Home>Production & Technology>Sheet Music>How To Transcribe Music To Sheet Music


Sheet Music
How To Transcribe Music To Sheet Music
Modified: February 22, 2024
Learn how to transcribe music to sheet music with our step-by-step guide. Start reading now and unlock the secrets of creating accurate and professional sheet music.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding the Basics of Music Transcription
- Choosing the Right Tools for Music Transcription
- Listening Techniques for Transcribing Music
- Note Identification and Notation
- Rhythmic Transcription and Interpretation
- Transcribing Chords and Harmony
- Advanced Techniques for Music Transcription
- Troubleshooting and Common Challenges in Music Transcription
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to the world of sheet music! Whether you’re a musician, music student, or simply someone with a passion for music, understanding and transcribing sheet music is an essential skill. Sheet music serves as a universal language that allows us to communicate and share musical ideas across time and space. It provides a visual representation of musical notes, rhythms, and other symbols, enabling musicians to accurately perform and interpret a piece of music.
Transcribing music to sheet music involves listening to a piece of music and notating it into written form. This process requires a deep understanding of musical concepts, including note identification, rhythmic interpretation, harmony, and more. It allows us to capture the nuances, intricacies, and emotions of a musical composition, preserving it for future generations to appreciate and learn from.
In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of music transcription and provide you with helpful tips and techniques for transcribing music to sheet music. Whether you are transcribing your own compositions, deciphering a song you heard on the radio, or studying a classic piece of music, this guide aims to equip you with the necessary knowledge and tools for successful music transcription.
We will delve into various aspects of music transcription, including note identification, rhythmic interpretation, chord transcription, and more. We will also cover common challenges and troubleshooting techniques that you may encounter during the transcription process. By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of how to transcribe music to sheet music and be well on your way to becoming a proficient transcriber.
So, grab your headphones, tune your ears, and get ready to embark on a musical journey as we dive into the art of music transcription. Let’s explore the tools, techniques, and strategies that will help you bring music to life through the written word.
Understanding the Basics of Music Transcription
Music transcription is the process of converting audio recordings or live performances into written notation. It requires a keen ear, a solid understanding of music theory, and the ability to translate what you hear into symbols on paper. Before diving into the intricacies of music transcription, it is essential to grasp the fundamental concepts that serve as the building blocks of this art form.
The first step in music transcription is developing a strong foundation in music theory. This includes understanding the different musical elements such as melody, harmony, rhythm, and dynamics. By familiarizing yourself with these concepts, you will be better equipped to discern and transcribe the various components of a musical piece.
Melody is the primary element of music and refers to the sequence of notes that form the main tune or theme. When transcribing melody, listen carefully to the pitch and rhythm of each note. Use your knowledge of music theory to identify the key signature and scale that the melody is based on.
Harmony is the combination of different notes played simultaneously, forming chords. When transcribing harmony, focus on identifying the types of chords used and their progression throughout the piece. Pay attention to the relationships between the notes and any inversions or voicings that are present.
Rhythm is the timing and pattern of the musical notes. Pay close attention to the length and placement of each note, including any syncopation or rhythmic variations. It can be helpful to tap your foot or use a metronome to keep track of the beat and accurately notate the rhythmic elements.
Dynamics refer to the volume and intensity of the music. Transcribing dynamics can be challenging, as they are subjective and can vary depending on the performer. Listen for changes in volume, accents, and other expressive markings that indicate the dynamic changes in the piece.
Once you have a solid understanding of these musical elements, it’s time to choose the right tools for your music transcription endeavors. There are several software programs and apps available that can assist in the transcription process, allowing you to input and edit the notated music more efficiently. Some popular options include Finale, Sibelius, and MuseScore.
However, it’s important to note that while these tools can be helpful, they should not replace the development of your own transcription skills. Transcribing music by hand forces you to actively engage with the music, enhancing your ear training and music theory knowledge.
