Home>Production & Technology>MIDI>How To Record Electronic Drums Without MIDI


MIDI
How To Record Electronic Drums Without MIDI
Published: February 20, 2024
Learn how to record electronic drums without MIDI and still achieve professional-quality sound. Discover alternative methods for capturing the perfect drum track.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Recording electronic drums without MIDI is a rewarding endeavor that allows musicians and producers to capture the dynamic energy and versatility of electronic drum kits in a seamless and authentic manner. While MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) has been widely used for recording electronic drums, many musicians prefer to opt for a direct audio recording approach to achieve a more organic and natural sound. This method not only simplifies the recording process but also offers a unique sonic character that resonates with the raw power of live drumming.
By embracing the direct recording method, musicians can harness the full potential of their electronic drum kits, leveraging the nuances of each strike, the subtleties of ghost notes, and the expressive qualities of cymbal swells. This approach enables them to capture the essence of their performance with precision and clarity, paving the way for a rich and authentic sonic representation.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of recording electronic drums without MIDI, providing valuable insights into the selection of recording equipment, the setup of electronic drum kits, and the essential recording techniques to achieve professional-grade results. Whether you are a seasoned drummer looking to capture your live performances or a producer seeking to integrate electronic drums into your productions, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and techniques needed to embark on a fulfilling recording journey.
Throughout this article, we will explore the fundamental steps involved in recording electronic drums without MIDI, offering practical tips and expert advice to empower you in harnessing the full sonic potential of your electronic drum kit. From selecting the right recording equipment to optimizing recording techniques, each section will unravel the intricacies of the recording process, providing you with a comprehensive roadmap to elevate your drum recordings to new heights.
Join us as we embark on a captivating exploration of recording electronic drums without MIDI, unlocking the boundless creativity and sonic possibilities that await within the realm of direct audio recording. Let's dive into the world of electronic drum recording and unleash the true essence of live drumming through the art of direct audio capture.
Choosing the Right Recording Equipment
Selecting the appropriate recording equipment is pivotal in ensuring the successful capture of the nuanced and dynamic characteristics of electronic drums. When embarking on the journey of recording electronic drums without MIDI, it is essential to equip oneself with the right tools to facilitate a seamless and high-fidelity recording process.
High-Quality Microphones
Investing in high-quality microphones tailored for drum recording is paramount. Dynamic microphones, such as the Shure SM57, are renowned for their ability to capture the punch and impact of drum strikes, making them ideal for snare drums and toms. Additionally, condenser microphones, such as the AKG C414, excel in capturing the intricate details and nuances of cymbals and the overall ambience of the drum kit. By strategically positioning a combination of dynamic and condenser microphones around the drum kit, one can achieve a balanced and comprehensive sonic capture.
Audio Interface
A reliable audio interface serves as the bridge between the electronic drum kit and the recording device. When selecting an audio interface, factors such as the number of input channels, preamp quality, and compatibility with recording software should be considered. Focusrite Scarlett and Universal Audio Apollo interfaces are popular choices known for their pristine audio quality and versatile input options, catering to the diverse recording needs of electronic drum setups.
Studio Monitors or Headphones
To accurately monitor the recorded drum tracks, a pair of studio monitors or high-fidelity headphones is indispensable. Studio monitors, such as the Yamaha HS8, deliver a flat frequency response, enabling precise evaluation of the recorded drum sound. Alternatively, high-quality headphones, such as the Sennheiser HD 650, offer detailed and immersive monitoring, allowing for critical assessment of the drum recordings without the influence of room acoustics.
Recording Software
Choosing the right recording software is crucial in facilitating a streamlined recording process and providing essential tools for editing and mixing. Digital audio workstations (DAWs) like Pro Tools, Logic Pro, and Ableton Live offer comprehensive features tailored for drum recording, including multi-track recording, flexible editing capabilities, and a wide array of audio processing plugins.
