Home>Instruments>Synthesizer>What Is A Synthesizer Keyboard


Synthesizer
What Is A Synthesizer Keyboard
Modified: February 20, 2024
Discover the world of synthesizers with a versatile and powerful synthesizer keyboard. Explore the endless possibilities of sound creation and music production.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Synthesizer keyboards have revolutionized the world of music, allowing musicians and enthusiasts to create a vast array of sounds and textures. These versatile instruments have become an integral part of countless genres, from electronic and pop music to film scores and experimental compositions. Whether you’re a professional musician or a hobbyist, understanding the fundamentals of synthesizer keyboards can enrich your musical journey.
At its core, a synthesizer keyboard is an electronic instrument that generates and manipulates sounds. Unlike traditional instruments that produce sound through physical vibrations, synthesizer keyboards use electronic circuits and software to generate and shape audio signals. This innovative approach gives musicians unprecedented control over the timbre, pitch, and dynamics of sounds, enabling them to create unique and expressive music.
The history of synthesizer keyboards dates back to the mid-20th century when pioneers like Robert Moog and Don Buchla made groundbreaking advancements in electronic music technology. These early synthesizers were large, modular systems that required extensive knowledge to operate. However, the development of integrated circuit technology in the 1970s led to the creation of more accessible and compact synthesizer keyboards that could be played like traditional pianos.
Today, synthesizer keyboards come in various shapes and sizes, catering to the diverse needs and preferences of musicians. From portable MIDI controllers to sophisticated workstation keyboards, the market offers a wide range of options for both beginners and professionals. Understanding the different types of synthesizers and their features is crucial for making an informed choice.
When playing a synthesizer keyboard, you can craft complex soundscapes by combining and modifying different waveforms, applying filters and effects, and utilizing various performance features such as arpeggiators and sequencers. The possibilities are virtually limitless, allowing musicians to unleash their creativity and bring their musical visions to life.
In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of synthesizer keyboards. We will explore their history, delve into the inner workings of these instruments, discuss the different types available, highlight notable brands, and provide tips on choosing the right synthesizer keyboard. Whether you’re a curious music lover or a seasoned musician looking for new horizons, this article will serve as a guide to the captivating world of synthesizer keyboards.
History of Synthesizer Keyboards
The history of synthesizer keyboards is a fascinating journey that showcases the innovative spirit of musicians and engineers. It all began in the mid-20th century when pioneers like Robert Moog, Don Buchla, and Raymond Scott started experimenting with electronic music technology.
In the 1960s, Robert Moog introduced the Moog synthesizer, a modular system that revolutionized the music industry. This groundbreaking instrument utilized voltage-controlled oscillators, filters, and amplifiers to generate and shape electronic sounds. The Moog synthesizer quickly gained popularity among musicians, and its influence can be heard in countless records from that era.
Around the same time, Don Buchla introduced the Buchla synthesizer, another modular system that offered a unique approach to electronic sound synthesis. Buchla’s instrument emphasized the use of control voltage to manipulate different parameters, allowing musicians to explore new sonic possibilities.
The 1970s marked a significant milestone in the history of synthesizer keyboards with the development of integrated circuit technology. This advancement paved the way for smaller, more affordable synthesizers that could be played like traditional keyboards.
One iconic synthesizer from the 1970s is the ARP Odyssey, which gained popularity for its compact design and versatile sound capabilities. Its distinctive sound can be heard in countless songs of that era.
As technology continued to advance, digital synthesis entered the scene. Digital synthesizers, such as the Yamaha DX7, offered a new realm of possibilities with their ability to create complex and realistic sounds. This marked the beginning of a shift towards more affordable and accessible synthesizers.
In the 1990s, virtual analog synthesizers emerged, blending the convenience and affordability of digital technology with the warm and rich sound of analog synths. Instruments like the Access Virus and Nord Lead became popular choices among musicians due to their versatility and sonic capabilities.
Today, synthesizer keyboards continue to evolve with the integration of computer-based music production and software synths. Virtual instruments and plugins provide musicians with a vast array of sounds and effects, all within the convenience of a computer-based setup.
