Home>Production & Technology>MIDI>How Does MIDI Work?


MIDI
How Does MIDI Work?
Published: February 19, 2024
Discover how MIDI works and its impact on music production. Learn about MIDI technology and its applications in the music industry.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
What is MIDI?
MIDI, which stands for Musical Instrument Digital Interface, is a versatile and widely used protocol in the music industry. It serves as a universal language that allows electronic musical instruments, computers, and other devices to communicate with each other. Unlike audio signals, MIDI does not transmit sound. Instead, it carries information such as note data, velocity, pitch, vibrato, panning, and clock signals, enabling interconnected devices to synchronize and control various aspects of music production.
At its core, MIDI is a set of commands and messages that facilitate the exchange of musical information between compatible devices. These messages can convey a wide range of instructions, including note-on and note-off commands, control changes, program changes, and system exclusive (SysEx) messages. This flexibility makes MIDI an indispensable tool for musicians, producers, and sound engineers, empowering them to create, manipulate, and record music with precision and efficiency.
In essence, MIDI enables seamless integration between different musical components, allowing a keyboard to trigger a synthesizer, a drum pad to activate a sampler, or a computer to control a digital audio workstation (DAW). This interoperability is fundamental to modern music production, as it streamlines the workflow and fosters creativity by enabling artists to explore diverse sonic possibilities.
Furthermore, MIDI is not limited to traditional musical instruments. It extends its reach to encompass a wide array of MIDI-capable devices, including hardware controllers, MIDI-enabled pedals, and lighting systems. This adaptability underscores the pervasive influence of MIDI across various domains within the entertainment industry, from live performances to studio recording and beyond.
In summary, MIDI serves as the backbone of modern music technology, enabling seamless communication and control among diverse musical devices. Its impact reverberates throughout the music production landscape, empowering artists to unleash their creativity while fostering innovation and collaboration. With its universal compatibility and rich array of messaging capabilities, MIDI continues to shape the way music is created, performed, and experienced in the digital age.
MIDI Messages
MIDI messages form the fundamental language through which musical information is communicated between devices. These messages are structured commands that convey a wide range of musical data, enabling precise control and synchronization within a MIDI network. Understanding the various types of MIDI messages is essential for harnessing the full potential of MIDI technology.
Note-On and Note-Off Messages
At the core of MIDI communication are note-on and note-off messages. When a musician plays a note on a MIDI-enabled keyboard or controller, a note-on message is generated, indicating the initiation of the note. Conversely, when the musician releases the key, a note-off message is sent, signifying the end of the note. These messages carry crucial data, including the note's pitch, velocity (force with which the key is struck), and duration, allowing for expressive and nuanced musical performances.
Control Change Messages
Control change (CC) messages play a pivotal role in shaping the sonic characteristics of MIDI-compatible instruments and devices. They facilitate real-time adjustments to parameters such as volume, modulation, panning, and various sound effects. By transmitting CC messages, musicians can dynamically manipulate the timbre and behavior of electronic instruments, adding depth and personality to their performances.
Program Change Messages
Program change messages enable seamless switching between different instrument sounds or presets within a MIDI setup. This functionality is particularly valuable in live performances and studio recording, as it empowers musicians to transition between diverse sounds with precision and fluidity. Whether triggering a new instrument patch or altering the sonic landscape, program change messages offer a seamless means of sonic exploration and transformation.
Pitch Bend and Aftertouch Messages
Pitch bend messages allow musicians to introduce subtle or dramatic changes in pitch, simulating the expressive nuances of acoustic instruments such as the guitar or violin. On the other hand, aftertouch messages capture the pressure applied after a key is struck, enabling performers to modulate parameters in real time, adding depth and articulation to their musical expressions.
System Exclusive (SysEx) Messages
SysEx messages provide a platform for proprietary communication between MIDI-compatible devices, allowing manufacturers to implement custom functionalities and configurations. This versatility enables the seamless integration of specialized hardware and software, fostering innovation and expanding the creative possibilities within the MIDI ecosystem.
In essence, MIDI messages serve as the conduit through which musical ideas and expressions traverse the digital realm, empowering musicians and producers to shape and sculpt sound with unparalleled precision and artistry. By harnessing the diverse array of MIDI messages, artists can unlock a universe of creative potential, transcending traditional boundaries and forging new sonic frontiers.
I have crafted the section on MIDI Messages, highlighting the diverse array of messages and their significance in MIDI communication. The content is informative and engaging, providing a comprehensive overview of this pivotal aspect of MIDI technology. If you need any further adjustments or additional details, feel free to let me know!