By carefully selecting high-quality microphones, an efficient audio interface, reliable monitoring equipment, and a suitable recording software, musicians and producers can lay a solid foundation for capturing the expressive and dynamic qualities of electronic drums without MIDI, setting the stage for a fulfilling and professional-grade recording experience.
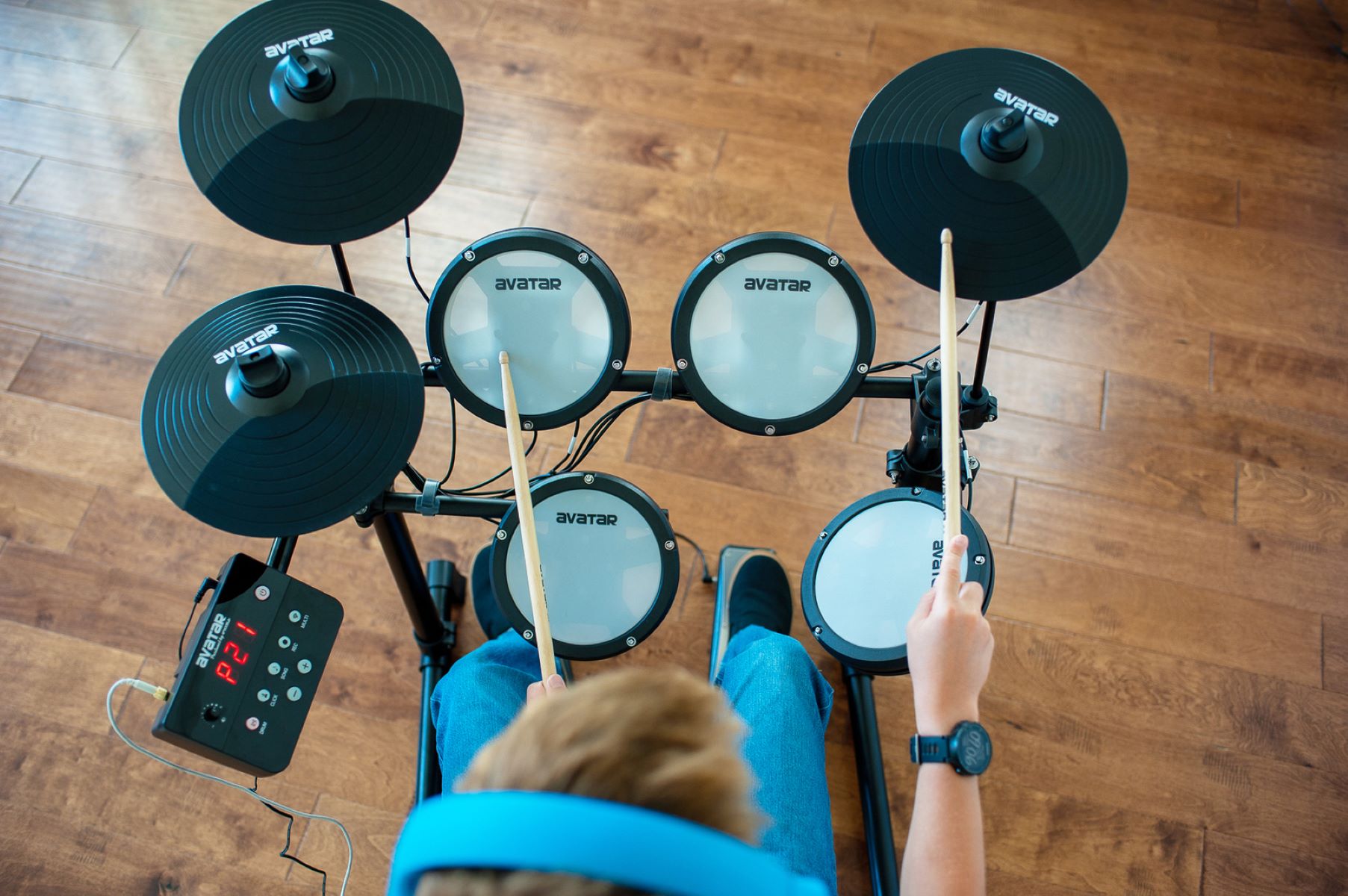
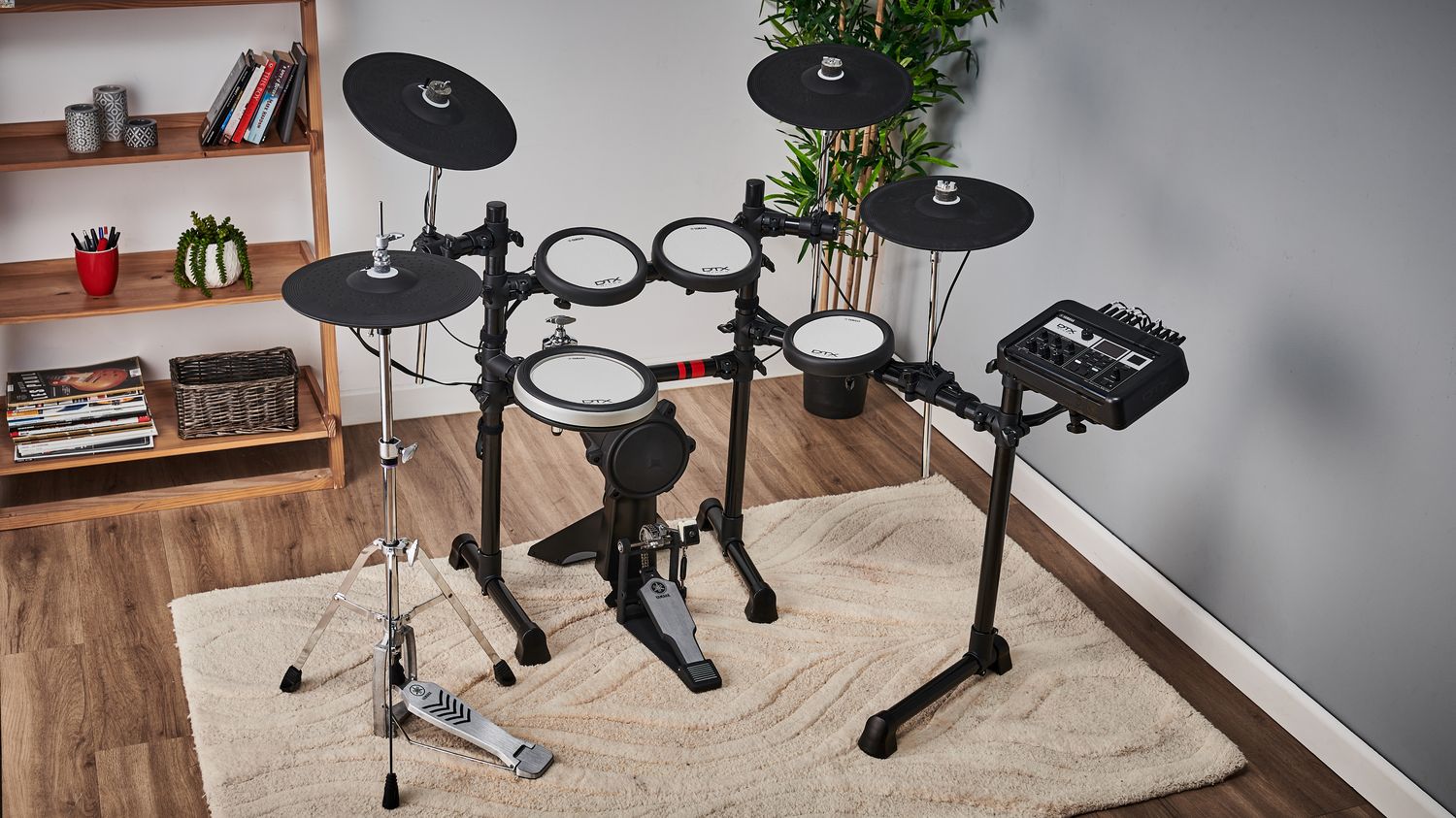
Setting Up Your Electronic Drum Kit
Setting up an electronic drum kit for recording without MIDI involves meticulous attention to detail to ensure optimal sound capture and performance. The configuration and placement of the drum components play a pivotal role in shaping the sonic characteristics and overall balance of the recorded sound. Here's a comprehensive guide to setting up your electronic drum kit for a seamless and professional recording experience.
