Home>Devices & Equipment>Music Box>How A Music Box Governor Works


Music Box
How A Music Box Governor Works
Published: January 11, 2024
Discover the inner workings of a music box governor and how it controls the speed of the music box mechanism. Explore the intricate mechanisms that make music boxes so enchanting.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
A music box is a charming and delightful device that has been captivating people’s hearts for centuries. Part of what makes a music box so enchanting is the intricate mechanical components that bring it to life. Among these components is the music box governor, an essential mechanism that plays a crucial role in controlling the speed of the music box’s tune.
In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of the music box governor. We will delve into its history, its components, and most importantly, how it works to regulate the speed of the music box. Whether you are a music box aficionado or simply curious about the inner workings of these magical instruments, this article will offer you a deeper understanding of the mesmerizing mechanism that is the music box governor.
So, prepare to be transported to a world of wonder as we unravel the secrets of the music box governor and discover the mechanism that brings the sweet melodies of a music box to life.
What is a Music Box Governor?
A music box governor is a mechanical device that regulates the speed of a music box’s tune. It is an integral component of the music box mechanism, working in tandem with other parts to ensure that the music plays at a consistent and controlled tempo. The governor’s primary function is to prevent the music box from playing too fast or too slow, allowing the melodies to be enjoyed in their intended rhythm.
Essentially, the music box governor acts as a speed regulator, maintaining a constant speed of rotation for the music box’s main spring. This ensures that the music plays smoothly and evenly, delivering a seamless and harmonious melody to the listener’s ears.
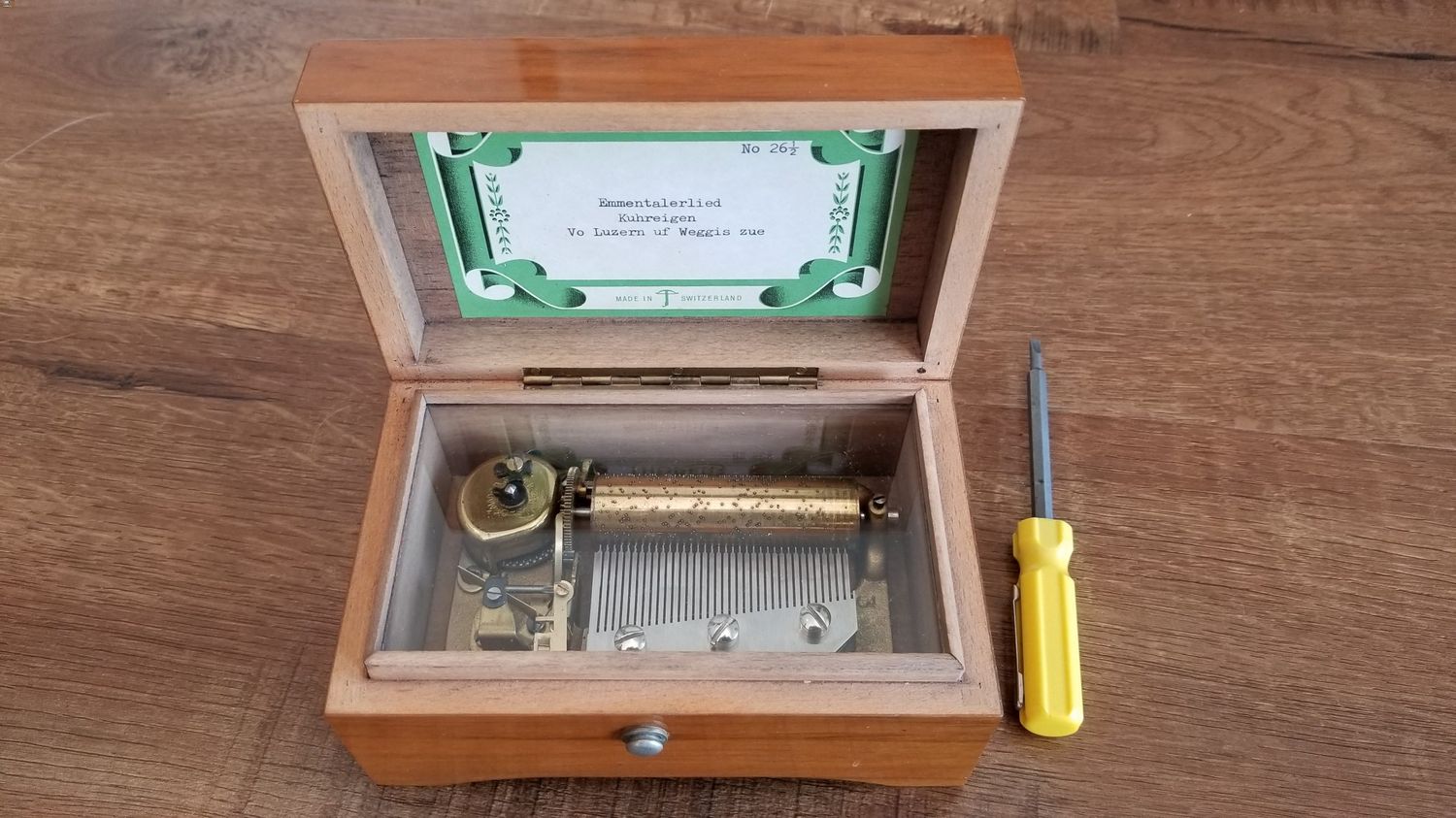
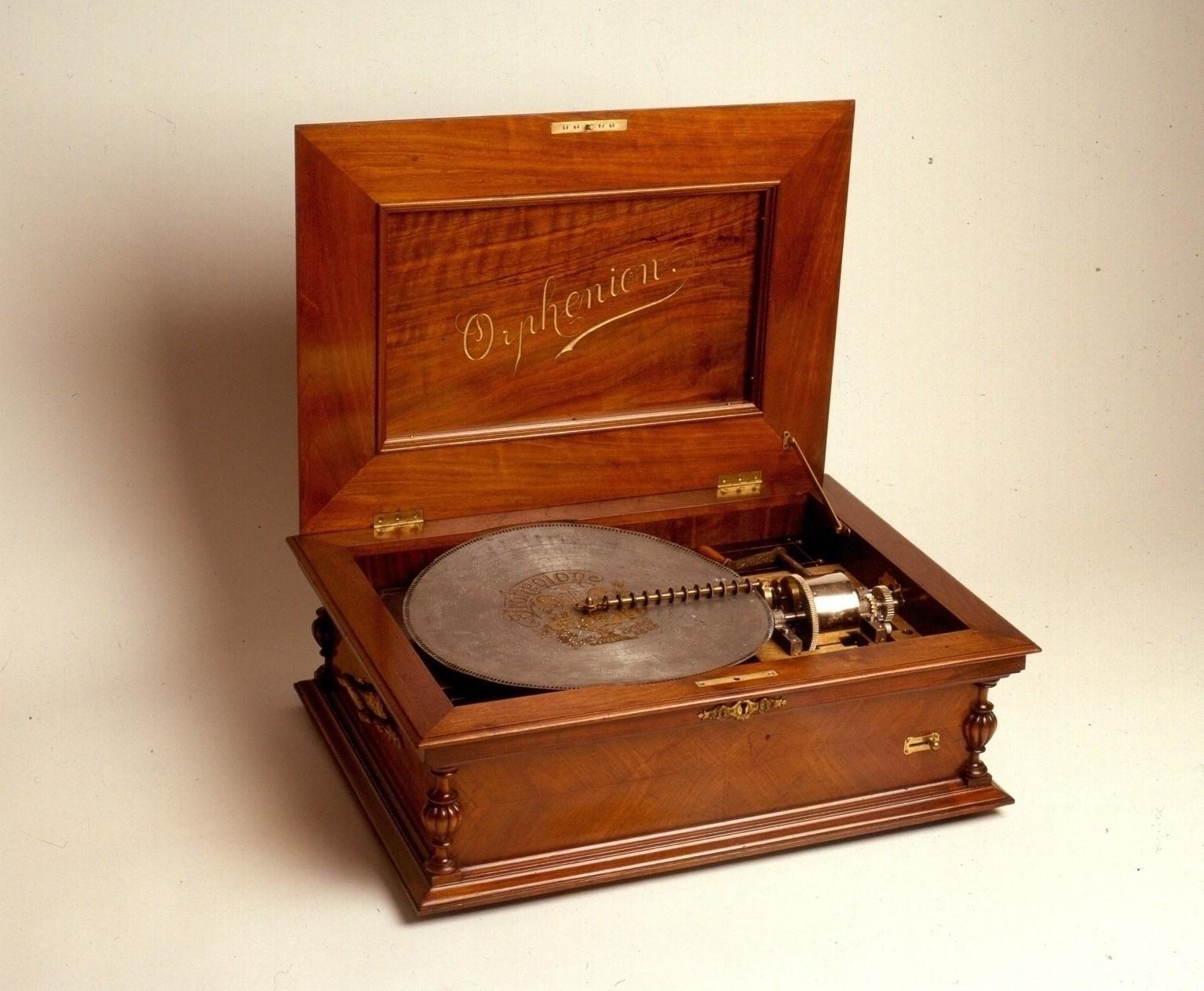
A typical music box governor consists of several key components, including a main spring, governor weight, governor gear assembly, and a speed regulation mechanism. These parts work together to ensure that the music box’s tune is played at the desired speed, creating a magical experience for those who listen.
