Home>Production & Technology>MIDI>How To Use MIDI


MIDI
How To Use MIDI
Modified: February 22, 2024
Learn how to use MIDI to control and synchronize electronic musical instruments and devices. Discover the basics of MIDI technology and its applications.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
What is MIDI?
MIDI, which stands for Musical Instrument Digital Interface, is a versatile and fundamental technology that has revolutionized the way music is created, recorded, and performed. It serves as a universal language for electronic musical instruments, computers, and other audio devices to communicate with each other. Unlike audio signals, MIDI data does not contain actual sound but rather transmits information about musical notes, velocity, pitch, modulation, and other performance parameters. This digital protocol enables seamless integration and synchronization between various musical devices, allowing for unprecedented creativity and flexibility in music production and performance.
At its core, MIDI operates by transmitting messages that represent musical events. These messages can include note-on and note-off commands, control changes, pitch bend, and various other instructions that control the behavior of electronic instruments and software. This means that MIDI can be used to trigger sounds from synthesizers, drum machines, and samplers, as well as control parameters such as volume, panning, and effects in real time.
One of the most significant advantages of MIDI is its non-proprietary nature, which means that MIDI-compatible devices from different manufacturers can communicate and work together seamlessly. This interoperability has been a driving force behind the widespread adoption of MIDI across the music industry, making it an essential tool for musicians, producers, and live performers.
