Home>Production & Technology>MIDI>What Is MIDI Device?


MIDI
What Is MIDI Device?
Modified: February 22, 2024
Discover the power of MIDI devices and how they revolutionize music production. Learn about the versatility and functionality of MIDI technology.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
MIDI, which stands for Musical Instrument Digital Interface, is a pivotal technology that has revolutionized the way music is created, recorded, and performed. It serves as a universal language for electronic musical instruments, computers, and other audio devices, enabling them to communicate and synchronize with each other seamlessly. MIDI devices have become indispensable tools for musicians, producers, and audio engineers, facilitating the realization of creative visions and the production of high-quality music.
The widespread adoption of MIDI devices has significantly transformed the music industry, empowering artists to explore innovative sounds and express their musical ideas with unprecedented flexibility and precision. Whether used in professional recording studios, live performances, or home-based music production setups, MIDI devices have become integral components of modern music creation.
In this article, we will delve into the evolution, functionality, and diverse applications of MIDI devices. By understanding the history, types, and benefits of MIDI devices, as well as their role in music production, readers will gain valuable insights into the profound impact of this technology on the art and science of making music. Let's embark on a journey to unravel the fascinating world of MIDI devices and discover the boundless possibilities they offer to music enthusiasts and professionals alike.
History of MIDI Devices
The history of MIDI devices traces back to the early 1980s when there was a pressing need for a standardized protocol that could facilitate communication between various electronic musical instruments. Prior to the development of MIDI, each manufacturer had its own proprietary system for controlling and synchronizing musical equipment, leading to compatibility issues and limited interoperability. In response to this challenge, a consortium of leading music technology companies, including Roland, Yamaha, Korg, and others, collaborated to create a universal interface that would enable different devices to communicate effectively.
In 1983, the MIDI 1.0 specification was officially unveiled, marking a significant milestone in the evolution of electronic music technology. This groundbreaking standardization initiative laid the foundation for the seamless integration of synthesizers, drum machines, sequencers, and other electronic instruments, regardless of their brand or model. The introduction of MIDI revolutionized the music industry by providing a common language for musical devices, thereby empowering musicians and producers to harness the full potential of their equipment in a coherent and synchronized manner.
One of the key features that set MIDI apart was its ability to transmit not only musical note data but also control messages, allowing for the manipulation of parameters such as pitch, velocity, modulation, and more. This versatility opened up new horizons for creative expression and experimentation, as artists could now use MIDI to shape and mold their sounds with unprecedented precision and flexibility.
Over the years, MIDI technology has continued to evolve, with advancements such as the introduction of MIDI Time Code (MTC) and MIDI Show Control (MSC) further expanding its capabilities. These developments have facilitated the seamless integration of MIDI devices into diverse applications, including music production, live performances, theatrical productions, and multimedia installations.
The enduring legacy of MIDI devices is evident in their widespread adoption across the music industry and beyond. From professional recording studios to home-based music production setups, MIDI devices have become indispensable tools for musicians, producers, and sound engineers, empowering them to realize their creative visions with unparalleled control and efficiency.
In summary, the history of MIDI devices is a testament to the transformative power of technology in shaping the landscape of music creation and performance. The standardization and universal compatibility offered by MIDI have not only simplified the integration of electronic musical instruments but have also fostered a culture of innovation and artistic exploration, making MIDI a cornerstone of modern music production and expression.
