Home>Instruments>Synthesizer>How Do You Play A Modular Synthesizer

Synthesizer
How Do You Play A Modular Synthesizer
Published: December 11, 2023
Learn how to play a modular synthesizer and create unique sounds with our comprehensive guide. Explore various modules, signal paths, and techniques for an immersive synthesizer experience.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding the Basics of Modular Synthesizers
- Exploring the Components of a Modular Synthesizer
- Connecting and Patching Modules
- Envelopes and Oscillators: Creating Sound
- Filters and Effects: Shaping the Sound
- Sequencing and Modulation: Adding Movement
- Tips and Techniques for Playing a Modular Synthesizer
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcoming to the realm of modular synthesizers, where creativity knows no bounds and sonic possibilities are endless. A modular synthesizer is a fascinating instrument that allows musicians and sound explorers to truly customize their sound creation process. With its modular nature, it is comprised of various individual modules that can be connected and combined in countless ways, unleashing a world of sonic experimentation and expression.
In this article, we will delve into the captivating world of modular synthesizers and explore how to play them. Whether you’re a curious beginner or a seasoned musician, this guide will provide you with an understanding of the basics, introduce you to the components of a modular synth, and guide you on how to connect and patch modules to create unique sounds.
Playing a modular synthesizer is not just about pressing keys and listening to pre-programmed sounds. It’s a journey of exploration and discovery, where every twist of a knob and patch cable connection can result in a new sonic creation. This article aims to demystify the process and empower you to navigate the intricate web of modules, envelopes, oscillators, filters, and more.
Understanding the Basics of Modular Synthesizers
Before we dive into playing a modular synthesizer, it’s important to grasp the fundamental concepts behind this unique instrument. Unlike traditional synthesizers with fixed architectures, a modular synthesizer allows you to build your own customized signal path by connecting individual modules together.
At the core of a modular synth are modules, which are self-contained units that perform specific functions. These can include oscillators (generators of sound waves), filters (modifiers of frequency content), envelopes (controllers of sound parameters over time), and more. The true magic happens when you start combining these modules and manipulating their parameters to create completely original sounds.
One of the key aspects of modular synthesis is the concept of voltage control. Each module is designed to accept and generate control voltages, which are essentially varying electrical signals that affect the behavior of the modules. By routing these control voltages through patch cables, you can create complex and dynamic soundscapes.
Another important concept to understand is the concept of signal flow. In a modular synthesizer, sound travels through a series of interconnected modules. Typically, the signal flows from the oscillator module, which generates the initial sound, to other modules such as filters and effects, which shape and modify the sound. Envelopes and other modulation sources can also be used to manipulate various parameters along the signal path.
It’s worth noting that modular synthesis is highly versatile and offers an immense degree of flexibility. While it may initially seem overwhelming, with patience and experimentation, you’ll gradually develop an intuitive understanding of how the different components interact, allowing you to unleash your creativity and sculpt sounds in ways you never thought possible.
Exploring the Components of a Modular Synthesizer
A modular synthesizer consists of various components, or modules, that work together to generate and shape sound. Each module serves a specific purpose and contributes to the overall sonic landscape. Let’s take a closer look at some essential modules you’ll find in a modular synthesizer:
- Oscillators: These modules generate the basic sound waves, such as sine, square, triangle, and sawtooth waves. They provide the foundation for creating different tones and timbres.
- Filters: Filters modify the frequency content of the sound by removing or emphasizing specific frequencies. They allow you to shape the character and tone of the sound.
- Envelopes: Envelopes control the parameters of a sound over time. They typically consist of four stages: attack, decay, sustain, and release. Envelopes are commonly used to shape volume, filter cutoff frequency, and other parameters.
- LFOs: Low-Frequency Oscillators generate repeating waveforms at slow frequencies. These waveforms are commonly used to modulate other parameters, creating evolving and rhythmic effects.
- Effects: Effects modules add depth and character to the sound. They can include delay, reverb, chorus, and other processing units that manipulate the audio signal.
- Sequencers: Sequencers allow you to program and control note patterns and rhythmic sequences. They can provide a sense of musical structure and control the timing of different sound events.
These are just a few examples of the modules that make up a modular synthesizer. It’s important to note that the variety and complexity of modules you can find in a modular system are vast. Different manufacturers offer unique modules that cater to various sonic needs and experimental desires.
As you explore and build your modular synthesizer setup, you’ll have the freedom to choose modules that align with your musical preferences and creative goals. The possibilities are truly endless, as you can continuously expand and modify your system to suit your evolving sound exploration.
