Home>Production & Technology>Audio Interface>What Should The MIDI From The Audio Interface Connect To


Audio Interface
What Should The MIDI From The Audio Interface Connect To
Modified: February 22, 2024
Discover how to connect MIDI from your audio interface and optimize your music production setup. Learn more about audio interfaces and MIDI connections.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of audio interfaces and MIDI connectivity! If you’re a musician or a producer looking to record and produce music, you’ve probably come across the term “audio interface” at some point. But what exactly is an audio interface, and how does it relate to MIDI?
In simple terms, an audio interface is a piece of hardware that connects your musical instruments, microphones, and studio monitors to your computer or recording device. It acts as a bridge between the analog and digital worlds, allowing you to capture high-quality audio and control various aspects of the recording process.
But what about MIDI? MIDI, which stands for Musical Instrument Digital Interface, is a protocol that allows electronic musical instruments, computers, and other devices to communicate and synchronize with each other. It’s the language that enables you to control and sequence your virtual instruments, record MIDI data, and trigger sounds and effects in your DAW (Digital Audio Workstation).
The MIDI signal, unlike audio signals, does not transmit sound. Instead, it carries data such as note information, control changes, and timing information. This data can be sent from a MIDI controller or software application to your audio interface, which then forwards it to the appropriate destination – be it a hardware synthesizer, virtual instrument, or other MIDI-enabled devices.
In this article, we will explore the different options you have for connecting MIDI from your audio interface to various devices. Whether you’re using hardware synthesizers or virtual instruments, we’ll guide you through the process and provide important tips for troubleshooting common MIDI connection issues.
So, let’s dive in and demystify the world of audio interface MIDI connectivity!
Understanding MIDI
Before we delve into the specifics of connecting MIDI from your audio interface, it’s essential to have a basic understanding of MIDI and its capabilities.
As mentioned earlier, MIDI is a protocol that allows electronic musical instruments and computers to communicate with each other. It was first introduced in the early 1980s and quickly became a standard in the music industry.
Unlike audio signals that transmit sound, MIDI carries instructions and data for controlling musical elements. These instructions include notes, velocities, durations, and control changes such as modulation, pitch bend, and volume. MIDI data can also include synchronization information for tempo and timing.
One of the significant advantages of MIDI is its ability to separate the control information from the actual sound generation process. This means that you can trigger sounds and control parameters on a separate MIDI-enabled device, such as a synthesizer or virtual instrument, without needing to physically play the instrument.
MIDI allows for precise and detailed control over various musical parameters. For example, you can program intricate sequences, automate effects, and layer multiple tracks using MIDI data. This versatility and flexibility make MIDI a powerful tool in modern music production.
It’s important to note that MIDI operates independently of the audio signal. MIDI messages are transmitted digitally and can be sent and received over different types of connections, such as USB, DIN cables, or even wirelessly.
Now that we have a solid understanding of MIDI let’s move on to exploring how you can connect MIDI from your audio interface to different devices.
Audio Interface Overview
An audio interface is a crucial piece of equipment in any home studio or music production setup. It serves as the central hub for connecting your instruments, microphones, and speakers to your computer or recording device.
Audio interfaces come in various shapes, sizes, and configurations, offering different input and output options to suit different needs. The most common types of audio interfaces are USB, Thunderbolt, and PCIe interfaces.
A USB audio interface is the most popular choice for home studios and beginners due to its affordability and ease of use. They connect to your computer via a USB cable and usually provide a range of inputs and outputs, including microphone preamps and instrument inputs.
Thunderbolt interfaces, on the other hand, offer faster data transfer rates and lower latency compared to USB interfaces. They are ideal for professional studios or those working with large projects and requiring the highest level of performance.
PCIe interfaces are internal audio interfaces that slot directly into your computer’s motherboard. They provide even lower latency and are typically used in high-end studio setups or specialized audio production workstations.
Regardless of the interface type, audio interfaces typically feature analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) for converting analog audio signals into digital data that your computer can process. They also have digital-to-analog converters (DACs) for converting digital audio back into analog signals for monitoring purposes.