The history of synthesizer keyboards is a testament to the ingenuity of musicians and engineers who pushed the boundaries of music technology. From the early modular systems to the modern digital and virtual instruments, synthesizers have shaped the sound of popular music and continue to inspire musicians around the world.
How a Synthesizer Keyboard Works
Understanding how a synthesizer keyboard works is key to unlocking its potential for creating innovative and unique sounds. At its core, a synthesizer keyboard generates sound through electronic circuits and software algorithms. Here are the fundamental components and processes that make a synthesizer keyboard work:
Oscillators: Oscillators are the building blocks of sound generation in a synthesizer. These electronic circuits generate waveform signals at specific frequencies. The most common waveforms are sine, triangle, sawtooth, and square waves. By combining and modulating these waveforms, a wide range of tones can be created.
Filters: Filters shape the sound by selectively attenuating or emphasizing certain frequencies. They control the brightness and timbre of the sound. Common filter types include low-pass, high-pass, and band-pass filters. By adjusting the filter cutoff and resonance, you can sculpt the character of the sound.
Amplifiers: Amplifiers control the volume and dynamics of the sound. They help shape the attack, sustain, decay, and release of a note. By adjusting the envelope settings (attack, decay, sustain, release), you can create a wide range of expressive sounds.
Modulation Sources and Destinations: Synthesizer keyboards offer various modulation sources, such as envelopes, LFOs (Low-Frequency Oscillators), and modulation wheels. These sources control parameters such as pitch, filter cutoff, and amplitude, adding movement and complexity to the sound. Modulation destinations are the parameters that can be modulated, such as oscillator pitch or filter cutoff frequency.
Effects: Many synthesizer keyboards include built-in effects like reverb, delay, chorus, and distortion. These effects further enhance and shape the sound, adding depth and character to your compositions.
MIDI and Connectivity: MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) allows synthesizer keyboards to communicate and synchronize with other MIDI-compatible devices. Through MIDI, you can control external sound modules, software synthesizers, and recording software. Additionally, most synthesizer keyboards feature audio outputs, MIDI inputs and outputs, and USB connectivity for interfacing with other equipment.