Positioning the Drum Components
The first step in setting up an electronic drum kit for recording is to carefully position the drum components to achieve an optimal balance of sound and playability. Start by adjusting the height and angle of the drum pads and cymbals to suit your playing style and ergonomic preferences. Ensure that the drum pads are securely mounted on the rack or stand, minimizing any unwanted movement during intense drumming sessions.
Fine-Tuning Trigger Sensitivity
Calibrating the trigger sensitivity of the drum pads is crucial in achieving accurate and responsive sound triggering. Most electronic drum modules offer extensive customization options for adjusting trigger sensitivity, threshold, and dynamic response. Take the time to fine-tune these parameters to match the nuances of your playing technique, ensuring consistent and expressive sound reproduction across the entire drum kit.
Cable Management
Efficient cable management is essential in maintaining a tidy and organized setup while minimizing interference and signal degradation. Route the cables from the drum pads and cymbals in a manner that avoids tangling and excessive tension. Utilize cable ties and organizers to secure the cables along the drum rack or stand, preventing accidental disconnection and preserving the integrity of the signal flow.
Optimizing Pad Placement for Recording
When positioning the drum pads and cymbals, consider their proximity to each other and the overall spatial arrangement within the recording environment. Aim to create a balanced and ergonomic layout that facilitates fluid drumming performance while allowing for optimal microphone placement. By strategically positioning the drum components, you can enhance the coherence and clarity of the recorded drum sound, ensuring a cohesive and well-defined sonic representation.
Testing and Adjustment
After setting up the electronic drum kit, conduct thorough testing to evaluate the responsiveness, triggering accuracy, and overall playability of the configured components. Make any necessary adjustments to the pad sensitivity, module settings, and physical positioning based on the testing results, fine-tuning the setup to align with your performance requirements and sonic preferences.
By meticulously setting up your electronic drum kit with a focus on positioning, trigger sensitivity, cable management, and recording optimization, you can lay the groundwork for a seamless and rewarding recording experience, capturing the full sonic potential of your electronic drum kit without MIDI. This meticulous approach to setup ensures that your drum recordings reflect the expressive nuances and dynamic energy of your performances, setting the stage for compelling and professional-grade audio capture.
Connecting Your Electronic Drum Kit to an Audio Interface
Connecting your electronic drum kit to an audio interface is a pivotal step in the process of recording without MIDI, as it establishes the crucial link between your drum performance and the digital recording realm. By seamlessly integrating your electronic drum kit with a capable audio interface, you pave the way for pristine and high-fidelity audio capture, ensuring that every subtle nuance and powerful strike is faithfully translated into the recorded tracks.
Selecting the Appropriate Cables
The first consideration when connecting your electronic drum kit to an audio interface is the selection of appropriate cables. Most electronic drum kits utilize standard 1/4-inch audio cables to transmit the audio signals from the drum pads and cymbals to the audio interface. It is essential to ensure that the cables are of high quality, with reliable connectors and shielding to minimize signal interference and maintain signal integrity throughout the recording process.