From vintage antique music boxes to modern variations, the music box governor has remained a vital element in the mechanism. It is a testament to the clever engineering and craftsmanship that goes into creating these extraordinary musical instruments.
Now that we have a basic understanding of what a music box governor is, let’s delve deeper into its history to gain a better appreciation of this fascinating mechanism.
History of the Music Box Governor
The concept of regulating the speed of a musical instrument dates back centuries, and it found its way into early music boxes. The origins of the music box governor can be traced back to the late 18th century when music boxes were becoming increasingly popular among the upper class.
Originally, music boxes were regulated manually by a lever or a stop-start mechanism. However, as the demand for more precise and consistent speed control grew, inventors started exploring ways to automate this process. This led to the development of the music box governor.
One of the earliest known versions of the music box governor was patented by Swiss clockmaker Antoine Favre in 1770. Favre’s design included a centrifugal speed regulator with two brass flaps that opened or closed depending on the speed of the music box’s rotation. This regulator ensured that the music played at a steady and controlled tempo.
Over time, the design and functionality of the music box governor continued to evolve. Different variations and improvements were made by skilled craftsmen and inventors from around the world. These advancements included the use of adjustable weights, gears, and more sophisticated speed regulation mechanisms.
During the 19th century, music box production flourished, and with it came innovations in governor design. Swiss music box manufacturers, such as Nicole Frères and Bremond, were at the forefront of these developments, creating intricate and precise governor mechanisms for their music boxes.
The popularity of music boxes continued well into the 20th century, with small handheld music boxes becoming cherished collectibles. Despite the rise of new technologies and electronic music devices, the charm and nostalgia of traditional music boxes have endured.
Today, music boxes and their governors continue to be crafted with intricate precision. While the mechanisms may have been refined and perfected over the years, the essence of the music box governor remains the same – to ensure that the melodies produced by these enchanting instruments are played with grace and harmony.
Now that we have explored the history of the music box governor, let’s move on to understanding its key components and how they work together to regulate the music box’s speed.
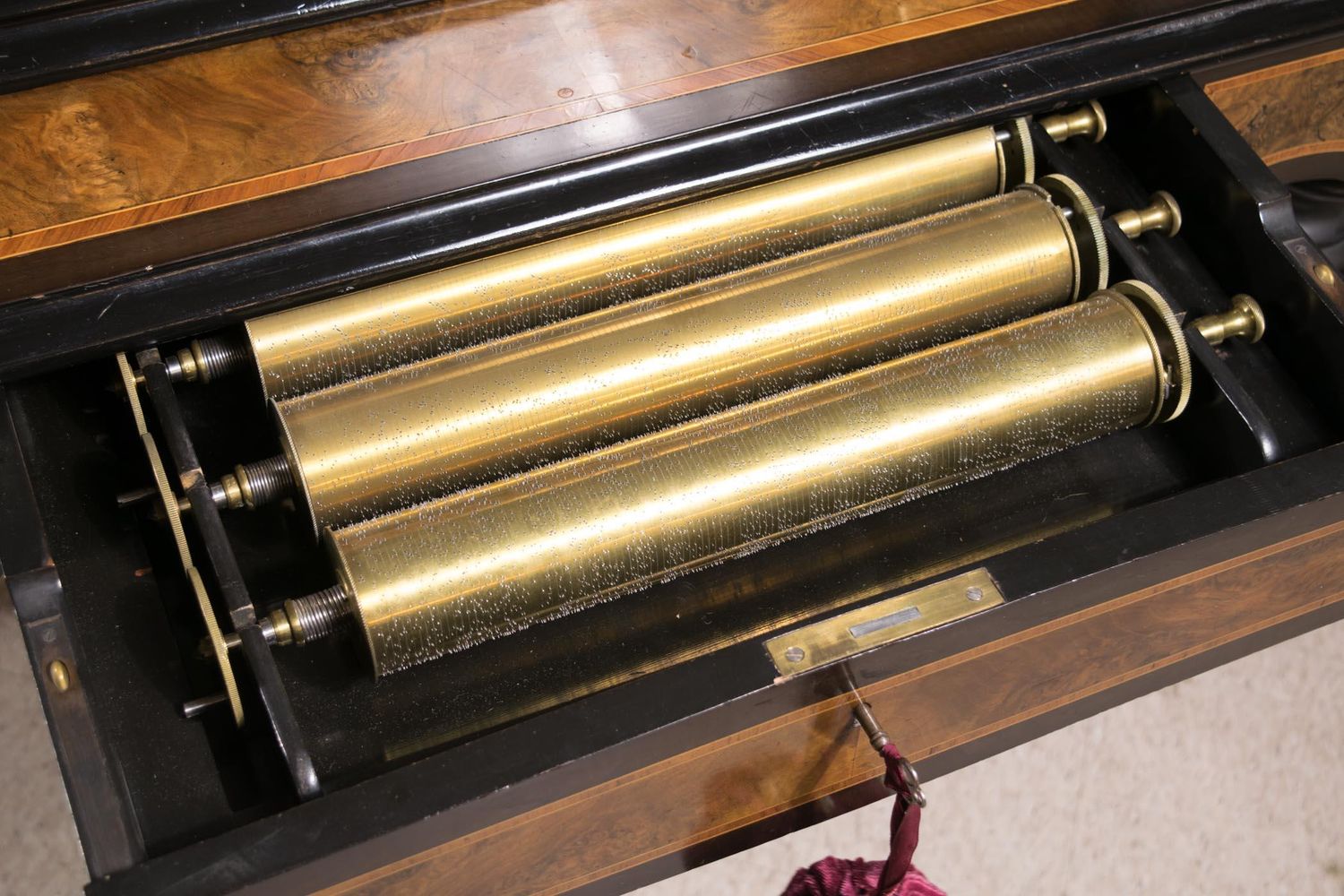
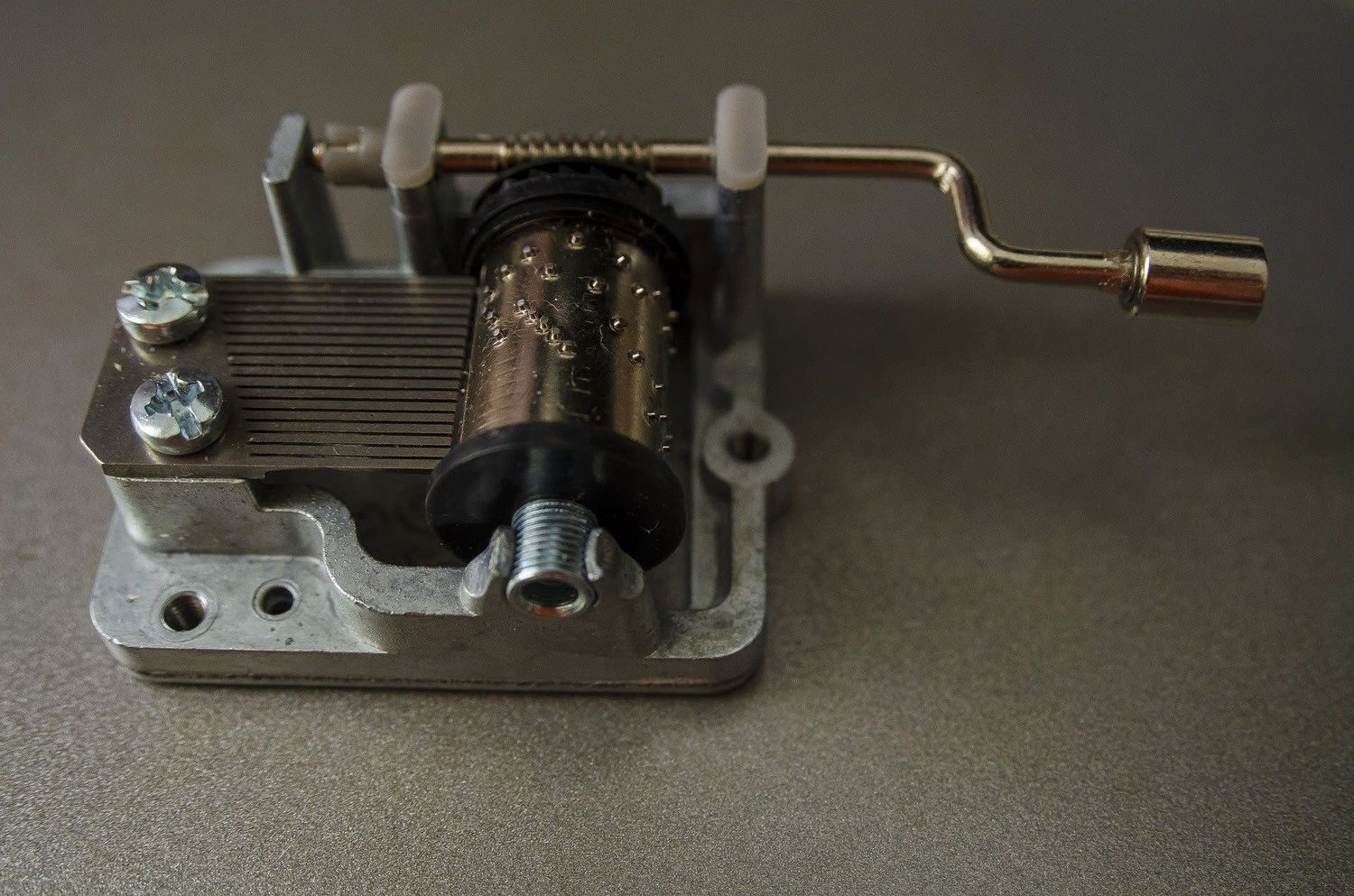
Components of a Music Box Governor
A music box governor is comprised of several essential components that work together to regulate the speed of the music box. These components include the main spring, governor weight, governor gear assembly, and a speed regulation mechanism.
