Home>Production & Technology>MIDI>What Is A MIDI Interface?


MIDI
What Is A MIDI Interface?
Modified: March 9, 2024
Learn about MIDI interfaces and their role in connecting electronic musical instruments and computers. Find out how MIDI technology revolutionizes music production and performance. Discover the benefits of using MIDI for musicians and producers.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the fascinating world of MIDI interfaces! If you're a music enthusiast, a budding musician, or a seasoned professional, you've likely encountered the term "MIDI" at some point. However, the concept of MIDI interfaces may still be shrouded in mystery for many. Fear not, as we embark on an enlightening journey to unravel the wonders of MIDI interfaces and their pivotal role in modern music production.
MIDI, which stands for Musical Instrument Digital Interface, has revolutionized the way music is created, performed, and recorded. It serves as the universal language that allows electronic musical instruments, computers, and audio devices to communicate seamlessly with each other. This opens up a world of possibilities, enabling musicians to unleash their creativity and produce awe-inspiring compositions with unparalleled precision and flexibility.
In this article, we'll delve into the intricacies of MIDI interfaces, shedding light on their functionalities, types, and practical applications. Whether you're a keyboard virtuoso, a drum aficionado, or a synth maestro, understanding MIDI interfaces is crucial for harnessing the full potential of your musical endeavors. So, fasten your seatbelts as we embark on an exhilarating exploration of MIDI interfaces and the boundless opportunities they offer for musical expression and innovation.
What is MIDI?
MIDI, an acronym for Musical Instrument Digital Interface, represents a standard protocol that facilitates communication between electronic musical instruments, computers, and other related devices. It serves as a bridge that enables seamless interaction between various components of a music production setup, such as keyboards, synthesizers, drum machines, and software applications.
At its core, MIDI does not transmit audio signals; instead, it conveys a series of digital messages that encompass musical notes, control parameters, and other performance data. These messages are transmitted in real-time, allowing for precise synchronization and coordination between different musical elements.
One of the key advantages of MIDI is its versatility. It empowers musicians and producers to manipulate and control a wide array of musical parameters, including note pitch, duration, velocity, and modulation, among others. This level of control fosters unparalleled creativity and precision in music composition and performance.
Moreover, MIDI is not limited to transmitting musical data alone. It also encompasses a range of control messages that govern various aspects of musical expression, such as volume, panning, and effects. This multifaceted nature of MIDI makes it an indispensable tool for shaping the sonic landscape of a musical piece.
In essence, MIDI serves as the backbone of modern music production, offering a standardized method for devices to communicate and collaborate harmoniously. Its impact extends beyond the realm of traditional musical instruments, encompassing a diverse range of equipment, including MIDI controllers, audio interfaces, and digital audio workstations (DAWs).
In summary, MIDI represents a powerful and flexible communication protocol that underpins the seamless integration of electronic musical devices. Its ability to transmit a wide spectrum of musical and control data has revolutionized the way music is created, performed, and recorded, cementing its status as an indispensable cornerstone of contemporary music production.
What is a MIDI Interface?
A MIDI interface serves as the vital link between musical instruments or controllers and a computer or other MIDI-enabled devices. It acts as a conduit for the seamless exchange of MIDI data, allowing musicians and producers to harness the full potential of their electronic instruments within a digital environment. Essentially, a MIDI interface serves as the intermediary translator, facilitating the bidirectional flow of MIDI messages between hardware and software components.
At its core, a MIDI interface typically features MIDI input and output ports, enabling the connection of external MIDI devices, such as keyboards, synthesizers, drum machines, and MIDI controllers. These ports serve as the communication channels through which MIDI data is transmitted to and from the connected instruments. Additionally, many modern MIDI interfaces also incorporate USB connectivity, offering a convenient and versatile means of interfacing with computers and mobile devices.
In essence, a MIDI interface acts as the gateway that bridges the analog realm of musical instruments with the digital domain of computers and software applications. By establishing this crucial connection, musicians and producers can leverage the expressive capabilities of their instruments while seamlessly integrating them into their digital audio workstations (DAWs) and music production setups.
