Home>Production & Technology>MIDI>How To Separate MIDI Drum Tracks

MIDI
How To Separate MIDI Drum Tracks
Modified: February 22, 2024
Learn how to separate MIDI drum tracks and customize your music production with our step-by-step guide. Perfect for MIDI enthusiasts and music producers.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Separating MIDI drum tracks is a valuable skill for musicians, producers, and audio engineers. By isolating individual drum components within a MIDI file, you gain the flexibility to manipulate and enhance the sound of each drum instrument. Whether you're aiming to fine-tune the kick drum's punchiness, polish the snare's crispness, or adjust the cymbals' shimmer, the ability to separate MIDI drum tracks opens up a world of creative possibilities.
In the realm of music production, MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) revolutionized the way electronic instruments communicate with computers. Unlike audio tracks, MIDI files contain data about musical notes, pitch, velocity, and more, offering a level of control and customization that goes beyond traditional audio recordings.
Separating MIDI drum tracks allows for precise editing and mixing, enabling you to sculpt the perfect drum sound for your compositions. Whether you're working on a rock anthem, a pop ballad, or an electronic dance track, having the ability to isolate and manipulate individual drum elements can elevate the overall quality and impact of your music.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the intricacies of separating MIDI drum tracks, exploring the tools and techniques that empower you to unlock the full potential of your drum recordings. From understanding the structure of MIDI drum tracks to utilizing specialized software and step-by-step separation methods, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to take your drum production to the next level.
So, whether you're a seasoned music producer looking to refine your drum tracks or a budding musician eager to explore the art of MIDI manipulation, join us on this journey as we unravel the art and science of separating MIDI drum tracks.
Understanding MIDI Drum Tracks
MIDI drum tracks serve as the backbone of rhythm in modern music production. Unlike audio recordings, MIDI data represents musical notes, velocities, and other performance parameters in a digital format, offering unparalleled flexibility and control. When it comes to MIDI drum tracks, the data is structured to encompass individual drum instruments, such as kick drums, snares, hi-hats, toms, and cymbals, each assigned to specific MIDI notes.
In a standard MIDI drum map, the kick drum is typically assigned to MIDI note C1, the snare drum to D1, and so on, following a consistent mapping convention. This mapping allows for seamless integration with drum sample libraries and virtual instruments, ensuring that the correct sound is triggered when the corresponding MIDI note is played.
Moreover, MIDI drum tracks capture not only the timing and intensity of each drum hit but also intricate nuances such as flam strokes, ghost notes, and drum rolls. This level of detail empowers producers and musicians to sculpt the dynamics and expressiveness of their drum performances with precision.
Understanding the structure and intricacies of MIDI drum tracks is pivotal for effective separation and manipulation. By gaining insight into how MIDI data represents drum instruments, you can navigate through the components of a drum performance with clarity and purpose. Whether you're aiming to adjust the timing of a snare hit, fine-tune the velocity of a kick drum, or layer additional percussion elements, a solid understanding of MIDI drum tracks forms the foundation for achieving your sonic vision.
In essence, MIDI drum tracks embody the essence of rhythmic expression in a digital domain, providing a canvas for creative exploration and sonic refinement. As we delve deeper into the tools and techniques for separating MIDI drum tracks, this foundational understanding will serve as a guiding light, empowering you to unlock the full potential of your drum recordings.
Understanding MIDI drum tracks is not merely about decoding data; it's about embracing the artistry of rhythm and harnessing the power of technology to shape and enhance musical performances. With this knowledge in hand, you're poised to embark on a transformative journey into the realm of MIDI drum track separation, where the boundaries of sonic possibilities are defined only by your imagination.
Tools for Separating MIDI Drum Tracks
When it comes to separating MIDI drum tracks, having the right tools at your disposal can significantly streamline the process and expand your creative capabilities. Here are some essential tools that empower you to effectively separate and manipulate MIDI drum tracks:
-
Digital Audio Workstation (DAW): A versatile DAW forms the central hub for MIDI drum track separation. Leading DAWs such as Ableton Live, FL Studio, Logic Pro, and Pro Tools offer robust MIDI editing capabilities, allowing you to isolate and manipulate individual drum elements within a MIDI file. These platforms provide intuitive interfaces for visualizing MIDI data, precise editing tools, and seamless integration with virtual instruments and drum sample libraries.
