Home>Instruments>Drums>How Many Mics Are Needed For Drums
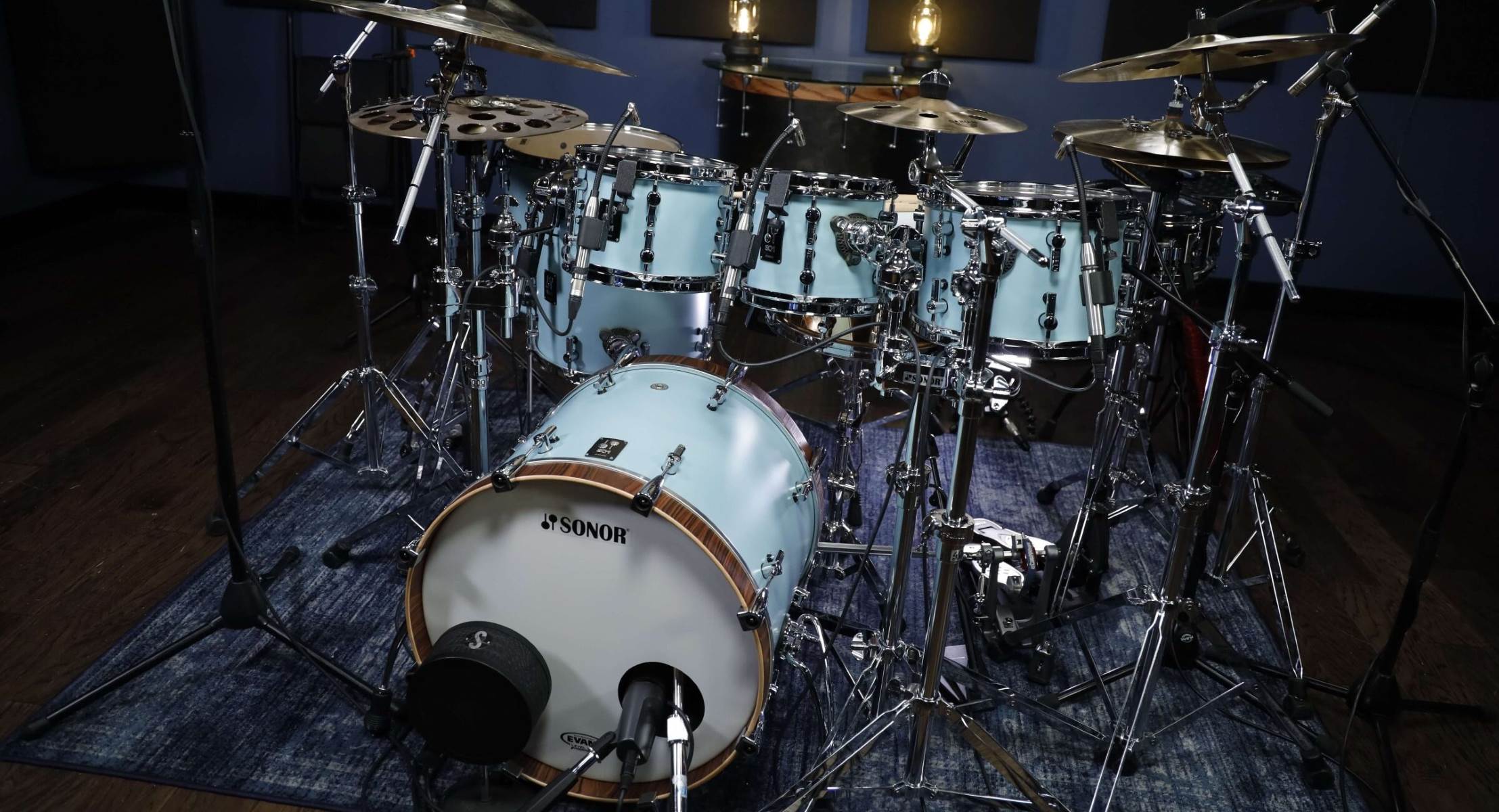


Drums
How Many Mics Are Needed For Drums
Published: February 7, 2024
Discover the ideal number of mics required for capturing the perfect drum sound. Learn the essential techniques for miking drums effectively. Gain insights on drum mic setups.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Are you ready to take your drumming to the next level? Whether you're a seasoned drummer or just starting out, the world of drum mics can be a game-changer for your sound. Capturing the nuances of your drumming performance is crucial for a high-quality audio output, and the right microphones can make all the difference. In this article, we'll explore the essential aspects of drum mics, including the types of mics available, the optimal number of mics needed, and the best placement techniques to achieve the perfect sound.