Furthermore, MIDI is not limited to traditional musical instruments; it can also be used to control lighting systems, visual effects, and other multimedia elements in live performances, creating immersive and synchronized audiovisual experiences.
In summary, MIDI serves as the backbone of modern music production and performance, enabling seamless communication and control between electronic musical devices. Its versatility, interoperability, and real-time control capabilities have made it an indispensable tool for musicians and audio professionals worldwide.
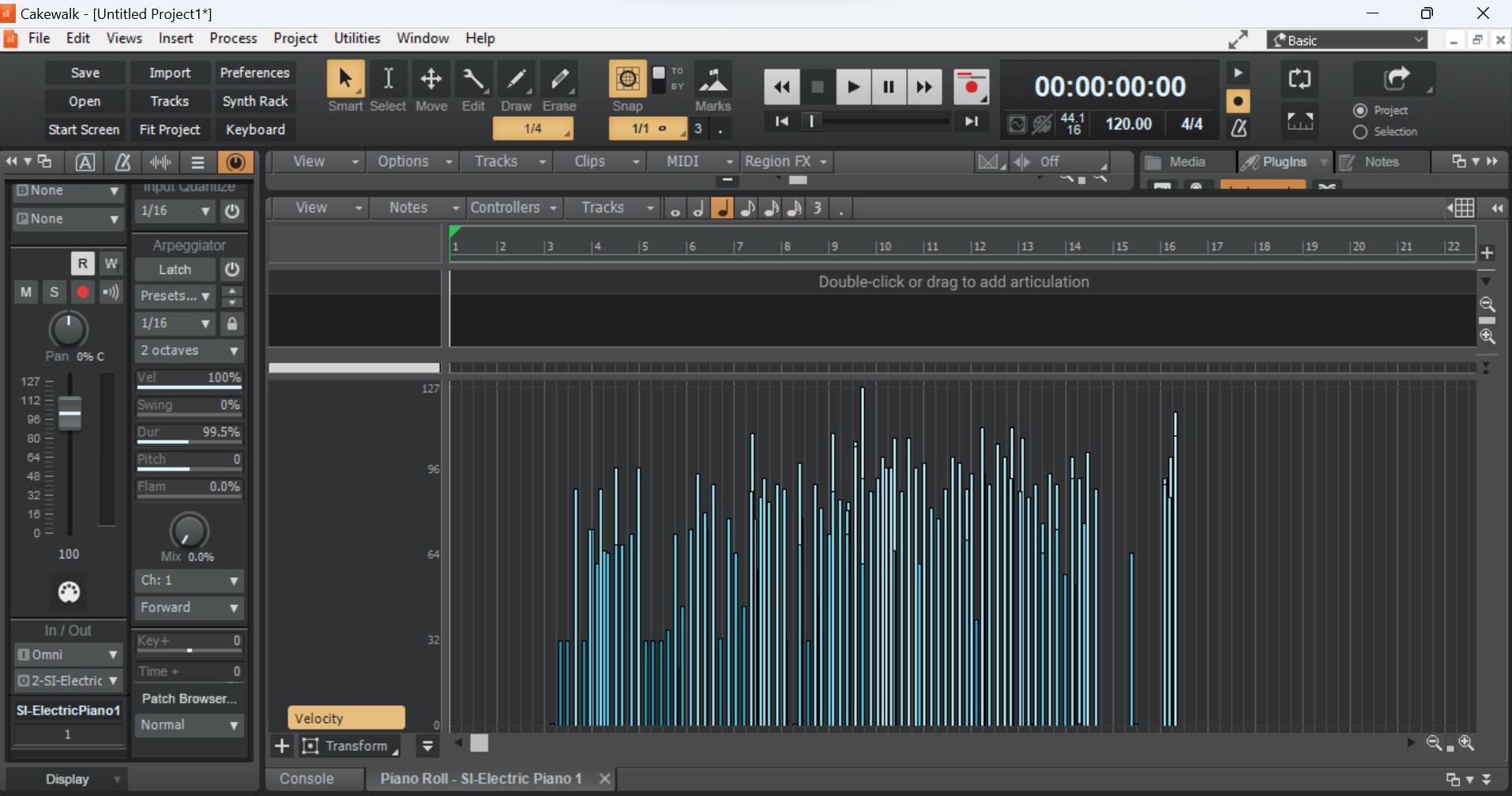
Setting up MIDI equipment
Setting up MIDI equipment is an essential step in creating a seamless and efficient music production environment. Whether you are a beginner or a seasoned professional, understanding the process of configuring MIDI devices is crucial for unleashing the full potential of your musical setup.
1. Connecting MIDI Devices
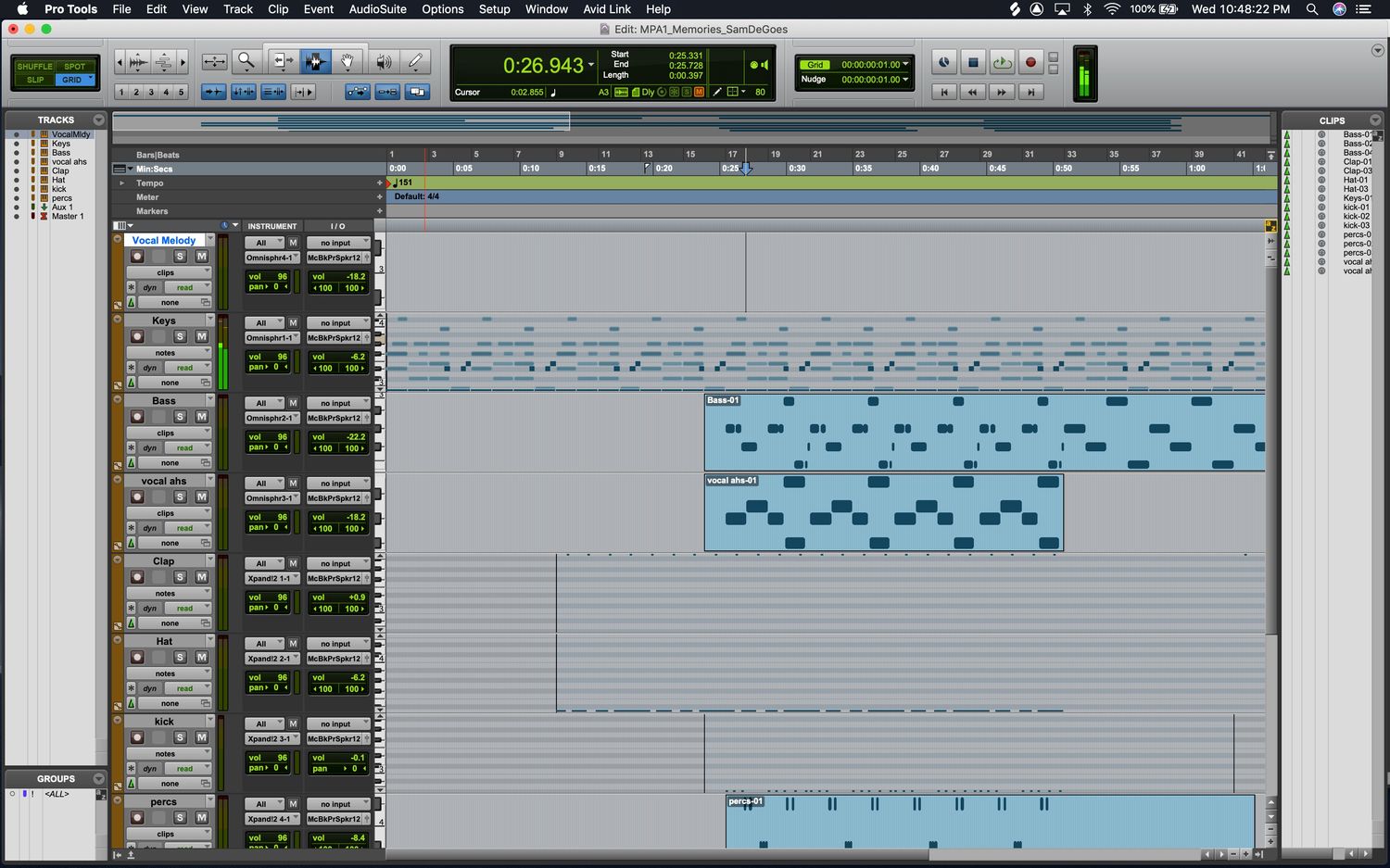
The first step in setting up MIDI equipment involves connecting your MIDI devices, such as keyboards, controllers, and interfaces, to your computer or audio interface. This is typically achieved using MIDI cables or USB connections, depending on the specific devices you are using. Most modern MIDI controllers and keyboards feature USB connectivity, allowing for straightforward integration with computer-based digital audio workstations (DAWs). Additionally, MIDI interfaces can be utilized to expand the number of MIDI ports available, enabling the connection of multiple devices simultaneously.
2. Configuring MIDI Settings in Software
Once the physical connections are established, it is crucial to configure the MIDI settings within your music production software. This involves selecting the appropriate MIDI input and output devices within the software's preferences or settings menu. By doing so, you ensure that your MIDI devices are recognized and can communicate with the software effectively.
