Home>Devices & Equipment>Microphone>How To Stop Microphone From Picking Up Breathing


Microphone
How To Stop Microphone From Picking Up Breathing
Published: February 16, 2024
Learn effective techniques to prevent your microphone from picking up unwanted breathing sounds. Follow these tips to improve your audio quality.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Understanding the Annoyance of Breathing Sounds in Microphones
Microphones are exceptional tools for capturing the human voice and various sounds, but they can also be incredibly sensitive, picking up even the subtlest of noises. One common issue that many individuals encounter when using microphones is the unwanted sound of breathing being picked up during recordings or live performances. This issue can be particularly frustrating, as it detracts from the overall audio quality and can be distracting to listeners.
Fortunately, there are several effective strategies to mitigate this problem and ensure that breathing sounds do not interfere with the desired audio. By implementing proper microphone positioning, utilizing pop filters, practicing effective breathing techniques, and leveraging noise reduction software, individuals can significantly reduce or eliminate the unwanted sounds of breathing in their recordings.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various methods to prevent microphones from picking up breathing sounds, providing practical solutions for professionals, content creators, podcasters, musicians, and anyone else seeking to optimize their audio recordings. By understanding the root causes of this issue and implementing the recommended techniques, individuals can achieve clearer, more professional-sounding audio that is free from the distractions of unwanted breathing sounds.
Understanding the Issue
Before delving into the solutions, it’s crucial to understand why microphones often capture the sound of breathing. Microphones, especially condenser microphones, are designed to be highly sensitive to sound waves, allowing them to accurately capture audio. However, this sensitivity also means that they can pick up ambient noises, including the sound of breathing, which can be particularly noticeable when recording vocals or spoken dialogue.
When a person speaks or sings into a microphone, the proximity of their mouth to the microphone’s diaphragm can result in the direct capture of breath sounds. Additionally, certain microphone placements, such as positioning the microphone too close to the mouth, can exacerbate this issue. The airflow from breathing can cause unwanted plosive sounds and low-frequency rumble, degrading the overall audio quality.
Furthermore, individuals who engage in activities that require physical exertion, such as podcasting, voice-over work, or live performances, may experience heightened breathing sounds due to increased respiration. This can pose a challenge for maintaining clear and uninterrupted vocal recordings, as the microphone may inadvertently pick up the inhalations and exhalations of the speaker.
Understanding the mechanics of how microphones capture sound, as well as the factors that contribute to the prominence of breathing sounds, is essential for implementing effective solutions. By addressing these underlying causes, individuals can take proactive measures to minimize the impact of breathing sounds on their audio recordings, ultimately achieving a more professional and polished sound.
Proper Microphone Positioning
One of the most fundamental aspects of preventing microphones from picking up breathing sounds is ensuring proper microphone positioning. The distance and angle between the microphone and the speaker’s mouth play a crucial role in minimizing the interference of breath sounds in recordings. Here are essential considerations for achieving optimal microphone positioning:
-
Distance from the Mouth: Positioning the microphone at an appropriate distance from the mouth is essential for reducing the capture of breath sounds. For vocal recordings, a general rule of thumb is to maintain a distance of approximately 6 to 12 inches between the microphone and the speaker’s mouth. This distance helps mitigate the direct capture of breath while still capturing clear and articulate vocals.
-
Angle and Directionality: The angle at which the microphone is oriented in relation to the speaker’s mouth can also impact the prominence of breathing sounds. Utilizing microphones with directional pickup patterns, such as cardioid or hypercardioid microphones, can help attenuate off-axis sounds, including breath noises, by focusing on the primary sound source while minimizing ambient noise.
-
Shock Mounts and Boom Arms: In some cases, utilizing shock mounts or boom arms for microphone placement can further isolate the microphone from handling noise and vibrations, contributing to cleaner audio recordings with reduced interference from breath sounds.
By adhering to these principles of proper microphone positioning, individuals can proactively mitigate the impact of breathing sounds on their recordings, leading to improved audio clarity and a more professional sound quality.
