations with renowned musicians such as Ella Fitzgerald, Duke Ellington, and Benny Goodman solidified his place in the pantheon of jazz greats.
Louis Armstrong’s legacy is imprinted in every aspect of jazz music. His technical innovations, such as his rhythmic phrasing and use of extended harmonies, continue to inspire musicians today. Moreover, his ability to capture the essence of human emotions through music transcends time and language, touching the hearts of listeners across generations.
In this article, we will delve into Louis Armstrong’s life and delve into his contributions to the jazz genre. From his early influences to his groundbreaking innovations, Armstrong’s impact on jazz remains unparalleled. Join us as we explore the legacy of this jazz icon and delve deeper into the world of Louis Armstrong and his lasting contributions to the world of music.
Early Life and Influences
Louis Armstrong’s early life was filled with poverty and challenges, but it was also a time when he was exposed to the rich musical heritage of New Orleans. He was born on August 4, 1901, into a poor African American family in the neighborhood known as “Storyville.” This vibrant area was a hotbed of jazz and blues, where musicians and artists thrived despite the social constraints of the time.
Growing up in a rough neighborhood, Armstrong faced many hardships, including a difficult childhood and a sporadic education. However, it was during these formative years that he discovered his passion for music. Armstrong’s first exposure to music came through the local parades, where brass bands played lively tunes that filled the streets with infectious energy.
As a young boy, Armstrong found himself drawn to the sound of the cornet, a brass instrument similar to a trumpet. He would listen intently to the street musicians and parade bands, soaking in the melodies and rhythms. Armstrong’s early musical influences included Joe “King” Oliver, who would become his mentor, as well as the legendary New Orleans cornetist Buddy Bolden.
In addition to the local jazz scene, Armstrong also drew inspiration from the vocal styles of blues singers such as Bessie Smith and Ma Rainey. Their soulful and expressive delivery left a lasting impact on his musical sensibilities. Armstrong’s love for blues and its heartfelt expression of human experience would later become an integral part of his own musical style.
Despite his difficult upbringing, Armstrong’s talent was undeniable, and he found solace in music. In 1913, at the age of 12, Armstrong found his first musical opportunity when he was admitted to the Colored Waif’s Home for Boys. It was there that he received formal music training and learned to play the cornet and eventually the trumpet.
At the Colored Waif’s Home, Armstrong had the chance to practice, receive instruction, and play in the band. This experience not only improved his technical skills, but it also exposed him to a wider range of music and allowed him to collaborate with other talented young musicians. The disciplined environment of the Home provided a nurturing space for Armstrong to grow as a musician and paved the way for his future success.
Louis Armstrong’s early life and influences set the stage for his remarkable musical journey. The vibrant streets of New Orleans and his exposure to the city’s jazz and blues scene shaped his musical sensibilities and ignited a passion within him. It was in these early years that Armstrong learned the language of jazz and developed the unique style that would make him one of the most influential figures in the history of music.
Through adversity and perseverance, Louis Armstrong emerged as a true musical pioneer, who would go on to shape the course of jazz and captivate audiences worldwide. As we delve deeper into his journey, we will explore how Armstrong’s unique style developed and how he went from a young aspiring musician to a legendary icon in the world of jazz.
Development of His Unique Style
Louis Armstrong’s musical journey was marked by the development of his unique style, which would become his trademark and a defining characteristic of his influence on jazz. From his early days as a street musician to his rise as a soloist, Armstrong honed his skills and crafted a style that was instantly recognizable and admired by audiences around the world.
One of the key aspects of Armstrong’s style was his virtuosic trumpet playing. His technical abilities on the instrument were unparalleled, and he possessed a remarkable range and control. Armstrong had the ability to effortlessly navigate intricate melodies, execute dazzling runs, and infuse his playing with soulful expression.
In addition to his technical prowess, Armstrong’s playing was characterized by his exceptional sense of rhythm. He had a natural instinct for swing, a rhythmic feel that gave jazz its infectious groove. Armstrong’s rhythmic phrasing was dynamic and energetic, adding a sense of liveliness to his performances.
But perhaps what set Armstrong apart from other musicians of his time was his ability to infuse his playing with raw emotion. His music spoke directly to the hearts of listeners, transcending language barriers and cultural divides. Whether he was playing a joyous and upbeat tune or a melancholic ballad, Armstrong had the uncanny ability to convey a wide range of emotions through his trumpet.
Another distinctive element of Armstrong’s style was his innovative use of improvised solos. He revolutionized the concept of solo performance in jazz, elevating it beyond mere accompaniment to a focal point of musical expression. Armstrong’s improvisations were full of creativity, spontaneity, and a sense of adventure. His solos were often filled with melodic variations, rhythmic surprises, and unexpected twists and turns, captivating listeners and leaving them in awe.