Types of MIDI Devices
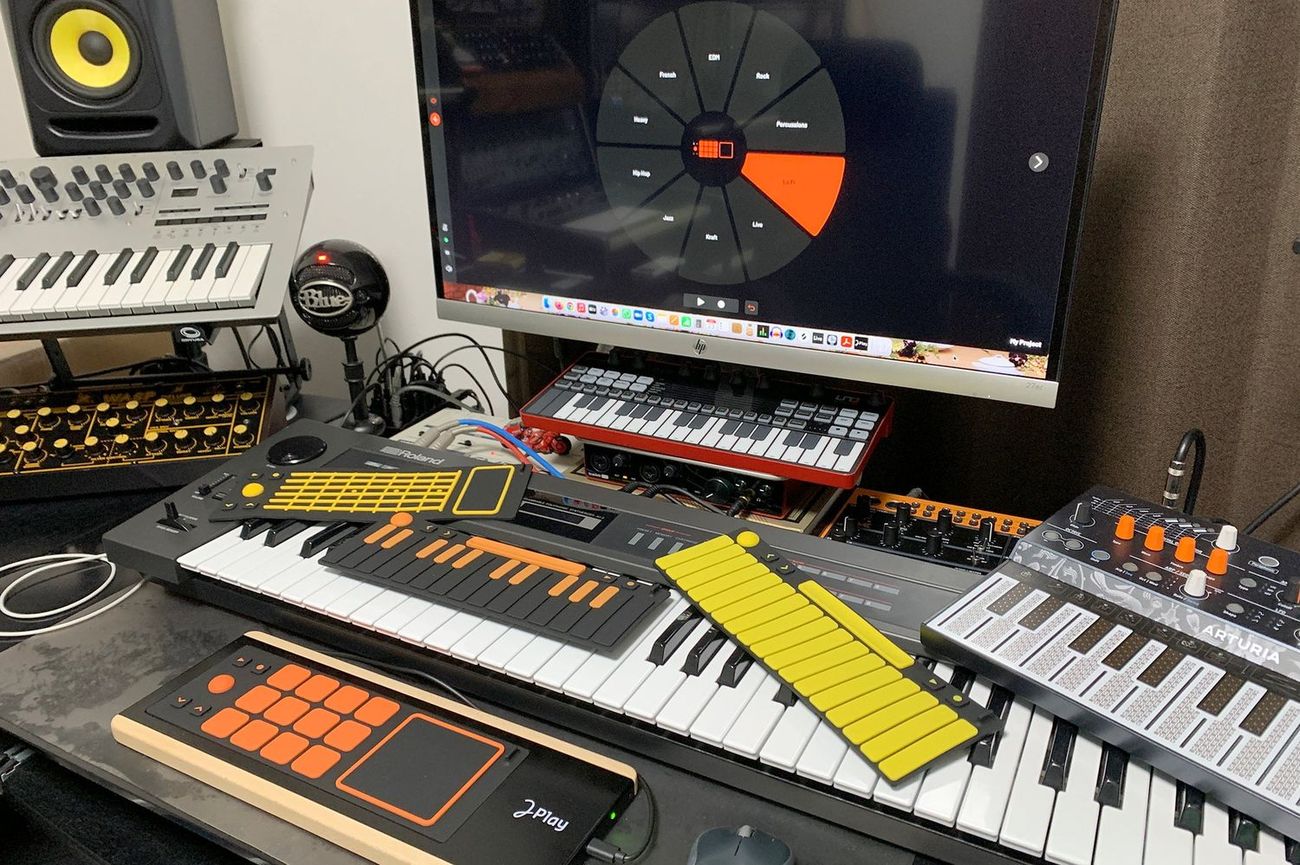
MIDI devices encompass a diverse array of tools and equipment that leverage the MIDI protocol to facilitate communication and control within the realm of music production and performance. These devices play a pivotal role in enabling musicians, producers, and audio engineers to harness the full potential of electronic musical