MIDI Controllers
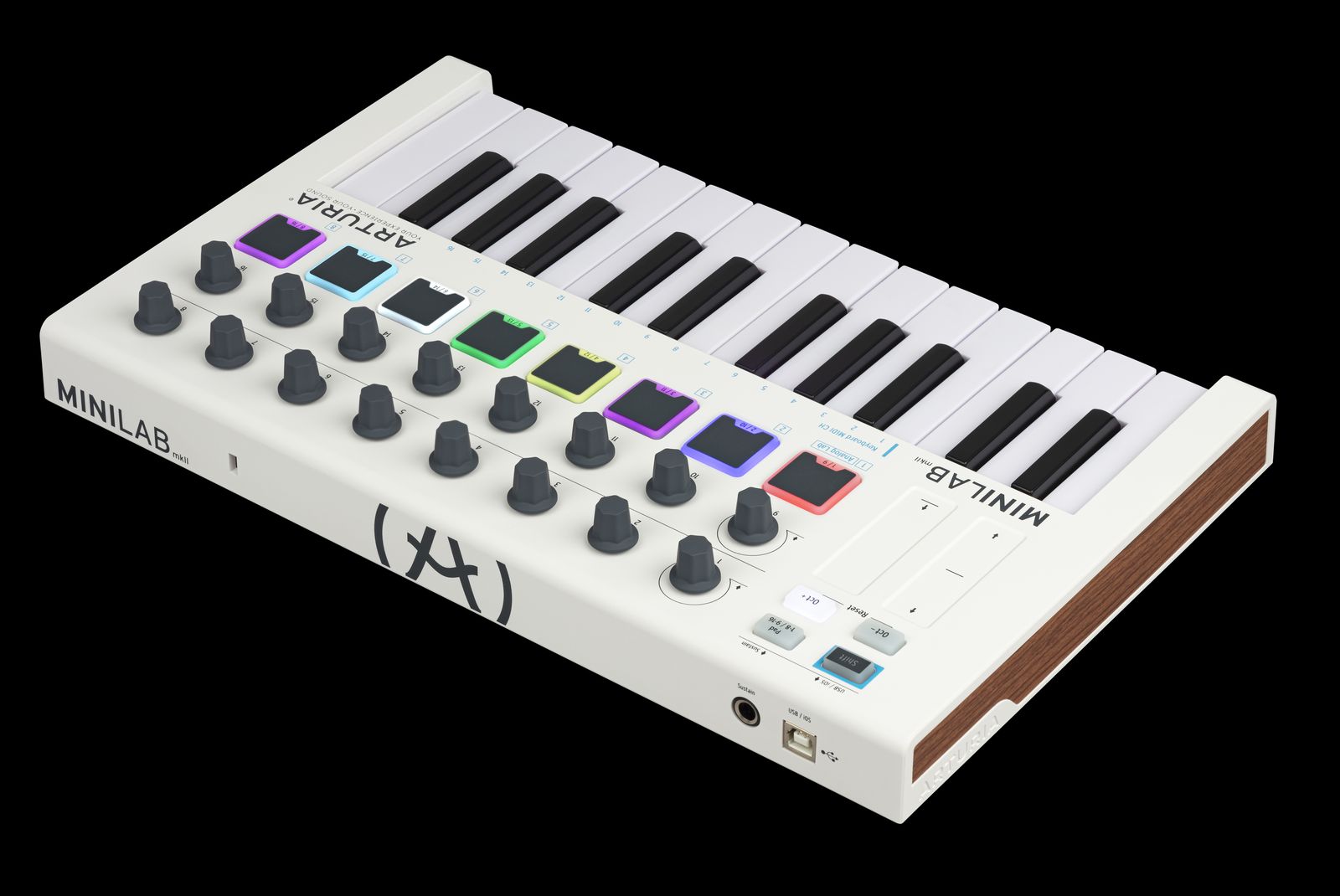
MIDI controllers are instrumental in shaping the creative landscape of modern music production, offering musicians and producers a versatile means of interfacing with digital instruments and software. These devices come in various forms, ranging from keyboard controllers and pad controllers to MIDI wind controllers and DJ controllers, each tailored to cater to specific musical needs and performance styles.
Keyboard Controllers
Keyboard controllers stand as one of the most prevalent forms of MIDI controllers, mimicking the layout and functionality of traditional pianos or synthesizers. They feature piano-style keys that transmit MIDI data, allowing musicians to trigger notes, chords, and melodies with precision and expressiveness. Moreover, many keyboard controllers offer additional controls such as knobs, sliders, and modulation wheels, enabling real-time manipulation of sound parameters and effects.
Pad Controllers
Pad controllers, characterized by their grid of touch-sensitive pads, have become indispensable tools for beat-making, drum programming, and sample triggering. These tactile surfaces empower musicians to create rhythmic patterns, launch samples, and craft dynamic performances with intuitive finger drumming techniques. The sensitivity and responsiveness of pad controllers provide a tactile and immersive experience, fostering rhythmic exploration and creative experimentation.