In addition to his instrumental prowess, Armstrong was also known for his distinctive vocal style. He pioneered the technique of scat singing, which involved using his voice as an instrument, without the use of actual lyrics. Armstrong would use syllables and nonsensical sounds to create melodic lines and improvisations. His scat singing added another layer of excitement and personality to his performances, showcasing his versatility as a musician.
Armstrong’s unique style was a result of his diverse influences and his passion for experimenting and pushing the boundaries of musical expression. His love for the blues, his exposure to New Orleans jazz, and his collaborations with other musicians all played a role in shaping his musical identity.
As Armstrong’s career progressed, his style continued to evolve and mature, but the essence of his playing remained constant. His innovative approach to improvisation, his infectious sense of swing, and his ability to connect emotionally with his audience set the standard for generations of jazz musicians to come.
Louis Armstrong’s development of his unique style solidified his status as a jazz icon. He carved a path for himself, defying conventions and inspiring countless musicians with his unparalleled talent and creativity. In the next section, we will explore how Armstrong’s popularity as a soloist helped to popularize jazz and bring it into the mainstream.
Popularizing Jazz as a Soloist
Louis Armstrong played a pivotal role in popularizing jazz as a soloist, elevating the genre from its roots as ensemble music to a form of individual expression and virtuosity. Through his groundbreaking performances and recordings, Armstrong captured the hearts of audiences worldwide and brought the vibrant sounds of jazz into the mainstream.
As a member of the influential King Oliver’s Creole Jazz Band in the early 1920s, Armstrong began to garner attention for his exceptional trumpet playing and improvisational skills. His solos were a highlight of the band’s performances, and word quickly spread about his remarkable talent.
In 1925, Armstrong began his solo career, recording a series of groundbreaking records known as the “Hot Five” and the “Hot Seven” sessions. These recordings showcased Armstrong as a bandleader and soloist, allowing him to truly shine and stretch the boundaries of jazz.
One of Armstrong’s most iconic recordings from this period is “West End Blues,” featuring his dazzling trumpet playing and soulful vocals. The song, with its complex harmonies and intricate melodic lines, demonstrated Armstrong’s virtuosity and mastery of his instrument. It was a defining moment in jazz history, showcasing Armstrong’s ability to bring the essence of jazz into a solo setting.
Armstrong’s popularity as a soloist grew rapidly, and he soon became a fixture in the jazz scene, performing at venues across the United States and Europe. His charismatic stage presence and infectious energy captivated audiences, and his live shows became legendary, filled with thrilling solos and joyful improvisation.
In addition to his live performances, Armstrong’s recorded output played a significant role in popularizing jazz. His recordings, with their captivating melodies and irresistible rhythms, reached a wider audience and helped introduce jazz to new listeners. Armstrong’s influence extended beyond the jazz community, as his music resonated with people from all walks of life, breaking down racial and cultural barriers.
Armstrong’s popularity as a soloist also led to collaborations with other musicians in a variety of genres. He worked with artists such as Ella Fitzgerald, Duke Ellington, and Benny Goodman, further expanding the reach of jazz and exposing it to new audiences. These collaborations brought jazz into the mainstream and solidified Armstrong’s position as a cultural icon.
Through his innovative approach to solo performance, Armstrong showed the world the true potential of jazz as a vehicle for individual expression. He brought a new level of artistry and improvisation to the genre, paving the way for future generations of jazz musicians to explore their own creative paths.
Louis Armstrong’s contributions to popularizing jazz as a soloist cannot be overstated. His virtuosic playing, infectious energy, and ability to connect with audiences on an emotional level made him a beloved figure in the world of music. His legacy as a trailblazer continues to inspire and shape the landscape of jazz today. As we delve deeper into Armstrong’s innovations and contributions, the next section will explore his impact on the development of jazz music as a whole.
Innovations and Contributions to Jazz Music
Louis Armstrong’s impact on jazz music goes far beyond his incredible playing and charismatic stage presence. He was a true innovator who revolutionized the genre and left an indelible mark on its development. From his groundbreaking improvisations to his technical innovations, Armstrong’s contributions to jazz music continue to shape and inspire musicians to this day.
One of Armstrong’s most significant contributions to jazz was his pioneering use of improvisation. He elevated the concept of soloing to new heights, introducing a level of creativity and spontaneity that became a hallmark of the genre. Armstrong’s improvisations were filled with melodic variations, rhythmic ingenuity, and a sense of adventure that captivated audiences and pushed the boundaries of what jazz could be.
