Home>Production & Technology>MIDI>How To Export As MIDI

MIDI
How To Export As MIDI
Modified: February 22, 2024
Learn how to export your music as MIDI files with our step-by-step guide. Convert your audio to MIDI and take your music to the next level.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Exporting audio files to MIDI format is a valuable skill for musicians, producers, and composers. MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) files are widely used for transferring musical data between different software applications and hardware devices. This versatile format allows for the seamless exchange of musical information, including note events, pitch, velocity, and more.
In this article, we will explore the step-by-step process of exporting audio files as MIDI, providing a comprehensive guide for both beginners and experienced music enthusiasts. Whether you're looking to extract a melody from an audio recording, transfer musical ideas between different platforms, or simply harness the flexibility of MIDI data, this tutorial will equip you with the knowledge and tools to accomplish your goals.
By understanding the intricacies of exporting audio to MIDI, you can unlock a world of creative possibilities. From transcribing live performances to manipulating MIDI data for innovative compositions, the ability to export audio as MIDI opens doors to new musical horizons. Additionally, leveraging MIDI files enables seamless integration with virtual instruments, synthesizers, and digital audio workstations (DAWs), empowering you to harness the full potential of your musical ideas.
Throughout this guide, we will delve into the fundamental steps required to export audio as MIDI, providing clear instructions and valuable insights to streamline the process. Whether you're working with a single track or a complex arrangement, the knowledge gained from this tutorial will empower you to navigate the intricacies of MIDI exportation with confidence.
Now, let's embark on this journey to demystify the process of converting audio to MIDI, empowering you to harness the boundless potential of this versatile musical format.
Step 1: Open your DAW software
Before initiating the process of exporting audio to MIDI, it's essential to open your Digital Audio Workstation (DAW) software. The DAW serves as the central hub for music production, offering a wide array of tools and functionalities to facilitate the creation and manipulation of musical content. Whether you're using industry-standard software like Ableton Live, Logic Pro, Pro Tools, or a user-friendly platform such as GarageBand, the first step is to launch the DAW and ensure that it is ready to receive and process audio data.
Upon opening your preferred DAW, you will be greeted by a user interface that encompasses various elements such as tracks, mixer controls, editing tools, and navigation options. Familiarizing yourself with the layout and features of the DAW is crucial for a seamless workflow. It's important to note that different DAWs may have varying interfaces and workflows, but the fundamental principles of exporting audio to MIDI remain consistent across platforms.
Once the DAW software is launched, you can proceed to access the audio content that you intend to export as MIDI. This may involve opening an existing project file or creating a new session to accommodate the audio material. Regardless of the specific workflow, ensuring that the audio source is readily accessible within the DAW environment is a pivotal preparatory step.
By opening your DAW software and positioning yourself within the creative workspace, you set the stage for the subsequent stages of the MIDI export process. The DAW serves as the canvas upon which musical ideas are realized and transformed, and by initiating the software, you embark on a journey of musical exploration and expression.
In the next step, we will delve into the process of selecting the track or tracks that you wish to export as MIDI, laying the groundwork for the seamless conversion of audio to MIDI data.
Step 2: Select the track or tracks you want to export
Once your DAW software is up and running, the next crucial step in the process of exporting audio to MIDI involves selecting the specific track or tracks that you intend to convert. Whether you're working with a single instrument recording, a multitrack arrangement, or a complex musical composition, the ability to pinpoint the relevant audio content is essential for a focused and efficient export process.
In most DAWs, tracks are represented visually within the software interface, often displayed as horizontal lanes that accommodate audio waveforms, MIDI data, or other types of musical content. To select a track for MIDI export, you'll typically interact with the track view or mixer section of the DAW, where individual tracks are visible and accessible for manipulation.
If you're dealing with a single-track scenario, the process of selection is straightforward. You can simply click on the designated track within the DAW interface, highlighting it for further action. This action signals to the DAW that the chosen track is the target for the upcoming export process. Whether it's a pristine vocal recording, a soul-stirring guitar performance, or a captivating synth melody, the act of selecting the track signifies its importance in the context of the MIDI export operation.
In more complex arrangements with multiple tracks, the selection process may involve identifying and highlighting specific tracks from a roster of interconnected musical elements. This could entail selecting individual instrument tracks, drum patterns, basslines, or any other sonic components that you aim to convert into MIDI format. The ability to discern and isolate the desired tracks within a bustling musical landscape demonstrates a keen understanding of the creative vision and technical requirements of the MIDI export endeavor.
Furthermore, some DAWs offer the flexibility to select and export multiple tracks simultaneously, streamlining the workflow for users dealing with intricate compositions or collaborative projects. This feature empowers you to consolidate diverse musical elements into a cohesive MIDI representation, paving the way for seamless integration and manipulation in subsequent stages of the music production process.
