Home>Devices & Equipment>Subwoofer>How Does A Subwoofer Work


Subwoofer
How Does A Subwoofer Work
Modified: February 18, 2024
Discover the inner workings of a subwoofer and learn how this powerful audio device delivers deep bass and enhances your listening experience. Uncover the secrets of subwoofer technology today!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of subwoofers, where deep bass and immersive audio experiences reign supreme. Whether you’re a music lover, a movie enthusiast, or a gaming aficionado, a subwoofer can take your audio setup to the next level by delivering low-frequency sounds with precision and power.
But what exactly is a subwoofer, and how does it work? In this article, we’ll dive deep into the realm of subwoofers to uncover the secrets behind their performance and the technologies that make them tick.
Before we embark on this exciting journey, let’s first understand the importance of sound reproduction and the role a subwoofer plays in enhancing our auditory experiences.
Sound reproduction is the art of recreating sound waves with accuracy and fidelity. When we listen to music, watch movies, or play video games, we want to immerse ourselves in the atmosphere and feel like we’re part of the experience. This is where subwoofers come into play.
A subwoofer is a specialized speaker designed to reproduce deep bass frequencies that are typically below 80Hz. These low frequencies add richness, depth, and impact to the audio, creating a more immersive and realistic soundstage. By focusing on reproducing the low-end frequencies, subwoofers offload this demanding task from the main speakers, allowing them to focus on delivering mid and high-range frequencies with greater clarity and detail.
To achieve this exceptional performance, subwoofers are equipped with specific components and designed with meticulous engineering. In the next sections of this article, we’ll explore the inner workings of a subwoofer, including its components, working principle, enclosure designs, crossover integration, types, and common applications.
So, buckle up and get ready to unravel the mysteries of subwoofers. Whether you’re a novice or an audiophile, this article aims to satisfy your curiosity and enlighten you about the fascinating world of subwoofer technology.
Understanding Sound Reproduction
Before delving into the intricacies of subwoofers, it’s essential to grasp the fundamentals of sound reproduction. Sound is created when an object vibrates, causing molecules in the air to move and create sound waves. These sound waves travel through the air and reach our ears, where they are interpreted by our brain as sound.
When it comes to audio reproduction, the goal is to recreate these sound waves with precision and accuracy, ensuring that the listener hears the intended frequencies and details as intended by the original source. This process involves capturing, processing, and reproducing the sound waves using various audio devices and technologies.
Traditional loudspeakers, also known as main speakers or full-range speakers, are designed to cover a wide frequency range, including low, mid, and high frequencies. While they do a decent job of reproducing all frequencies, they often struggle when it comes to the deep bass frequencies, typically below 80Hz.
This is where subwoofers come into play. By dedicating themselves solely to the reproduction of low-frequency sounds, subwoofers excel at delivering impactful and immersive bass experiences that can be felt as much as heard. They fill the void left by traditional speakers by reproducing frequencies that are typically beyond their capabilities.
Subwoofers achieve this by utilizing specialized components and engineering techniques that allow them to accurately reproduce low-frequency content. These components include a specially designed woofer driver, an amplifier, an enclosure, and a crossover network.
With a better understanding of sound reproduction and the role of subwoofers in enhancing the audio experience, we can now explore the inner workings of subwoofers in greater detail. In the next section, we’ll delve into the components that make up a subwoofer and how they work together to produce those deep, impactful bass tones.
The Role of a Subwoofer
When it comes to audio reproduction, a subwoofer plays a crucial role in enhancing the overall sound quality and creating a more immersive listening experience. Its primary function is to reproduce low-frequency sounds, commonly referred to as bass, with accuracy, depth, and impact.
Why is the role of a subwoofer so important? Well, low-frequency sounds play a vital role in music, movies, and gaming. They add a sense of realism, depth, and excitement to audio content. Think of the thumping bass in your favorite song, the rumbling explosion in an action-packed movie, or the deep growl of a car engine in a racing game. These low-frequency effects are what make the audio experience more immersive and engaging.
One of the main reasons a subwoofer is necessary is that traditional speakers, while capable of producing mid and high-range frequencies with clarity, struggle to reproduce the deep bass. This is due to physical limitations in the size and design of a typical speaker. Attempting to reproduce these low frequencies with regular speakers can result in distortion, muddiness, and a lack of impact.