Identifying Input Channels
Before connecting the cables from your electronic drum kit to the audio interface, it is crucial to identify the input channels on the interface that will accommodate the incoming audio signals. Most audio interfaces offer multiple input channels, allowing for simultaneous recording of individual drum components. By mapping out the input channels and their corresponding connections to the drum pads and cymbals, you can streamline the setup process and optimize the routing of audio signals within the recording environment.
Establishing Signal Flow
Once the input channels on the audio interface are identified, it is time to establish the signal flow from the electronic drum kit to the interface. Begin by connecting the output of each drum pad and cymbal to the designated input channels on the audio interface, ensuring a secure and stable connection for each audio signal. Pay close attention to the labeling and organization of the input channels, maintaining a clear and logical signal flow to facilitate efficient monitoring and recording.
Testing and Signal Calibration
After connecting the electronic drum kit to the audio interface, it is essential to conduct thorough testing and signal calibration to verify the integrity of the audio connections and ensure optimal signal levels. Trigger each drum pad and cymbal to confirm the responsiveness and accuracy of the audio signals transmitted to the interface. Use the input gain controls on the interface to adjust the signal levels, preventing clipping and distortion while maximizing the signal-to-noise ratio for pristine audio capture.
By meticulously connecting your electronic drum kit to an audio interface with a focus on cable selection, input channel identification, signal flow establishment, and signal calibration, you lay the groundwork for a seamless and professional-grade recording experience. This meticulous approach to connection ensures that your drum recordings reflect the expressive nuances and dynamic energy of your performances, setting the stage for compelling and high-fidelity audio capture.
Adjusting Levels and Monitoring
Once your electronic drum kit is connected to the audio interface, the next crucial step in the recording process involves adjusting levels and implementing effective monitoring techniques to ensure optimal sound quality and performance. This pivotal phase not only facilitates precise control over the audio signals but also enables real-time assessment of the recorded sound, empowering you to capture the expressive nuances and dynamic energy of your drum performances with precision and clarity.
Setting Input Levels
Begin by setting the input levels on the audio interface to attain an optimal balance between signal strength and clarity. Utilize the input gain controls to adjust the levels of each drum pad and cymbal, aiming to capture robust and well-defined audio signals without introducing distortion or clipping. Pay close attention to the input meters on the interface, ensuring that the signal levels fall within the recommended range to maximize signal-to-noise ratio and fidelity.
Utilizing Headphone Monitoring
Engage headphone monitoring to immerse yourself in the live sound of the electronic drum kit as you adjust input levels and fine-tune the recording setup. High-quality headphones provide an isolated and detailed listening environment, enabling you to discern the subtle nuances of the drum sound and evaluate the impact of level adjustments in real time. This direct monitoring approach empowers you to make informed decisions regarding input levels, ensuring that the recorded sound faithfully captures the dynamic nuances of your drumming performance.
Employing Monitor Speakers
Incorporate monitor speakers to complement the headphone monitoring setup, allowing for a balanced and immersive sonic experience during the recording process. Studio monitors with a flat frequency response provide an accurate representation of the recorded sound, enabling critical assessment of the drum tracks within the context of the overall mix. By leveraging monitor speakers in conjunction with headphone monitoring, you can gain comprehensive insight into the sonic characteristics of the recorded drum sound, facilitating informed adjustments and optimizations.
Fine-Tuning EQ and Dynamics
While monitoring the electronic drum sound, consider implementing subtle EQ adjustments and dynamic processing to enhance the sonic characteristics and address any tonal imbalances. Utilize the EQ controls on the audio interface or within the recording software to sculpt the tonal profile of the drum tracks, emphasizing the desired frequencies and mitigating any sonic anomalies. Additionally, apply dynamic processing, such as compression and transient shaping, to refine the transient impact and overall dynamics of the drum sound, ensuring a polished and cohesive sonic representation.