Sound Libraries and Patch Memories: Synthesizer keyboards often include sound libraries or patch memories where you can store and recall presets. These presets are pre-programmed settings that allow you to instantly access different sounds and settings. Some synthesizers also allow you to create your own patches, giving you complete control over the sound design process.
By understanding the inner workings of a synthesizer keyboard, you can unleash your creativity and explore a vast sonic landscape. Experimenting with oscillators, filters, modulation, and effects will enable you to craft sounds that are unique to your musical vision.
Types of Synthesizer Keyboards
Synthesizer keyboards come in various types, each catering to specific musical needs and preferences. Here are some of the most common types of synthesizer keyboards:
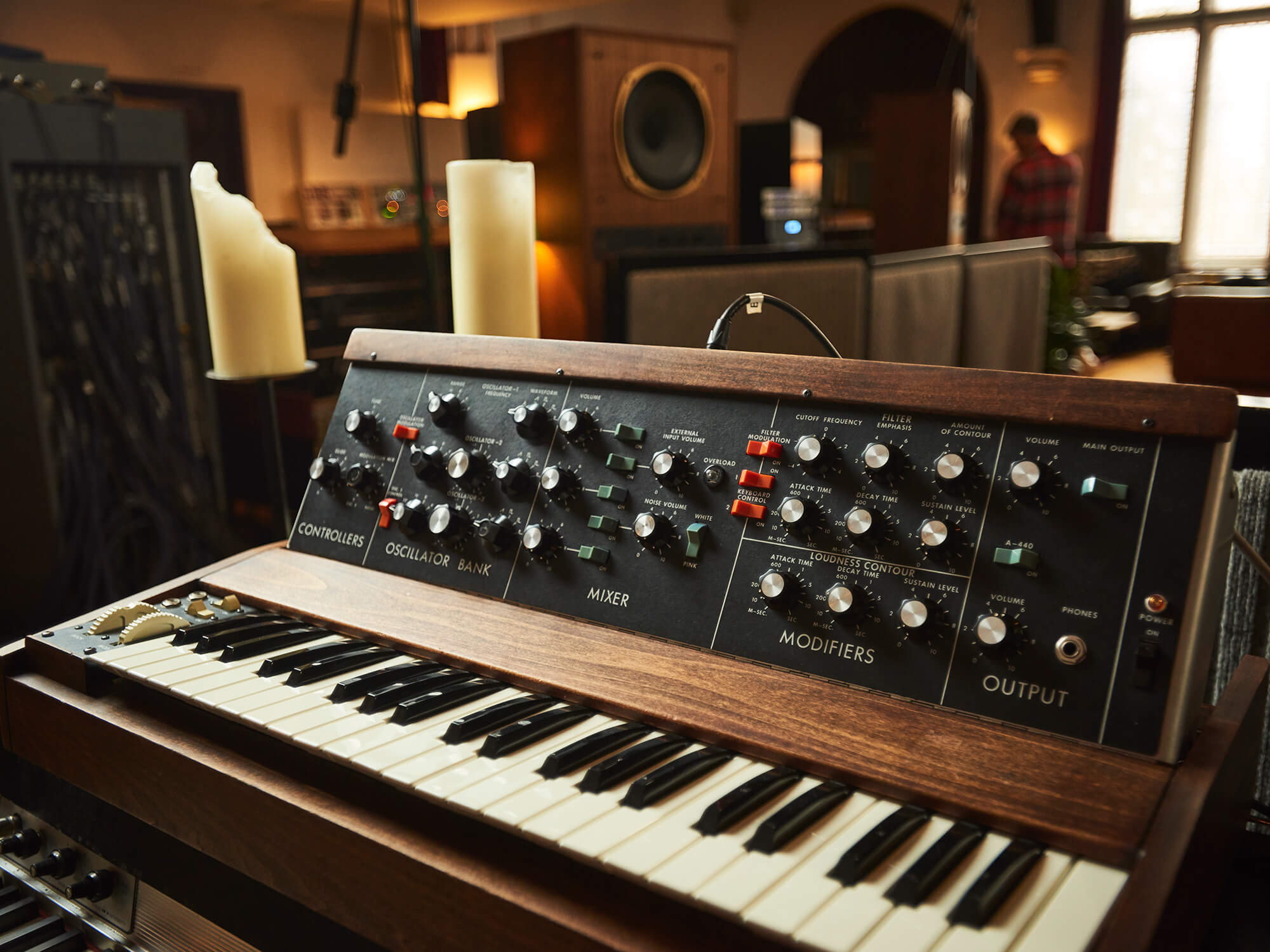
Analog Synthesizers: Analog synthesizers are revered for their rich, warm, and often vintage sound. They use analog circuits and components to generate and shape audio signals. Analog synthesizers are known for their raw and organic sound, and they are a favorite among musicians seeking a vintage or retro vibe.
Virtual Analog Synthesizers: Virtual analog synthesizers, also known as software synthesizers or soft synths, emulate the sound and functionality of analog synthesizers using digital algorithms. Despite being software-based, virtual analog synthesizers can produce high-quality and versatile sounds that closely resemble their analog counterparts. They offer the convenience and flexibility of digital technology while capturing the essence of analog synthesis.
FM Synthesizers: FM (Frequency Modulation) synthesizers utilize complex algorithms to generate sounds through the manipulation of multiple oscillators. FM synthesis produces harmonically rich and intricate tones, allowing for the creation of unique and evolving timbres. The Yamaha DX7, one of the most iconic FM synthesizers, played a pivotal role in shaping the sound of the 1980s.
Sampling Synthesizers: Sampling synthesizers use recorded sounds, or samples, as the basis for sound generation. These samples can be played at different pitches and manipulated in various ways to create realistic and expressive sounds. Sampling synthesizers excel in recreating acoustic instruments, as well as creating unique sound effects and textures.
Workstation Keyboards: Workstation keyboards are comprehensive music production tools that integrate various features, including synthesizers, sequencers, audio recording capabilities, and built-in effects. These all-in-one instruments are ideal for musicians who want to create, record, and perform music without the need for additional equipment or software.