3. Assigning MIDI Channels and Parameters
In many cases, MIDI devices feature multiple channels and assignable parameters that can be customized to suit your specific workflow. This may involve assigning different MIDI channels to individual instruments or configuring MIDI control messages to manipulate various parameters within your software instruments or effects. Understanding how to assign MIDI channels and parameters empowers you to tailor your MIDI setup to meet the unique requirements of your music production projects.
4. Testing MIDI Connectivity
After setting up your MIDI equipment, it is advisable to conduct thorough testing to ensure that all devices are communicating as intended. This can involve playing notes on your MIDI keyboard or controller and verifying that the corresponding MIDI data is being received by your software. Additionally, testing MIDI control messages, such as modulation and pitch bend, can help confirm that your setup is fully operational.
By following these steps and gaining a solid understanding of MIDI equipment setup, you can optimize your music production workflow and unlock the creative potential of your MIDI devices. Whether you are crafting intricate melodies, controlling software instruments, or integrating hardware synthesizers, a well-configured MIDI setup forms the foundation for a seamless and inspiring music production environment.
Using MIDI in music production
MIDI plays a pivotal role in modern music production, offering unparalleled flexibility and creative possibilities for composers, producers, and sound designers. By harnessing the power of MIDI, musicians can craft intricate compositions, manipulate virtual instruments, and breathe life into their musical ideas with remarkable precision and expressiveness.