Furthermore, MIDI interfaces often feature additional functionalities, such as MIDI merging, splitting, and routing. These capabilities empower users to manipulate and route MIDI data streams with precision, enabling complex setups and workflows. For instance, MIDI merging allows multiple MIDI input sources to be combined into a single output, facilitating the integration of diverse MIDI controllers and instruments.
Moreover, MIDI interfaces may incorporate features such as MIDI timecode synchronization, which ensures precise alignment between MIDI devices and external clock sources. This synchronization capability is invaluable for maintaining temporal coherence within a multi-device MIDI setup, enabling seamless synchronization of musical elements across different instruments and software applications.
In summary, a MIDI interface serves as the linchpin of modern music production, enabling the seamless integration of electronic instruments with digital audio workstations and software applications. Its role in facilitating the exchange of MIDI data, as well as providing advanced routing and synchronization capabilities, underscores its significance as a fundamental tool for musicians, producers, and audio engineers alike.
Types of MIDI Interfaces
When exploring the realm of MIDI interfaces, it becomes evident that these indispensable tools come in various forms, each tailored to specific needs and preferences of musicians, producers, and audio engineers. Understanding the different types of MIDI interfaces is crucial for selecting the optimal solution that aligns with one's musical workflow and technical requirements. Let's delve into the diverse array of MIDI interfaces and unravel their unique characteristics:
-
USB MIDI Interfaces: These compact and versatile interfaces leverage USB connectivity to establish seamless communication between MIDI-enabled instruments and computers. They often feature multiple MIDI input and output ports, allowing for the simultaneous connection of multiple devices. USB MIDI interfaces are prized for their plug-and-play functionality, making them ideal for musicians seeking a hassle-free setup process.
-
MIDI Interface Modules: These standalone units are designed to provide comprehensive MIDI connectivity and routing capabilities. Equipped with an array of MIDI input and output ports, as well as advanced routing and merging functionalities, MIDI interface modules cater to the needs of professional studios and complex MIDI setups. They offer unparalleled flexibility and control, enabling users to orchestrate intricate MIDI configurations with precision and efficiency.