instruments, computers, and audio hardware. Understanding the different types of MIDI devices is essential for grasping the breadth of their applications and the versatility they offer in various musical contexts.
-
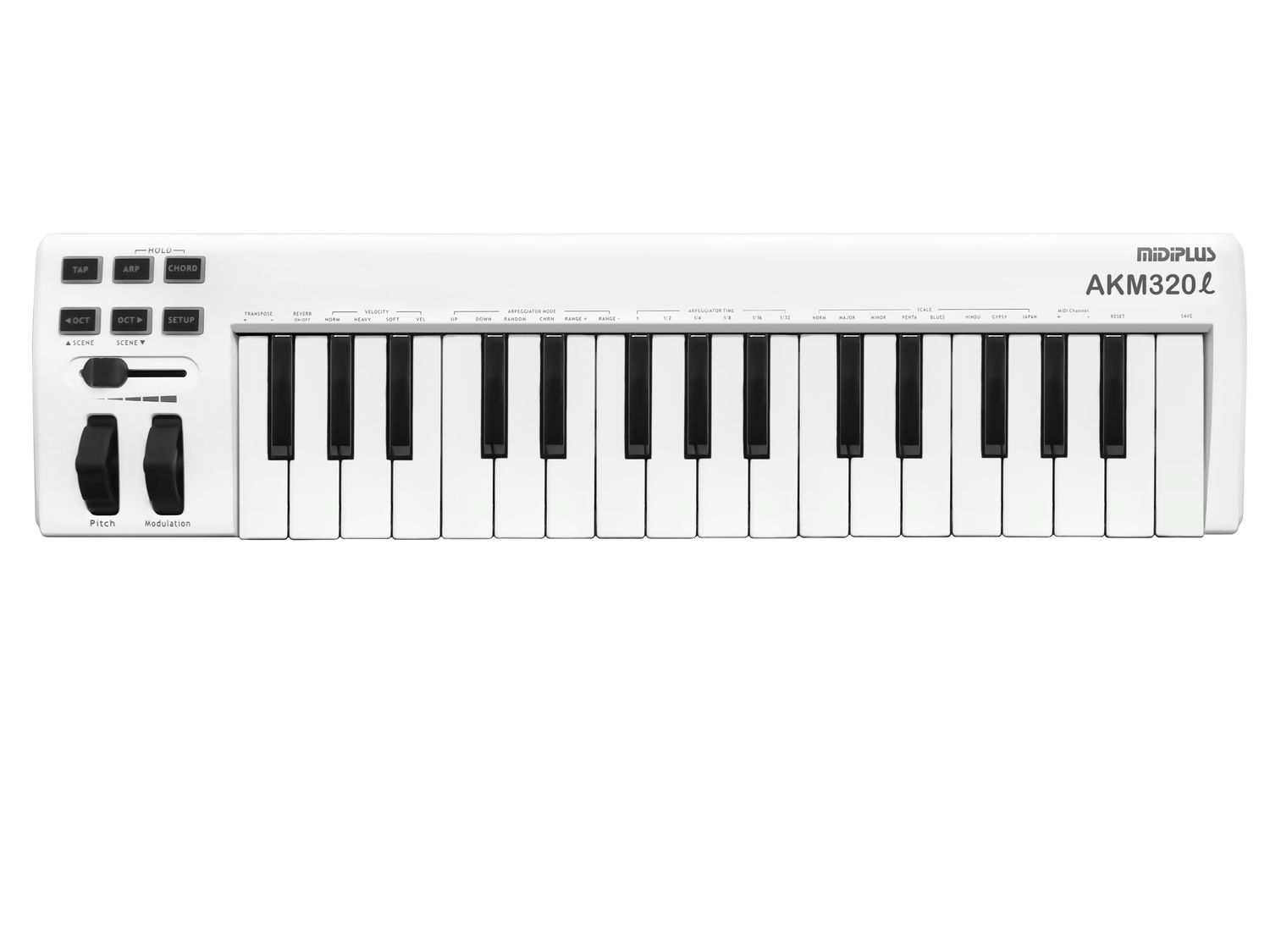
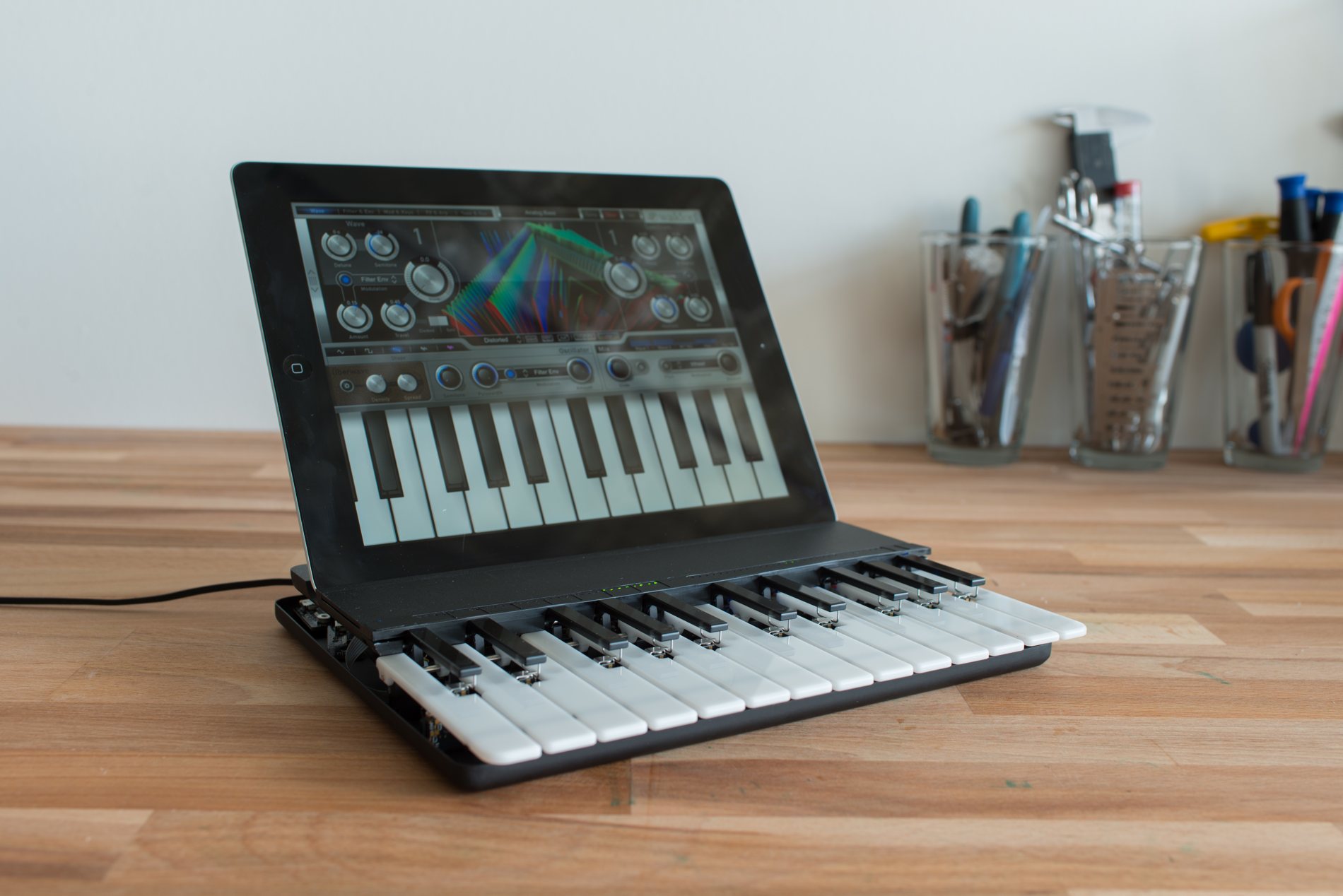
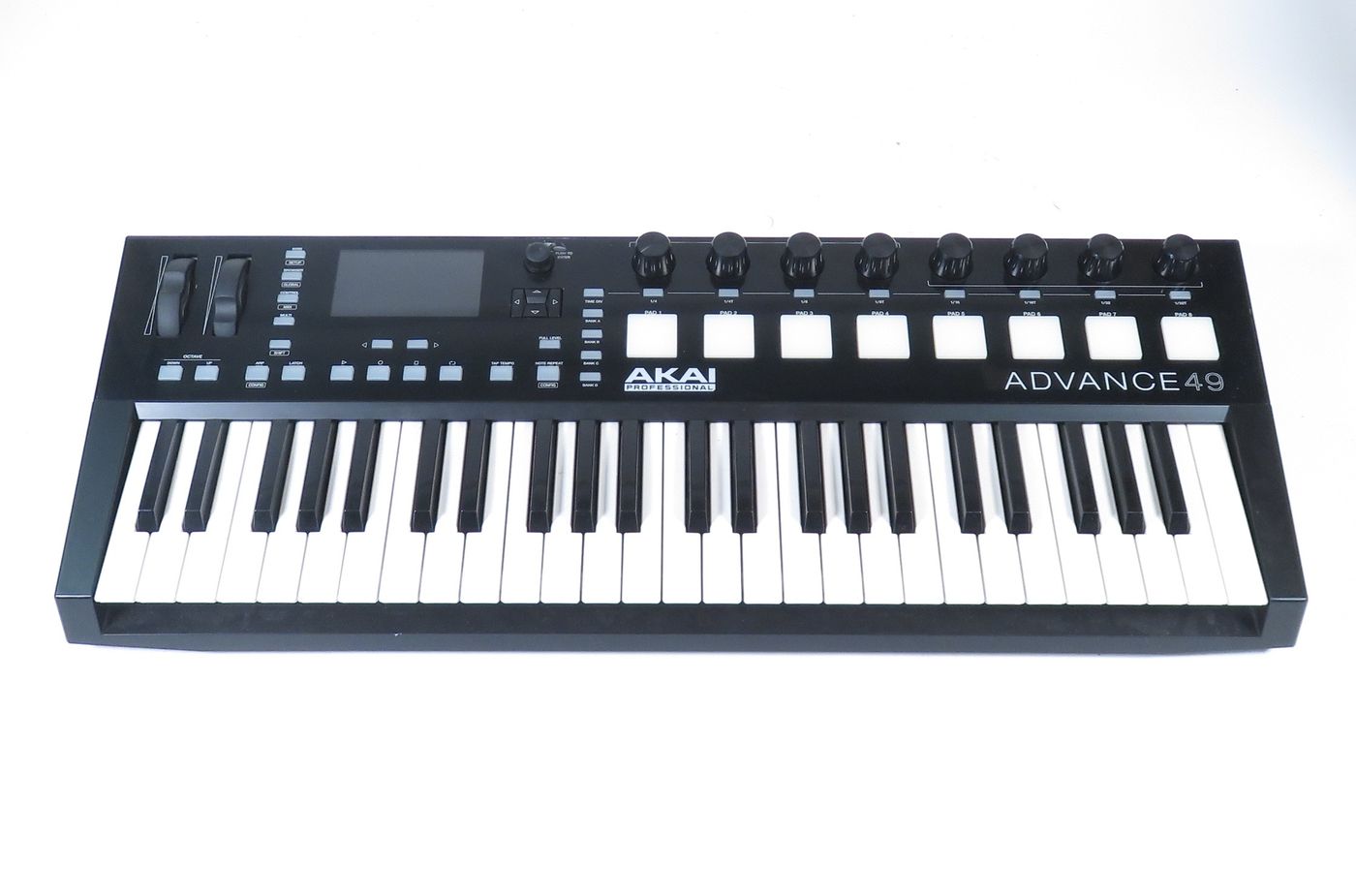
MIDI Keyboards: MIDI keyboards, also known as MIDI controllers, are perhaps the most ubiquitous type of MIDI device. These versatile instruments feature piano-style keys that transmit MIDI data to external devices, such as synthesizers, samplers, and digital audio workstations (DAWs). MIDI keyboards come in various configurations, including compact portable models and full-sized, weighted-key instruments, catering to the diverse needs and preferences of musicians and producers.