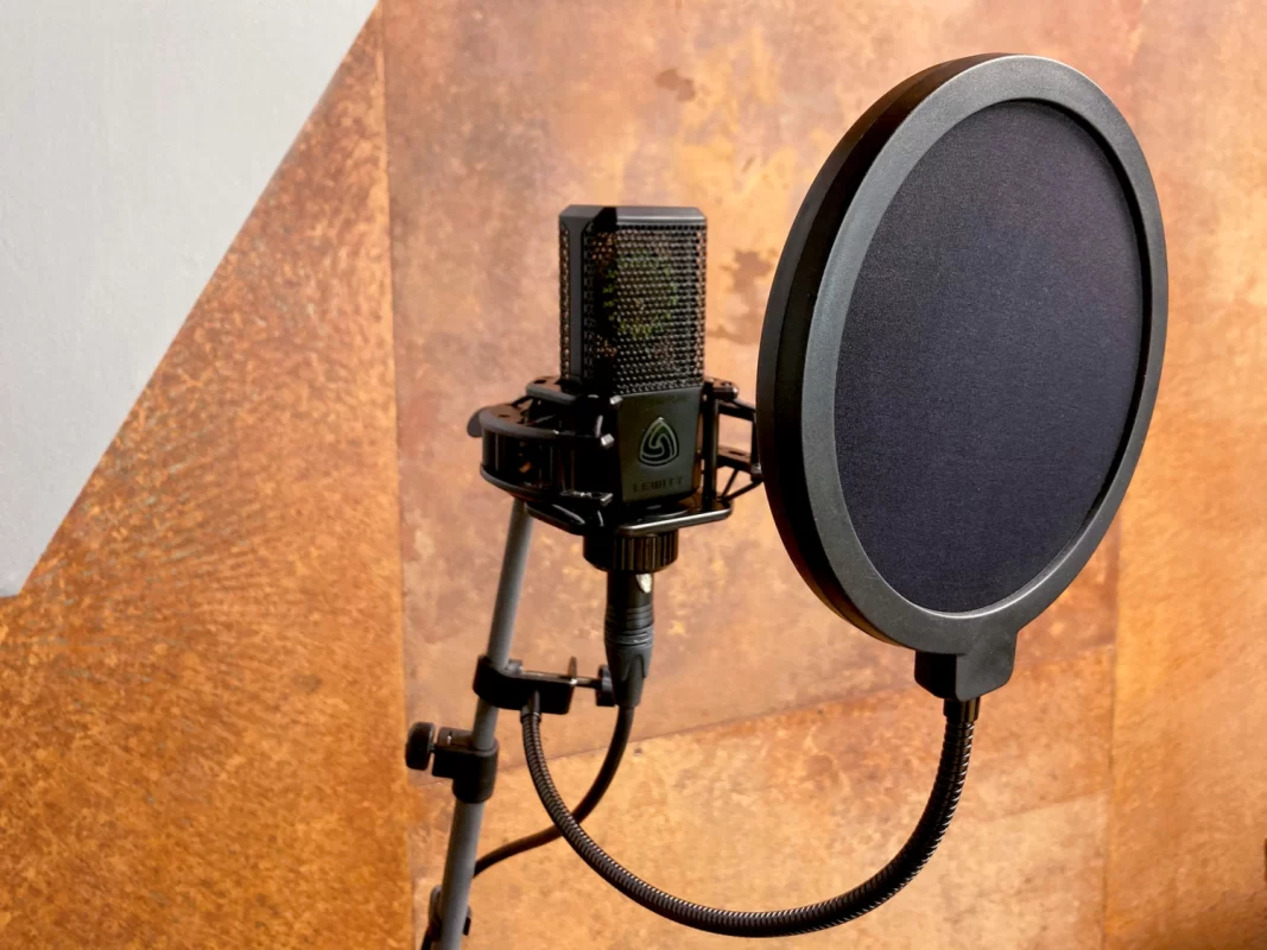
Use of Pop Filters
Pop filters, also known as pop shields or windshields, are essential accessories for mitigating the impact of plosive sounds and breath noises on microphone recordings. These simple yet effective tools are designed to intercept the puffs of air produced during speech, preventing them from reaching the microphone diaphragm and causing disruptive low-frequency thumps and pops. When addressing the issue of breathing sounds in microphones, the strategic use of pop filters can significantly contribute to improved audio quality. Here’s how pop filters can effectively minimize the interference of breath sounds:
-
Plosive Prevention: Pop filters excel at reducing plosive sounds, which are caused by the rapid expulsion of air when pronouncing certain consonants, such as “p” and “b.” By diffusing the force of the air and dispersing it over a wider area, pop filters effectively diminish the impact of plosives on microphone recordings, resulting in smoother and more consistent audio.
-
Breath Sound Diffusion: In addition to addressing plosive sounds, pop filters act as a barrier against the direct transmission of breath noises into the microphone. The fine mesh or fabric of the pop filter serves to diffuse the airflow from breathing, reducing its prominence in the recorded audio and contributing to a cleaner, more polished sound.
-
Versatile Compatibility: Pop filters are compatible with a wide range of microphones, making them a versatile solution for addressing breathing sounds across various recording setups. Whether used in vocal recording studios, podcasting environments, or live performance settings, pop filters offer consistent and reliable breath noise reduction.
By incorporating pop filters into their recording setups, individuals can effectively minimize the impact of breathing sounds on their microphone recordings, resulting in clearer, more professional audio that is free from distracting breath noises.