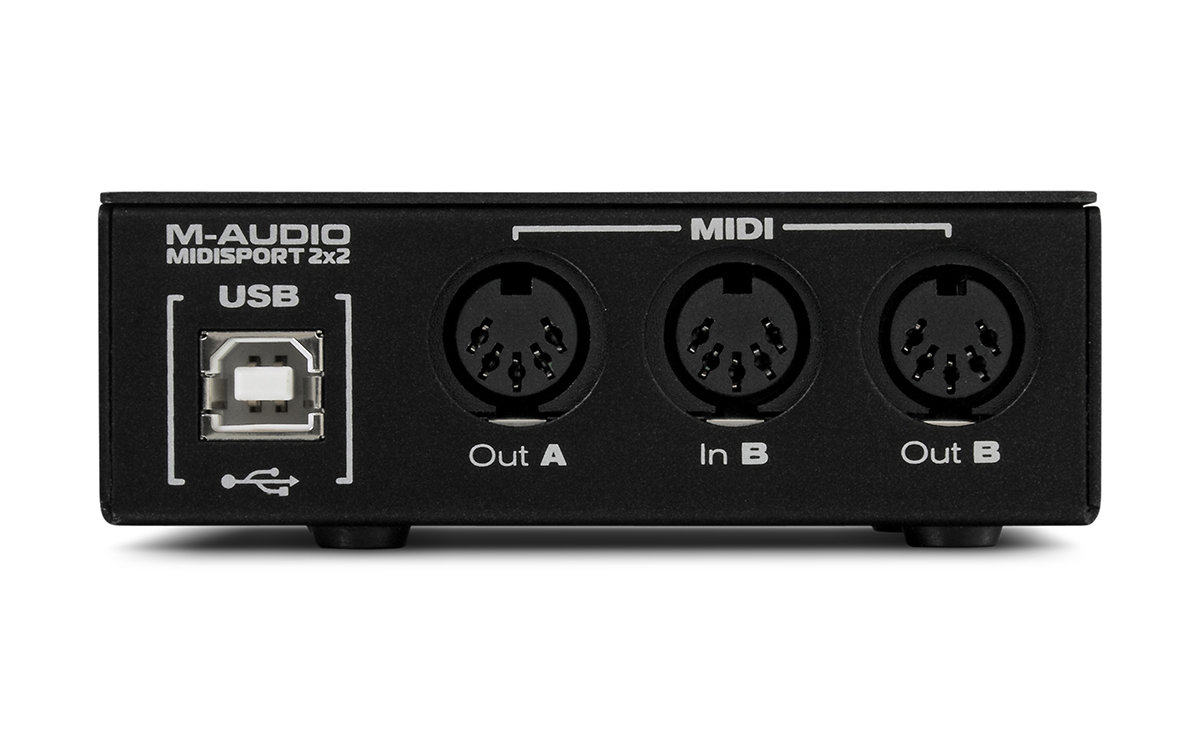
Many audio interfaces also come with MIDI input and output ports, allowing you to connect MIDI devices directly to the interface. This integration simplifies the routing and management of MIDI signals, making it easier to connect and control MIDI-enabled instruments and devices.
It’s important to consider the number and types of inputs and outputs you require when choosing an audio interface. Think about the number of microphones, instruments, and other audio sources you plan to connect, as well as your future expansion needs.
With a solid understanding of audio interfaces, let’s explore the different options you have for connecting MIDI from your audio interface to your hardware synthesizers or virtual instruments.
Options for MIDI Connection
When it comes to connecting MIDI from your audio interface, there are several options available, depending on your setup and the devices you want to connect.
1. MIDI DIN Cables: Many audio interfaces feature standard MIDI DIN ports, allowing you to connect your MIDI-enabled devices directly using MIDI cables. These cables have a round, five-pin connector and are widely used in the music industry. Simply connect the MIDI output from the audio interface to the MIDI input on your hardware synthesizer or other MIDI devices, and vice versa for MIDI input.
2. USB MIDI: Some audio interfaces have built-in USB MIDI functionality, eliminating the need for MIDI DIN cables. These interfaces provide a USB connection that allows you to directly connect your MIDI-enabled devices to the interface using a standard USB cable. This option is convenient if you want to connect devices that have USB MIDI ports, such as MIDI controllers or certain virtual instruments.
