Home>Production & Technology>Metronome>What Is The Period And Frequency Of A Metronome Set At 180


Metronome
What Is The Period And Frequency Of A Metronome Set At 180
Published: January 14, 2024
Discover the period and frequency of a metronome set at 180. Learn how this tempo affects your music practice.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
A metronome is a valuable tool for musicians of all levels, helping them maintain a consistent tempo and rhythm while practicing or performing. It acts as a reliable timekeeper, producing regular beats at a specific speed. Among the many settings available, one of the commonly used tempos is 180 beats per minute (BPM). In this article, we will explore the period and frequency of a metronome set at 180 BPM, and how it can benefit musicians in their musical endeavors.
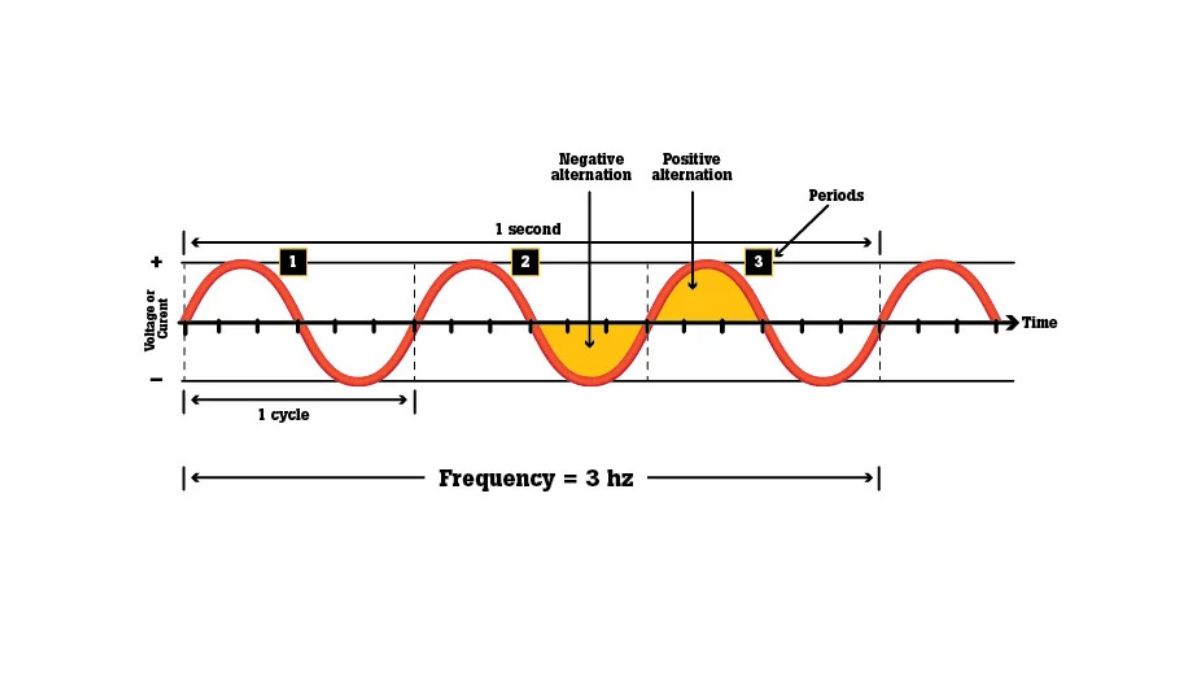
Understanding the concept of period and frequency is crucial to comprehend the functioning of a metronome. The period refers to the time it takes for one complete cycle of the metronome beat, while frequency is the number of cycles completed per unit of time. In the case of a metronome set at 180 BPM, the period would be 1/180th of a minute, or approximately 333 milliseconds, while the frequency would be 180 cycles per minute.
Metronomes come in various forms, from traditional mechanical ones with a swinging pendulum to modern digital ones with digital screens and sound options. Regardless of their design, their primary function remains the same – to provide a steady and consistent beat for musicians to follow. By setting a metronome to a specific tempo, musicians can develop their timing, improve their accuracy, and enhance their overall musical performance.
Understanding Period and Frequency
Before delving into the specifics of a metronome set at 180 BPM, it’s important to have a clear understanding of what period and frequency mean in relation to musical timing.