Breathing Techniques
While addressing microphone sensitivity to breathing sounds, it’s essential to consider the role of the speaker’s breathing techniques in minimizing unwanted breath noises in recordings. Implementing proper breathing techniques can significantly contribute to reducing the prominence of breath sounds picked up by microphones. Here are some effective breathing techniques to enhance the quality of vocal recordings and spoken dialogue:
-
Diaphragmatic Breathing: Encouraging speakers to practice diaphragmatic breathing, also known as belly breathing, can help minimize the audible impact of breathing on microphone recordings. By focusing on deep, controlled inhalations and exhalations that engage the diaphragm, individuals can reduce the intensity of breath sounds, leading to smoother and more consistent vocal performances.
-
Controlled Exhalation: Emphasizing the importance of controlled exhalation during vocal delivery can aid in mitigating breath noises. Encouraging speakers to regulate the speed and force of exhalation when delivering speech or singing can contribute to a more balanced and controlled airflow, reducing the prominence of breath sounds captured by the microphone.
-
Positioning and Posture: Educating speakers on maintaining optimal positioning and posture during vocal recordings is crucial for minimizing the impact of breath noises. Encouraging an upright posture and proper microphone distance can facilitate more controlled breathing patterns, resulting in reduced interference from breath sounds.
By incorporating these breathing techniques into their vocal performances and recording practices, individuals can effectively minimize the prominence of breath noises captured by microphones, ultimately leading to clearer and more professional audio recordings.
Noise Reduction Software
When addressing the issue of breathing sounds picked up by microphones, utilizing noise reduction software can serve as an effective post-processing solution to minimize the prominence of unwanted breath noises in recordings. Noise reduction software offers advanced algorithms and tools designed to identify and attenuate specific types of unwanted noise, including breath sounds, without compromising the overall audio quality. Here’s how noise reduction software can contribute to mitigating the impact of breathing sounds:
-
Spectral Editing: Noise reduction software often incorporates spectral editing capabilities, allowing users to visually identify and target specific frequencies associated with breath noises. By isolating and attenuating these frequencies, the software can effectively reduce the prominence of breath sounds in recorded audio, resulting in cleaner and more polished vocal performances.
-
Noise Print Analysis: Many noise reduction tools feature noise print analysis, enabling users to create a profile of the unwanted noise, such as breath sounds, within a recording. This feature facilitates precise noise reduction by allowing the software to intelligently differentiate between the desired audio and the unwanted noise, leading to more accurate and targeted noise reduction results.
-
Adaptive Algorithms: Advanced noise reduction software utilizes adaptive algorithms to dynamically adjust the noise reduction parameters based on the characteristics of the input audio. This adaptive approach ensures that breath noises are effectively attenuated while preserving the natural timbre and articulation of the vocals, resulting in high-quality audio with minimized interference from unwanted breath sounds.
By leveraging noise reduction software as part of their post-processing workflow, individuals can significantly reduce the impact of breathing sounds on their microphone recordings, achieving clearer and more professional audio with enhanced clarity and intelligibility.
Conclusion
Addressing the issue of microphones picking up breathing sounds is essential for achieving clear, professional-quality audio recordings. By implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, individuals can effectively minimize the interference of unwanted breath noises in their microphone recordings, ultimately enhancing the overall audio quality and maintaining a polished sound. From optimizing microphone positioning and utilizing pop filters to incorporating effective breathing techniques and leveraging noise reduction software, there are various proactive measures that can be taken to mitigate the impact of breathing sounds on audio recordings.
Understanding the sensitivity of microphones to breath noises and the factors that contribute to their prominence is crucial for implementing targeted solutions. Proper microphone positioning, including maintaining an optimal distance from the mouth and utilizing directional pickup patterns, can significantly reduce the capture of breath sounds. Additionally, the strategic use of pop filters serves as an effective barrier against plosive sounds and breath noises, contributing to smoother and more consistent audio recordings.
Furthermore, encouraging speakers to practice controlled breathing techniques, such as diaphragmatic breathing and regulated exhalation, can minimize the audible impact of breathing on microphone recordings. By incorporating these techniques into vocal performances, individuals can achieve more controlled and balanced airflow, reducing the prominence of breath noises in their recordings.
Moreover, the utilization of noise reduction software offers a powerful post-processing solution for attenuating specific frequencies associated with breath noises, resulting in cleaner and more polished vocal performances. By leveraging the spectral editing, noise print analysis, and adaptive algorithms offered by noise reduction software, individuals can achieve high-quality audio with minimized interference from unwanted breath sounds.
Ultimately, by combining these approaches and techniques, individuals can proactively address the issue of microphones picking up breathing sounds, leading to clearer, more professional audio recordings that are free from distracting breath noises. Whether in the context of music production, podcasting, voice-over work, or live performances, the implementation of these strategies can significantly enhance the overall audio quality and deliver a more immersive and engaging listening experience for audiences.