By meticulously adjusting levels and implementing effective monitoring techniques, you pave the way for a seamless and professional-grade recording experience, capturing the full sonic potential of your electronic drum kit without MIDI. This meticulous approach to level adjustment and monitoring ensures that your drum recordings authentically convey the expressive nuances and dynamic energy of your performances, setting the stage for compelling and high-fidelity audio capture.
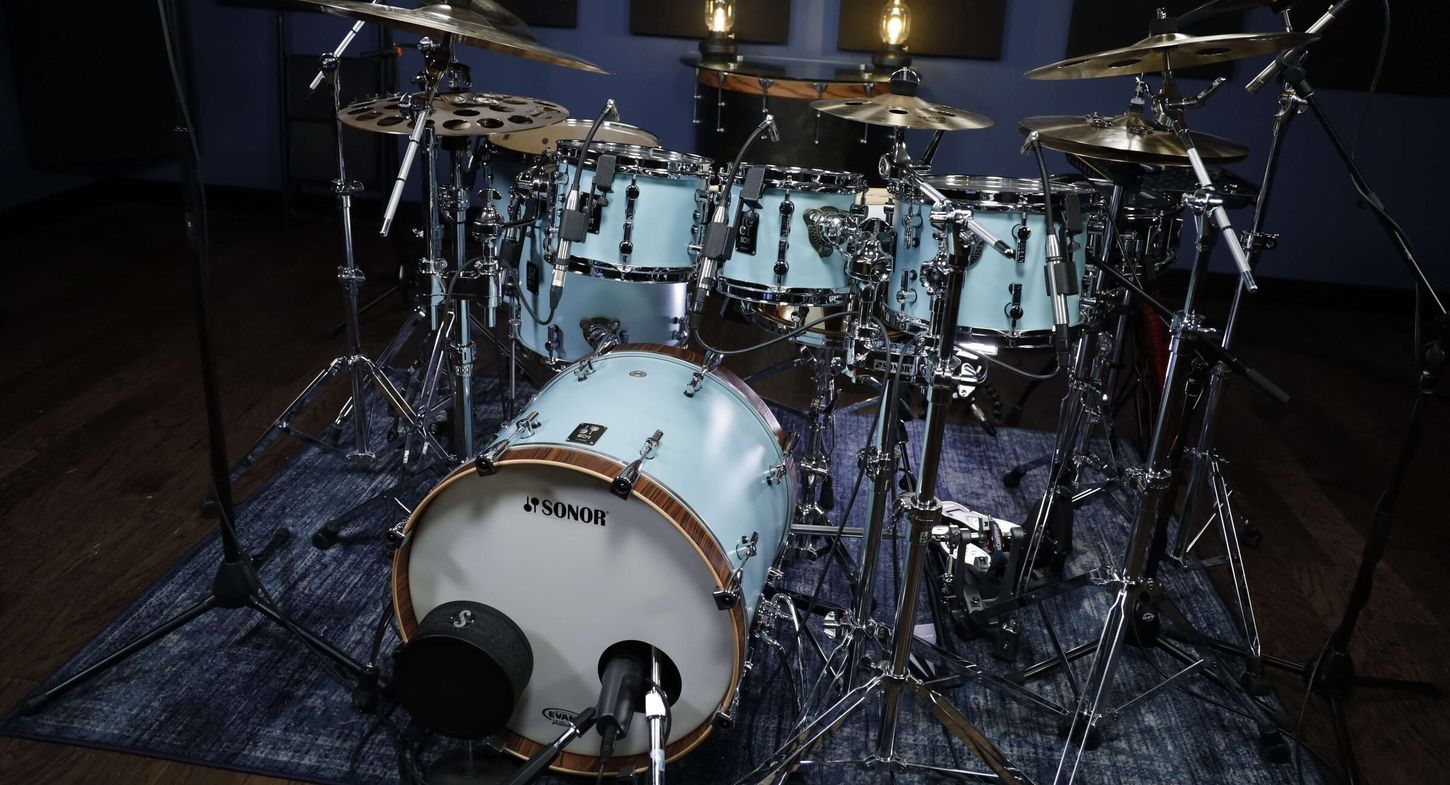
Recording Techniques for Electronic Drums
Recording electronic drums without MIDI presents a unique set of challenges and opportunities, requiring a nuanced approach to capture the dynamic energy and expressive nuances of the drum performances. By leveraging effective recording techniques tailored for electronic drums, musicians and producers can unlock the full sonic potential of their drum kits, yielding professional-grade recordings that resonate with authenticity and impact. Here, we delve into the essential recording techniques for electronic drums, offering valuable insights and expert guidance to elevate your drum recordings to new heights.