A subwoofer, on the other hand, is specifically designed to excel in this frequency range. It contains a larger woofer driver, typically ranging from 8 to 18 inches in diameter, which can move more air and produce the low-frequency sounds with greater accuracy and power.
By offloading the reproduction of low frequencies to a dedicated subwoofer, the main speakers can focus on delivering mid and high-range frequencies with improved clarity and detail. This separation of frequencies ensures that each component of the audio spectrum is handled by the most appropriate speaker, resulting in a more balanced and immersive soundstage.
Furthermore, a well-integrated subwoofer impacts the overall sound quality of an audio system. It can improve the overall tonal balance, providing a more natural and full-bodied sound. It can also extend the frequency response of the system, allowing for an even greater dynamic range and a more impactful listening experience.
Ultimately, the role of a subwoofer is to enhance the audio experience by faithfully reproducing low-frequency sounds, adding depth and impact to music, movies, and games. Whether you’re a music enthusiast, a cinephile, or a gaming fanatic, a subwoofer is an essential component that elevates the overall sound quality and immerses you in the audio content like never before.
Components of a Subwoofer
A subwoofer is a complex audio device that comprises several components working together to produce deep, impactful bass. Understanding these components will give us insights into the inner workings of a subwoofer and how it achieves its impressive performance.
The main components of a subwoofer include the woofer driver, amplifier, enclosure, and crossover network.
The woofer driver is the heart of the subwoofer. It is responsible for converting electrical signals into sound waves. Unlike regular speakers, subwoofer drivers are larger and capable of moving more air, which is necessary for reproducing the low-frequency sounds accurately. The size of the driver, along with its construction and materials, affects the overall performance and efficiency of the subwoofer.
The amplifier is another critical component that powers the subwoofer driver. It provides the necessary electrical current to drive the driver’s movements and produce sound. The amplifier should be specifically designed for subwoofers, as it needs to deliver sufficient power to handle the demanding low-frequency signals. Class D amplifiers are commonly used in subwoofer designs due to their high efficiency.
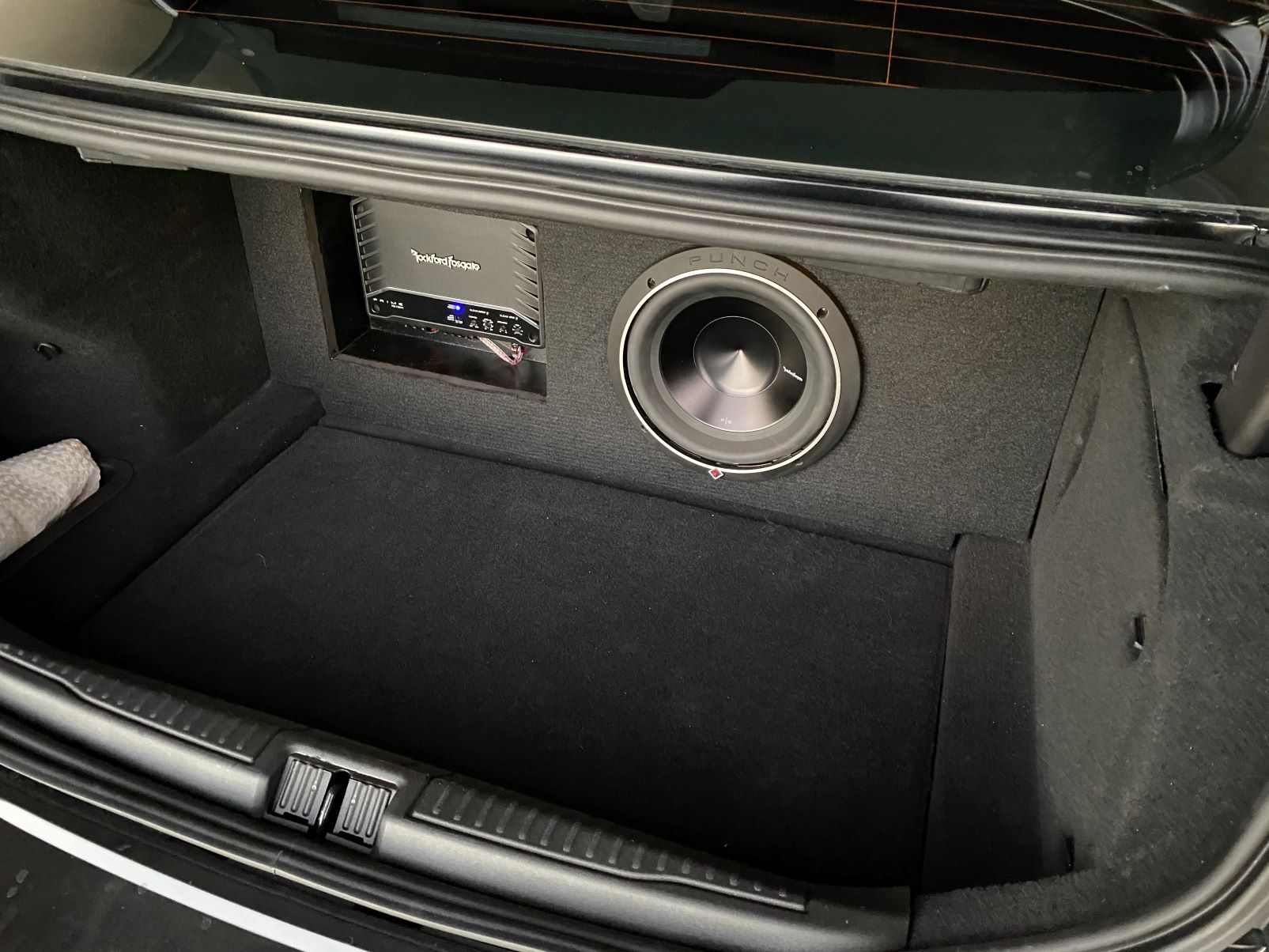
The enclosure is the housing that contains the woofer driver and contributes to the subwoofer’s overall performance. Enclosures come in various designs, including sealed, ported, and bandpass enclosures. Each design has its own characteristics and advantages. Sealed enclosures provide accurate and tight bass response, while ported enclosures enhance low-frequency output. Bandpass enclosures offer a combination of both by utilizing a chambered design.