1. Composition and Arrangement
MIDI serves as a foundational tool for composing and arranging music within digital audio workstations (DAWs). It allows musicians to input, edit, and manipulate musical notes and phrases with ease, providing a versatile platform for crafting melodies, harmonies, and rhythms. Additionally, MIDI data can be easily modified, transposed, and quantized, enabling composers to refine their musical compositions with meticulous detail.
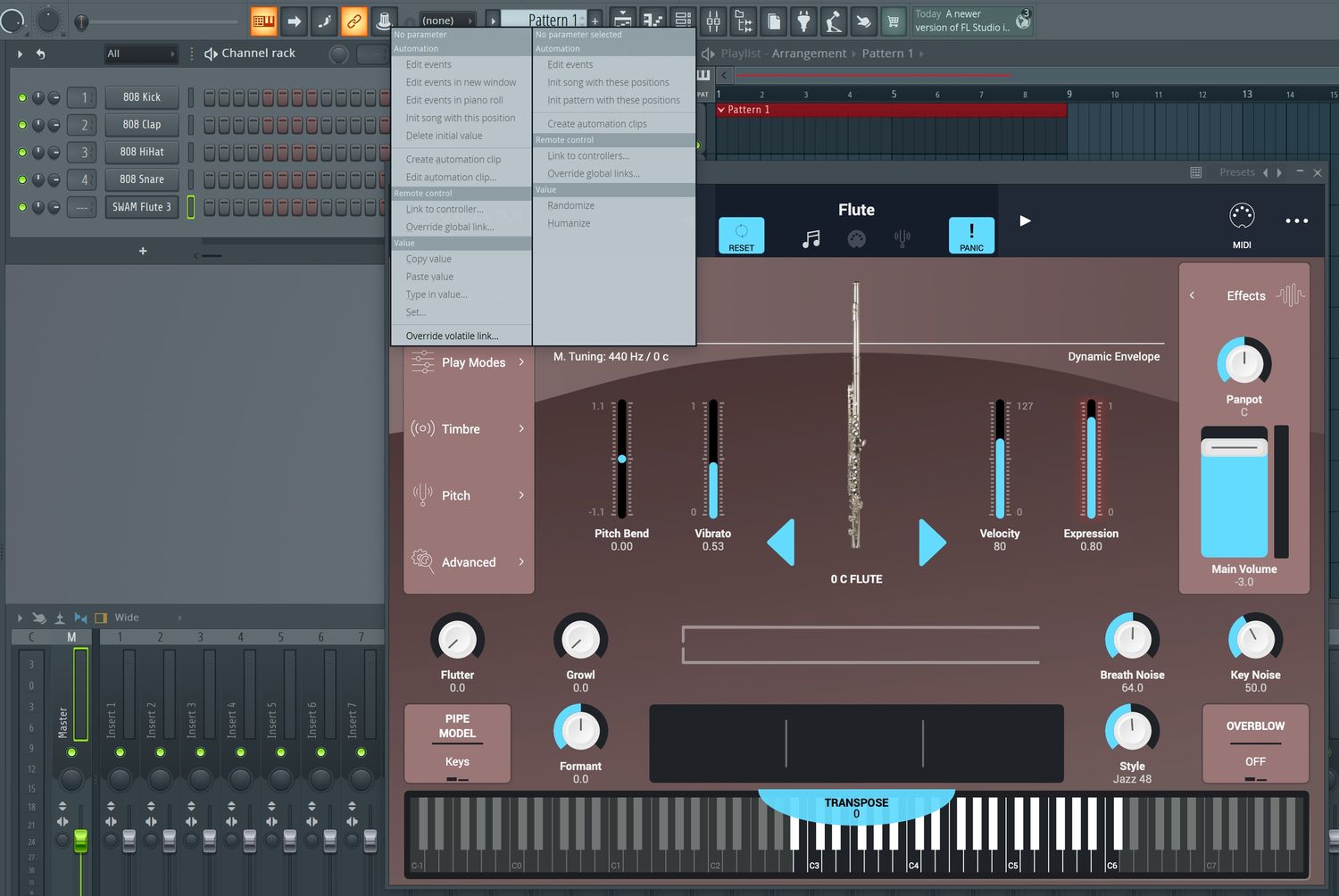
2. Virtual Instrumentation
One of the most compelling applications of MIDI in music production is its integration with virtual instruments. By utilizing MIDI to trigger software synthesizers, sample libraries, and virtual drum kits, musicians can access an expansive palette of sounds and textures. Furthermore, MIDI enables real-time control over various parameters of virtual instruments, such as filter cutoff, resonance, and envelope settings, allowing for dynamic and expressive performances.