The period of a metronome refers to the time it takes for one complete cycle of the metronome beat. It can be measured in various units, but in the case of BPM (beats per minute), the period is typically expressed as a fraction of a minute. For example, if a metronome is set to 60 BPM, the period would be one second since there are 60 seconds in a minute.
Frequency, on the other hand, is the number of cycles completed in a specific unit of time. In the context of a metronome, the frequency represents the number of beats or cycles produced in one minute. It is directly related to the BPM setting of the metronome. Higher BPM settings will result in a higher frequency, meaning more beats per minute, while lower BPM settings will have a lower frequency.
Now let’s focus on a metronome set at 180 BPM. This means that the metronome will produce 180 beats or cycles in one minute. To calculate the period, we divide one minute by the BPM setting. In this case, the period would be approximately 333 milliseconds. This means that each beat or cycle of the metronome lasts for about 333 milliseconds.
Understanding the period and frequency of a metronome is crucial for musicians, as it helps them develop a strong sense of timing and rhythm. By practicing with a metronome and internalizing the tempo, musicians can improve their ability to stay in sync with other musicians, maintain a consistent tempo throughout a piece, and ultimately enhance their overall musical performance.
Metronomes and Their Function
Metronomes have been used by musicians for centuries to improve their timing and maintain a steady tempo. These devices come in various shapes and sizes, but their primary function remains consistent: to provide a precise and consistent beat for musicians to follow.
Traditional metronomes are mechanical devices that consist of a pendulum or a weighted arm that swings back and forth. As the pendulum swings, it produces an audible click, indicating the tempo and rhythm. These mechanical metronomes allow for visual and auditory cues, providing a clear reference point for musicians.
On the other hand, digital metronomes have gained popularity in recent years. They often feature a compact design with a digital screen or LED lights that display the tempo and other settings. Digital metronomes offer more flexibility, allowing users to adjust not only the tempo but also the sound and volume of the beats. Some digital options even include additional features like different time signatures, subdivision options, and the ability to save custom tempo settings.
The function of a metronome goes beyond simply keeping time; it helps musicians in several important ways:
- Develop Timing: Practicing with a metronome helps musicians develop a strong sense of timing and rhythm. By playing along with the steady beats, they learn to internalize the tempo and subconsciously maintain it during performances.
- Improve Accuracy: A metronome serves as a reliable reference point, helping musicians play with precision and accuracy. It trains them to execute intricate passages, complex rhythms, and syncopated patterns with accuracy.
- Build Speed: Gradually increasing the tempo on a metronome allows musicians to build their speed and dexterity. By starting at a comfortable pace and gradually pushing themselves, they can improve their technical abilities and play challenging pieces more effortlessly.
- Enhance Musicality: While metronomes provide a consistent beat, they also allow musicians to explore nuances in phrasing and musical expression. By working with a metronome, musicians can focus on adding dynamics, articulation, and musical interpretation to their playing.
Overall, metronomes are an invaluable tool for musicians of all levels. They offer a structured and disciplined approach to practicing, aiding in the development of timing, accuracy, speed, and musicality. Incorporating regular metronome practice into musical routines can greatly enhance musicians’ performance abilities and help them achieve their musical goals.
Setting a Metronome at 180
Setting a metronome at 180 beats per minute (BPM) can be beneficial for musicians who are looking to challenge their speed and precision. To set a metronome at this tempo, follow these steps:
- Select the Metronome: Choose a metronome that allows you to adjust the tempo settings. This can be a traditional mechanical metronome or a digital metronome with a BPM function.
- Set the Tempo: Locate the tempo control on the metronome. Depending on the model, this may be a dial, buttons, or a touchscreen display. Adjust the setting to 180 BPM.
- Choose the Sound: Some metronomes offer different sound options, such as clicks, beeps, or even musical tones. Select a sound that is clear and audible to you, as it will serve as your auditory cue for staying on beat.
- Start Playing: Once you have set the metronome to 180 BPM and chosen the preferred sound, start playing your instrument or practicing your musical piece.
- Focus on Accuracy: The metronome at 180 BPM will provide a rapid and challenging tempo. Concentrate on playing with precision and accuracy, ensuring that each note falls exactly on the beat.