Now that we have established the foundational concepts of music transcription and the tools at your disposal, it’s time to dive into the techniques and strategies that will help you excel in transcribing music to sheet music. In the next section, we will explore specific listening techniques that will sharpen your ear and improve your ability to transcribe accurately.
Choosing the Right Tools for Music Transcription
When it comes to music transcription, having the right tools can significantly enhance your efficiency and accuracy. While it is possible to transcribe music using pen and paper, there are various software programs and apps available that can streamline the process and provide additional features to aid in your transcription efforts.
One of the most popular software programs for music transcription is Finale. Finale offers a comprehensive set of tools for composers, arrangers, and transcribers. It allows you to input notes and symbols directly onto the score, edit and playback the music, and generate professional-looking sheet music. With its extensive library of musical symbols, you can easily notate complex rhythms, chords, and articulations.
Sibelius is another widely used software program that provides a user-friendly interface and powerful transcription capabilities. Its intuitive layout and advanced features make it an excellent choice for both beginners and experienced transcribers. Sibelius also allows for seamless integration with other music software and MIDI devices, making the transcription process more efficient.
If you’re looking for a free alternative, MuseScore is an excellent option. MuseScore provides many of the same features as commercial software programs, including score creation, playback, and editing. It also has an active online community where you can find and share sheet music and collaborate with other musicians.
In addition to these software programs, there are also mobile apps available for music transcription. Apps like Notion, for example, offer a simplified interface for transcribing on the go. With its touch-based input and playback features, you can easily capture musical ideas and transcribe them into sheet music directly from your phone or tablet.
When choosing a tool for music transcription, consider your specific needs and preferences. Think about the level of complexity and flexibility you require, the learning curve of the software, and any compatibility requirements with other music software or devices. It’s also essential to ensure that the tool you choose supports the file formats you need, such as MIDI or MusicXML, for easy integration with other music software or sharing with other musicians.
Ultimately, the best tool for music transcription is one that allows you to efficiently capture and notate the nuances of the music while fitting your workflow preferences. Experiment with different software programs and apps to find the one that best suits your needs and helps you achieve accurate and professional-looking sheet music.
In the next section, we will explore various listening techniques that will sharpen your ear and improve your ability to transcribe accurately.
Listening Techniques for Transcribing Music
When it comes to transcribing music, developing strong listening skills is crucial. The ability to accurately hear and interpret musical elements such as melody, harmony, and rhythm is essential for successful transcription. Here are some techniques to help sharpen your ear and improve your transcription abilities:
1. Active Listening: Transcription requires active engagement with the music. Listen attentively to the piece you are transcribing, focusing on the details of each note, chord, and rhythm. Train your ear to identify subtle nuances and variations in pitch, timing, and dynamics. Pay attention to the overall structure and form of the music, as this will provide important cues for notating the piece accurately.
2. Slow Down the Music: When faced with complex or fast-paced music, it can be challenging to fully grasp every note and rhythm. Utilize technology or software features that allow you to slow down the music without altering the pitch. This technique enables you to dissect intricate passages and capture intricate details more effectively.
3. Break It Down: Rather than trying to transcribe an entire song in one go, break it down into smaller sections. Focus on one phrase or segment at a time, allowing yourself to fully comprehend and notate each section accurately before moving on to the next. This approach helps prevent overwhelm and allows for more precise transcription.
4. Use Visual Aids: Visual aids can be helpful tools in capturing the nuances of music. Consider using a spectrogram, which provides a visual representation of the audio spectrum. Spectrograms can help identify specific frequencies and harmonics, aiding in identifying notes and chords.
5. Sing or Play Along: Actively engage with the music by singing or playing along with the recording. This not only helps you internalize the melody and rhythm but also engrains a deeper understanding of the musical patterns and phrasing. Experiment with different instruments or vocal ranges to gain a comprehensive understanding of the musical composition.