By meticulously selecting the track or tracks that align with your creative objectives, you lay the groundwork for a focused and purposeful MIDI export operation. This deliberate action sets the stage for the transformation of audio content into MIDI data, marking the transition from auditory expression to digital musical information.
In the subsequent step, we will delve into the critical process of locating the export option within your DAW, propelling us closer to the realization of our MIDI export aspirations.
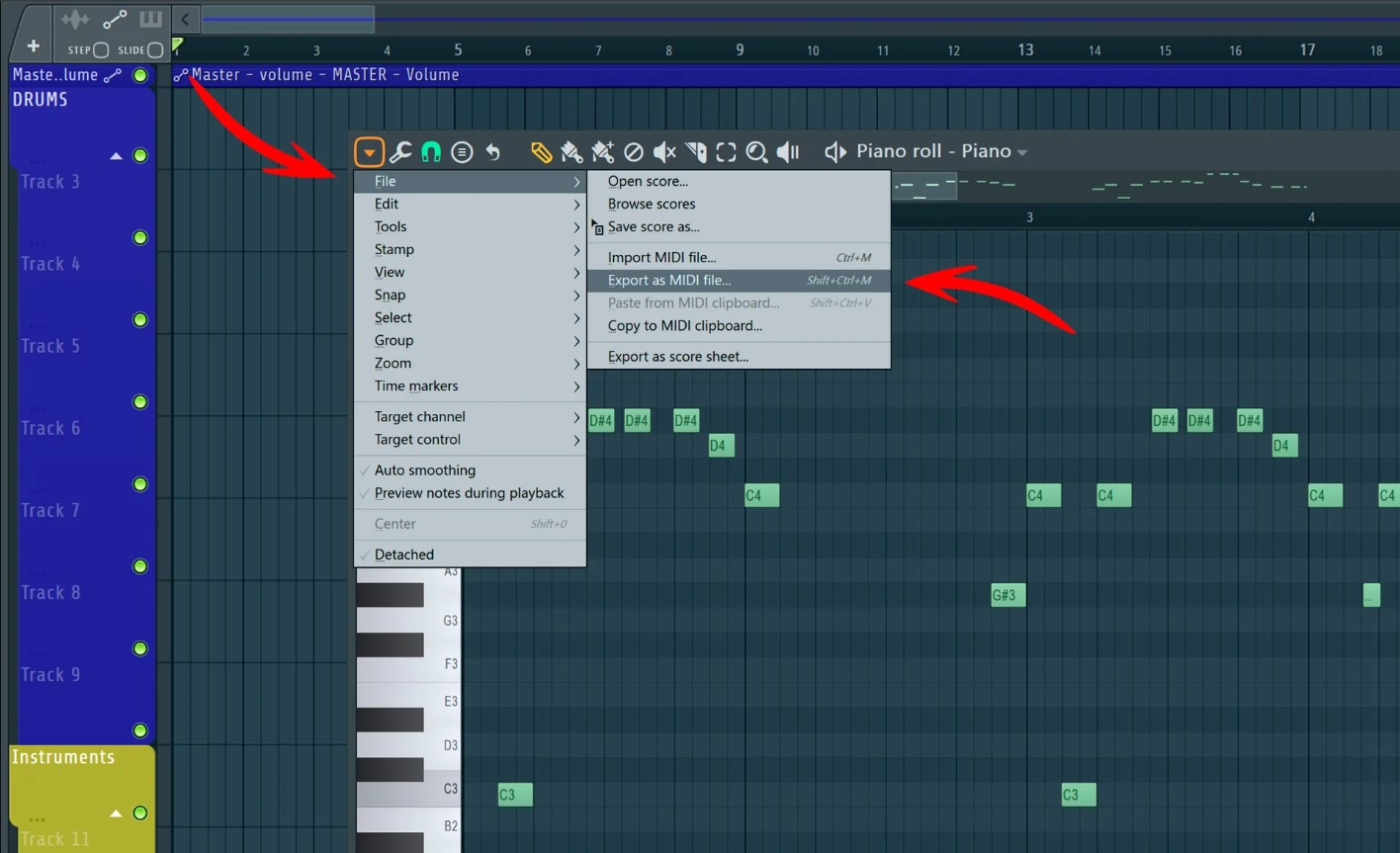
Step 3: Locate the export option
After selecting the track or tracks that you wish to export as MIDI, the next pivotal step in the process involves locating the export option within your Digital Audio Workstation (DAW). This crucial stage serves as the gateway to initiating the conversion of audio content into MIDI format, setting the wheels in motion for a seamless transition between sonic realms.
The location of the export option may vary depending on the specific DAW you are using, but the fundamental principle remains consistent across different software platforms. In most cases, the export functionality is nestled within the menu bar or a dedicated section of the user interface, offering a streamlined pathway to access a diverse range of export options, including MIDI.