Armstrong’s innovative approach to improvisation was accompanied by his use of extended harmonies. He expanded the harmonic language of jazz, introducing complex chord progressions and advanced harmonic concepts into his playing. This added depth and richness to the music, taking jazz beyond its traditional roots and into more sophisticated and complex territory.
Another notable innovation from Armstrong was his use of scat singing. Through his vocalizations of nonsensical syllables and sounds, Armstrong transformed his voice into an instrument, adding an entirely new dimension to his performances. His scat singing was an extension of his improvisational abilities, allowing him to create spontaneous melodies and engage in musical conversations with his fellow musicians.
Armstrong also played a crucial role in bridging the gap between traditional jazz and the swing era. With his impeccable sense of rhythm and infectious swing feel, he helped popularize the transition from the early New Orleans style to the more modern and syncopated sounds of the swing era. His recordings with his big bands, such as “Struttin’ with Some Barbecue” and “Weather Bird,” showcased his ability to incorporate the ensemble into his improvisational style, creating a cohesive and dynamic musical experience.
In addition to his musical innovations, Armstrong’s contributions extended to the realm of song interpretation. He had a unique ability to infuse lyrics with emotion, bringing the storytelling aspect of jazz to life. His interpretations of songs like “What a Wonderful World” and “Stardust” became iconic, showcasing his ability to connect deeply with listeners through his soulful and heartfelt performances.
Furthermore, Armstrong’s influence extended beyond his music. He broke down racial barriers by becoming one of the first African American musicians to achieve mainstream success and recognition. His success paved the way for other black musicians, opening doors and inspiring generations of jazz artists.
Louis Armstrong’s innovations and contributions to jazz music shaped the trajectory of the genre and continue to reverberate throughout the music world. His use of improvisation, extended harmonies, scat singing, and swing feel pushed the boundaries of what jazz could be. His masterful interpretations brought a new level of emotional depth to the music, touching the hearts of millions. Armstrong’s impact on jazz and the music industry as a whole is immeasurable and his legacy as a pioneer and musical genius remains unchallengeable.
Collaborations and Influence on Other Musicians
Louis Armstrong’s influence on jazz extends beyond his own performances and recordings. He was also a collaborator and mentor to many other musicians, shaping the course of their careers and leaving a lasting impact on the jazz community. Through his collaborations and mentorship, Armstrong’s influence reverberated throughout the jazz world, helping to elevate the genre and inspire future generations of musicians.
One of Armstrong’s most notable collaborations was with legendary jazz pianist and bandleader Duke Ellington. In 1961, Armstrong and Ellington joined forces to record the album “The Great Summit.” Their collaboration showcased a meeting of two musical giants, combining Armstrong’s powerful trumpet playing and expressive vocals with Ellington’s sophisticated arrangements and innovative compositions. This iconic collaboration highlighted the mutual respect and admiration between the two artists and further solidified Armstrong’s influence on the jazz community.
Another significant collaboration in Armstrong’s career was with the incomparable jazz vocalist Ella Fitzgerald. The two joined forces on several occasions, recording albums together and performing live. Their chemistry and musicality were unparalleled, as they effortlessly traded melodies and harmonized with each other. Their recordings, such as “Ella and Louis” and “Porgy and Bess,” showcased their mastery of jazz interpretation and their ability to connect with each other on a deeply musical level.
In addition to his collaborations with established musicians, Armstrong also served as a mentor and inspiration to younger generations of jazz artists. One notable example is his influence on trumpet player and bandleader Dizzy Gillespie. Gillespie credited Armstrong as one of his primary influences, recognizing Armstrong’s technical skill and innovative approach to improvisation as a pivotal force in shaping his own playing style. Armstrong’s impact can also be seen in the playing of trumpet virtuosos such as Miles Davis, who acknowledged Armstrong’s influence on his approach to melody and improvisation.
Beyond his collaborations and mentorship, Armstrong’s influence can be seen in the broader evolution of jazz music. His innovative use of improvisation, extended harmonies, and scat singing inspired countless musicians to push the boundaries of their own creativity. His masterful sense of rhythm and swing helped shape the development of the swing era and influenced subsequent jazz styles.
Armstrong’s larger-than-life personality and infectious stage presence also left an impression on those who witnessed his performances. His joyful spirit and charismatic persona inspired musicians to bring their own unique personalities and energy to the stage, leaving a lasting impact on the live performance aspect of jazz.
Louis Armstrong’s collaborations and influence on other musicians were instrumental in shaping the evolution of jazz. Through his mentorship and collaborations, he shared his innovative approach to music and inspired generations of musicians to explore their own artistic paths. His legacy as a trailblazer and musical genius lives on in the countless artists who continue to be inspired by his groundbreaking contributions to the world of jazz.