MIDI Controllers: MIDI controllers are stripped-down synthesizer keyboards that focus primarily on transmitting MIDI data to other devices. With no built-in sounds of their own, MIDI controllers serve as a versatile interface for controlling software synthesizers, hardware sound modules, and other MIDI-compatible devices.
Performance Synthesizers: Performance synthesizers are designed with live performance in mind. These keyboards offer features like split and layer modes for playing multiple sounds simultaneously, extensive control options, and intuitive interfaces for seamless on-stage operation. Performance synthesizers are popular among stage performers, bands, and electronic music artists.
Understanding the different types of synthesizer keyboards will help you choose the one that aligns with your musical style and creative needs. Whether you prefer the vintage charm of analog synthesizers, the versatility of virtual analog instruments, or the comprehensive capabilities of workstation keyboards, there is a synthesizer keyboard out there that will empower you to explore new sonic territories.
Features and Functions of Synthesizer Keyboards
Synthesizer keyboards offer a wide range of features and functions that enhance the sound creation and performance experience. Understanding these features will allow you to unleash your creativity and take full advantage of the capabilities of your synthesizer. Here are some of the key features and functions commonly found in synthesizer keyboards:
Sound Generation: Synthesizers utilize various methods of sound generation, including oscillators, filters, and amplifiers. The number and type of oscillators, waveform options, filter types, and modulation capabilities impact the sonic versatility and richness of the synthesizer.
Polyphony: Polyphony refers to the number of voices a synthesizer can play simultaneously. Higher polyphony allows for more complex and layered sounds, making it ideal for creating lush pads, thick chords, and intricate arrangements.
Keyboard: The keyboard of a synthesizer allows you to play notes and melodies. Synthesizer keyboards come in different sizes, ranging from compact 25-key models to full-sized 88-key pianos. Keyboard action types, such as weighted, semi-weighted, and synth-action, provide different playing experiences to suit various musical styles and preferences.
Modulation and Performance Controls: Synthesizers often feature modulation sources, like envelopes and LFOs, allowing you to shape and manipulate parameters such as pitch, filter cutoff, and amplitude. Performance controls like pitch bend and modulation wheels, touchstrips, and assignable knobs provide expressive control over the sound in real-time.
Sequencers and Arpeggiators: Many synthesizer keyboards include built-in sequencers and arpeggiators. Sequencers allow you to create and edit musical patterns and sequences, which can be played back continuously or triggered manually. Arpeggiators generate repeating patterns from held chords or notes, creating rhythmic and melodic motifs.
Effects: Built-in effects like reverb, delay, chorus, and distortion add depth, spatialization, and character to the sound. These effects can be applied to individual sounds or the overall mix, transforming the sonic palette and creating immersive textures.
Sound Libraries and Presets: Synthesizer keyboards often come with a variety of built-in sounds and presets. These pre-programmed settings allow for quick access to different sounds, ranging from classic to modern synth tones. Some synthesizers offer expandable sound libraries or the ability to load custom samples and patches.
Connectivity: Synthesizers feature various connectivity options for integration with external gear. These include MIDI inputs and outputs, USB ports for connecting to computers and controllers, audio outputs for connecting to mixers or audio interfaces, as well as CV/Gate outputs for interfacing with modular synthesizers.
Understanding and utilizing the features and functions of a synthesizer keyboard will expand your creative possibilities and help you shape unique and compelling sounds. Take the time to explore and experiment with these features, and you’ll be amazed at the sonic landscapes you can create.
Popular Synthesizer Keyboard Brands
Synthesizer keyboards are produced by numerous manufacturers, each offering their own unique take on sound design and performance capabilities. Here are some of the most notable and popular synthesizer keyboard brands:
- Moog Music: Moog is renowned for its iconic analog synthesizers. Known for their warm, fat, and expressive sounds, Moog synthesizers have played a significant role in shaping the history of electronic music. Their flagship models, such as the Moog Minimoog Model D and the Moog Subsequent 37, continue to be highly coveted by professionals and enthusiasts alike.