6. Employ Transcription Exercises: Regularly practice transcription exercises to improve your listening skills. Start with simple melodies and progress to more complex pieces. Use resources such as ear-training apps or websites that provide exercises specifically designed to improve transcription abilities.
7. Seek Reference Recordings: Listening to reference recordings of the piece you are transcribing can be invaluable. Professional recordings can provide insight into interpretation, phrasing, and articulation. Compare your transcription to the reference recording to refine your notations and ensure accuracy.
Remember, transcription is a skill that develops over time with consistent practice and dedication. As you continue to apply these listening techniques and actively engage with music, your transcription abilities will improve, allowing you to capture the essence and intricacies of any musical piece.
In the next section, we will delve into note identification and notation techniques, which are essential components of music transcription.
Note Identification and Notation
One of the core skills in music transcription is note identification and notation. Being able to accurately identify and notate individual notes is essential for capturing the melody, harmony, and overall musical structure. Here are some techniques to help you improve your note identification and notation abilities:
1. Develop Ear Training: Ear training exercises are invaluable for honing your ability to identify and differentiate between different pitches. Practice listening to intervals, scales, and chords to train your ear to recognize specific musical patterns. There are many online resources and mobile apps available that offer interactive ear training exercises to help improve your note recognition skills.
2. Start with the Melody: When transcribing a piece of music, begin by focusing on the melody. Listen carefully to the pitch of each note and identify its placement on the musical staff. Use your knowledge of music theory and the key signature to determine the correct letter name for each note. Notate the melody in the appropriate duration, whether it be a whole note, half note, or any other rhythmic value.
3. Transcribe in Layers: As you progress with the transcription process, notate additional layers of the music, such as harmony or counter melodies. Pay attention to the relationships between the notes and their vertical alignment to indicate chords or intervals. Use your understanding of chord progressions and harmonic analysis to accurately transcribe the underlying harmony. Be aware of any accidental notes or key changes that may occur throughout the piece.
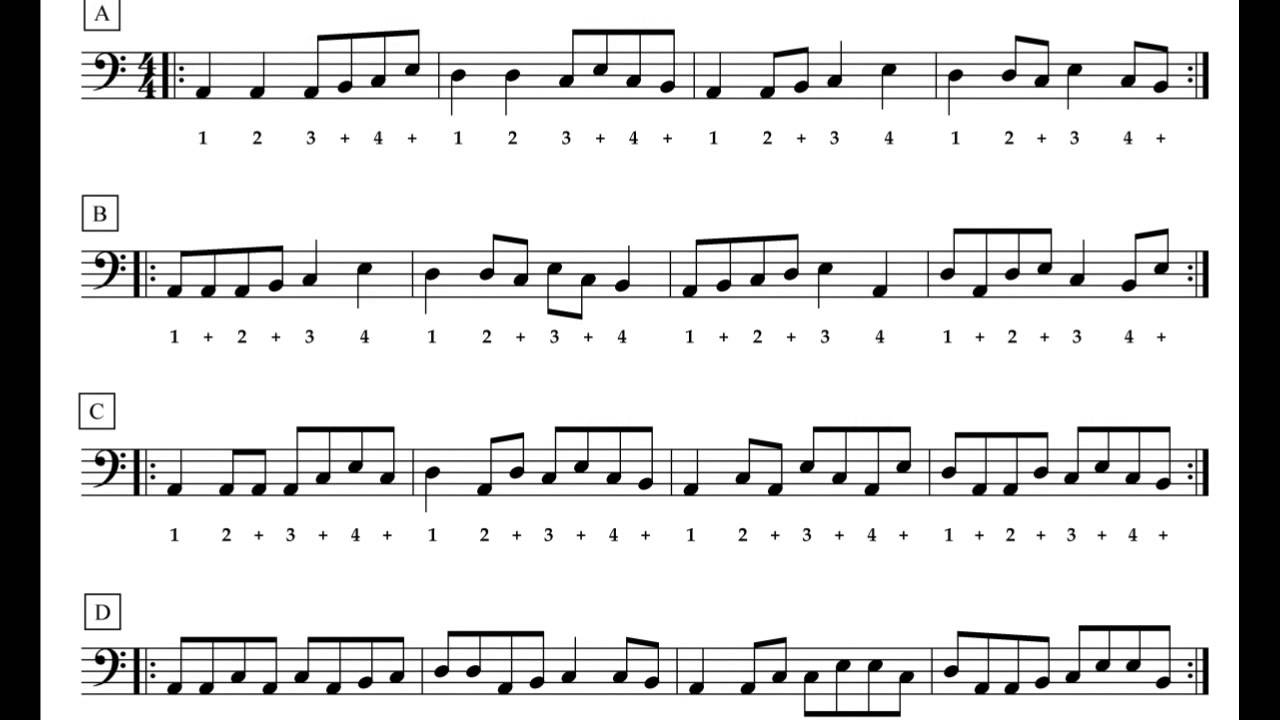
4. Use Standard Notation Symbols: Familiarize yourself with standard music notation symbols, such as note heads, stems, and flags/beams. This will allow you to accurately notate the duration and rhythmic values of each note. Understand the difference between different note values, such as quarter notes, eighth notes, and sixteenth notes. Use ties and rests when necessary to ensure the correct rhythmic representation.