The crossover network is an essential component that determines which frequencies are sent to the subwoofer driver and which frequencies are directed to the main speakers. It helps ensure that the subwoofer only handles the low frequencies it is designed to reproduce, while allowing the main speakers to focus on the mid and high-range frequencies. The crossover network can be either passive or active, depending on the overall audio system setup.
In addition to these main components, subwoofers may also incorporate other features such as controls for adjusting the volume, phase, and crossover frequency. These controls provide flexibility in tuning the subwoofer’s performance to match the acoustic characteristics of the listening environment and the preferences of the user.
By understanding the function of each component, we can better appreciate the engineering and design that goes into creating a high-quality subwoofer. The interaction between these components is key to achieving accurate and powerful bass reproduction, enabling us to feel the impact of low-frequency sounds and elevate our audio experiences to new heights.
Working Principle of a Subwoofer
Understanding the working principle of a subwoofer is essential to comprehend how it reproduces low-frequency sounds with precision and impact. At its core, a subwoofer operates on the same principles as regular speakers but with a specialized focus on handling low-frequency content.
The working principle of a subwoofer begins with the electrical signals. These signals, which represent audio content, are fed into the amplifier of the subwoofer. The amplifier then converts the electrical signals into a stronger signal that can drive the movement of the subwoofer’s woofer driver.
The woofer driver contains a cone-shaped diaphragm, also known as a woofer cone, which is connected to a voice coil. The voice coil is placed within a magnetic field created by a permanent magnet. As the amplified electrical signals flow through the voice coil, it generates an electromagnetic field that interacts with the permanent magnet, causing the voice coil and the woofer cone to move back and forth.
This back-and-forth motion of the woofer cone creates compression and rarefaction of the surrounding air, generating sound waves. The frequency and amplitude of these sound waves correspond to the low-frequency signals being reproduced by the subwoofer.
Subwoofers are designed to handle frequencies typically below 80Hz. Their larger woofer drivers and specialized enclosures allow for greater air movement, enabling them to reproduce these low-frequency sound waves with accuracy and power. The enclosure design, whether sealed, ported, or bandpass, also affects the way the sound waves are delivered and the characteristics of the bass response.