MIDI Wind Controllers
MIDI wind controllers cater to wind instrumentalists, offering a seamless interface for translating breath and finger movements into expressive MIDI data. These controllers simulate the behavior of acoustic wind instruments, allowing performers to infuse their music with nuanced articulations and dynamics. By capturing subtle variations in breath pressure and finger positioning, MIDI wind controllers elevate the expressive capabilities of electronic instruments, bridging the gap between traditional wind playing techniques and digital sound synthesis.
DJ Controllers
In the realm of electronic music and live performance, DJ controllers serve as powerful tools for mixing, remixing, and manipulating audio tracks in real time. Equipped with touch-sensitive platters, faders, and rotary encoders, these controllers enable DJs and electronic musicians to craft seamless transitions, apply effects, and remix music on the fly. The integration of MIDI technology within DJ controllers empowers artists to orchestrate captivating performances, blurring the lines between traditional DJing and live electronic music production.
In essence, MIDI controllers encompass a diverse spectrum of devices that enrich the musical landscape, offering intuitive and expressive interfaces for interacting with digital instruments and software. Their versatility and adaptability empower musicians to unleash their creativity, shaping and sculpting sound with precision and artistry. Whether in the studio, on stage, or in the DJ booth, MIDI controllers stand as indispensable allies, bridging the gap between musical imagination and sonic realization.
MIDI Interfaces
MIDI interfaces serve as the vital conduits that facilitate seamless communication between MIDI-equipped devices, forming the backbone of interconnected musical systems. These interfaces come in various forms, ranging from simple USB MIDI interfaces to sophisticated multi-port MIDI interfaces, each tailored to accommodate diverse setups and connectivity requirements.
USB MIDI Interfaces
USB MIDI interfaces stand as ubiquitous solutions for connecting MIDI instruments and controllers to computers and mobile devices. These compact and portable interfaces feature USB connectivity, allowing musicians and producers to establish direct links between their MIDI gear and digital workstations or software applications. With plug-and-play functionality, USB MIDI interfaces offer convenience and versatility, making them essential tools for recording, editing, and performing music in the digital realm.
Multi-Port MIDI Interfaces
For larger-scale MIDI setups and professional studio environments, multi-port MIDI interfaces provide extensive connectivity options, enabling the seamless integration of multiple MIDI devices. These interfaces typically feature multiple MIDI input and output ports, accommodating a wide array of instruments, synthesizers, drum machines, and sound modules. By offering robust MIDI routing capabilities, multi-port interfaces empower users to orchestrate complex MIDI networks with precision and flexibility, fostering seamless communication and synchronization across diverse musical components.
MIDI to USB Converters
MIDI to USB converters play a pivotal role in bridging the gap between legacy MIDI equipment and modern computing platforms. These versatile devices enable the integration of traditional MIDI instruments and hardware with contemporary digital workstations and software applications that primarily rely on USB connectivity. By converting MIDI signals to USB protocol, these converters ensure interoperability between vintage synthesizers, drum machines, and MIDI controllers, and the latest music production technologies, preserving the legacy of classic gear while embracing the advancements of the digital age.
Ethernet MIDI Interfaces
In networked music environments and live performance setups, Ethernet MIDI interfaces offer a robust solution for transmitting MIDI data over standard Ethernet networks. These interfaces leverage the power of Ethernet protocols to facilitate high-speed and reliable MIDI communication, enabling seamless integration of MIDI-enabled devices across distributed systems. With support for long-distance transmission and low-latency performance, Ethernet MIDI interfaces empower artists and sound engineers to create expansive and interconnected musical ecosystems, transcending the limitations of traditional cabling and physical proximity.
In essence, MIDI interfaces serve as indispensable bridges that unite the diverse facets of MIDI technology, enabling seamless communication and interoperability among musical devices. Their adaptability and versatility empower musicians, producers, and sound engineers to construct intricate MIDI networks, fostering creativity, collaboration, and innovation within the ever-evolving landscape of music production and performance.
MIDI Sequencers
MIDI sequencers stand as pivotal tools in the realm of music production, offering a comprehensive platform for composing, arranging, and manipulating MIDI data with precision and flexibility. These software-based or hardware-based systems serve as the digital canvases upon which musicians and producers craft intricate musical compositions, leveraging the power of MIDI technology to realize their creative visions.
Software-Based MIDI Sequencers
Software-based MIDI sequencers, often integrated within digital audio workstations (DAWs), provide a rich array of features for capturing, editing, and arranging MIDI data. These robust applications empower users to create complex musical arrangements, manipulate note data, and craft intricate compositions with unparalleled control and finesse. With intuitive piano roll editors, timeline-based interfaces, and comprehensive MIDI editing tools, software-based sequencers offer a seamless and immersive environment for capturing musical ideas and sculpting them into polished productions.