5. Consider Articulation and Expression: Music notation goes beyond just note identification and duration. Pay attention to the articulation and expression markings in the music. Notate staccatos, slurs, dynamics, and other performance markings to accurately represent the intended interpretation of the music. These subtle nuances can greatly impact the overall feel and emotion of the piece.
6. Take Advantage of Technology: Utilize music notation software such as Finale, Sibelius, or MuseScore to streamline the notation process. These software programs provide a wide range of tools and shortcuts to input and edit musical notation more efficiently. With features like MIDI input or the ability to import MIDI files, you can even use a MIDI keyboard or other MIDI devices to help with note input.
7. Double-Check and Refine: Once you have completed your transcription, take the time to double-check your work. Listen to the recorded music while following along with your notation to ensure accuracy. Fix any errors or inconsistencies and make any necessary revisions to improve the overall quality of your transcription.
Remember, note identification and notation is a skill that improves with practice. The more you transcribe and notate music, the more proficient you will become. Take the time to study and analyze sheet music from different genres and composers to expand your musical knowledge and transcription abilities.
In the next section, we will explore rhythmic transcription and interpretation, another crucial aspect of music transcription.
Rhythmic Transcription and Interpretation
Rhythm is a fundamental element of music that drives its energy and groove. Transcribing rhythm accurately is essential for capturing the essence and feel of a musical piece. Here are some techniques to help you improve your rhythmic transcription and interpretation:
1. Develop a Strong Sense of Time: One of the most critical aspects of rhythmic transcription is having a solid sense of time. Practice tapping or counting along with music to internalize its pulse and meter. Use a metronome to improve your sense of timing and to maintain a consistent beat while transcribing.
2. Break Down Complex Rhythms: Complex rhythms can be challenging to transcribe, especially when they involve syncopation or intricate patterns. Break down these rhythms into smaller units and analyze them individually. Count each beat and subdivision, focusing on the timing and placement of each note. Consider using rhythmic notation such as dotted rhythms, tied notes, or rests to accurately represent the rhythm.
3. Pay Attention to Rests and Ties: Rests are just as important as notes when transcribing rhythm. Take note of any silent beats or breaks in the music and ensure they are accurately represented in your transcription. Ties are used to connect notes of the same pitch across beats or measures, indicating a sustained sound. Use ties to indicate long notes or sustained sounds in the music.