- Korg: Korg is a leading manufacturer of synthesizer keyboards, offering a diverse range of models to suit different musical styles and budgets. From the legendary Korg MS-20 to the popular Korg Minilogue, their instruments are known for their powerful sound engines, intuitive interfaces, and innovative features like motion sequencing and wavetable synthesis.
- Roland: Roland has a rich legacy in the synthesizer world, producing iconic instruments such as the Roland Jupiter-8 and the Roland TB-303. Today, they continue to offer a wide range of synthesizer keyboards, including the flagship Roland Jupiter-X series and the versatile Roland System-8, known for their exceptional sound quality and performance capabilities.
- Novation: Novation is revered for its innovative and user-friendly synthesizer keyboards, particularly in the realm of virtual analog synthesis. The Novation Peak and Novation Circuit are highly regarded for their versatile sound engines, intuitive interfaces, and seamless integration with computer-based music production setups.
- Yamaha: Yamaha is a prominent player in the synthesizer market, catering to different types of musicians. Their instruments range from entry-level options like the Yamaha Reface series to professional workstations like the Yamaha Montage. Known for their reliability, sound quality, and extensive features, Yamaha synthesizers are widely used across different music genres.
- Nord: Nord synthesizer keyboards are renowned for their exceptional sound quality, innovative features, and stage-worthy designs. Their instruments, like the Nord Lead and Nord Stage series, offer expressive control, realistic emulations, and a vast library of high-quality sounds. Nord synthesizers are favored by live performers and studio musicians.
These are just a few examples of popular synthesizer keyboard brands, and there are many other notable manufacturers making significant contributions to the world of synthesizers. When choosing a synthesizer keyboard, consider factors such as sound quality, features, user interface, and your specific musical requirements to find the brand and model that best suits your needs.
Choosing the Right Synthesizer Keyboard
Choosing the right synthesizer keyboard is an important decision that depends on your musical goals, preferences, and budget. With the wide variety of options available on the market, it’s essential to consider several factors when making your choice. Here are some key considerations to help you find the perfect synthesizer keyboard:
Sound: Consider the type of sound you want to create. Do you prefer warm analog tones, versatile digital sounds, or realistic sample-based instruments? Each synthesizer offers its own unique sonic characteristics, so listen to demos, read reviews, and consider the genres and styles of music the keyboard is best suited for.
Features: Determine the features that are most important to you. Do you need advanced modulation capabilities, an extensive effects section, a built-in sequencer, or performance controls like pitch bend and mod wheels? Make a list of the features you prioritize to ensure the synthesizer meets your specific needs.
Keyboard Size and Action: Consider the size and action of the keyboard. Would you prefer a compact and portable MIDI controller or a full-sized keyboard with weighted or semi-weighted keys? The keyboard size and action will affect the playability and feel of the instrument, so choose a keyboard that suits your playing style and comfort.
Budget: Set a budget range for your purchase. Synthesizer keyboards vary widely in price, from affordable entry-level models to high-end professional instruments. Determine how much you’re willing to spend and explore the options within that price range.
Expandability: Consider the expandability of the synthesizer. Some keyboards allow for additional sound libraries, software updates, or the ability to connect to external modules or controllers. If you anticipate wanting to expand and customize your sound in the future, choosing a synthesizer with expandable options is beneficial.
User Interface: Evaluate the user interface of the synthesizer. Does it have an intuitive layout and easy-to-use controls? Will you be able to navigate through the menus and parameters efficiently? A well-designed and intuitive user interface will make it easier for you to access and manipulate the features of the synthesizer.
Ergonomics and Portability: Consider the ergonomics and portability of the synthesizer. If you plan to travel or perform live, a compact and lightweight synthesizer may be more suitable. On the other hand, if you primarily work in a studio setting, a larger and more robust keyboard may be preferable.
Reviews and Recommendations: Read reviews and seek recommendations from other musicians, experts, or online communities. Their insights and experiences can provide valuable guidance in your decision-making process.