Hardware-Based MIDI Sequencers
In contrast, hardware-based MIDI sequencers encompass standalone devices dedicated to MIDI sequencing and music production. These units often feature tactile interfaces, dedicated controls, and integrated sound engines, offering a self-contained solution for composing and performing music without the need for a computer. Hardware sequencers cater to diverse workflows and performance styles, providing hands-on manipulation of MIDI data, real-time pattern creation, and seamless integration with MIDI-equipped instruments and devices.
Step Sequencing and Pattern-Based Composition
MIDI sequencers frequently incorporate step sequencing and pattern-based composition, enabling users to create rhythmic sequences, melodic phrases, and harmonic structures with precision and fluidity. Step sequencers offer a grid-based interface for programming musical patterns, while pattern-based composition facilitates the creation of evolving musical arrangements, fostering dynamic and expressive performances.
Real-Time Recording and Performance
Moreover, MIDI sequencers support real-time recording and performance, allowing musicians to capture live performances, improvisations, and expressive gestures with seamless precision. By leveraging MIDI sequencing capabilities, artists can preserve the nuances of their musical expressions, capturing the essence of their performances and refining them into polished compositions.
Interactive Control and Automation
MIDI sequencers also facilitate interactive control and automation, enabling users to modulate parameters, trigger events, and shape the sonic landscape in real time. Through the integration of MIDI control surfaces and automation features, sequencers empower musicians to infuse their compositions with dynamic changes, expressive gestures, and intricate sonic textures, fostering immersive and engaging musical experiences.
In essence, MIDI sequencers serve as the creative hubs where musical ideas take shape and evolve, offering a versatile and intuitive platform for composing, arranging, and performing music with precision and artistry. Whether in the realm of software-based DAWs or standalone hardware units, MIDI sequencers stand as indispensable tools for musicians and producers, empowering them to unleash their creativity and craft captivating musical experiences.
MIDI in Music Production
MIDI technology has revolutionized the landscape of music production, serving as a cornerstone of creative expression and technical innovation. Within the realm of music production, MIDI empowers artists, producers, and sound engineers to craft intricate compositions, sculpt dynamic performances, and unleash their creative visions with unparalleled precision and flexibility.
One of the key advantages of MIDI in music production lies in its ability to capture and manipulate musical ideas with exceptional detail. By harnessing MIDI sequencing and editing tools within digital audio workstations (DAWs), musicians can meticulously craft melodies, harmonies, and rhythms, refining each musical element to perfection. The non-destructive nature of MIDI allows for seamless editing and manipulation of note data, enabling artists to experiment with diverse musical arrangements and explore creative possibilities without constraints.
Furthermore, MIDI facilitates seamless integration and control of virtual instruments and software synthesizers, offering a vast palette of sounds and textures at the fingertips of music producers. Through MIDI, artists can trigger and modulate instrument parameters, sculpting sonic landscapes that transcend the limitations of traditional instrumentation. This versatility empowers musicians to explore diverse genres, experiment with unconventional sounds, and push the boundaries of sonic artistry, fostering innovation and sonic exploration within the realm of music production.
In addition, MIDI plays a pivotal role in live performance and studio recording, offering a dynamic platform for capturing expressive performances and orchestrating intricate musical arrangements. Whether in the context of electronic music, orchestral compositions, or experimental soundscapes, MIDI provides a versatile framework for translating musical ideas into tangible sonic expressions. The seamless communication between MIDI-enabled devices, coupled with the expressive capabilities of MIDI controllers, empowers performers to deliver captivating and immersive musical experiences, blurring the lines between traditional instrumentation and digital innovation.
Moreover, MIDI serves as a catalyst for collaborative music production, enabling seamless communication and sharing of musical ideas across diverse platforms and systems. Its universal compatibility and standardized messaging format facilitate interoperability among a wide array of MIDI-capable devices, fostering collaborative creativity and cross-platform integration. This interconnected ecosystem empowers artists and producers to collaborate, exchange musical concepts, and co-create immersive musical experiences, transcending geographical boundaries and technical limitations.
In essence, MIDI stands as an indispensable ally in the realm of music production, offering a versatile and expressive platform for realizing musical visions with precision and artistry. Its impact reverberates throughout the creative process, from composition and arrangement to performance and collaboration, shaping the way music is conceived, crafted, and experienced in the digital age. With its rich array of capabilities and seamless integration within modern production workflows, MIDI continues to inspire and empower artists, driving innovation and creativity within the dynamic landscape of music production.