Legacy and Impact on the Jazz Genre
Louis Armstrong’s legacy and impact on the jazz genre are immeasurable. His contributions as an instrumentalist, vocalist, and innovator continue to shape the landscape of jazz and resonate with musicians and audiences worldwide. From his technical virtuosity to his infectious stage presence, Armstrong’s influence can be felt in every corner of the jazz world.
One of Armstrong’s most significant contributions to the jazz genre is his role in popularizing it as a form of artistic expression. Through his captivating performances and recordings, Armstrong brought jazz into the mainstream, making it accessible to a wider audience. He transformed the perception of jazz from simply background music to a sophisticated art form, appreciated for its intricacies and emotional depth.
Armstrong’s incredible trumpet playing remains a benchmark for aspiring jazz musicians. His technical prowess, melodic creativity, and rhythmic precision set a standard that musicians strive to emulate. His influence can be heard in the playing of countless trumpeters, who incorporate Armstrong’s innovations in their own music and carry on his legacy.
In addition to his instrumental mastery, Armstrong’s warm and soulful vocals left an indelible mark on the jazz genre. His interpretations of songs brought a unique blend of emotion and storytelling, captivating listeners and conveying a deep sense of musicality. Armstrong’s vocal style has influenced generations of jazz singers, who draw inspiration from his phrasing, intonation, and ability to connect with listeners on a deeply personal level.
Beyond his musical contributions, Armstrong’s charismatic personality and positive outlook on life left a lasting impact on jazz and popular culture as a whole. His infectious energy and joyful stage presence brought an element of showmanship to jazz performances, captivating audiences around the world. His larger-than-life persona helped shape the image of jazz as an exciting and dynamic genre.
Armstrong’s influence goes well beyond his own lifetime. His contribution to jazz paved the way for future generations of musicians to experiment, innovate, and push the boundaries of the genre. His focus on individual expression and improvisation encouraged artists to find their unique voice and contribute their own creative ideas to the evolving jazz landscape.
Moreover, Armstrong’s impact on breaking down racial barriers cannot be understated. As one of the first African American musicians to achieve mainstream success, Armstrong served as a role model for aspiring musicians of all races and backgrounds. His success helped challenge societal norms and contributed to the ongoing fight for racial equality in the music industry.
In recognition of his monumental contributions to jazz, Louis Armstrong received numerous accolades and honors throughout his career, including a Grammy Lifetime Achievement Award and induction into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame. His iconic recordings, such as “What a Wonderful World” and “Hello, Dolly!,” continue to be celebrated and cherished by audiences today.
Louis Armstrong’s legacy as a jazz pioneer, virtuoso performer, and cultural icon is firmly embedded in the fabric of American music history. His innovations, influence, and timeless recordings continue to inspire and shape the jazz genre. Whether it’s his electrifying trumpet solos, powerful vocals, or infectiously joyful spirit, Louis Armstrong’s impact on jazz music remains as vibrant and relevant today as ever.
Conclusion
Louis Armstrong’s impact on jazz is immeasurable. His unique style, technical innovations, and captivating stage presence have solidified his place as one of the greatest musicians in history. Through his remarkable career, Armstrong popularized jazz as a soloist, breaking down barriers and bringing the genre into the mainstream.
From his humble beginnings in New Orleans to his international acclaim, Armstrong’s journey is intertwined with the history of jazz itself. His influence can be heard in the playing of countless musicians, both trumpet players and vocalists, who strive to emulate his virtuosity and sense of musicality.
Armstrong’s contributions as an innovator in jazz are unmatched. His improvisational skills, extended harmonies, and scat singing techniques pushed the boundaries of what jazz could be, inspiring generations of musicians to explore new horizons of musical expression.
But beyond his technical prowess, Armstrong’s lasting legacy is the joy and emotion he brought to his music. His infectious energy and larger-than-life persona continue to inspire and uplift audiences, transcending time and cultural barriers.
Furthermore, Armstrong’s impact extends beyond music. As a groundbreaking African American artist, he shattered racial barriers and opened doors for future generations of black musicians. His success paved the way for a more inclusive and diverse jazz community, contributing to the ongoing fight for equality and justice.
In conclusion, Louis Armstrong’s contributions to jazz music are immeasurable. His innovative style, masterful playing, and pioneering spirit have left an indelible mark on the genre. As we celebrate his legacy, we recognize the profound impact he has had on generations of musicians and the enduring power of his music. Louis Armstrong is and will forever be remembered as a true jazz legend.