-
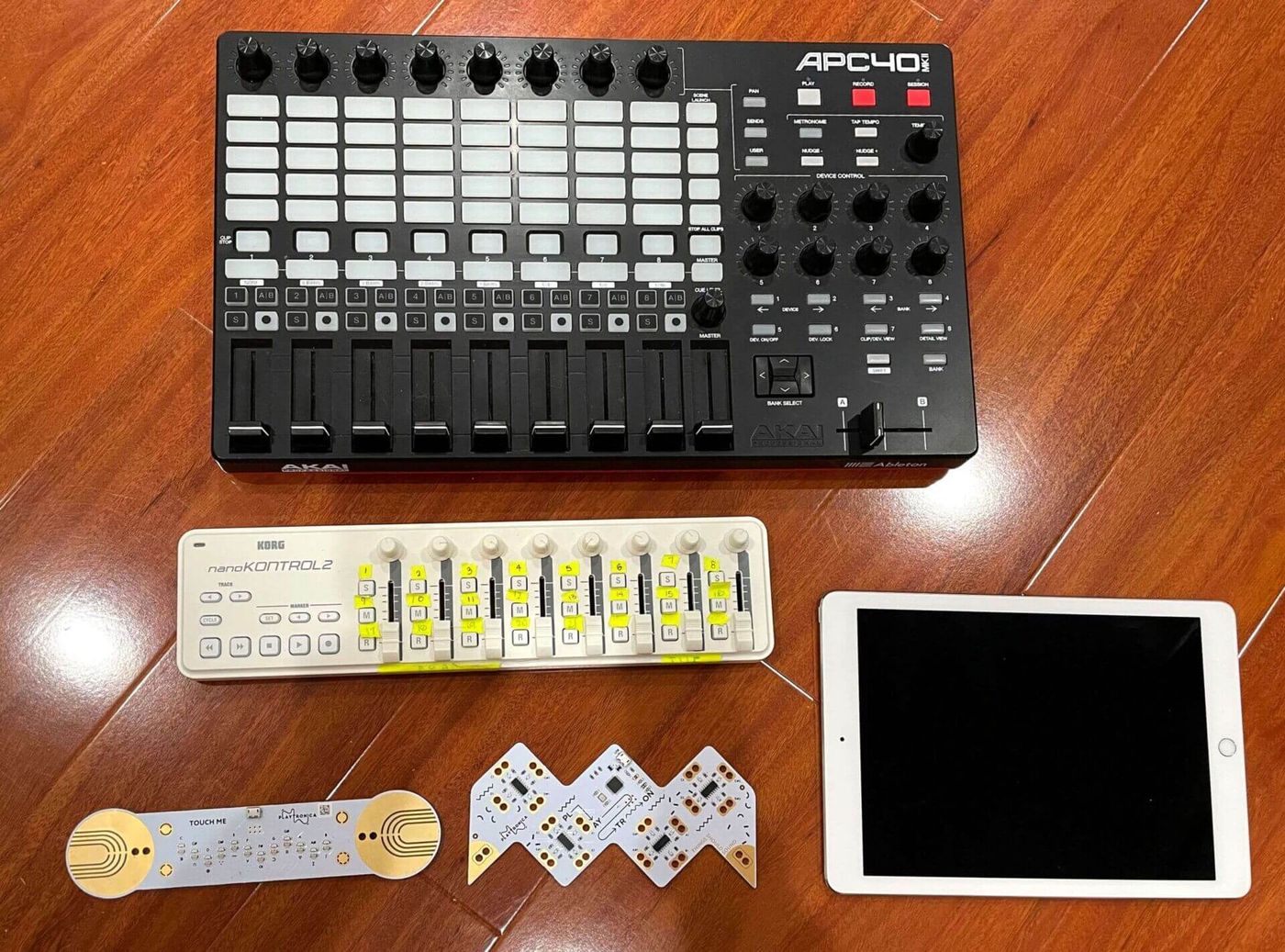
MIDI Pad Controllers: Designed for triggering samples, sequencing beats, and controlling various parameters within music production software, MIDI pad controllers offer a tactile and expressive interface for creating rhythm and texture. These devices typically feature an array of pressure-sensitive pads that can be assigned to trigger sounds, loops, and effects, providing intuitive hands-on control over musical elements.