Drum mics are specially designed to capture the dynamic range and tonal intricacies of a drum kit. They come in various types, each serving a specific purpose in the quest for impeccable sound reproduction. Understanding the nuances of drum mics is essential for drummers, sound engineers, and anyone involved in recording or amplifying drum performances.
Whether you're playing in a studio, on stage, or in a practice space, the right combination of drum mics can elevate your sound to new heights. By strategically placing mics and selecting the appropriate types for each drum component, you can achieve a balanced, powerful, and authentic representation of your drumming style.
In the following sections, we'll delve into the different types of drum mics, discuss the optimal number of mics needed for various setups, and explore the art of mic placement to unleash the full sonic potential of your drum kit. Whether you're aiming for a crisp, punchy sound for rock and pop music or a warm, resonant tone for jazz and acoustic settings, mastering the art of drum miking will empower you to shape your sound with precision and artistry. Let's embark on this sonic journey and unlock the secrets of capturing the heartbeat of the music – the drums.
Types of Drum Mics
When it comes to capturing the diverse range of tones and dynamics produced by a drum kit, employing the right types of microphones is essential. There are several specialized drum mics designed to capture the unique characteristics of different drum components, ensuring a balanced and authentic representation of the entire kit. Understanding the distinct roles of these microphones is crucial for achieving optimal sound quality in both live and studio settings.
1. Kick Drum Mic: The kick drum, being the heartbeat of the rhythm, requires a microphone capable of capturing its deep, low-frequency punch. Dynamic microphones are commonly used for kick drums due to their ability to handle high sound pressure levels and emphasize the low-end frequencies, resulting in a powerful and focused kick drum sound.
2. Snare Drum Mic: The snare drum is the centerpiece of the drum kit, and a well-captured snare sound is pivotal for a balanced drum mix. Dynamic microphones are popular choices for snare drums, offering high SPL handling and focused midrange response to capture the snare’s crisp attack and body.
3. Tom Mics: Each tom in the drum kit can benefit from individual microphone placement to capture their unique tonal characteristics. Dynamic or condenser microphones are commonly used for toms, with dynamic mics providing robust sound reinforcement and condensers offering extended frequency response and nuanced transient capture.
4. Overhead Mics: Overhead mics play a crucial role in capturing the overall ambience and cymbal sounds of the drum kit. Condenser microphones are often preferred for overhead miking due to their sensitivity and ability to capture the high-frequency details and spatial nuances of the drum kit’s sound.
5. Room Mic: In addition to close miking individual drum components, a room mic can be strategically placed to capture the overall acoustic environment, adding depth and natural reverb to the drum mix. Condenser microphones are commonly used as room mics to capture the spaciousness and resonance of the drum kit in the recording space.
By incorporating a combination of dynamic and condenser microphones tailored to each drum component, drummers and sound engineers can create a comprehensive and detailed sonic image of the entire drum kit, allowing for nuanced control and shaping of the drum mix.
Number of Mics Needed
One common question that arises when setting up drum mics is, “How many mics are needed to capture the full range of sounds produced by a drum kit?” The answer to this question depends on various factors, including the size of the drum kit, the desired level of sonic detail, and the available audio equipment. While there is no one-size-fits-all solution, understanding the general principles can guide the selection of an optimal number of mics for different drum setups.
For a basic drum miking setup, a minimum of three microphones is often recommended to capture the essential components of the drum kit – the kick drum, snare drum, and overheads. This setup allows for the fundamental elements of the drum kit to be individually miked, providing a solid foundation for balancing the sound and achieving clarity in the mix.
As the complexity of the drum kit increases, additional microphones may be employed to capture the tonal nuances of each drum component. For instance, in setups featuring multiple toms, individual mics for each tom can be utilized to capture their distinct tonal characteristics and provide greater control over the drum mix.
When aiming for a more detailed and expansive drum sound, incorporating room mics can significantly enhance the overall sonic depth and ambience of the drum mix. Room mics capture the acoustic characteristics of the recording space, adding a sense of space and natural reverberation to the drum sound, thereby contributing to a more immersive and dynamic listening experience.
In larger-scale productions or studio recordings, the number of mics used for drum capture can vary widely based on the specific sonic requirements and creative vision of the recording engineer or producer. Experimentation with different mic configurations and placements can lead to unique and compelling drum sounds, allowing for artistic expression and sonic innovation.