3. MIDI over Network: Some audio interfaces offer the ability to transmit MIDI data over a network connection, either via Ethernet or Wi-Fi. This feature allows you to connect multiple MIDI-enabled devices to your audio interface without the need for physical cables. It’s a flexible option for larger setups or situations where you want to connect devices in different locations within your studio.
4. Software Virtual MIDI: Certain audio interfaces come with software that allows you to create virtual MIDI connections within your computer. This means that you can route MIDI data from your audio interface directly to virtual instruments or other MIDI-enabled software applications without the need for physical cables. It’s a convenient option for working entirely within your DAW and eliminates the need for additional hardware connections.
It’s important to check the specifications and features of your audio interface to determine which MIDI connection options are available. Some interfaces may offer multiple MIDI connection methods, giving you the flexibility to choose the most suitable option for your specific needs.
Now that we have explored the different options, let’s look at how to connect MIDI from your audio interface to hardware synthesizers.
Connecting MIDI from Audio Interface to Hardware Synthesizers
If you have a hardware synthesizer or other MIDI-enabled devices, connecting them to your audio interface is relatively straightforward.
1. Using MIDI DIN Cables: If your audio interface has MIDI DIN ports, simply connect the MIDI output of the audio interface to the MIDI input of your hardware synthesizer using standard MIDI DIN cables. Likewise, connect the MIDI output of the synthesizer to the MIDI input of the audio interface if you want to send MIDI data from the synthesizer to your computer or other devices.
2. Using USB MIDI: If your audio interface supports USB MIDI, you can connect your hardware synthesizer directly to the interface using a USB cable. Check if your synthesizer has a USB MIDI port and connect it to the USB port on the audio interface. This allows for a direct and convenient connection without the need for additional MIDI cables.
Once the hardware synthesizer is connected to your audio interface, the MIDI data flows seamlessly between the devices. You can control the synthesizer from your MIDI controller or software application, or send MIDI data from the synthesizer to your computer for recording and playback.
It’s worth noting that some hardware synthesizers may have multiple MIDI ports, allowing you to connect them to different devices simultaneously. This flexibility enables you to integrate your synthesizer into a more complex MIDI setup with multiple controllers, interfaces, and software applications.
Now that you know how to connect MIDI from your audio interface to hardware synthesizers let’s explore connecting MIDI to virtual instruments.
Connecting MIDI from Audio Interface to Virtual Instruments
Virtual instruments, or software synthesizers, have become an integral part of modern music production. Connecting MIDI from your audio interface to virtual instruments allows you to control and play these software instruments using MIDI data.
There are a few different ways to connect MIDI from your audio interface to virtual instruments:
1. Direct Software Integration: Many virtual instrument plugins and software applications have the capability to directly receive MIDI data from your audio interface. In your DAW, set the MIDI input of the virtual instrument track to the corresponding MIDI input of your audio interface. Now, when you play your MIDI controller, the MIDI data will be sent from the audio interface to the virtual instrument, triggering the sounds and responding to your performance.
2. Virtual MIDI Routing: Some audio interfaces come with software that allows for virtual MIDI routing within your computer. This means you can route the MIDI data from your audio interface directly to your virtual instruments without physical connections. With this setup, you can easily connect multiple virtual instruments and control them simultaneously using different MIDI channels.
3. MIDI Loopback: Another option is to use a MIDI loopback software or virtual MIDI cable. This software creates virtual MIDI ports within your computer, allowing you to route MIDI data between different software applications. You can send MIDI data from your audio interface to the virtual MIDI cable, and then use the virtual cable as the MIDI input for your virtual instrument. This method provides flexibility and allows for more complex MIDI routing configurations.
Regardless of the method you choose, connecting MIDI from your audio interface to virtual instruments allows you to take advantage of the vast array of sounds and capabilities offered by software synthesizers. You can use your MIDI controller or even program MIDI sequences in your DAW to control and manipulate the virtual instrument’s parameters in real-time.