4. Analyze Accents and Articulations: Accents and articulations greatly enhance the rhythmic interpretation of a piece. Listen for accents or emphasized notes and capture them in your transcription. Pay attention to staccatos, legatos, and other articulation markings that affect the length and attack of each note. Notating these markings accurately is crucial for recreating the intended feel and expression of the music.
5. Use Descriptive Text: In addition to standard rhythmic notation, consider using descriptive text to clarify rhythmic patterns or interpretations. This can include terms such as “swung,” “syncopated,” or “rubato” to convey specific rhythmic qualities. The text can provide additional context and help bring the rhythm to life in your transcription.
6. Listen for Subtle Variations: Depending on the genre or style of the music, there may be subtle variations in the rhythm. Listen for grace notes, ornaments, or rhythmic embellishments that may be incorporated into the performance. Notate these variations to capture the unique character of the music accurately.
7. Practice Clapping and Playing Along: Actively engage with the rhythm by clapping or playing along with the music. This physical involvement helps internalize the rhythmic patterns and improves your ability to transcribe them accurately. Experiment with different instruments or percussion sounds to explore the rhythmic possibilities of the music.
Remember, rhythmic transcription is not just about capturing the specific durations and positions of notes but also about conveying the energy and groove of the music. As you practice and refine your rhythmic transcription skills, you will become more adept at interpreting and notating the rhythmic intricacies of any musical piece.
In the next section, we will delve into transcribing chords and harmony, another vital element of music transcription.
Transcribing Chords and Harmony
Transcribing chords and harmony is a crucial aspect of music transcription, as it provides the foundation and structure of a musical piece. Understanding and accurately notating chords and harmonic progressions allows for a comprehensive and complete transcription. Here are some techniques to help you improve your chord transcription and harmonization skills:
1. Analyze the Key and Key Signature: Begin by identifying the key of the piece you are transcribing. The key will determine the set of notes and chords that are commonly used. Look for key signatures and any changes or modulations throughout the piece. Understanding the key will guide your chord selection and provide context for harmonic analysis.
2. Listen for Bass Notes: Pay close attention to the lowest notes in the music, as they often indicate the root or bass note of the chord being played. Identify the movement and relationships between bass notes to determine the chord progression. Use your knowledge of music theory and chord structures to identify the quality (major, minor, diminished, etc.) of each chord.
3. Recognize Common Chord Progressions: Familiarize yourself with common chord progressions found in the genre or style of music you are transcribing. This will give you a starting point and help you anticipate the chords that are likely to be used. Common progressions such as the I-IV-V in major keys or the ii-V-I in jazz can be a helpful guide.
4. Listen for Voicings and Inversions: In addition to identifying the root note of each chord, listen for the arrangement of the other notes within the chord. This includes identifying chord inversions (where the root is not the lowest note) and different voicings (different arrangements of the notes within a chord). Notating these voicings and inversions accurately adds depth and accuracy to your transcription.
5. Harmonize the Melody: As you transcribe the melody, harmonize it by determining the chords that accompany each note. Listen for notes that appear to create harmony with the melody and align them with appropriate chords. Use your knowledge of chord progressions and harmonic analysis to make informed decisions, ensuring that the harmony fits the melody seamlessly.
6. Consider Rhythmic and Articulation Cues: The rhythm and articulation of the music can provide valuable clues for chord changes. Listen for rhythmic patterns that often coincide with chord changes or accents on specific notes that suggest chord transitions. The rhythmic and articulation cues can help you identify the timing and placement of chord changes in your transcription.
7. Verify with Reference Recordings and Sheet Music: While transcribing chords and harmony, it can be helpful to consult reference recordings and existing sheet music arrangements of the piece. Listen to reference recordings to compare your transcription and ensure accuracy. Additionally, sheet music arrangements can provide insights into harmonic choices and voicings.
Remember, transcribing chords and harmony can be a complex process that requires knowledge, careful listening, and analysis. With practice and experience, your ability to accurately transcribe and notate chords will improve, allowing you to create comprehensive and well-structured musical transcriptions.
