Home>Production & Technology>MIDI>How Do You Extract MIDI Channels From A Single Track In Sonar?

MIDI
How Do You Extract MIDI Channels From A Single Track In Sonar?
Modified: February 22, 2024
Learn how to extract MIDI channels from a single track in Sonar to streamline your music production process. Find step-by-step instructions for separating MIDI channels easily.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
MIDI, short for Musical Instrument Digital Interface, has revolutionized the music industry by enabling electronic musical instruments, computers, and other devices to communicate and synchronize with each other. It has become an integral part of music production, allowing musicians and producers to create, edit, and play back music with incredible flexibility and precision.
In the world of digital audio workstations (DAWs), Sonar stands out as a powerful and versatile software for music production. It offers a wide range of features and tools, making it a popular choice among musicians, composers, and audio engineers.
One of the key elements of MIDI is its ability to transmit multiple channels of musical information within a single track. Each MIDI channel can carry data for a specific instrument or sound, allowing for intricate and layered compositions. However, there are instances where you may need to extract MIDI channels from a single track in Sonar to manipulate or process them individually. This process can be particularly useful for refining the nuances of each instrument, applying unique effects, or rearranging musical elements within a composition.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of MIDI channels, explore the significance of extracting MIDI channels in Sonar, and provide a comprehensive guide on how to accomplish this task effectively. Whether you are a seasoned music producer or a budding enthusiast, understanding the process of extracting MIDI channels in Sonar will undoubtedly enhance your music production capabilities and open up a world of creative possibilities.
Understanding MIDI Channels
MIDI channels play a crucial role in the realm of music production, offering a method for organizing and transmitting musical data within a single track. Think of MIDI channels as individual pathways through which musical information flows, allowing for the simultaneous control and playback of multiple instruments or sound sources within a DAW.
-
Versatility and Organization: MIDI channels provide a means of organizing different musical elements within a composition. Each channel can be assigned to a specific instrument or sound, facilitating the seamless integration of diverse musical components. This versatility empowers musicians and producers to craft complex and multi-layered compositions with ease.
-
Control and Articulation: By assigning distinct MIDI channels to various instruments or sections of a composition, producers can exercise precise control over each element's articulation, dynamics, and expression. This level of granularity enables the manipulation of individual musical components, enhancing the overall depth and richness of the music.
-
Enhanced Creativity: MIDI channels serve as a conduit for unleashing creativity and experimentation. They allow for the exploration of unique sound combinations, intricate arrangements, and innovative musical ideas. With the ability to extract and manipulate MIDI channels, producers can delve into the intricacies of each musical element, fostering a dynamic and expressive sonic landscape.
-
Compatibility and Interoperability: MIDI channels facilitate seamless communication between different devices and software applications. Whether it's integrating hardware synthesizers, virtual instruments, or external MIDI controllers, the use of MIDI channels ensures that musical data is transmitted accurately and efficiently, fostering a cohesive and interconnected music production environment.
-
Layered Compositions and Orchestration: MIDI channels are instrumental in the creation of layered compositions and orchestral arrangements. By assigning distinct channels to individual instruments within an ensemble, producers can craft intricate and nuanced musical pieces, harnessing the full potential of MIDI's polyphonic capabilities.
Understanding the significance and functionality of MIDI channels is essential for harnessing the full potential of MIDI-based music production. With a firm grasp of MIDI channels, producers can leverage the intricacies of musical expression and technical control to elevate their compositions to new heights of artistry and innovation.
Extracting MIDI Channels in Sonar
In Sonar, the process of extracting MIDI channels from a single track is a valuable technique that empowers music producers to refine and manipulate individual musical elements with precision and creativity. Whether you are looking to apply unique effects to specific instruments, fine-tune the dynamics of different musical components, or rearrange musical passages within a composition, the ability to extract MIDI channels in Sonar opens up a myriad of possibilities for sonic exploration and artistic expression.