-
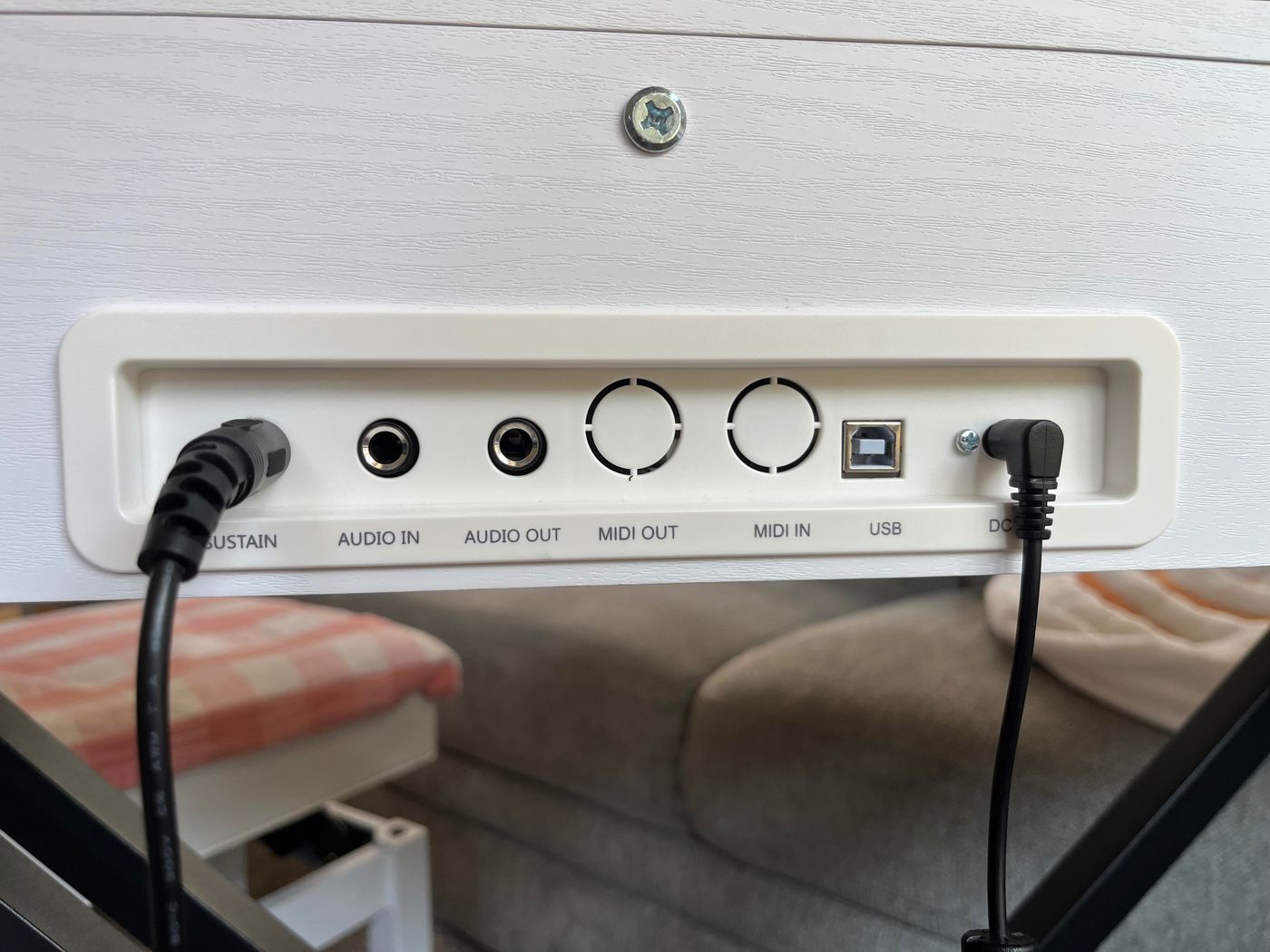
MIDI Interfaces: MIDI interfaces serve as the bridge between MIDI-equipped instruments and computers or other hardware devices. These interfaces facilitate the seamless transfer of MIDI data, allowing users to connect multiple MIDI instruments and controllers to a computer for recording, sequencing, and playback. MIDI interfaces come in various configurations, including USB, FireWire, and Ethernet connectivity options, catering to different setup requirements.