-
MIDI Editor Plugins: Dedicated MIDI editor plugins, such as XLN Audio's XO and Toontrack's EZdrummer, are designed specifically for working with MIDI drum tracks. These plugins offer comprehensive features for visualizing, editing, and separating drum components within MIDI patterns. With functionalities like note velocity adjustment, pattern sequencing, and drum instrument layering, MIDI editor plugins provide a focused environment for refining the nuances of drum performances.
-
Drum Replacement Plugins: Utilizing drum replacement plugins, such as Steven Slate Drums 5 and Waves Smack Attack, can enhance the process of separating MIDI drum tracks. These plugins enable you to replace or augment individual drum hits within MIDI patterns with high-quality drum samples, effectively allowing for the isolation and customization of specific drum sounds. By leveraging drum replacement plugins, you can refine the sonic character of each drum instrument, elevating the overall impact of your drum tracks.
-
MIDI Mapping Tools: MIDI mapping tools, such as Bome MIDI Translator Pro and MIDI-OX, provide advanced functionalities for remapping MIDI notes within drum patterns. This capability is particularly useful for customizing the MIDI note assignments of individual drum instruments, aligning them with the specific requirements of virtual drum instruments and sample libraries. By employing MIDI mapping tools, you can ensure seamless integration and accurate representation of drum sounds within your MIDI tracks.
-
Virtual Drum Instruments and Sample Libraries: Access to high-quality virtual drum instruments and sample libraries, such as Native Instruments' Battery and Toontrack's Superior Drummer, enriches the process of separating MIDI drum tracks. These resources offer an extensive array of meticulously recorded drum sounds, encompassing diverse drum kits, percussion elements, and expressive articulations. By leveraging virtual drum instruments and sample libraries, you can augment and replace individual drum components within MIDI patterns, refining the sonic palette of your drum tracks.
By harnessing these tools in your music production arsenal, you can embark on a journey of precision, creativity, and sonic refinement in separating MIDI drum tracks. Each tool plays a crucial role in empowering you to isolate, manipulate, and enhance the individual elements of your drum performances, ultimately shaping the rhythmic foundation of your musical compositions.
Step-by-Step Guide to Separating MIDI Drum Tracks
-
Select the MIDI Drum Track: Open your preferred Digital Audio Workstation (DAW) and load the MIDI drum track you intend to separate. Ensure that the MIDI data is displayed in a clear and comprehensible format within the DAW's interface.
-
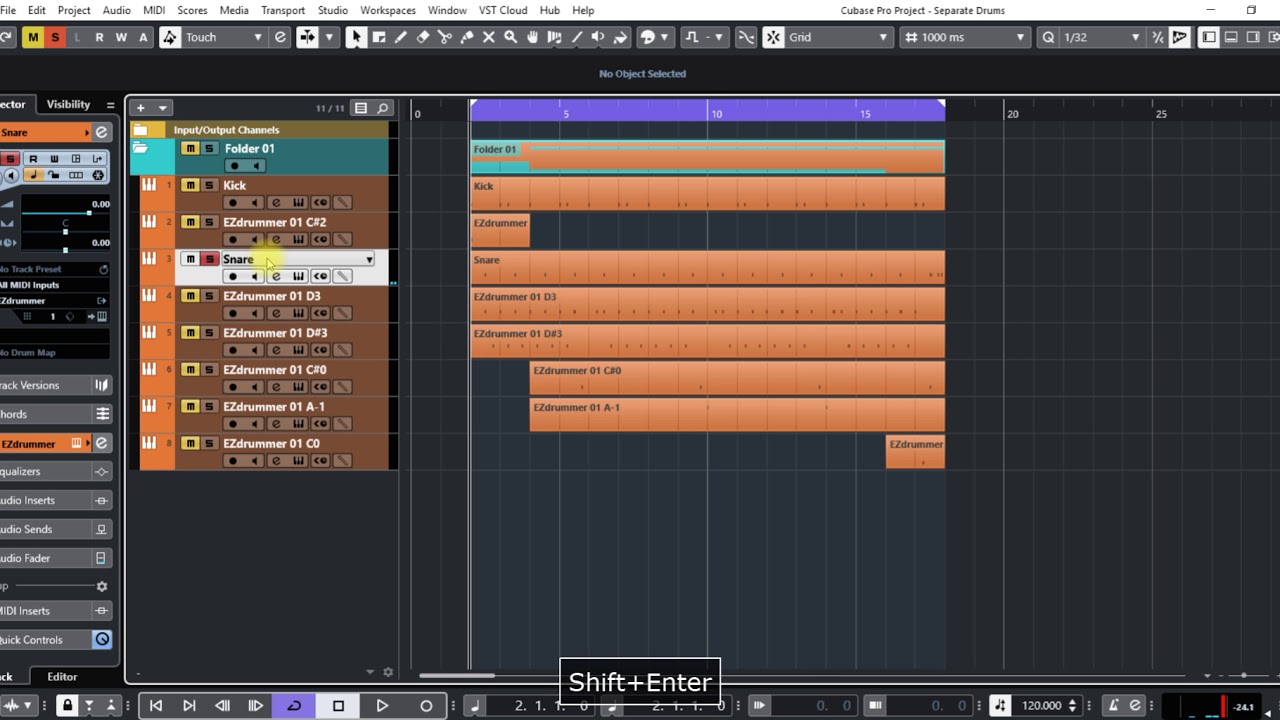