In the next section, we will explore advanced techniques for music transcription that can further enhance the accuracy and quality of your transcriptions.
Advanced Techniques for Music Transcription
Once you have mastered the fundamentals of music transcription, there are advanced techniques that you can employ to further enhance the accuracy and quality of your transcriptions. These techniques will challenge your skills and enable you to capture even the most intricate details of a musical piece. Here are some advanced techniques for music transcription:
1. Analyzing Complex Rhythms: Advanced music often contains complex rhythmic patterns that can be challenging to transcribe accurately. Break down these rhythms into smaller subdivisions and count them meticulously. Use tools like slow-down software or metronomes to help dissect and comprehend intricate rhythms. Additionally, focus on identifying and notating polyrhythms or irregular meter changes that may be present in the music.
2. Harmonic Analysis: Dive deeper into harmonic analysis by exploring extended chords, chord substitutions, and modal interchange. Understand the function of different chords within the key and identify any non-diatonic chords or borrowed chords. Analyzing the harmonic structure will provide a more comprehensive understanding of the music and assist in crafting accurate transcriptions.
3. Transcribing Ornamentation and Expressive Techniques: Advanced music often incorporates ornamentation and expressive techniques, such as trills, grace notes, bends, and slides. Train your ear to identify these embellishments and notate them appropriately. Pay attention to any specific articulation markings that indicate the desired expressive qualities of the music and strive to capture those nuances in your transcription.
4. Notating Dynamics and Phrasing: Dynamics and phrasing play a crucial role in conveying the emotions and nuances of a musical piece. Advanced transcriptions should include accurate dynamics markings, such as piano, forte, crescendos, and decrescendos. Identify phrasing and interpretative cues to notate the musical phrases and their articulation accurately.
5. Capturing Performance Techniques: Consider incorporating performance techniques into your transcriptions to accurately represent the style and intentions of the performer. This may involve notating specific guitar techniques, such as palm muting or fingerpicking patterns, or capturing the nuanced bowing techniques for string instruments. Transcribing these performance techniques can add depth and authenticity to your transcription.
6. Utilizing Music Theory Knowledge: Advanced transcriptions require a strong foundation in music theory. Apply your knowledge of scales, modes, and chord progressions to identify and notate complex harmonic and melodic sequences accurately. Understanding the theoretical underpinnings of the music will allow you to make informed decisions and create more refined transcriptions.
7. Cross-Referencing Multiple Recordings and Sources: When working on complex or ambiguous sections, consult multiple recordings and sheet music arrangements to cross-reference and validate your transcription. Different interpretations can provide valuable insights and help you make informed decisions and achieve a more accurate transcription.
Remember, advanced music transcription is a continuous learning process that requires a deep understanding of musical concepts and careful attention to detail. With practice and dedication, you can refine your skills and create transcriptions that capture the essence and complexity of any musical piece.
In the next section, we will address common challenges and offer troubleshooting tips to overcome obstacles that may arise during the music transcription process.
Troubleshooting and Common Challenges in Music Transcription
Music transcription is a complex process that can present various challenges along the way. Understanding these challenges and having strategies to overcome them will help you navigate through the transcription process more effectively. Here are some common challenges in music transcription and troubleshooting tips:
1. Difficult Passage Recognition: Some musical passages can be particularly challenging to decipher due to fast tempos, intricate rhythms, or complex harmonies. If you encounter a difficult passage, break it down into smaller sections and analyze each part individually. Use tools like slow-down software or metronomes to help you carefully identify and transcribe each note and rhythm accurately.
2. Ambiguous Chord Progressions: In certain pieces, the harmony may present ambiguous or unconventional chord progressions that are not easily identifiable. When faced with ambiguous chords, listen closely to the surrounding melody and bass notes to determine the possible chord options. Experiment with different voicings and inversions that fit the given notes and harmonically make sense. Consulting transcriptions or recordings by experienced musicians can also provide valuable insights in such cases.