By considering these factors, you can narrow down your options and find a synthesizer keyboard that aligns with your musical style, budget, and creative aspirations. Remember to take your time, explore different models, and try them out whenever possible to ensure the keyboard feels comfortable and inspires your musical journey.
Tips for Playing a Synthesizer Keyboard
Playing a synthesizer keyboard is not only about mastering the technical aspects of the instrument but also about expressing your musicality and creativity. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced player, these tips will help you get the most out of your synthesizer playing experience:
1. Learn the Basics: Familiarize yourself with the fundamental concepts of synthesizers, such as oscillators, filters, and modulation. Understanding how these components work together will give you a solid foundation for sound design and manipulation.
2. Experiment with Different Sound Sources: Don’t be afraid to explore various sound sources, such as different waveforms, samples, or presets. Experiment with combining and layering sounds to create unique textures and sonic landscapes.
3. Master the Art of Modulation: Modulation adds depth and movement to your sounds. Learn how to use envelopes, LFOs, and modulation wheels to create evolving textures and dynamic changes in your playing.
4. Use Effects Wisely: Effects can enhance and shape your sound, but it’s important to use them judiciously. Experiment with different types of effects and learn how to apply them tastefully to create the desired mood or atmosphere.
5. Explore Performance Controls: Take advantage of the performance controls on your synthesizer, such as pitch bend and mod wheels. Utilize them to add expressiveness and nuances to your playing, imitating the characteristics of traditional instruments like guitars or orchestral instruments.
6. Practice Playing Expressively: Focus on playing with dynamics and expression. Use velocity and aftertouch to add variations in volume and timbre. This will give your performance a more human and emotive quality.
7. Experiment with Different Playing Techniques: Explore different playing techniques to create unique sounds. Try using the sustain pedal, varying your touch, or experimenting with unconventional approaches to achieve interesting textures and effects.
8. Learn Basic Music Theory: Having a basic understanding of music theory will help you make informed choices when creating melodies, chords, and harmonies. It will also enhance your ability to improvise and compose music on the synthesizer.
9. Collaborate and Learn from Others: Connect with other musicians, join online communities, or participate in jam sessions. Collaborating with others will expose you to new ideas, techniques, and playing styles, helping you grow as a synthesizer player.
10. Experiment and Have Fun: Ultimately, the synthesizer is your playground for creativity. Don’t be afraid to explore, experiment, and have fun with your instrument. Let your curiosity guide you and embrace the joy of creating unique sounds and music.
By incorporating these tips into your practice and performance routines, you’ll develop a deeper understanding of the synthesizer keyboard and unlock its full potential for creative expression.
Conclusion
Synthesizer keyboards have revolutionized the world of music, offering musicians and enthusiasts an unparalleled realm of sonic possibilities. From the early days of analog synthesis to the modern digital and virtual instruments, synthesizers have evolved into powerful tools that empower musicians to create unique and expressive music.
In this article, we’ve explored the history of synthesizer keyboards, delving into the innovations of pioneers like Robert Moog and Don Buchla. We’ve examined how synthesizer keyboards work, discussing the fundamental components and processes involved in sound generation. We’ve also explored the different types of synthesizer keyboards available, from analog and virtual analog to FM and sampling-based instruments.
Understanding the features and functions of synthesizer keyboards is crucial for choosing the right instrument. From sound generation and modulation capabilities to keyboard action and expandability, these factors play a vital role in shaping your musical experience.
Popular synthesizer keyboard brands like Moog, Korg, Roland, Novation, Yamaha, and Nord offer a diverse range of instruments, each with its unique sonic characteristics and performance capabilities. Exploring these brands and their offerings will help you find the synthesizer keyboard that resonates with your musical style and creative vision.
Lastly, we provided valuable tips for playing a synthesizer keyboard, emphasizing the importance of experimentation, expressive playing, and continuous learning. By embracing these tips, you’ll not only master the technical aspects but also infuse your playing with emotion and creativity.
Whether you’re a professional musician, a studio producer, or an aspiring enthusiast, synthesizer keyboards have the power to unlock new dimensions of music creation. So, dive into the world of synthesizer keyboards, explore their vast sonic landscapes, and unleash your musical imagination.