It’s important to note that subwoofers are not limited to reproducing only the extremely low bass frequencies. They can also effectively handle the lower end of the mid-range frequencies, adding depth and richness to the overall audio reproduction. This versatility allows subwoofers to seamlessly integrate with the main speakers and complement their performance.
The combination of the subwoofer’s amplified electrical signals, the interaction between the voice coil and the magnetic field, and the resulting cone movement all work together to produce the deep, impactful bass that subwoofers are famous for.
By focusing on dedicated low-frequency reproduction and employing specialized components and engineering techniques, subwoofers elevate the audio experience by adding depth, realism, and excitement. Whether you’re listening to music, watching a movie, or playing games, the working principle of a subwoofer ensures that you not only hear the bass but feel it too, immersing you in a world of powerful and immersive sound.
Enclosure Designs for Subwoofers
Enclosures play a crucial role in the performance and sound reproduction of subwoofers. They not only provide a housing for the woofer driver but also influence the overall bass response and efficiency of the subwoofer. Different enclosure designs offer unique characteristics and cater to specific audio preferences and room setups.
Let’s explore some of the common enclosure designs used in subwoofers:
- Sealed Enclosures: Sealed enclosures, also known as acoustic suspension enclosures, are a popular choice for subwoofers. These enclosures are airtight and provide a tight, controlled bass response. The sealed design allows the subwoofer to produce accurate and precise bass with quick transient response. Sealed enclosures are ideal for music enthusiasts who prefer accurate bass reproduction without excessive booming or resonance.
- Ported Enclosures: Ported enclosures, also referred to as bass reflex enclosures, incorporate a port or a tuned vent in addition to the enclosure. This port allows air to flow in and out of the cabinet, augmenting the low-frequency output of the subwoofer. Ported enclosures are known for their increased efficiency and enhanced bass response in the lower frequency range. They tend to produce a more pronounced and boomy bass, making them popular for home theater and movie enthusiasts seeking a more impactful and immersive bass experience.
- Bandpass Enclosures: Bandpass enclosures are more complex in design and consist of two chambers. One chamber is sealed, housing the woofer driver, while the other chamber is ported. The design allows certain frequencies to pass through the ported chamber, resulting in a more focused and higher output of specific bass frequencies. Bandpass enclosures offer a combination of both sealed and ported designs, providing a controlled and punchy bass with increased efficiency. They are widely used in professional audio setups and applications where maximum impact and output are desired.
The choice of enclosure design depends on several factors, including personal preference, room acoustics, and the desired audio experience. Sealed enclosures are suitable for critical music listening or smaller rooms where precise bass control is desired. Ported enclosures are often favored for home theater setups, as they provide a more dramatic and pronounced bass impact. Bandpass enclosures are commonly used in professional sound systems for venues such as clubs and concerts, where maximum output and extended low-frequency response are essential.
Additionally, the size and construction materials of the enclosure influence the overall performance of the subwoofer. High-density materials, such as medium-density fiberboard (MDF), are commonly used for their sturdiness and resonance-dampening properties, enhancing the overall bass reproduction.
It’s worth noting that each enclosure design has its own set of advantages and limitations. Proper integration and tuning of the subwoofer in its respective enclosure design are crucial to achieve optimal performance and seamless integration with the main speakers or audio system.
Ultimately, the choice of enclosure design for a subwoofer depends on personal preference, intended use, and the desired audio characteristics. Whether you prefer tight and controlled bass, booming and powerful impact, or a balance between the two, there is an enclosure design suited to amplify your audio experience and unleash the full potential of your subwoofer.
Crossover and Integration with Speaker Systems
When it comes to incorporating a subwoofer into a speaker system, proper crossover integration plays a vital role in achieving a seamless and balanced audio experience. The crossover acts as a filter that determines which frequencies are sent to the main speakers and which frequencies are directed to the subwoofer.
The purpose of the crossover is to ensure that each speaker in the system handles the frequencies it is best suited for, leading to improved clarity, accuracy, and overall audio performance. By sending the appropriate frequencies to the subwoofer, it allows the main speakers to focus on reproducing mid and high-range frequencies with greater detail and efficiency.
There are two types of crossovers commonly used for integrating subwoofers with a speaker system: passive crossovers and active crossovers.