-
MIDI Drum Machines: As the name suggests, MIDI drum machines are specialized devices dedicated to producing and sequencing drum patterns and percussion sounds. These instruments offer a wide range of drum and percussion sounds, along with comprehensive sequencing capabilities, enabling users to create dynamic rhythm tracks and beats with precision and flair.
-
MIDI Synthesizers: MIDI synthesizers are electronic instruments that generate sound using various synthesis techniques, such as subtractive, additive, and wavetable synthesis. These instruments can be controlled and manipulated via MIDI, allowing for expressive performance and intricate sound design. MIDI synthesizers come in hardware and software formats, catering to different workflow preferences and sonic capabilities.
-
MIDI Foot Controllers: Designed for hands-free control over various parameters and functions, MIDI foot controllers are essential for musicians and performers who require on-the-fly access to effects, presets, and performance elements. These devices typically feature footswitches, expression pedals, and assignable controls, offering a versatile platform for enhancing live performances and studio setups.
-
MIDI Control Surfaces: MIDI control surfaces are dedicated hardware interfaces that provide tactile control over DAWs, virtual instruments, and software-based mixing environments. These surfaces feature faders, knobs, buttons, and displays, mirroring the functionality of traditional mixing consoles and offering an intuitive workflow for hands-on control and automation within music production and mixing.
In summary, the diverse landscape of MIDI devices encompasses a wide range of tools and instruments, each serving unique functions and catering to specific creative needs. From expressive MIDI keyboards and pad controllers to versatile interfaces and specialized synthesizers, MIDI devices continue to empower musicians and producers with the tools they need to craft compelling and innovative music.
How MIDI Devices Work
MIDI devices operate on a standardized protocol that enables the transmission of musical performance data, control signals, and synchronization information between interconnected instruments, computers, and audio hardware. At the core of MIDI communication are a set of commands and messages that convey musical gestures and performance parameters, allowing for seamless interaction and coordination within a musical setup.
When a musician plays a note on a MIDI keyboard or triggers a pad on a MIDI controller, the device translates the physical action into digital data in the form of MIDI messages. These messages typically include information such as note-on and note-off commands, pitch, velocity, and channel assignments, capturing the nuances of the performance with precision. This data is then transmitted via standard MIDI cables, USB connections, or wireless protocols to other MIDI-equipped devices within the setup.
Upon receiving the MIDI data, the receiving device interprets the messages and translates them into audible sound, control changes, or other designated actions. For example, a MIDI synthesizer processes note-on messages to trigger the generation of sound, while a MIDI drum machine utilizes MIDI note data to produce rhythmic patterns and percussive elements. In addition to musical note data, MIDI messages also encompass control information, such as modulation, pitch bend, and sustain commands, enabling expressive manipulation of sound parameters and performance nuances.
In the realm of music production, MIDI devices play a crucial role in facilitating the creation, recording, and manipulation of musical elements. Digital audio workstations (DAWs) leverage MIDI data to sequence virtual instruments, trigger samples, and automate parameters, offering a flexible and dynamic environment for composing and arranging music. MIDI interfaces enable seamless integration between hardware instruments and software environments, allowing for the seamless exchange of MIDI data for recording and playback.
Furthermore, MIDI devices are designed to operate on multiple channels, enabling the simultaneous control and communication of diverse musical elements within a setup. This multi-channel capability empowers musicians and producers to orchestrate complex arrangements, layer sounds, and create intricate performances with ease. Whether used in a studio recording session, live performance, or multimedia production, MIDI devices provide a versatile and adaptable framework for realizing creative visions and musical expressions.
In essence, MIDI devices function as the conduits of musical expression and control, enabling seamless communication and interaction between diverse musical instruments and technology. By harnessing the power of MIDI, musicians and producers can unlock a world of creative possibilities, shaping and sculpting sound with precision, passion, and innovation.
Benefits of Using MIDI Devices
MIDI devices offer a myriad of benefits that significantly enhance the music creation and production process, empowering musicians, producers, and audio engineers with unparalleled control, flexibility, and creative potential. These benefits span across various aspects of music production and performance, making MIDI devices indispensable tools in modern music-making. Let's explore the compelling advantages of using MIDI devices:
-
Versatility and Interoperability: MIDI devices facilitate seamless integration and communication between a wide range of musical instruments, software applications, and audio hardware. This interoperability allows musicians to combine diverse sound sources, control parameters, and performance elements within a unified ecosystem, fostering limitless creative possibilities.
-
Expressive Control and Performance: MIDI devices enable musicians to imbue their performances with nuanced expression and dynamics. From manipulating note velocities and articulations to applying real-time control changes, MIDI empowers performers to convey emotion and musicality with precision, adding depth and authenticity to their music.