1. Main Spring: The main spring is one of the foundational components of a music box governor. It is responsible for storing the mechanical energy that powers the music box. The main spring is wound up manually, typically by turning a key or knob, and it slowly releases its energy to drive the movement of the music box mechanism.
2. Governor Weight: The governor weight is a crucial element of the music box governor. It is usually composed of one or more weighted arms or balls that rotate as the main spring unwinds. The centrifugal force generated by the rotation of the governor weight plays a key role in regulating the speed of the music box.
3. Governor Gear Assembly: The governor gear assembly consists of gears and mechanisms that connect the governor weight to the music box’s rotating shaft. As the governor weight rotates, it interacts with the gear assembly, influencing the speed of the music box’s movement. This assembly ensures that the speed of the music box remains consistent and controlled.
4. Speed Regulation Mechanism: The speed regulation mechanism is responsible for adjusting the tension and speed of the main spring. It employs various techniques to control the flow of energy from the main spring to the rest of the music box, ensuring that the tunes are played at the desired tempo. The speed regulation mechanism may include features such as flywheels, escapements, or governor flaps, which regulate the release of energy to achieve the desired speed.
These components work together harmoniously to regulate the speed of the music box. The governor weight, controlled by the rotation of the main spring, interacts with the gear assembly, ultimately influencing the speed of the music box’s movement. The speed regulation mechanism further fine-tunes this process, ensuring that the music plays at a consistent and pleasurable tempo.
Now that we have explored the components of a music box governor, let’s delve into the inner workings of this fascinating mechanism and understand how it regulates the speed of a music box in greater detail.
How Does a Music Box Governor Work?
A music box governor works by utilizing centrifugal force and mechanical mechanisms to regulate the speed of the music box. Let’s break down the process step by step:
1. Winding the Main Spring: The music box is wound up by manually turning a key or knob. This action tightens the main spring, storing mechanical energy that will power the movement of the music box.
2. Main Spring Unwinding: As the main spring slowly unwinds, it transfers the stored energy to the rest of the music box mechanism. This energy is responsible for driving the movement of the rotating shaft, which ultimately plays the music.
3. Governor Weight Rotation: As the main spring unwinds, the governor weight begins to rotate. The governor weight is typically located near the rotating shaft and is composed of weighted arms or balls. As it rotates, the centrifugal force is generated, which influences the governor’s speed.
4. Governor Gear Assembly Interaction: The rotating governor weight interacts with the governor gear assembly. This gear assembly consists of gears and mechanisms that connect the governor weight to the rotating shaft. The interaction between the governor weight and the gear assembly helps regulate the speed of the music box.
5. Speed Regulation Mechanism: The music box governor also incorporates a speed regulation mechanism that fine-tunes the process. This mechanism may include features such as flywheels, escapements, or governor flaps. These components control the release of energy from the main spring to ensure that the music plays at the desired tempo. They adjust the tension and speed of the main spring to achieve a consistent and controlled music box performance.
Together, these components work in harmony to regulate the speed of the music box. The rotational speed of the governor weight, controlled by the unwinding main spring, interacts with the gear assembly, ultimately influencing the speed of the rotating shaft. The speed regulation mechanism further refines this process, ensuring that the music plays at a consistent and pleasurable tempo.
Understanding the inner workings of the music box governor gives us a glimpse into the extraordinary engineering and craftsmanship behind these magical musical instruments. Now that we have explored how a music box governor functions, let’s move on to some of the key components in more detail, starting with the main spring.
The Main Spring
The main spring is a vital component of the music box governor that stores the mechanical energy needed to power the movement of the music box. It is typically made of coiled metal and is responsible for driving the rotation of the music box’s shaft.
When the music box is wound up, turning the key or knob, the main spring tightens, storing potential energy. As the spring unwinds, this stored energy is gradually released, transferring power to the rest of the music box mechanism.
The tension of the main spring plays a crucial role in determining the speed at which the music box operates. A tightly wound main spring will release energy more quickly, resulting in a faster tempo, while a loosely wound spring will release energy more slowly, creating a slower pace.
To control the speed of the music box’s rotation, the main spring may incorporate a speed regulation mechanism. This mechanism includes features such as flywheels, escapements, or governor flaps, which help fine-tune the tension and release of energy from the main spring.