Connecting and Patching Modules
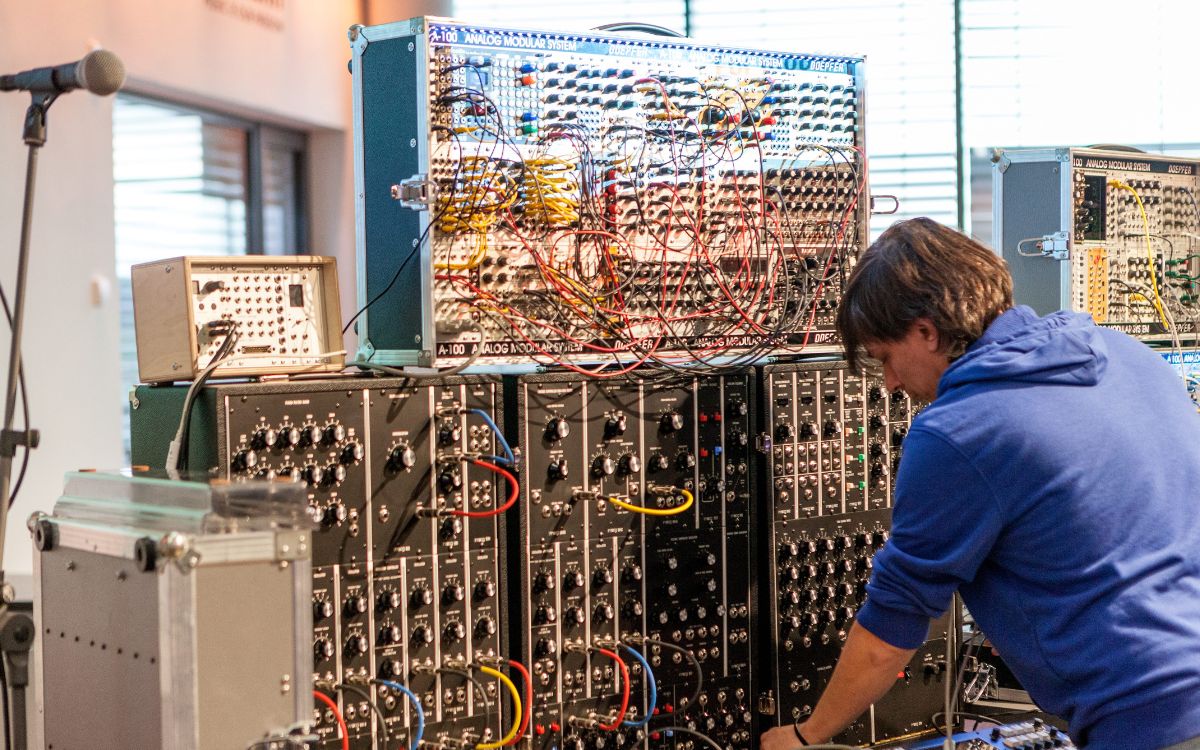
One of the most exciting aspects of playing a modular synthesizer is the ability to connect and patch different modules together. The physical act of routing signals using patch cables adds a hands-on and tactile element to the creative process. Let’s explore how to connect and patch modules:
1. Understanding Patch Cables: Patch cables are essential for connecting modules in a modular synthesizer. These cables have a 3.5mm plug on each end and are used to transmit audio and control signals between modules. Each cable represents a pathway through which signals flow.
2. Input and Output Jacks: Modules typically have input and output jacks labeled with specific functions such as CV (control voltage) input, audio output, gate input, and more. These jacks allow you to send and receive signals between modules.
3. Making Connections: To create a connection, simply plug one end of a patch cable into an output jack of one module and the other end into an input jack of another module. This connects the output signal of one module to the input of another, allowing them to interact.
4. Experimenting with Signal Paths: The beauty of modular synthesis is the flexibility to experiment with signal paths. By connecting modules in different ways, you can create a multitude of sonic possibilities. For example, you can connect the output of an oscillator module to a filter module, and then route the filtered signal to an envelope module for further shaping.
5. Multiple Connections: A modular synthesizer allows for multiple connections to be made simultaneously. This means you can send the output of a single module to several other modules, creating complex and layered sounds. Be mindful of signal levels and the potential for overloading or distorting the audio.
6. Experiment and Explore: Don’t be afraid to experiment and try different patch configurations. Unleash your creativity and let your ears guide you. The beauty of a modular synthesizer lies in its ability to surprise and inspire, so allow yourself the freedom to explore and discover new sonic territories.
Remember, there are no set rules when it comes to patching a modular synthesizer. It’s all about finding what works for you and letting your imagination run wild. So, grab those patch cables and start creating unique and captivating sounds!