Step-by-Step Guide
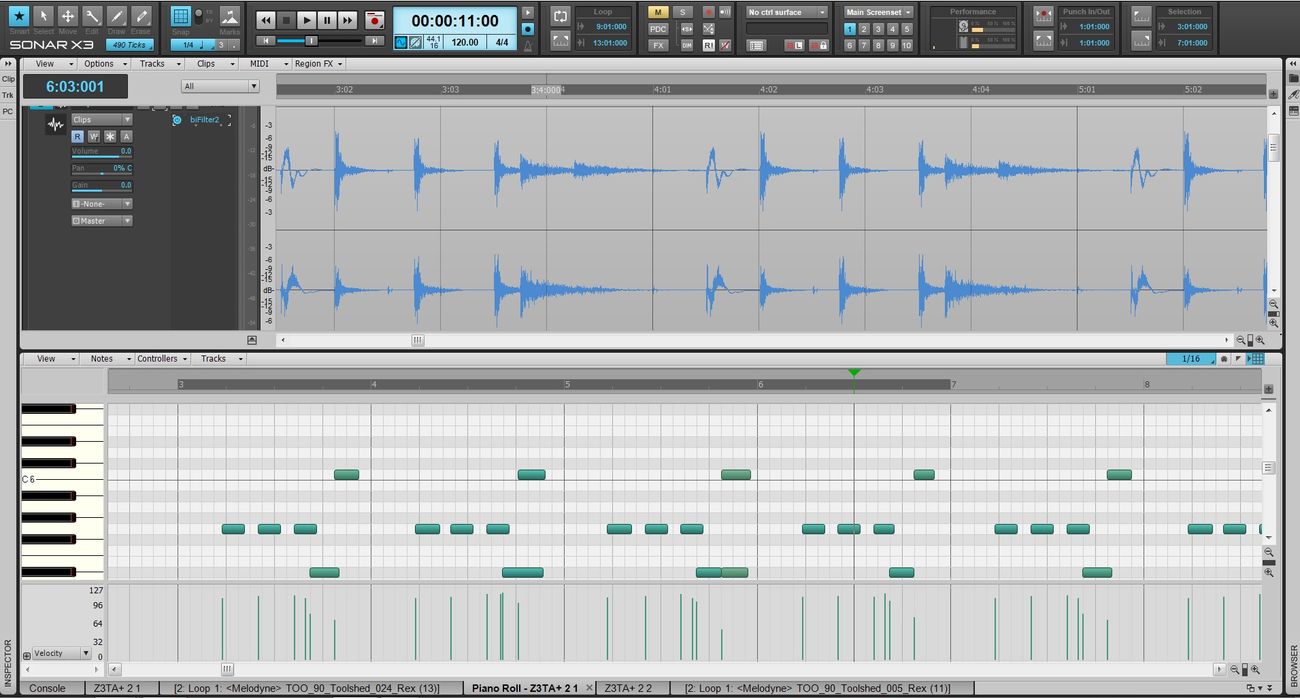
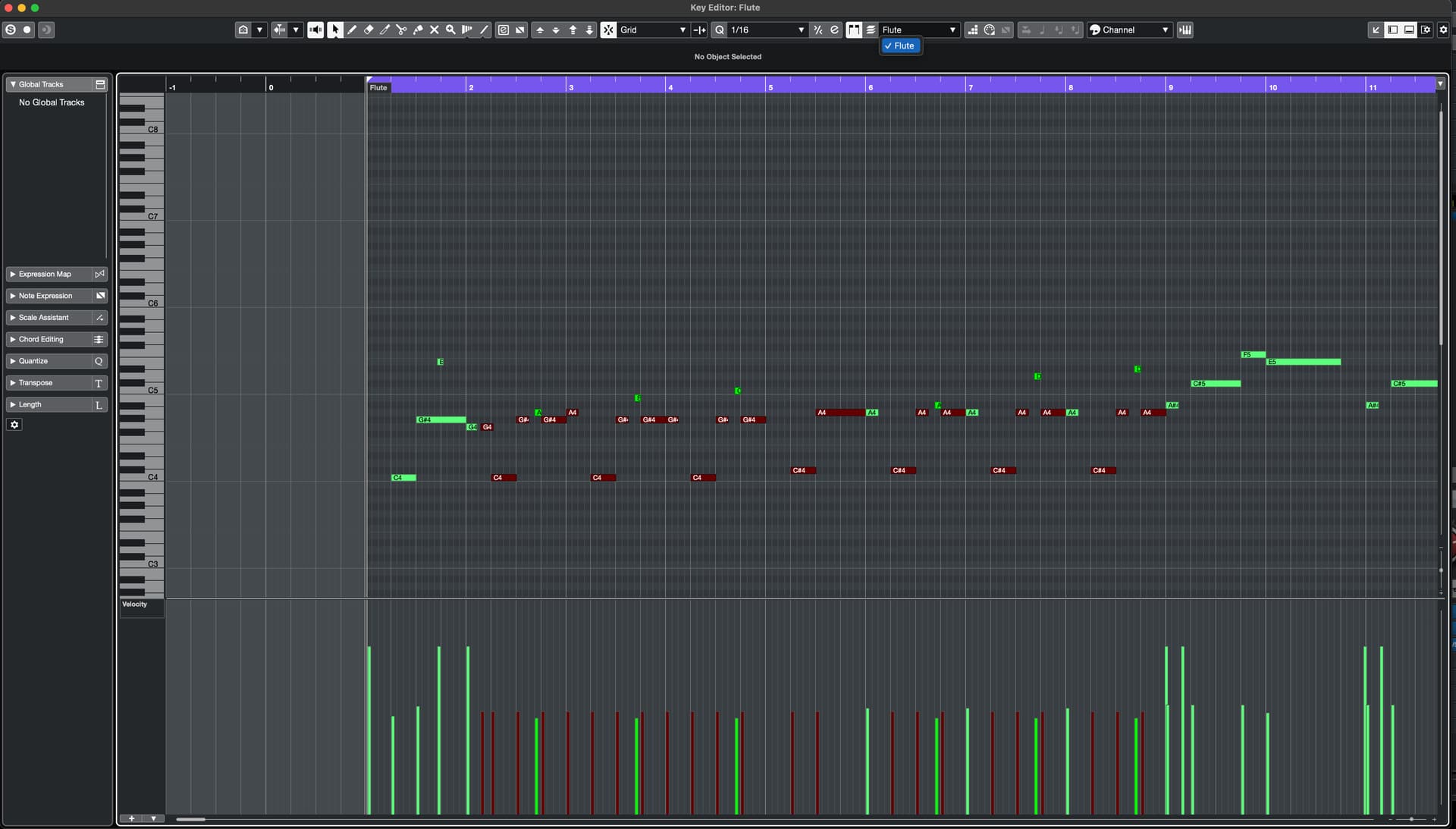
1. Accessing the Piano Roll View
To begin the process of extracting MIDI channels in Sonar, navigate to the desired MIDI track within the Sonar interface. Once selected, access the Piano Roll view, which provides a visual representation of the MIDI data contained within the track.