Now that you know how to connect MIDI from your audio interface to hardware synthesizers and virtual instruments, let’s discuss some troubleshooting tips for common MIDI connection issues.
Tips for Troubleshooting MIDI Connection Issues
While connecting MIDI from your audio interface to hardware synthesizers or virtual instruments is usually straightforward, you may encounter some common issues along the way. Here are some tips to help you troubleshoot and resolve any MIDI connection problems:
1. Check Cable Connections: Ensure that all MIDI cables are securely connected to the correct ports on both the audio interface and the MIDI devices. Loose or faulty connections can result in intermittent or no MIDI signal transmission.
2. Verify MIDI Channel Settings: Check the MIDI channel settings on both your audio interface and the MIDI device. They should be set to the same MIDI channel for proper communication. Misconfigured MIDI channels can cause MIDI data to be sent to the wrong device or not received at all.
3. Restart Your Devices: Sometimes, a simple restart can solve MIDI connectivity issues. Turn off and then on your audio interface, MIDI devices, and computer to reset the connections and ensure they are properly recognized.
4. Update Drivers and Firmware: Check for any available driver or firmware updates for your audio interface and MIDI devices. Outdated drivers can cause compatibility issues, while firmware updates often address bugs and improve overall performance.
5. Check MIDI Thru:
If you’re using multiple MIDI devices connected in a daisy-chained setup or via a MIDI thru box, verify that the MIDI thru functionality is enabled correctly. Improperly configured MIDI thru settings can disrupt the flow of MIDI data to subsequent devices.
6. Test with Different Cables and Ports: If you suspect a faulty cable or port, try using different cables or switching to alternative MIDI ports on your audio interface or devices. This can help isolate any issues related to specific connections.
7. Check MIDI Channel and Mapping in Software: If you’re experiencing issues with virtual instruments, verify that the MIDI channel settings and mapping are correctly configured within the software. Ensure that the MIDI input from your audio interface is recognized and properly routed to the virtual instrument.
8. Consider MIDI Monitoring Tools: MIDI monitoring software or utility can be helpful in troubleshooting MIDI connection issues. These tools allow you to visualize and analyze MIDI data flow, helping you identify any errors or latency in the MIDI signal.
9. Consult Manufacturer Support: If you’ve tried all the troubleshooting steps and are still experiencing MIDI connection problems, reach out to the manufacturer’s support team for further assistance. They can provide specific guidance and help resolve any hardware or software-related issues.
Remember, troubleshooting MIDI connection issues can sometimes be trial-and-error. Being patient and methodical in your approach will help you identify and resolve any problems that may arise.
With these troubleshooting tips in mind, you’re now ready to connect MIDI from your audio interface successfully. Let’s summarize what we’ve covered in this article.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding how to connect MIDI from your audio interface is essential for expanding your musical possibilities. Whether you’re connecting to hardware synthesizers or virtual instruments, MIDI connectivity allows you to control, sequence, and manipulate sounds with precision.
We began by gaining a basic understanding of MIDI and its role in music production. MIDI provides a powerful means of communication between devices, enabling you to control various musical elements and synchronize audio and MIDI data.
We then explored the different options for connecting MIDI from your audio interface. Whether using MIDI DIN cables, USB MIDI, MIDI over networks, or virtual MIDI routing, there are versatile methods to suit your specific needs and setup.
For hardware synthesizers, connecting MIDI involved simple cabling or utilizing USB MIDI ports. Virtual instruments, on the other hand, can be integrated directly into your DAW software, or you can use virtual MIDI routing or MIDI loopback options for more complex configurations.
If you encounter any MIDI connection issues, we provided troubleshooting tips, including checking cable connections, verifying MIDI settings, updating drivers and firmware, and testing with different cables or ports. Additionally, considering MIDI monitoring tools and seeking manufacturer support can further assist in resolving any problems.
By successfully connecting MIDI from your audio interface, you can unleash the full potential of your musical creativity. Whether you’re recording MIDI performances, programming intricate sequences, or controlling virtual instruments, MIDI connectivity opens up a world of possibilities in your music production journey.
So go ahead, experiment, and have fun exploring the endless sonic possibilities that MIDI connection from your audio interface has to offer!