Envelopes and Oscillators: Creating Sound
At the heart of a modular synthesizer are two crucial components: envelopes and oscillators. Envelopes allow you to shape the characteristics of a sound over time, while oscillators generate the fundamental tones and waveforms. Let’s explore these components in more detail:
Oscillators: Oscillators are the sound generators within a modular synthesizer. They produce different waveforms, such as sine, square, triangle, and sawtooth waves, which form the basis of the sound you create. Oscillators typically have controls to adjust the pitch, waveform shape, and modulation options. You can use multiple oscillators together to create rich and complex sonic textures.
Envelopes: Envelopes determine how a sound evolves over time, controlling its shape and dynamics. They consist of several stages: attack, decay, sustain, and release (ADSR). The attack stage represents the initial transient of the sound, how quickly it reaches its peak volume. Decay controls the time it takes for the volume to decrease after the attack. Sustain maintains a steady volume level while a key or trigger is held. Release determines how long it takes for the sound to fade out after the key or trigger is released.
By patching an envelope output to different parameters within a modular synthesizer, you can sculpt and modulate various aspects of the sound. For example, you can connect an envelope output to control the filter cutoff frequency, creating dynamic and expressive timbral changes.
When working with oscillators and envelopes, it’s important to experiment with different combinations and settings. For example, you can use a fast attack and short decay envelope for percussive sounds, or a slow attack and long release for ambient pads. By modulating envelope parameters, such as sustain or release, you can bring movement and life to your sound.
Additionally, incorporating modulation sources, such as LFOs (Low-Frequency Oscillators), allows for further sound manipulation. LFOs generate cyclic, slow-moving waveforms that can be patched to control various parameters, including oscillator pitch, filter cutoff, or even modulating other LFOs or envelopes. This creates evolving and rhythmic effects that add depth and interest to your sounds.
Remember, the combination of oscillators and envelopes is the foundation of sound creation in a modular synthesizer. Mastering the control and manipulation of these components will unlock endless creative possibilities, allowing you to craft unique and expressive sonic landscapes.
Filters and Effects: Shaping the Sound
In a modular synthesizer, filters and effects modules play a vital role in shaping and sculpting the sound. Filters allow you to selectively modify the frequency content of a signal, while effects add depth and character to your sounds. Let’s explore these components in more detail:
Filters: Filters are modules that alter the frequency components of a sound. They can emphasize or attenuate specific frequencies, allowing you to shape the tonal characteristics of your sound. Common types of filters found in modular synthesizers include low-pass filters, high-pass filters, band-pass filters, and notch filters. By adjusting parameters like cutoff frequency and resonance, you can create a wide range of timbral variations, from dark and mellow to bright and biting.
Filters provide a powerful tool for shaping both static and dynamic sounds. For example, by modulating the cutoff frequency of a filter with an envelope or an LFO, you can create dynamic and evolving timbral changes over time. This adds movement and interest to your sound, contributing to a sense of organic and expressive synthesis.
Effects: Effects modules add another layer of creativity and sonic manipulation to your modular synthesizer. They can include modules such as delays, reverbs, choruses, phasers, and more. These effects can transform your sound, adding space, texture, and character. By patching an effects module into your signal path, you can achieve a wide range of sonic textures and atmospheres.
Effects modules can be used in combination with filters to create complex soundscapes. For example, by filtering a sound and then applying a delay effect, you can create ethereal and spacious textures. Experimenting with different effects and their parameters will allow you to add depth, movement, and unique qualities to your sound.
Remember to explore and experiment with various filter and effect combinations to achieve the desired sonic results. Every modular synthesizer setup is unique, and by combining different modules and patching configurations, you can create your own signature sound.
Whether you are looking to shape your sound with precise filtering or add captivating effects to create a sense of ambiance, filters and effects modules provide immense versatility and creative potential. Embrace their power and transform your modular synthesizer into a sonic playground.
Sequencing and Modulation: Adding Movement
In the world of modular synthesis, sequencing and modulation play crucial roles in adding movement and dynamics to your sound. These components allow you to create rhythmic patterns, control parameters over time, and generate evolving textures. Let’s explore how sequencing and modulation can enhance your modular synthesizer playing:
Sequencers: Sequencers are modules that enable you to program and control note patterns and rhythmic sequences. They provide a structured and repetitive framework to your music, allowing you to create melodic phrases and rhythmic grooves. With a sequencer, you can define the pitch, duration, and velocity of each step in the sequence, creating complex and evolving musical patterns.
Sequencers come in various forms, including traditional step sequencers with knobs or sliders, grid-based sequencers with buttons, or even more advanced sequencers with digital screens. They offer a wide range of creative possibilities, from simple repeating sequences to intricate polyphonic melodies. By patching the sequencer’s output to different parameters, such as oscillator pitch or filter cutoff frequency, you can dynamically control and manipulate your sound.