3. Automation and Control
MIDI facilitates precise automation of parameters within a DAW, offering unparalleled control over aspects such as volume, panning, and effects. This level of automation empowers producers to sculpt the sonic characteristics of their music with meticulous detail, creating evolving soundscapes and captivating musical dynamics. Additionally, MIDI control surfaces and hardware controllers provide tactile interfaces for manipulating software parameters, enhancing the hands-on experience of music production.
4. Hybrid Music Production
In contemporary music production, MIDI often serves as a bridge between analog and digital realms. It enables seamless integration of hardware synthesizers, drum machines, and effects units with computer-based systems, fostering a hybrid approach to music creation. This integration allows for the best of both worlds, combining the tactile immediacy of analog gear with the limitless possibilities offered by digital audio technologies.
5. Orchestration and Sound Design
MIDI empowers composers and sound designers to explore vast sonic landscapes, from lush orchestral arrangements to futuristic soundscapes. By leveraging MIDI, musicians can intricately orchestrate symphonic compositions, experiment with complex sound design techniques, and breathe life into cinematic scores. The ability to manipulate MIDI data with precision enables the realization of intricate musical visions with unparalleled detail and nuance.
In essence, MIDI stands as a cornerstone of modern music production, offering a versatile and dynamic platform for musical expression. Its seamless integration with virtual instruments, precise automation capabilities, and role in hybrid music production make it an indispensable tool for realizing artistic visions and pushing the boundaries of musical creativity.
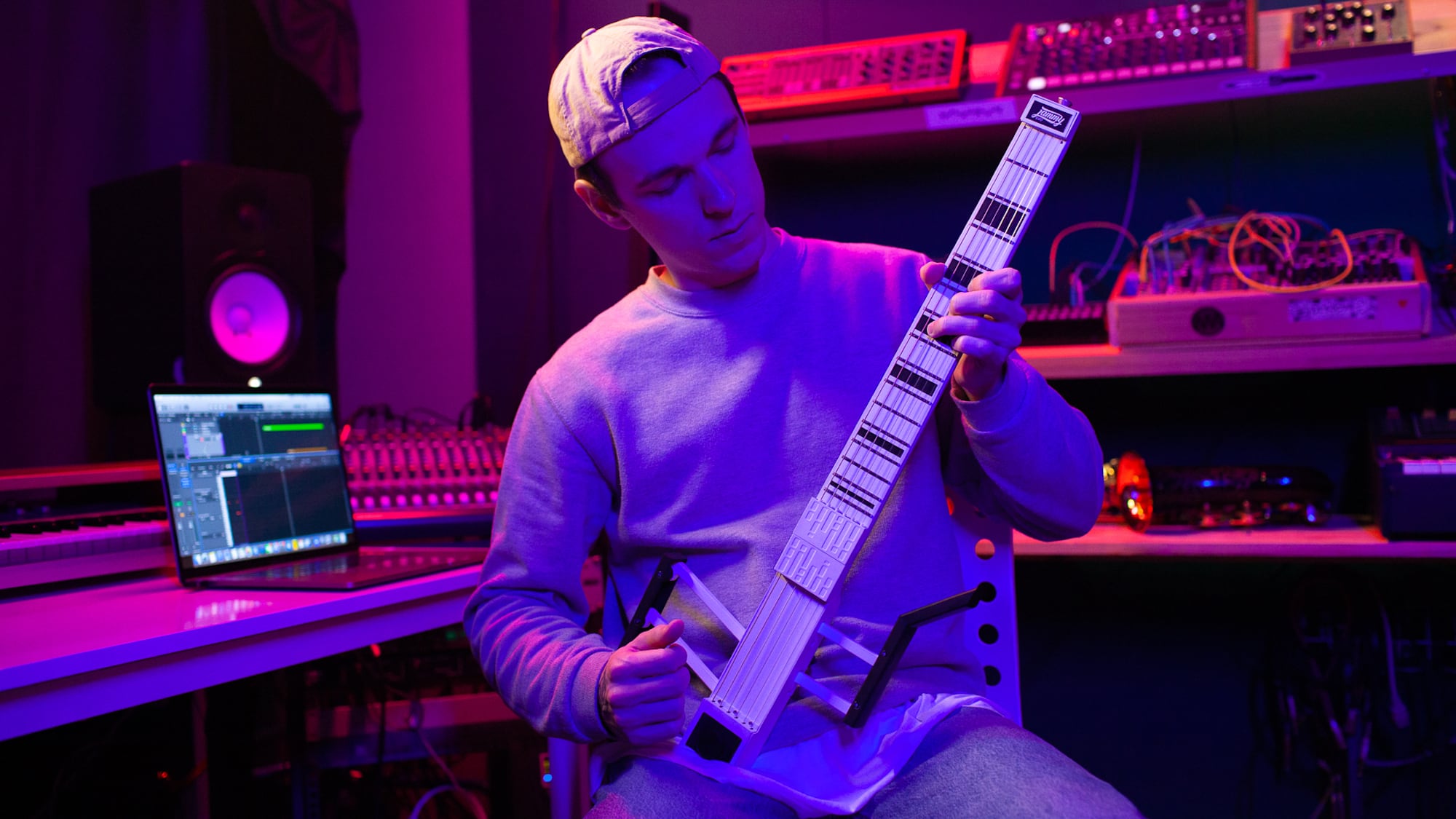
MIDI controllers and instruments
MIDI controllers and instruments represent a diverse array of musical tools that harness the power of MIDI to enable expressive performances, precise control, and immersive music creation experiences. These devices encompass a wide range of forms, from compact pad controllers to full-sized keyboard instruments, each offering unique capabilities that cater to the creative needs of musicians, producers, and performers.