Ultimately, the number of mics needed for drum capture is determined by the desired level of sonic detail, the complexity of the drum kit, and the creative objectives of the recording or performance. By strategically selecting and placing microphones to capture the individual and collective nuances of the drum kit, drummers and audio professionals can sculpt a captivating and expressive drum sound that elevates the musical experience.
Placement of Mics
The placement of drum mics plays a pivotal role in capturing the nuanced tonal characteristics and dynamic range of a drum kit. Strategic mic placement can significantly impact the balance, clarity, and sonic depth of the drum mix, allowing for precise control and shaping of the overall sound. Each drum component requires specific mic placement techniques to optimize its sonic capture, ensuring a cohesive and impactful representation of the entire kit.
1. Kick Drum Mic Placement: When miking the kick drum, the microphone is typically placed inside the drum, near the beater, to capture the deep thump and low-end resonance. Alternatively, some engineers prefer placing the mic just outside the drum’s sound hole to capture a more balanced representation of the kick drum’s sound. Experimentation with mic placement can help achieve the desired balance between attack, body, and low-frequency punch.
2. Snare Drum Mic Placement: To capture the crisp attack and body of the snare drum, the microphone is commonly positioned above the rim, pointing toward the center of the drumhead. This placement allows the mic to capture the snare wires’ response and the drum’s tonal characteristics, providing a balanced representation of the snare sound.
3. Tom Mic Placement: For tom miking, individual microphones are placed near each tom, typically positioned above the drumhead to capture the drum’s resonance and attack. Adjusting the mic placement closer to the drum’s rim or center can yield varying tonal characteristics, allowing for customization of the tom sound based on the desired sonic profile.
4. Overhead Mic Placement: Overhead mics are strategically positioned above the drum kit to capture the overall ambience, cymbal sounds, and the collective tonal blend of the drum components. Placing the overhead mics at an optimal distance and angle from the drum kit can ensure a balanced representation of the entire kit’s sound, capturing the spatial nuances and stereo imaging of the drum mix.
5. Room Mic Placement: When incorporating room mics, placement in the recording space plays a crucial role in capturing the ambient characteristics and natural reverberation of the drum sound. Room mics are often placed at a distance from the drum kit, allowing them to capture the spaciousness and resonance of the recording environment, contributing to the overall depth and immersive quality of the drum mix.
By carefully considering the placement of drum mics and experimenting with different configurations, drummers and audio engineers can sculpt a rich and detailed sonic landscape that captures the essence of the drum kit’s dynamic and tonal intricacies. The art of mic placement empowers creators to shape the drum sound with precision, artistry, and a deep understanding of sonic capture techniques.
Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of drum mics, it becomes evident that the art of capturing the diverse and dynamic sounds of a drum kit is a multifaceted endeavor. The selection, placement, and number of mics used in drum capture play a crucial role in shaping the sonic identity of the drum sound, whether in live performances, studio recordings, or practice sessions.
Understanding the distinct roles of various drum mics – from kick drum and snare mics to overheads and room mics – empowers drummers and audio professionals to craft a balanced, detailed, and expressive representation of the drum kit’s sonic palette. Each microphone type serves a specific purpose in capturing the unique tonal characteristics and dynamic range of different drum components, contributing to a cohesive and impactful drum mix.
When determining the number of mics needed for drum capture, considerations such as the size of the drum kit, sonic objectives, and available audio equipment come into play. From a basic three-mic setup to more elaborate configurations featuring individual mics for each drum component and room mics for ambient capture, the number of mics used can be tailored to the specific sonic requirements and creative vision of the production or performance.
Furthermore, the strategic placement of drum mics is instrumental in achieving an authentic and balanced representation of the drum kit’s sonic nuances. By carefully positioning mics for the kick drum, snare drum, toms, overheads, and room capture, creators can sculpt a rich and immersive sonic landscape that captures the essence of the drum performance with precision and artistry.
Ultimately, the world of drum mics offers a wealth of possibilities for shaping and enhancing the drum sound, allowing for creative expression, sonic innovation, and an elevated musical experience. Whether aiming for a thunderous, punchy rock sound, a crisp and articulate jazz texture, or a warm and resonant acoustic ambience, the art of drum miking empowers drummers and audio professionals to unleash the full sonic potential of the drums.
As drummers and sound engineers continue to explore the realm of drum mics, they embark on a sonic journey filled with endless opportunities for sonic exploration, artistic expression, and the pursuit of sonic excellence. With the right combination of mics, thoughtful placement techniques, and a deep understanding of sonic capture principles, the heartbeat of the music – the drums – can be authentically and powerfully brought to life, enriching the musical landscape with its rhythmic vitality and expressive depth.