-
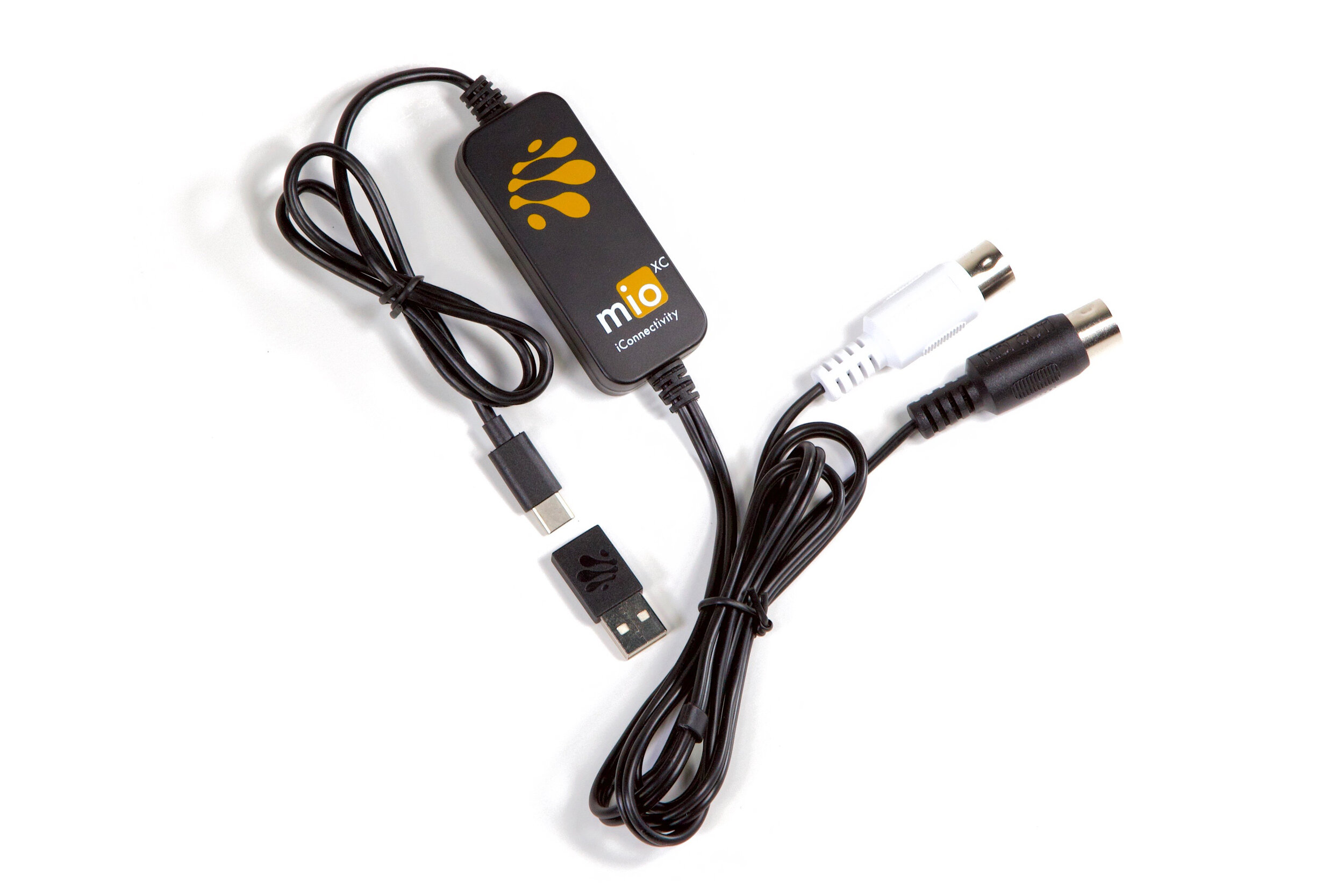
MIDI to USB Converters: These specialized interfaces serve as the bridge between traditional MIDI devices and modern computer systems equipped with USB ports. By converting MIDI signals to USB-compatible data, these converters enable seamless integration of legacy MIDI instruments with contemporary digital audio workstations and software applications. MIDI to USB converters breathe new life into classic MIDI gear, ensuring their relevance in the digital age.
-
Ethernet MIDI Interfaces: Leveraging Ethernet connectivity, these interfaces facilitate MIDI communication over local area networks (LANs) and the internet. They are particularly valuable for collaborative music production scenarios, enabling musicians and producers to exchange MIDI data over long distances. Ethernet MIDI interfaces empower remote musical collaboration and live performances, transcending geographical barriers.
-
Wireless MIDI Interfaces: Embracing the convenience of wireless technology, these interfaces liberate musicians from the constraints of physical cables, offering seamless MIDI connectivity via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. Wireless MIDI interfaces are well-suited for live performances, allowing for unrestricted movement on stage without compromising on MIDI connectivity. They embody the fusion of mobility and versatility in modern music production.
In essence, the diverse landscape of MIDI interfaces encompasses a spectrum of solutions tailored to the evolving needs of musicians and producers. Whether seeking streamlined USB connectivity, comprehensive MIDI routing capabilities, legacy instrument integration, networked collaboration, or wireless freedom, there exists a MIDI interface perfectly suited to elevate the musical journey to new heights.
How to Use a MIDI Interface
Using a MIDI interface involves a seamless integration of electronic musical instruments with computers, digital audio workstations (DAWs), and other MIDI-enabled devices. The following steps outline the process of effectively utilizing a MIDI interface to unlock the full potential of MIDI-based music production:
-
Connection Setup: Begin by connecting the MIDI interface to your computer or mobile device using the appropriate interface ports, such as USB or MIDI connections. Ensure that the interface is securely connected and recognized by your operating system.