Passive crossovers are most commonly found within the main speaker enclosures. They are typically a network of capacitors, inductors, and resistors that divide the audio signal into different frequency bands. Passive crossovers are relatively simple and cost-effective but have limitations in their flexibility and customization. They rely on the speaker’s internal wiring to split the frequencies between the subwoofer and the main speakers.
Active crossovers, on the other hand, are external devices that are placed between the audio source or preamplifier and the amplifier. They provide more precise control over the crossover frequencies, slopes, and levels. Active crossovers are often used in setups with dedicated amplifiers for the subwoofer and main speakers. Using separate amplification for each allows for better power distribution and control over the individual speakers.
The crossover point, or frequency at which the crossover starts redirecting the signal to the subwoofer, is typically set between 80Hz to 120Hz. This range is chosen because it allows for a smooth transition between the subwoofer and the main speakers, ensuring that neither the subwoofer nor the main speakers are reproducing frequencies that they are not optimized for. It is important to experiment with different crossover points to find the best integration for your specific speakers and room setup.
Properly integrating a subwoofer with a speaker system goes beyond using the correct type of crossover. Calibration and adjustment are also critical to achieving optimal performance. This includes adjusting the phase and volume controls of the subwoofer to ensure that it blends seamlessly with the main speakers and creates a cohesive soundstage.
Integration of a subwoofer with a speaker system requires an understanding of the characteristics of both the subwoofer and the main speakers, as well as careful consideration of the room acoustics. By properly implementing the crossover and fine-tuning the settings, you can achieve a balanced, immersive audio experience that brings out the best in all speakers and delivers deep, impactful bass reproduction.
Types of Subwoofers
Subwoofers come in various types, each offering distinct characteristics and catering to different audio preferences and setups. Understanding the different types of subwoofers can help you choose the one that best suits your needs and enhances your audio experience.
- Powered Subwoofers: Powered subwoofers, also known as active subwoofers, have a built-in amplifier. This eliminates the need for an external amplifier and simplifies the setup process. Powered subwoofers offer convenience and are an excellent choice for those who want a self-contained solution with minimal equipment.
- Passive Subwoofers: Passive subwoofers, as the name suggests, require an external amplifier to power them. They do not have a built-in amplifier and thus require an additional device to drive the subwoofer. Passive subwoofers offer flexibility in terms of amplifier selection and are often used in high-end audio setups that prioritize customization and fine-tuning.
- In-Wall and In-Ceiling Subwoofers: In-wall and in-ceiling subwoofers are designed to be installed flush with the wall or ceiling, providing a discreet and aesthetically pleasing audio solution. They are commonly used in home theater setups or multi-room audio systems where space is limited, or a clean and minimalistic look is desired.
- Front-Firing Subwoofers: Front-firing subwoofers feature the woofer driver and port, if applicable, located on the front panel of the enclosure. They radiate sound waves directly towards the listener, offering greater placement flexibility and producing a more upfront and focused bass presentation.
- Down-Firing Subwoofers: Down-firing subwoofers have the woofer driver and, if applicable, the port pointing towards the floor. The sound waves are directed downwards and reflect off the floor, creating a dispersed and omnidirectional bass response. Down-firing subwoofers are known for their ability to fill a room with bass and provide a more even bass distribution.
- Subwoofers with Multiple Drivers: Some subwoofers feature multiple woofers or drivers to improve bass output and dispersion. These subwoofers can have dual, triple, or even more drivers, offering increased power handling and allowing for more even distribution of bass frequencies. Multiple driver configurations are commonly found in high-end home theater setups and professional audio systems.
Each type of subwoofer has its own strengths and advantages, and the choice depends on factors such as personal preference, room size, listening environment, desired bass output, and integration with the existing audio setup.
It’s also worth mentioning that subwoofers can vary in size, with larger subwoofers typically capable of producing deeper and more powerful bass. However, smaller subwoofers can still provide impressive performance, especially in smaller rooms or when paired with other speakers in a surround sound setup.
Ultimately, the type of subwoofer you choose should align with your audio goals and fit within your specific needs and constraints. Whether you opt for a compact powered subwoofer, a customizable passive subwoofer, or an in-wall solution, the right subwoofer will elevate your audio experience by delivering the deep and impactful bass that truly immerses you in the sound.