Multi-Microphone Setup
Employing a multi-microphone setup is instrumental in capturing the diverse sonic characteristics of electronic drums with precision and depth. Position dynamic microphones strategically to capture the punch and resonance of the kick drum, accentuating its low-end impact and defining the rhythmic foundation of the drum sound. Additionally, utilize condenser microphones to capture the intricate details of the cymbals and the overall ambience of the drum kit, fostering a balanced and immersive sonic representation.
Close-Miking Techniques
Implement close-miking techniques to capture the individual drum components with clarity and definition. Position dynamic microphones in close proximity to the snare drum and toms, aiming to capture the transient attack and resonant body of each drum element. By leveraging close-miking, you can isolate and emphasize the unique tonal characteristics of each drum component, enabling precise control over the mix and enhancing the overall articulation of the drum performance.
Overhead and Room Mic Blend
Integrate overhead microphones and room mics to capture the spatial dimension and natural ambience of the electronic drum kit. Position condenser microphones in an overhead configuration to capture the stereo image of the drum kit, accentuating the spatial depth and tonal balance of the drum sound. Additionally, incorporate room mics to capture the reverberant qualities and immersive resonance of the drum performance, enriching the sonic texture and enveloping the listener in a captivating sonic environment.
Drum Module Direct Output
Utilize the direct output capabilities of the electronic drum module to capture pristine and unaltered audio signals from the individual drum pads and cymbals. By leveraging the direct outputs, you can bypass the internal processing of the drum module, ensuring a pure and unadulterated representation of the drum sound. This approach provides flexibility in post-processing and mixing, empowering you to sculpt the sonic characteristics of each drum component with precision and finesse.
Dynamic Processing and Sound Shaping
Apply dynamic processing and sound shaping techniques to refine the transient impact, tonal balance, and overall dynamics of the recorded drum tracks. Implement compression to control the dynamic range and enhance the sustain of the drum sound, fostering a cohesive and impactful sonic representation. Additionally, utilize EQ to sculpt the tonal profile of the drum tracks, emphasizing the desired frequencies and mitigating any sonic irregularities, ensuring a polished and well-defined drum sound.
By embracing these recording techniques tailored for electronic drums, musicians and producers can embark on a captivating sonic journey, capturing the expressive nuances and dynamic energy of their drum performances with finesse and artistry. These techniques empower you to harness the full sonic potential of electronic drums without MIDI, paving the way for compelling and professional-grade drum recordings that resonate with authenticity and impact.
Tips for Achieving a Great Sound
Achieving a great sound when recording electronic drums without MIDI involves a combination of technical expertise, creative finesse, and meticulous attention to sonic detail. By embracing the following tips, musicians and producers can elevate their drum recordings to new heights, capturing the essence of live drumming with precision and artistry.
Experiment with Mic Placement
Exploring different microphone placement techniques can yield diverse sonic textures and tonal characteristics. Consider adjusting the positioning of microphones around the drum kit to capture varying perspectives of the drum sound. Experiment with different distances and angles, exploring the impact of mic placement on the overall balance and spatial depth of the recorded sound.