It is important to note that the main spring requires periodic winding to keep the music box functioning. The frequency of winding will depend on the specific music box and its design. Some music boxes may need to be wound daily, while others may only require winding once a week or less frequently.
The main spring is a fundamental component of the music box governor, providing the necessary power for the music box to play melodies. It is through the controlled release of this stored energy that the music box is able to create its enchanting tunes.
Now that we have explored the main spring, let’s move on to another essential component of the music box governor – the governor weight.
The Governor Weight
The governor weight is a critical component of the music box governor that plays a key role in regulating the speed of the music box. It is typically made of metal and is designed to rotate as the main spring unwinds and powers the music box mechanism.
Located near the rotating shaft of the music box, the governor weight consists of one or more weighted arms or balls. As the main spring releases its energy, the governor weight starts to rotate due to the centrifugal force generated by the unwinding spring.
The rotation of the governor weight is essential in regulating and controlling the speed of the music box. As the weight rotates faster, the centrifugal force increases, causing the movement to slow down. Conversely, when the weight rotates slower, the centrifugal force decreases, resulting in a faster tempo.
By varying the weight and size of the governor weight, music box makers can fine-tune the speed regulation. Heavier weights generally slow down the music box’s movement, while lighter weights allow for faster speeds. The precise balance and size of the governor weight are carefully calculated to achieve the desired tempo and maintain the consistent flow of the music.
In some more elaborate music box governors, multiple governor weights may be used. These weights can be adjusted or arranged in a specific configuration to further customize the speed regulation of the music box.
It is important to note that the interaction between the governor weight and the other components of the music box governor, such as the gear assembly and the speed regulation mechanism, is crucial in achieving precise speed control. Together, they work in harmony to create a synchronized and balanced musical experience.
The governor weight is a fascinating and vital part of the music box governor. Its rotation and interaction with other components ensure that the music box plays at the desired speed, enchanting listeners with its melodious tunes.
Now that we have explored the governor weight, let’s move on to another key component of the music box governor – the governor gear assembly.
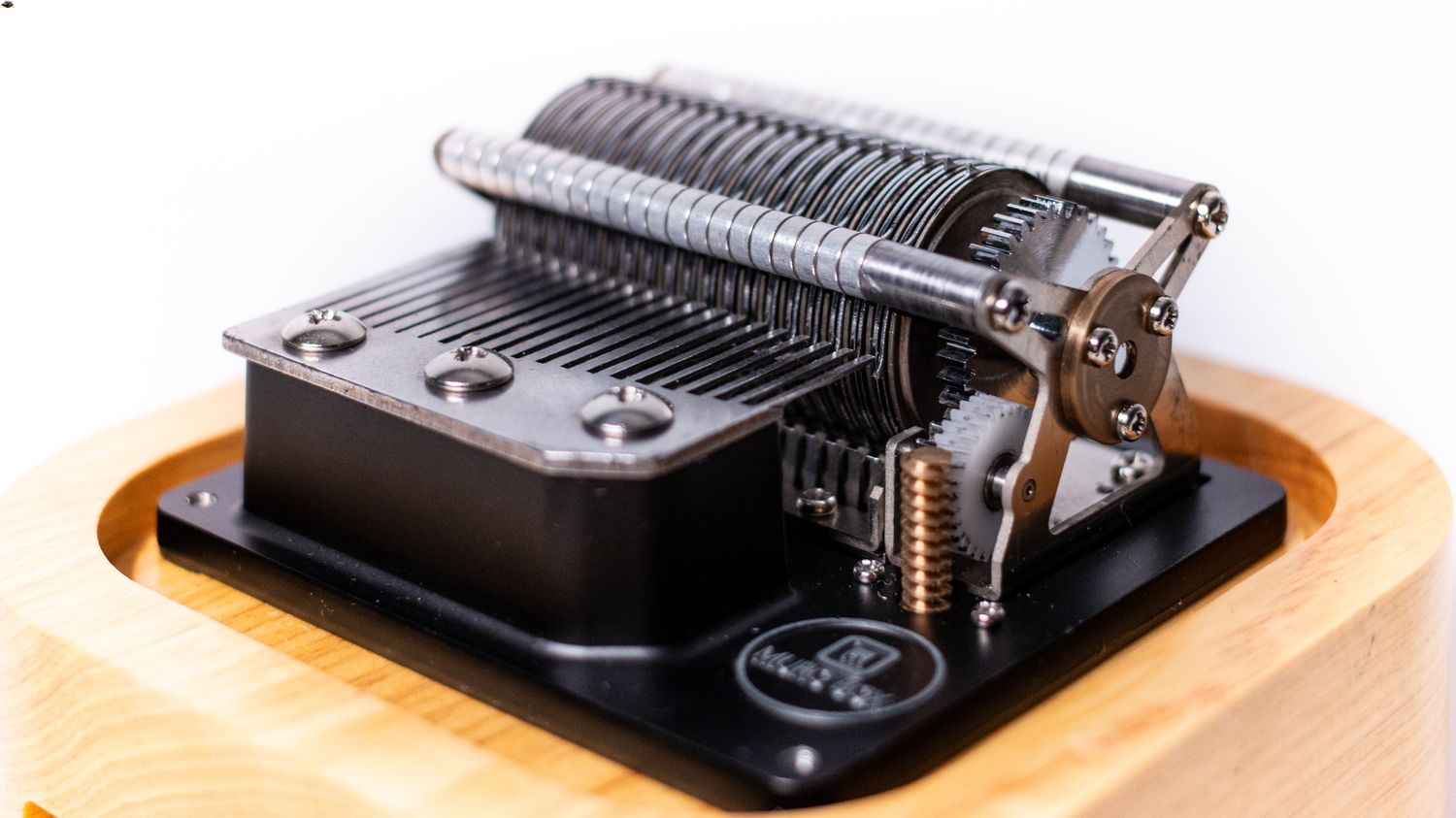
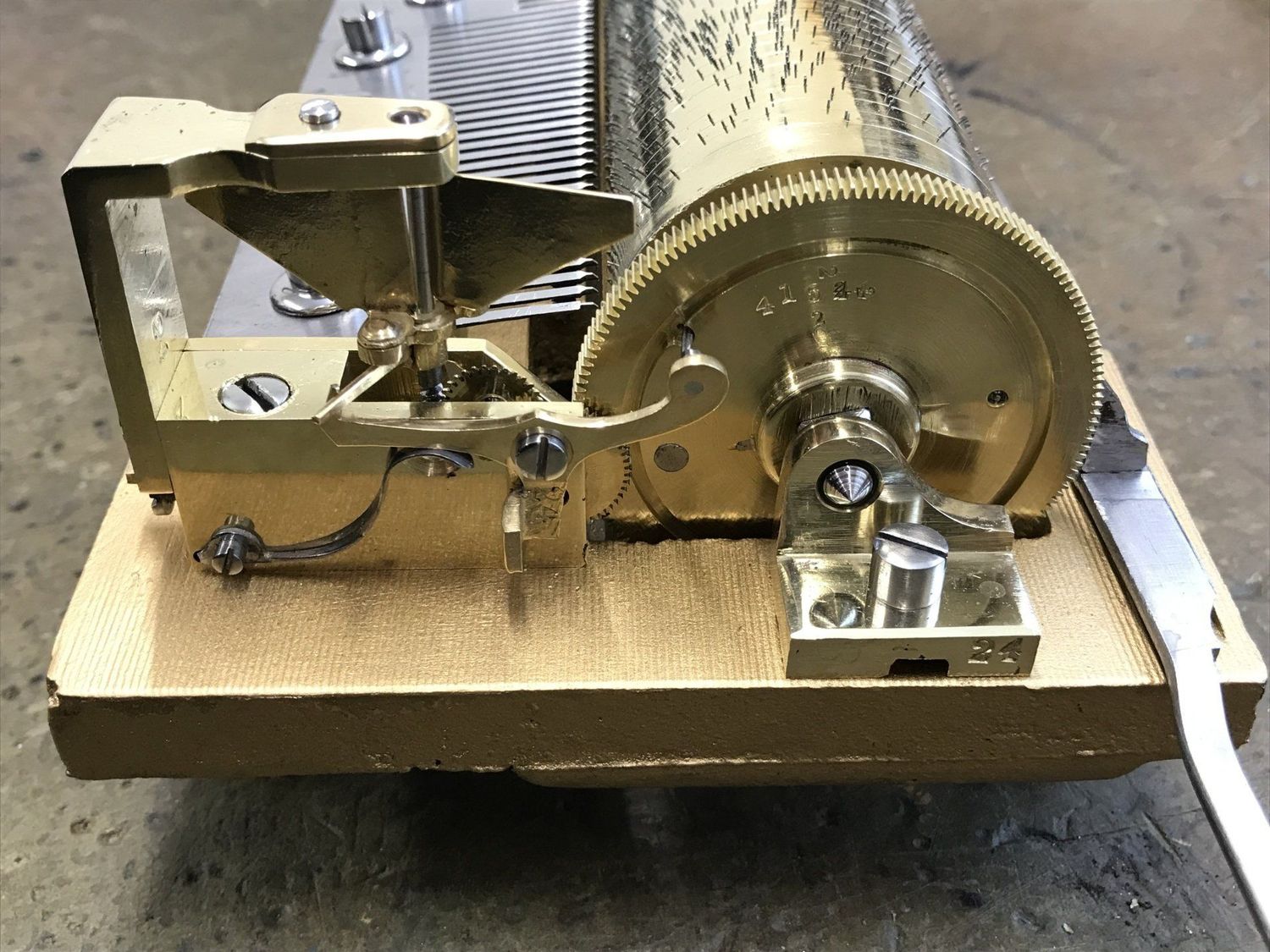
The Governor Gear Assembly
The governor gear assembly is a crucial component of the music box governor that plays a significant role in regulating the speed of the music box. It consists of gears and mechanisms that connect the rotating governor weight to the music box’s rotating shaft.