Identify Drum Instruments: Visualize the MIDI notes within the drum track to identify the specific drum instruments present, such as kick drums, snares, hi-hats, toms, and cymbals. Familiarize yourself with the MIDI note assignments corresponding to each drum instrument, as per the standard MIDI drum mapping convention.
-
Isolate Individual Drum Components: Utilize the DAW's MIDI editing capabilities to isolate individual drum components within the MIDI track. This can be achieved by selecting specific MIDI notes corresponding to a particular drum instrument and separating them onto separate MIDI tracks for focused manipulation.
-
Adjust Note Velocities and Timing: Fine-tune the velocities and timing of individual drum hits to enhance the dynamics and groove of the drum performance. By adjusting note velocities, you can impart varying degrees of intensity to each drum hit, while precise timing adjustments allow for rhythmic refinement.
-
Layer Additional Percussion: Explore the option to layer additional percussion elements, such as tambourines, shakers, or electronic samples, alongside the existing drum components to enrich the sonic texture and depth of the drum track.
-
Utilize Drum Replacement Plugins: If desired, employ drum replacement plugins to augment or replace specific drum hits with alternative drum samples. This process can be particularly useful for refining the tonal characteristics of individual drum instruments within the MIDI track.
-
Customize MIDI Note Assignments: If necessary, utilize MIDI mapping tools to customize the MIDI note assignments of individual drum instruments, ensuring seamless integration with virtual drum instruments and sample libraries.
-
Refine Drum Performance: Continuously iterate and refine the separation process, focusing on the nuanced expression and cohesion of the individual drum components. Pay attention to the overall balance and interaction of the drum instruments within the MIDI track.
-
Save and Export Separated Tracks: Once satisfied with the separation and manipulation of the MIDI drum tracks, save the individual drum components as separate MIDI files or audio stems, ready for further processing and integration within your music production projects.
By following this step-by-step guide, you can effectively separate MIDI drum tracks, unlocking the potential for precise editing, creative manipulation, and sonic enhancement within your music production endeavors.
Tips and Tricks for Better Separation
-
Fine-Tune Velocity and Timing: Pay attention to the velocity and timing of individual drum hits within the MIDI track. Adjusting the velocity adds depth and dynamics to the drum performance, while refining the timing ensures a cohesive and groove-oriented rhythm.
-
Layer Percussion Elements: Experiment with layering additional percussion elements, such as subtle shakers or tambourines, to complement the existing drum components. This technique enhances the overall sonic texture and depth of the drum track, adding subtle nuances to the rhythm.