- Gradually Increase Speed: If you find that playing at 180 BPM is too challenging initially, you can start at a slower tempo and gradually work your way up. Once you have mastered playing accurately at a slower tempo, increase the metronome setting by a few BPM until you reach the desired 180 BPM mark.
- Practice Consistently: Regular practice with the metronome at 180 BPM will help build your speed, coordination, and overall musical performance. Set aside dedicated practice sessions where you focus on playing at this tempo.
Setting a metronome at 180 BPM can be demanding, but it offers a great opportunity to refine your technical abilities and push your musical boundaries. It challenges your coordination, builds muscle memory, and trains your sense of timing. Incorporate this tempo into your practice routine to enhance your playing skills and develop a strong command over fast-paced music.
Applications and Benefits
The use of a metronome set at 180 beats per minute (BPM) carries several applications and benefits for musicians across various genres and skill levels. Let’s explore some of the key applications and the advantages they offer:
- Developing Speed: Setting a metronome at 180 BPM is an excellent way to develop speed and dexterity on an instrument. This tempo provides a challenging pace that pushes musicians to play faster passages with precision and control.
- Improving Technical Skills: Playing at a high tempo requires enhanced technical skills. Practicing with a metronome at 180 BPM can help musicians improve their finger coordination, timing, and fluency in complex musical passages.
- Preparing for High-energy Performances: Many musical styles, such as rock, punk, and metal, feature fast-paced, high-energy performances. Setting a metronome at 180 BPM can prepare musicians for the demanding tempo and intensity of live performances in these genres.
- Sharpening Rhythmic Accuracy: Playing along with a metronome at 180 BPM helps musicians develop a sharp sense of rhythmic accuracy. It trains them to align their playing precisely with the metronome beats, improving their ability to stay in time with other musicians during ensemble performances.
- Enhancing Musical Timing: Playing at a consistent tempo is crucial for musicians. Practicing with a metronome at 180 BPM allows them to internalize and solidify their sense of timing. This, in turn, helps musicians maintain a steady beat, execute proper rhythmic subdivisions, and play with rhythmically tight and cohesive ensembles.
- Building Endurance: Playing at a high tempo for extended periods can challenge the physical and mental endurance of musicians. Regular practice with a metronome at 180 BPM can gradually build stamina and increase endurance, allowing musicians to sustain their performance quality even during physically demanding passages.
- Improving Overall Musicality: Practicing with a metronome helps musicians develop discipline and precision in their playing. By working with a metronome set at 180 BPM, musicians can refine their technique, improve their dynamic control, and enhance their overall musical expression.
Ultimately, the application of a metronome set at 180 BPM depends on the musical goals and needs of each musician. Whether you’re aiming to increase speed, hone technical skills, prepare for high-energy performances, or refine your overall musicality, incorporating practice sessions with a metronome at this challenging tempo can yield significant benefits for your musical journey.
Conclusion
A metronome set at 180 beats per minute (BPM) serves as a valuable tool for musicians looking to improve their timing, precision, and overall musical performance. By understanding the concepts of period and frequency, musicians can effectively utilize the metronome’s steady beats to enhance their playing.
Metronomes, whether traditional mechanical ones or modern digital ones, offer musicians a reliable reference point for maintaining a consistent tempo. When set at 180 BPM, the metronome provides a challenging tempo that helps musicians develop speed, technical skills, and rhythmic accuracy. With regular practice, musicians can build endurance, improve their musical timing, and enhance their overall musicality.
The applications and benefits of using a metronome set at 180 BPM are numerous. It is particularly useful for musicians preparing for high-energy performances in genres such as rock, punk, and metal, where fast-paced playing is often required. It aids in developing finger coordination, timing, and fluency in complex musical passages, sharpening musicians’ technical abilities.
Moreover, practicing with a metronome at 180 BPM cultivates a strong sense of rhythm, aiding musicians in playing with precision alongside other musicians during ensemble performances. It also builds stamina and endurance, allowing musicians to maintain performance quality even during physically demanding passages. Beyond technical skills, the metronome fosters discipline, enhances dynamic control, and refines musicians’ overall musical expression.
In conclusion, incorporating a metronome set at 180 BPM into practice routines can have a transformative impact on a musician’s playing. It offers a structured approach to developing timing, accuracy, speed, and musicality. By utilizing the metronome effectively, musicians can elevate their performance abilities and reach new levels of musical proficiency.