-
Instrument Connection: Next, establish connections between your MIDI instruments, such as keyboards, synthesizers, or MIDI controllers, and the MIDI interface. Utilize the MIDI input and output ports on the interface to establish bi-directional communication with your instruments.
-
Software Configuration: Access your preferred digital audio workstation or music production software and configure the MIDI interface as the designated input and output device. This step ensures that MIDI data can be transmitted to and from your instruments through the interface.
-
MIDI Mapping: Within your software application, map the MIDI inputs from your instruments to specific functions or parameters. This may involve assigning MIDI notes to trigger virtual instruments, controlling software parameters using MIDI knobs or faders, and mapping MIDI drum pads to trigger samples or loops.
-
Recording and Playback: With the MIDI interface properly configured, you can now record MIDI performances directly into your software, capturing the nuances of your musical expression. Additionally, the MIDI interface facilitates the playback of MIDI sequences, allowing you to hear the musical data generated by your instruments.
-
Advanced Routing and Control: For advanced users, MIDI interfaces offer features such as MIDI merging, splitting, and routing. These capabilities enable the manipulation and distribution of MIDI data streams, allowing for intricate control over multiple MIDI devices and software instruments.
-
Synchronization and Tempo Control: If your MIDI interface supports synchronization features, utilize them to align the timing of MIDI devices with external clock sources or other MIDI-enabled equipment. This ensures precise synchronization of musical elements within your setup.
By following these steps, you can effectively harness the capabilities of a MIDI interface to seamlessly integrate your electronic instruments into your digital music production environment. Whether you're creating intricate compositions, triggering virtual instruments, or controlling software parameters, a MIDI interface serves as the conduit that empowers you to unleash your musical creativity with precision and finesse.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the realm of MIDI interfaces represents a dynamic nexus where the artistry of traditional musical instruments converges with the boundless possibilities of modern technology. These indispensable tools serve as the linchpin of contemporary music production, empowering musicians, producers, and audio engineers to sculpt sonic landscapes with unparalleled precision and creativity.
Through our exploration of MIDI interfaces, we have unveiled their pivotal role in facilitating seamless communication between electronic instruments and digital audio workstations. From USB MIDI interfaces that offer plug-and-play convenience to MIDI interface modules catering to the demands of professional studios, the diverse array of MIDI interfaces caters to a spectrum of musical workflows and technical requirements.
Furthermore, the advent of MIDI to USB converters, Ethernet MIDI interfaces, and wireless MIDI interfaces has broadened the horizons of musical connectivity, transcending traditional limitations and fostering innovative modes of musical collaboration and performance. These advancements underscore the evolutionary trajectory of MIDI interfaces, reflecting a commitment to enhancing the accessibility and versatility of MIDI-based music production.
The utilization of a MIDI interface entails a harmonious fusion of hardware and software, enabling musicians to capture the nuances of their performances, trigger virtual instruments, and orchestrate intricate MIDI configurations with finesse. Moreover, the advanced routing, merging, and synchronization capabilities offered by MIDI interfaces empower users to orchestrate complex musical setups with precision and efficiency, amplifying the creative potential of their musical endeavors.
As we embrace the transformative influence of MIDI interfaces, it becomes evident that these tools embody the spirit of innovation and collaboration, fostering a vibrant ecosystem where musical expression knows no bounds. Whether in the confines of a professional studio, on stage during a live performance, or in the context of remote musical collaboration, MIDI interfaces stand as the unifying force that harmonizes the diverse elements of modern music production.
In essence, MIDI interfaces are not merely technical conduits; they are catalysts for artistic expression, enabling musicians to transcend conventional boundaries and embark on a journey of sonic exploration. As we look to the future, the evolution of MIDI interfaces will continue to shape the landscape of music production, ushering in new possibilities and empowering creative visionaries to redefine the art of sound.