Within the context of popular DAWs such as Ableton Live, Logic Pro, Pro Tools, FL Studio, and others, the export option is often prominently positioned within the main menu structure, denoting its significance in the overall music production workflow. By navigating to the designated export section, you gain access to a treasure trove of export-related features, encompassing audio formats, settings, and parameters tailored to accommodate diverse user preferences and project requirements.
Upon locating the export option, you may encounter a submenu or dialog box that presents an array of export formats and settings. It is within this interface that you will identify and select MIDI as the desired export format, signaling to the DAW that you intend to transform the selected audio content into MIDI data. This pivotal decision sets the stage for the conversion process, aligning the export operation with your creative intentions and technical specifications.
Furthermore, some DAWs offer customizable export settings, allowing users to fine-tune parameters such as tempo, time signature, and track routing before executing the export operation. This level of flexibility empowers musicians and producers to tailor the MIDI export process to suit the unique characteristics of their musical material, ensuring a seamless transition from audio to MIDI with precision and finesse.
By successfully locating the export option within your DAW and setting the stage for MIDI conversion, you embark on a transformative journey that transcends traditional audio boundaries, embracing the boundless potential of MIDI as a conduit for musical expression and innovation. This pivotal step propels us closer to the realization of our MIDI export aspirations, laying the groundwork for the subsequent stages of the export process.
In the following step, we will delve into the intricate process of choosing MIDI as the export format, unraveling the intricacies of format selection and its implications for the final MIDI output.
Step 4: Choose MIDI as the export format
Having successfully located the export option within your Digital Audio Workstation (DAW), the pivotal decision of choosing MIDI as the export format marks a significant milestone in the process of converting audio to MIDI. This crucial step aligns the export operation with the specific requirements and creative intentions, laying the foundation for a seamless transition from audio to MIDI data.
When presented with the array of export formats and settings within the DAW interface, the distinct option of MIDI stands out as a gateway to unlocking the transformative potential of musical information. By selecting MIDI as the export format, you signify your intent to harness the versatile nature of MIDI data, encapsulating the nuances of musical expression in a digital format that transcends traditional audio boundaries.
The choice of MIDI as the export format opens doors to a myriad of creative possibilities, allowing for the preservation and manipulation of musical elements with unparalleled flexibility. Whether you seek to extract melodic motifs from audio recordings, transfer rhythmic patterns between different software environments, or integrate expressive performances into electronic compositions, MIDI serves as a conduit for seamless musical exchange and adaptation.
Furthermore, the selection of MIDI as the export format empowers you to leverage the inherent advantages of MIDI data, including the ability to manipulate note events, adjust timing and velocity, and integrate with a wide range of virtual instruments and synthesizers. This level of adaptability and interoperability positions MIDI as a cornerstone of modern music production, offering a standardized format for capturing and transmitting musical ideas across diverse platforms and technologies.
In addition, the choice of MIDI as the export format may entail considerations of tempo, time signature, and track routing, allowing you to tailor the export process to suit the specific characteristics of your musical material. This level of customization ensures that the exported MIDI data aligns seamlessly with your creative vision, preserving the integrity of the original audio content while embracing the transformative potential of MIDI representation.
By choosing MIDI as the export format, you embark on a journey of musical transformation, harnessing the power of digital musical data to transcend conventional audio limitations. This pivotal decision propels us closer to the realization of our MIDI export aspirations, setting the stage for the subsequent stages of the export process.
Step 5: Set the export options
Once you have chosen MIDI as the export format within your Digital Audio Workstation (DAW), the next critical step involves setting the export options to fine-tune the parameters that will govern the MIDI conversion process. This stage empowers you to tailor the export operation to align with the specific characteristics of your audio content, ensuring a seamless transition to MIDI format with precision and finesse.
The export options may encompass a diverse range of settings, offering a comprehensive toolkit to accommodate various user preferences and project requirements. Among the key parameters that you may encounter within the export options interface are tempo, time signature, track routing, and MIDI channel assignments. These settings play a pivotal role in shaping the characteristics of the exported MIDI data, allowing you to exert meticulous control over the transformation process.
Adjusting the tempo setting enables you to dictate the pace and rhythmic feel of the MIDI output, ensuring that the converted musical information aligns harmoniously with the original audio material. Whether you seek to maintain the tempo integrity of the source audio or introduce deliberate variations to infuse the MIDI data with dynamic nuances, the tempo setting serves as a cornerstone for preserving the rhythmic essence of the music.
Similarly, the time signature setting offers a platform to define the rhythmic structure and phrasing of the MIDI output, providing a canvas for expressing the inherent musicality of the source material. By configuring the time signature parameters, you can imbue the MIDI data with the rhythmic intricacies and emotive cadences that define the essence of the original audio content.