2. Identifying MIDI Channels
Within the Piano Roll view, each MIDI channel will be represented by distinct note data corresponding to the assigned instrument or sound source. By visually inspecting the MIDI data, you can identify the specific channels associated with different musical elements within the track.
3. Selecting and Extracting MIDI Data
Sonar offers intuitive tools for selecting and extracting MIDI data based on individual channels. Utilizing the selection tools within the Piano Roll view, you can isolate and extract the MIDI data corresponding to a particular channel, effectively separating it from the rest of the musical content within the track.
4. Manipulating Extracted MIDI Channels
Once the MIDI channels have been extracted, Sonar provides a comprehensive set of editing and processing tools for manipulating the isolated musical data. This includes the ability to apply custom effects, adjust note velocities, fine-tune timing and articulation, and explore creative arrangements within the extracted channels.
5. Integration and Playback
After refining and processing the extracted MIDI channels, seamlessly reintegrate them into the original composition within Sonar. By combining the modified channels with the existing musical content, you can experience the enhanced depth and intricacy of the composition, brought to life through the individualized treatment of each MIDI channel.
Unlocking Creative Potential
The process of extracting MIDI channels in Sonar serves as a gateway to unleashing the full creative potential of music production. By delving into the nuanced details of each musical element and exercising precise control over their expression and articulation, producers can sculpt dynamic and captivating compositions that resonate with depth and emotion.
In essence, the ability to extract MIDI channels in Sonar transcends traditional music production techniques, offering a pathway to artistic innovation and sonic craftsmanship. As you embark on this journey of sonic exploration within Sonar, embrace the boundless opportunities to shape and refine your musical vision, channel by channel, ultimately weaving a tapestry of sound that captivates and inspires.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the process of extracting MIDI channels from a single track in Sonar represents a pivotal technique that empowers music producers to delve into the intricate layers of their compositions, refine individual musical elements, and unleash a world of creative possibilities. By understanding the significance of MIDI channels and harnessing the capabilities of Sonar's intuitive tools, producers can elevate their music production endeavors to new heights of artistry and innovation.
The journey of extracting MIDI channels in Sonar transcends traditional music production techniques, offering a pathway to artistic innovation and sonic craftsmanship. It enables producers to delve into the nuances of each musical element, exercise precise control over their expression and articulation, and sculpt dynamic and captivating compositions that resonate with depth and emotion.
As producers navigate the process of extracting MIDI channels in Sonar, they embark on a sonic exploration that fosters a deep connection with their music. The ability to isolate, manipulate, and reintegrate individual MIDI channels enriches the compositional landscape, allowing for the seamless integration of diverse musical elements and the realization of a cohesive and expressive sonic vision.
Ultimately, the process of extracting MIDI channels in Sonar embodies the spirit of creative freedom and technical precision, offering a platform for producers to unleash their full creative potential. Whether it's refining the nuances of a piano melody, shaping the dynamics of a pulsating bassline, or orchestrating a symphony of electronic textures, the extraction of MIDI channels in Sonar empowers producers to sculpt their sonic tapestries with unparalleled depth and sophistication.
As the music production journey unfolds, the ability to extract MIDI channels in Sonar becomes a catalyst for artistic exploration and sonic innovation. It paves the way for producers to craft compositions that resonate with authenticity, emotion, and ingenuity, ultimately leaving an indelible mark on the sonic landscape.
In essence, the process of extracting MIDI channels in Sonar is not merely a technical endeavor; it is a voyage of creative discovery, a testament to the boundless potential of music production, and a celebration of the artistry that thrives within every musical composition.