Common Applications of Subwoofers
Subwoofers are versatile audio devices that find their applications in a variety of settings, catering to different audio needs and preferences. Let’s explore some of the common applications where subwoofers excel:
- Home Theater Systems: Subwoofers are a staple component of home theater systems, providing the low-frequency impact necessary for a truly immersive movie-watching experience. Whether it’s the rumbling explosions in an action film or the subtle bass notes in a dramatic scene, a subwoofer adds depth, realism, and excitement to the audio, making you feel like you’re part of the action.
- Music Listening: Whether you’re an audiophile or a casual music listener, adding a subwoofer to your audio setup can greatly enhance the enjoyment of your favorite tunes. Subwoofers bring out the lower end of the audio spectrum, adding warmth and fullness to the sound. From the thumping basslines in electronic music to the rich low notes in classical compositions, a subwoofer delivers depth and impact, allowing you to fully appreciate the music.
- Gaming: The gaming world is full of sound effects that greatly enhance the gameplay experience. Subwoofers play a crucial role in reproducing the deep, rumbling bass that brings explosions, gunfire, and intense moments to life. The immersive audio provided by a subwoofer can make you feel like you’re right in the middle of the gaming action, adding a whole new dimension to your gameplay.
- Live Performances and Events: Subwoofers are widely used in professional audio setups for live music performances, concerts, and events. They ensure that the audience gets to experience the full impact of the music, providing deep and powerful bass that can be felt throughout the venue. Subwoofers help create a dynamic and immersive atmosphere, enhancing the overall live music experience.
- Car Audio Systems: Car audio enthusiasts often incorporate subwoofers into their car audio systems to bring the bass experience on the road. Subwoofers designed specifically for car installations deliver the deep low frequencies that can rock your vehicle and make your music drive even more enjoyable. They allow you to feel every beat and bassline, transforming your car into a concert-like audio environment.
- Professional Audio and Recording Studios: In professional audio and recording studios, subwoofers are used for mixing and mastering purposes. They help engineers accurately monitor and control the low-frequency content of the audio material, ensuring that the final product sounds balanced and translates well across various playback systems.
These are just a few examples of the common applications of subwoofers. Their ability to reproduce deep bass frequencies with precision and impact makes them a valuable addition to any audio system in various settings.
Whether you’re enjoying a movie at home, immersing yourself in your favorite music, gaming, attending a live concert, or fine-tuning audio in a professional setting, a subwoofer adds that extra dimension of bass that takes the experience to a whole new level.
Conclusion
Subwoofers are essential components that bring low-frequency sounds to life, enhancing our audio experiences with depth, impact, and immersion. Whether you’re listening to music, watching movies, gaming, or attending live events, a subwoofer has the ability to transform the way you perceive and enjoy sound.
Throughout this article, we have explored the various aspects of subwoofers, from their role in sound reproduction to their working principles and components. We’ve discussed different enclosure designs, crossover integration, and the types of subwoofers available in the market. Furthermore, we have seen the common applications of subwoofers in home theaters, music listening, gaming, live performances, car audio, and professional audio setups.
Choosing the right subwoofer and integrating it properly into your audio system can greatly enhance the overall sound quality and take your audio experience to new heights. Whether you prefer the convenience of a powered subwoofer, the customization options of a passive subwoofer, or the discreet installation of in-wall or in-ceiling subwoofers, there is a subwoofer that suits your needs and preferences.
By understanding the working principles and components of subwoofers, you can make an informed decision about the type of subwoofer that best fits your audio setup. Whether you prioritize accuracy and precision or crave the deep, booming bass, subwoofers provide the foundation for a well-rounded and immersive soundstage.
When used in synergy with the main speakers and properly integrated through crossovers, subwoofers refine and optimize the audio reproduction, delivering a balanced, lifelike, and captivating audio experience across various applications.
So, whether you’re a music enthusiast seeking fuller and more impactful sound, a movie lover yearning for a cinematic audio experience, or a gamer wanting to be completely immersed in the gameplay, a subwoofer is an essential component that can satisfy your audio cravings and elevate your listening pleasure.
Embrace the power of deep bass, feel the rumble, and let the subwoofer take you on an auditory journey that leaves a lasting impression.