1. Keyboard Controllers
Keyboard controllers, often referred to as MIDI keyboards, stand as one of the most ubiquitous and versatile MIDI instruments. These controllers come in various configurations, ranging from compact, portable models to elaborate, fully weighted keyboards that emulate the feel of acoustic pianos. MIDI keyboards provide a platform for playing and controlling virtual instruments, software synthesizers, and digital audio workstations, offering musicians an intuitive interface for composing, performing, and recording music.
2. Pad Controllers
Pad controllers are designed to facilitate rhythmic programming, beat-making, and live performance. These devices feature an array of touch-sensitive pads that can be used to trigger drum sounds, samples, and loops with precision and expressive dynamics. With the ability to assign different sounds to individual pads and manipulate various parameters in real time, pad controllers empower musicians to craft intricate rhythms and dynamic performances with unparalleled flexibility.
3. MIDI Guitar Controllers
MIDI guitar controllers bridge the gap between traditional guitar playing and electronic music production. These innovative instruments capture the nuances of guitar performance and translate them into MIDI data, allowing guitarists to access a vast array of virtual instruments and synths. By leveraging MIDI guitar controllers, musicians can explore new sonic possibilities, seamlessly integrate guitar-based performances into electronic music, and unlock the expressive potential of their instrument in the digital realm.
4. Wind and Brass Controllers
For wind and brass instrumentalists, MIDI controllers offer a gateway to expanding their sonic palette and exploring electronic music production. These controllers, often designed to emulate the fingerings and techniques of traditional wind instruments, enable players to access a wide range of synthesized sounds and manipulate them with precision. By harnessing MIDI, wind and brass musicians can delve into electronic music genres, experiment with sound design, and contribute unique textures to musical compositions.