As the governor weight rotates due to the unwinding of the main spring, it interacts with the gear assembly. This interaction transfers the rotational energy of the governor weight to the rotating shaft of the music box.
The governor gear assembly ensures that the speed of the music box remains consistent and controlled. It acts as a link between the governor weight and the music box’s mechanism, allowing the energy generated by the governor weight to be transferred smoothly.
The gears within the assembly are carefully designed and sized to accurately transfer the rotational energy. They transmit the motion from the governor weight to the rotating shaft, maintaining the desired tempo and rhythm of the music.
In more intricate music box governors, the gear assembly may incorporate additional mechanisms such as flywheels or escapements. These mechanisms further assist in controlling the speed and maintaining the constant rotation of the music box’s shaft.
The governor gear assembly, along with the governor weight, main spring, and other components of the music box governor, work together to regulate the speed of the music box. Their coordinated movement and interaction ensure that the melodies produced by the music box are played at the desired tempo.
Now that we have explored the governor gear assembly, let’s move on to the speed regulation mechanism – another essential component of the music box governor.
Speed Regulation Mechanism
The speed regulation mechanism is a vital component of the music box governor that fine-tunes the speed at which the music box operates. It is responsible for controlling the tension and release of energy from the main spring, ensuring that the music plays at the desired tempo.
This mechanism incorporates various features and techniques to achieve precise speed regulation. Some common elements found in the speed regulation mechanism include:
1. Flywheels: Flywheels are often used in the speed regulation mechanism to help maintain a consistent tempo. These rotating discs or wheels store rotational energy, acting as a buffer to even out any variations in the release of energy from the main spring. Flywheels allow for smoother, more balanced music playback.
2. Escapements: Escapements are mechanisms that control the release of energy from the main spring in a controlled manner. They consist of a toothed wheel and an anchor mechanism that alternately engage and disengage, releasing a small amount of energy with each tooth engagement. This regulation mechanism ensures that the energy is released in measured increments, resulting in a steady and regulated tempo.
3. Governor Flaps: Some music box governors incorporate flaps or vanes, also known as governor flaps, within the speed regulation mechanism. These flaps react to changes in the rotational speed of the governor weight. As the governor weight rotates faster, the flaps open to allow more air resistance, slowing down the music box’s movement. Conversely, when the governor weight rotates slower, the flaps close, reducing air resistance and allowing for a faster tempo.
These are just a few examples of the speed regulation mechanisms that may be present in a music box governor. The specific design and implementation can vary depending on the type of music box and the desired level of speed control.
The speed regulation mechanism works in tandem with the other components of the music box governor, such as the main spring, governor weight, and governor gear assembly. Together, they ensure that the music box operates at a consistent and controlled speed, delivering melodies that are pleasing to the ear.
Now that we have explored the speed regulation mechanism, we have gained a comprehensive understanding of the components and inner workings of the music box governor. Let’s conclude our journey and reflect on the beauty and magic of these enchanting musical instruments.
Conclusion
The music box governor is a captivating and essential component of a music box. By regulating the speed of the music box’s tune, it ensures that melodies play at the desired tempo, creating a harmonious and enchanting experience. Throughout history, the music box governor has undergone developments and refinements to achieve precise speed control.
We explored the components of a music box governor, including the main spring, governor weight, governor gear assembly, and speed regulation mechanism. Each of these components plays a vital role in maintaining the speed and rhythm of the music box.
From its early origins in the late 18th century to the sophisticated mechanisms used in modern music boxes, the music box governor has evolved alongside technology. Throughout the years, skilled craftsmen and inventors have dedicated their talents to perfecting the governor’s design, resulting in mechanisms that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
By understanding how a music box governor works, we gain a deeper appreciation for the artistry and engineering behind these magical musical instruments. The interplay between the components and the intricate balance required to achieve consistent speed regulation highlights the craftsmanship and attention to detail involved in creating music boxes.
Whether showcasing vintage antique music boxes or modern variations, the music box governor continues to enchant and captivate audiences. Its ability to ensure the music plays at a controlled tempo adds to the charm and allure of these remarkable instruments.
Next time you listen to the delicate melodies of a music box, take a moment to appreciate the intricate mechanisms within. The music box governor, with its fascinating components and mechanisms, serves as a reminder of the beauty and magic that can be found within the heart of a music box.