-
Utilize Dynamic Processing: Apply dynamic processing techniques, such as compression and transient shaping, to individual drum components. This helps in smoothing out inconsistencies in the drum performance and accentuating the transient impact, resulting in a polished and cohesive drum sound.
-
Explore Drum Instrument Articulations: Dive into the diverse articulations offered by virtual drum instruments and sample libraries. Utilize techniques such as flams, rolls, and ghost notes to infuse expressive nuances into the drum performance, elevating the overall musicality of the track.
-
Employ Micro-Editing Techniques: Embrace micro-editing to meticulously adjust the start and end points of individual drum hits. This level of precision ensures seamless transitions between drum elements and contributes to a tight and professional-sounding drum track.
-
Experiment with Panning and Spatial Effects: Explore spatial effects and panning to create a sense of depth and movement within the drum mix. By placing individual drum components in specific spatial locations, you can enhance the stereo image and overall impact of the drum track.
-
Utilize Drum Group Processing: Consider grouping related drum components, such as kick and snare, and applying group processing techniques. This approach allows for cohesive treatment of specific drum elements, facilitating a unified and balanced drum mix.
-
Embrace Creative Automation: Leverage automation to introduce dynamic changes in drum parameters, such as panning, EQ settings, and effects levels. This creative use of automation adds movement and interest to the drum track, enhancing its overall impact within the mix.
-
Seek Inspiration from Reference Tracks: Draw inspiration from reference tracks with exemplary drum production. Analyze the nuances of drum separation and processing in professional productions to gather insights and ideas for refining your own drum tracks.
-
Trust Your Ears: Ultimately, trust your ears as the ultimate judge of a well-separated drum track. Continuously listen and critically evaluate the individual drum components within the context of the entire mix, ensuring that each element contributes harmoniously to the overall musical expression.
By incorporating these tips and tricks into your MIDI drum track separation process, you can elevate the quality, expressiveness, and impact of your drum productions, unlocking a world of sonic possibilities and creative exploration.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the art of separating MIDI drum tracks represents a pivotal aspect of modern music production, offering a gateway to unparalleled creativity, precision, and sonic refinement. Through the comprehensive understanding of MIDI drum tracks, the utilization of specialized tools, and the application of step-by-step separation techniques, producers, musicians, and audio engineers can sculpt the rhythmic foundation of their compositions with meticulous detail and expressive nuance.
The journey of separating MIDI drum tracks is not merely a technical endeavor but a harmonious fusion of art and technology. It embodies the convergence of rhythmic expression, digital innovation, and creative exploration, empowering individuals to shape the sonic landscape of their musical visions. By delving into the intricacies of MIDI drum tracks, one gains insight into the heartbeat of rhythm, where each drum hit becomes a brushstroke in the canvas of musical expression.
As we navigate through the process of isolating and manipulating individual drum components, we embark on a transformative odyssey of sonic craftsmanship. The ability to fine-tune velocities, adjust timings, layer percussion elements, and explore dynamic processing techniques elevates the drum track from a mere rhythmic backdrop to a vibrant tapestry of sonic artistry. It is within this realm of precision and creativity that the true essence of MIDI drum track separation unfolds, offering a playground for sonic experimentation and boundless musical innovation.
Moreover, the tips and tricks for better separation serve as guiding beacons, illuminating the path towards sonic excellence. From embracing micro-editing techniques to harnessing the power of creative automation, these insights empower individuals to infuse their drum tracks with depth, expressiveness, and captivating musicality. It is through these nuanced refinements and artistic interventions that the drum track transcends its role, becoming a living, breathing entity within the musical narrative.
Ultimately, the journey of separating MIDI drum tracks transcends the realm of technical proficiency, resonating with the soul of musical expression. It is a testament to the unyielding pursuit of sonic excellence, where each drum hit carries the weight of emotion, energy, and musical intent. As we conclude this exploration, we stand at the threshold of infinite sonic possibilities, armed with the knowledge, tools, and creative spirit to breathe life into every beat, every rhythm, and every moment of musical magic.