3. Instrument-Specific Challenges: Transcribing music for instruments with unique playing techniques can pose challenges. Each instrument has its own set of notational conventions, ornamentations, and expressive techniques. Research and study the specific techniques and notation used for the instrument you are transcribing for. Consult instructional resources, method books, or recordings specifically intended for that instrument to gain a better understanding of its unique characteristics.
4. Poor Audio Quality: Low-quality audio recordings can make it difficult to accurately transcribe music. If the recording is unclear or muffled, try adjusting the equalization on your audio equipment or software to emphasize the desired frequencies. Seek out higher-quality recordings or alternative performances of the same piece that provide better clarity and tonal balance. Additionally, utilizing headphones or good quality speakers can help you hear the nuances and details more clearly.
5. Transcribing Complex Orchestral Scores: Transcribing for large orchestral ensembles can be challenging due to the vast number of instruments and intricate counterpoint. In these cases, it may be helpful to start by analyzing the individual sections or families of instruments. Focus on transcribing the primary melodies and harmonic progressions to establish a foundation. Then, gradually add in the remaining instrumental voices, taking note of any orchestration techniques or divisi parts.
6. Enharmonic Spelling: Enharmonic spelling refers to using different notation for the same pitch, such as writing a G♯ as an A♭. Enharmonic spelling can vary depending on the context and key signature. Use your musical knowledge and context clues to determine the most appropriate enharmonic spelling. Pay attention to harmonic and melodic implications to ensure the accurate representation of the music.
7. Notating Expressive Details: Capturing expressive details, such as dynamics, phrasing, and articulations, can be challenging in a transcription. Focus on careful listening to the performance and take note of any distinctive expressive markings. Consult performance guides, recordings, or sheet music editions to gain insights into the composer’s intended expressiveness. Implement descriptive notation, symbols, or textual descriptions to convey these expressive details in your transcription.
Remember, music transcription requires patience, perseverance, and an attention to detail. Embrace the challenges as opportunities to refine your skills and deepen your understanding of the music. With practice and experience, you will become more adept at troubleshooting and overcoming obstacles that may arise during the transcription process.
In the final section, we will conclude our discussion on music transcription and highlight the importance of this skill in preserving and sharing musical heritage.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You have now reached the end of our comprehensive guide to music transcription. Throughout this article, we have explored the basics of music transcription, provided tips for choosing the right tools, and discussed various techniques for accurate transcriptions. We covered topics such as note identification, rhythmic transcription, chord notation, and advanced techniques to tackle complex musical passages.
Music transcription is an art that requires a blend of technical knowledge, attentive listening, and creative interpretation. It is a skill that allows us to preserve musical compositions and share them with others. Transcribing music to sheet music not only serves as a record of the music, but it also facilitates communication and collaboration among musicians.
As you embark on your music transcription journey, remember to cultivate your listening skills, deepen your understanding of music theory, and embrace the challenges that arise along the way. With practice and perseverance, your transcription abilities will continue to grow, allowing you to capture the essence, emotion, and intricacies of any piece of music.
It’s also important to keep in mind that music transcription is not just a technical exercise – it is an opportunity for you to engage deeply with the music, to breathe life into the written symbols, and to convey the artistry and expression of the original composition. Embrace your creativity and strive to deliver not just a faithful representation of the music, but a transcription that captures and communicates the soul of the music.
So, whether you are transcribing your own compositions, deciphering a popular song, or delving into the works of classical composers, know that you are part of a rich tradition of music transcription. Few things are as rewarding as the moment when you can hold a well-transcribed piece of sheet music in your hands, knowing that you have unlocked the magic of the music and can share it with others.
Now, go forth and continue your exploration of music transcription. Immerse yourself in the world of sheet music, and let your transcriptions resonate with the beauty and power of the music you love.