Furthermore, the option to customize track routing and MIDI channel assignments empowers you to orchestrate the spatial and tonal characteristics of the exported MIDI data. This level of control enables you to designate specific MIDI channels for individual tracks, facilitating seamless integration with external MIDI devices and software instruments, while also ensuring clarity and organization within the MIDI output.
In addition to these fundamental settings, some DAWs offer advanced export options that delve into the intricacies of MIDI data manipulation, including quantization, velocity scaling, and pitch correction. These features provide a playground for refining the expressive nuances of the MIDI output, allowing you to sculpt the musical information with meticulous attention to detail.
By setting the export options with precision and care, you pave the way for a transformative MIDI conversion process that encapsulates the essence of the original audio content while embracing the boundless potential of MIDI as a conduit for musical expression and innovation. This pivotal stage propels us closer to the realization of our MIDI export aspirations, laying the groundwork for the subsequent stage of executing the MIDI export operation.
Step 6: Export the MIDI file
With the export options meticulously configured to align with the specific characteristics of the audio content, the final step in the process involves executing the MIDI export operation. This pivotal stage marks the culmination of meticulous preparation and deliberate decision-making, propelling the selected audio material into the realm of MIDI data with precision and finesse.
Initiating the MIDI export process within your Digital Audio Workstation (DAW) typically involves interacting with a dedicated export button or menu option, signaling to the software that you are ready to convert the selected audio content into MIDI format. This decisive action sets the wheels in motion for a seamless transition, harnessing the transformative power of MIDI as a conduit for musical expression and innovation.
Upon triggering the MIDI export operation, the DAW diligently processes the audio content based on the configured export options, encapsulating the nuances of pitch, timing, and dynamics within the digital realm of MIDI data. This transformation transcends traditional audio boundaries, capturing the essence of the original musical material while embracing the inherent flexibility and adaptability of MIDI representation.
As the export process unfolds, the DAW meticulously generates the MIDI file, encapsulating the musical information within a standardized format that facilitates interoperability and integration across diverse software platforms and hardware devices. The resulting MIDI file serves as a digital blueprint of the original audio content, preserving its expressive qualities and structural intricacies in a format that transcends the constraints of traditional audio recordings.
Upon successful completion of the export operation, the DAW presents the newly created MIDI file, ready for seamless integration into your music production workflow. This pivotal moment signifies the culmination of your efforts to convert audio to MIDI, unlocking a world of creative possibilities and musical exploration.
By executing the MIDI export operation with precision and care, you solidify the transition from audio to MIDI, harnessing the boundless potential of digital musical data to breathe new life into your creative endeavors. This transformative process empowers you to seamlessly integrate the MIDI file into your compositions, arrangements, and productions, leveraging the expressive depth and adaptability of MIDI to elevate your musical creations to new heights.
In the wake of the MIDI export operation, you stand poised to explore, manipulate, and innovate with the newly minted MIDI file, embarking on a journey of musical discovery and artistic expression fueled by the transformative power of MIDI representation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the process of exporting audio to MIDI represents a transformative journey that transcends traditional audio boundaries, unlocking a world of creative possibilities and musical exploration. By navigating through the fundamental steps of selecting, configuring, and executing the MIDI export operation within a Digital Audio Workstation (DAW), musicians, producers, and composers can harness the boundless potential of MIDI as a conduit for musical expression and innovation.
The journey begins with the opening of the DAW software, positioning the user within a creative workspace teeming with potential. The act of selecting the track or tracks for MIDI export signifies a deliberate focus on specific musical elements, setting the stage for a purposeful and efficient conversion process. Locating the export option within the DAW interface serves as a gateway to accessing a diverse range of export formats and settings, culminating in the pivotal decision to choose MIDI as the export format.
Setting the export options empowers users to fine-tune parameters such as tempo, time signature, and track routing, ensuring a seamless transition to MIDI format with precision and care. This meticulous preparation culminates in the execution of the MIDI export operation, marking the transformation of audio content into MIDI data with unparalleled flexibility and adaptability.
Ultimately, the journey concludes with the presentation of the newly created MIDI file, ready to seamlessly integrate into the music production workflow. This pivotal moment signifies the culmination of efforts to convert audio to MIDI, unlocking a world of creative possibilities and musical exploration. With the MIDI file at their disposal, users stand poised to explore, manipulate, and innovate, embarking on a journey of musical discovery and artistic expression fueled by the transformative power of MIDI representation.
In essence, the process of exporting audio to MIDI transcends mere technical operation; it represents a gateway to musical transformation and innovation. By embracing the boundless potential of MIDI, musicians and producers can breathe new life into their creative endeavors, leveraging the expressive depth and adaptability of MIDI to elevate their musical creations to new heights. As the journey concludes, the stage is set for a new chapter of musical exploration, driven by the transformative power of MIDI representation and the endless possibilities it affords to the creative mind.