Modulation: Modulation is the process of varying parameters over time. In modular synthesis, modulation sources such as envelopes, LFOs, and other modulation modules are used to dynamically control various parameters within the synthesizer. By patching modulation sources to different target parameters, you can create dynamic and evolving soundscapes.
For example, by using an LFO to modulate the filter cutoff frequency, you can achieve a wobbling or pulsating effect. Modulating the oscillator pitch with an envelope can add rhythmic and tonal variations to your sound. Experimenting with different modulation sources, destinations, and modulation depths will allow you to create expressive and evolving sonic textures.
By combining sequencing and modulation, you can create intricate and evolving compositions. For instance, you can use a sequencer to drive the pitch of an oscillator while modulating the filter cutoff frequency with an LFO. This combination can lead to rhythmic variations and dynamic tonal changes, adding depth and movement to your music.
Remember, sequencing and modulation are powerful tools for adding depth and creativity to your modular synthesizer playing. Embrace the rhythmic possibilities of sequencers and the dynamic control of modulation sources to create evolving and expressive sonic landscapes.
Tips and Techniques for Playing a Modular Synthesizer
Playing a modular synthesizer is a unique and exciting experience that allows for endless sonic exploration. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced musician, here are some tips and techniques to enhance your modular synthesizer playing:
- Start Small: If you’re new to modular synthesis, it can be overwhelming to have a large collection of modules. Start with a small setup and gradually expand as you gain familiarity with the modules and their interactions. This will help you develop a deeper understanding of the system and prevent you from feeling overwhelmed.
- Experiment with Patching: Patching is at the core of modular synthesis. Don’t be afraid to experiment and try different patch configurations. Unusual connections and unexpected combinations can lead to surprisingly unique sounds. Let your creativity guide you!
- Understand Signal Flow: Having a clear understanding of signal flow can help you make more informed decisions when patching. Understand the path the audio signal takes, from oscillators through filters, envelopes, and effects. This will help you shape and manipulate the sound effectively.
- Explore Modulation: Modulation is key to creating dynamic and evolving sounds. Experiment with different modulation sources and destinations to add movement and expression to your patches. Modulate parameters such as pitch, filter cutoff, and waveform shape to bring your sounds to life.
- Utilize External Gear: Don’t limit yourself to just your modular synthesizer. Incorporate external effects, processors, or instruments to further expand your sonic palette. External gear can add depth and dimension to your modular setups.
- Document Your Patches: Modular synthesis is a highly exploratory and spontaneous process. Taking the time to document your patches, either through notes, photos, or video recordings, can be invaluable. It allows you to revisit and recreate patches, learn from previous experiments, and share your discoveries with others.
- Embrace Happy Accidents: Modular synthesis is full of happy accidents and serendipitous discoveries. When something unexpected happens in your patch, embrace it and explore the new sound or texture it creates. Sometimes, the best results come from unconventional and unplanned events.
- Learn from Others: Join online forums, communities, and social media groups dedicated to modular synthesis. Engage with fellow enthusiasts, share your experiences, and learn from others. Collaboration and knowledge-sharing can greatly enhance your understanding of modular synthesis.
Remember, playing a modular synthesizer is all about exploration, experimentation, and pushing the boundaries of sound. Embrace the journey, trust your instincts, and allow yourself to create unique and captivating sonic experiences.
Conclusion
Congratulations on embarking on your journey into the captivating world of modular synthesizers. Throughout this article, we have explored the basics of modular synthesis, the components of a modular synthesizer, and various techniques for playing and shaping sound.
By understanding the fundamentals of modular synthesis and familiarizing yourself with modules such as oscillators, filters, envelopes, effects, sequencers, and modulation sources, you have gained the foundational knowledge to create unique and expressive sounds.
Remember to approach modular synthesis with a sense of curiosity and experimentation. Embrace the flexibility and versatility that modular synthesizers offer, allowing you to shape and sculpt sound in ways that traditional synthesizers cannot.
As you continue to explore and play your modular synthesizer, don’t be afraid to try new patch configurations, experiment with modulation, and incorporate external gear to expand your sonic palette. Embrace the unexpected and capture your creative moments through documentation.
Engaging with the modular synthesis community, whether online or in person, can provide additional inspiration, learning opportunities, and a space to share your discoveries.
In the end, modular synthesis is a deeply personal and artistic process. It is a medium through which you can express your unique musical voice and create sonic landscapes that resonate with your vision. So, let your imagination run wild, and may your modular synthesizer journey be filled with endless exploration and sonic bliss.