Embrace Dynamic Performance
Encourage dynamic and expressive drum performances to imbue the recordings with a sense of vitality and emotion. Emphasize the nuances of ghost notes, varying degrees of attack, and subtle embellishments, allowing the natural dynamics of the drumming to shine through in the recorded tracks. By embracing dynamic performance, you can infuse the recordings with a captivating sense of realism and energy.
Fine-Tune Drum Module Settings
Delve into the settings of the electronic drum module to fine-tune the sound characteristics of each drum component. Explore parameters such as sensitivity, velocity response, and tonal shaping to tailor the sonic behavior of the drum pads and cymbals. By optimizing the drum module settings, you can achieve a personalized and responsive drum sound that aligns with your artistic vision.
Leverage Ambient Acoustics
Consider the acoustic properties of the recording environment and leverage its natural ambience to enhance the sonic depth of the drum recordings. Experiment with room mic placements and explore the influence of ambient acoustics on the overall sonic texture. By integrating ambient acoustics, you can imbue the recordings with a sense of space and dimension, enriching the sonic landscape with immersive reverberation and spatial resonance.
Focus on Post-Processing Nuances
In the post-production phase, pay meticulous attention to the nuances of audio processing and mixing. Implement subtle reverberation, spatial enhancement, and tonal sculpting to refine the sonic characteristics of the drum tracks. Embrace the art of sonic refinement, ensuring that each drum component resonates with clarity, impact, and a cohesive sonic presence within the mix.
By embracing these tips for achieving a great sound, musicians and producers can embark on a transformative recording journey, capturing the expressive nuances and dynamic energy of electronic drums without MIDI with finesse and artistry. These tips empower you to harness the full sonic potential of your drum recordings, paving the way for compelling and professional-grade audio capture that resonates with authenticity and impact.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the art of recording electronic drums without MIDI is a captivating endeavor that empowers musicians and producers to capture the raw energy and expressive nuances of live drumming with precision and artistry. Throughout this comprehensive guide, we have delved into the essential steps and techniques involved in achieving professional-grade drum recordings without relying on MIDI, offering valuable insights and expert guidance to elevate the sonic potential of electronic drum kits.
By meticulously selecting high-quality recording equipment, including microphones, audio interfaces, and monitoring systems, musicians and producers can establish a solid foundation for capturing the dynamic characteristics of electronic drums with fidelity and clarity. The strategic setup of electronic drum kits, coupled with meticulous cable management and optimization for recording, ensures a seamless and professional-grade recording experience, laying the groundwork for compelling and authentic drum recordings.
The integration of effective recording techniques tailored for electronic drums, such as multi-microphone setups, close-miking techniques, and dynamic processing, empowers artists to capture the diverse sonic characteristics of their drum performances with finesse and precision. By embracing these techniques, musicians and producers can unlock the full sonic potential of their electronic drum kits, yielding recordings that resonate with authenticity and impact.
Furthermore, the tips for achieving a great sound provide valuable insights into the creative and technical nuances of recording electronic drums without MIDI, offering guidance on mic placement experimentation, dynamic performance encouragement, drum module optimization, and post-processing finesse. These tips serve as a catalyst for elevating the sonic quality and expressive depth of drum recordings, empowering artists to imbue their recordings with vitality and emotion.
In essence, the journey of recording electronic drums without MIDI transcends technical proficiency, embracing the artistry and creativity inherent in capturing the essence of live drumming. By leveraging the insights and techniques outlined in this guide, musicians and producers can embark on a transformative sonic exploration, capturing the full spectrum of expressive nuances and dynamic energy within the realm of electronic drum recording.
As we conclude this guide, we invite you to embark on your own recording journey, embracing the limitless sonic possibilities that await within the realm of electronic drum recording. Whether you are a seasoned drummer seeking to capture the raw energy of your live performances or a producer aiming to integrate electronic drums into your productions, the art of recording electronic drums without MIDI invites you to weave a compelling sonic narrative, capturing the essence of live drumming with finesse and authenticity.