5. Hybrid MIDI Instruments
Innovations in MIDI technology have led to the development of hybrid instruments that blend traditional acoustic elements with MIDI capabilities. For example, acoustic pianos equipped with MIDI functionality allow pianists to access virtual instrument libraries, record performances with MIDI data, and integrate their playing into digital environments. Similarly, hybrid drum kits combine acoustic drum pads with MIDI triggers, enabling drummers to blend acoustic and electronic sounds seamlessly.
In essence, MIDI controllers and instruments encompass a rich tapestry of musical tools that empower musicians to explore new sonic territories, express their creativity with precision, and seamlessly integrate electronic elements into their performances. Whether through keyboard controllers, pad devices, or innovative MIDI guitar interfaces, these instruments stand as essential conduits for bridging the gap between traditional musical techniques and the boundless possibilities of electronic music production.
Troubleshooting MIDI connectivity issues
Troubleshooting MIDI connectivity issues is an essential skill for musicians and producers who rely on MIDI technology for music production and live performances. While MIDI offers unparalleled flexibility and control, encountering connectivity issues can disrupt creative workflows and hinder the seamless integration of musical devices. By understanding common MIDI connectivity challenges and employing effective troubleshooting techniques, individuals can overcome obstacles and ensure the reliable operation of their MIDI setups.
Identifying Potential Issues
When faced with MIDI connectivity problems, the first step is to identify potential sources of the issue. This can include examining physical connections, checking device settings, and assessing software configurations. Common issues may arise from faulty cables, incompatible MIDI channels, incorrect device settings, or software conflicts within digital audio workstations (DAWs).
Testing MIDI Devices and Connections
To pinpoint the root cause of MIDI connectivity issues, it is crucial to conduct systematic testing of MIDI devices and connections. This involves verifying the functionality of MIDI cables, ensuring proper power and signal flow in MIDI interfaces, and confirming that MIDI controllers and instruments are transmitting and receiving data as expected. Additionally, testing MIDI input and output ports on computers or audio interfaces can help isolate potential hardware-related issues.
Software Configuration and Compatibility
In many cases, MIDI connectivity issues can stem from software configuration and compatibility challenges. Ensuring that MIDI devices are properly recognized within music production software, checking for driver updates, and confirming MIDI routing settings are essential steps in troubleshooting software-related problems. Additionally, verifying the compatibility of MIDI devices with specific operating systems and software versions can help resolve compatibility issues that may impede proper MIDI communication.
Diagnosing MIDI Signal Flow
Diagnosing MIDI signal flow is a critical aspect of troubleshooting connectivity issues. This involves tracking the flow of MIDI data from input devices, such as keyboards or controllers, to software instruments and external MIDI modules. By monitoring MIDI signal indicators within software interfaces and hardware devices, individuals can identify potential bottlenecks or interruptions in MIDI communication, allowing for targeted troubleshooting and resolution of signal flow issues.
Firmware and Driver Updates
Keeping MIDI devices' firmware and drivers up to date is instrumental in addressing connectivity issues. Manufacturers often release firmware updates and driver patches to improve device performance, address compatibility issues, and enhance overall MIDI functionality. By regularly checking for updates and applying the latest firmware and driver releases, individuals can mitigate potential connectivity problems stemming from outdated software components.
Seeking Community Support and Resources
In complex cases where MIDI connectivity issues persist, seeking support from online communities, forums, and technical resources can provide valuable insights and solutions. Engaging with fellow musicians, audio professionals, and MIDI enthusiasts can offer alternative perspectives, troubleshooting tips, and specific recommendations for resolving intricate MIDI connectivity challenges.
By employing these troubleshooting techniques and maintaining a proactive approach to MIDI connectivity, individuals can mitigate potential issues, streamline their music production workflows, and ensure the seamless operation of MIDI devices and software interfaces. Through systematic testing, software optimization, and collaboration with the MIDI community, musicians and producers can overcome connectivity hurdles and harness the full potential of MIDI technology in their creative endeavors.