-
Efficient Composition and Arrangement: In the realm of music production, MIDI devices streamline the composition and arrangement process, offering a non-destructive and flexible workflow. Musicians can easily edit, rearrange, and manipulate MIDI data within a digital audio workstation (DAW), allowing for iterative exploration and refinement of musical ideas.
-
Sound Design and Synthesis Flexibility: MIDI devices, particularly MIDI synthesizers and controllers, provide a rich palette for sound design and synthesis exploration. With MIDI, users can modulate, layer, and sculpt sonic textures and timbres, unleashing their creativity in shaping unique and captivating sounds.
-
Automation and Precision: MIDI facilitates precise automation of parameters, enabling users to program intricate changes in volume, panning, effects, and other sonic attributes. This level of automation empowers producers to craft polished and dynamic mixes, adding depth and movement to their productions.
-
Live Performance Capabilities: MIDI devices play a pivotal role in live performances, offering musicians real-time control over instruments, effects, and backing tracks. From triggering samples and loops to manipulating sound parameters on the fly, MIDI empowers performers to deliver captivating and immersive live experiences.
-
Streamlined Recording and Editing: MIDI devices simplify the recording and editing process, allowing for accurate capture and manipulation of musical performances. MIDI data can be easily edited, quantized, and fine-tuned to achieve precise musical phrasing and timing, enhancing the overall quality of recorded tracks.
-
Scalability and Expandability: MIDI setups can be easily expanded and scaled to accommodate evolving creative needs. Whether integrating new instruments, controllers, or software, MIDI provides a modular framework for building versatile and personalized music production environments.
In essence, the benefits of using MIDI devices encompass a wide spectrum of advantages, ranging from expressive performance capabilities to streamlined production workflows. By harnessing the power of MIDI, musicians and producers can elevate their creative output, realizing their musical visions with precision, artistry, and innovation.
Common MIDI Devices in Music Production
In the realm of music production, a diverse array of MIDI devices serves as indispensable tools for shaping, recording, and manipulating musical elements with precision and creativity. These devices play pivotal roles in empowering musicians, producers, and sound engineers to craft compelling compositions, dynamic arrangements, and immersive sonic experiences. Let's explore some of the common MIDI devices that are integral to the music production process:
MIDI Keyboards:
MIDI keyboards, also known as MIDI controllers, stand as ubiquitous instruments in music production setups. They provide a tactile interface for playing and controlling virtual instruments, synthesizers, and samplers within digital audio workstations (DAWs). With a range of key configurations and expressive features, MIDI keyboards enable musicians to perform, record, and manipulate melodic and harmonic elements with nuanced expression and fluidity.
MIDI Pad Controllers:
Designed for rhythmic composition, beat production, and sample triggering, MIDI pad controllers offer a dynamic platform for creating percussive patterns, triggering loops, and manipulating rhythmic elements within music production software. Equipped with pressure-sensitive pads and assignable controls, these devices empower producers to craft intricate drum patterns, dynamic grooves, and textured rhythmic layers with intuitive hands-on control.
MIDI Interfaces:
MIDI interfaces serve as the bridge between MIDI-equipped instruments and computers, facilitating the seamless exchange of MIDI data for recording, sequencing, and playback. These interfaces come in various connectivity options, including USB, FireWire, and Ethernet, providing versatile solutions for integrating hardware synthesizers, drum machines, and controllers into digital production environments.
MIDI Drum Machines:
Dedicated to rhythm production and percussion sequencing, MIDI drum machines offer a comprehensive suite of drum and percussion sounds, along with intuitive sequencing capabilities. These devices enable users to create dynamic and expressive rhythm tracks, layering beats, and crafting intricate percussive arrangements with precision and flair.
MIDI Synthesizers:
MIDI synthesizers, available in hardware and software formats, unlock a world of sonic exploration and sound design possibilities. These instruments leverage MIDI control to shape and modulate intricate timbres, textures, and musical motifs, offering a versatile palette for crafting unique and evocative sounds within music productions.
MIDI Control Surfaces:
Dedicated hardware interfaces, such as MIDI control surfaces, provide tactile control over DAWs, virtual instruments, and software-based mixing environments. With faders, knobs, and transport controls, these surfaces offer an intuitive platform for hands-on mixing, automation, and parameter manipulation, enhancing the precision and fluidity of music production workflows.
In summary, these common MIDI devices form the backbone of music production setups, offering versatile and expressive tools for composing, arranging, and producing music with finesse and artistry. Whether used in professional studios, home-based production environments, or live performance setups, these devices empower creators to realize their musical visions with unparalleled control and creativity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, MIDI devices have profoundly shaped the landscape of music production and performance, offering a versatile and interconnected framework for musicians, producers, and sound engineers to realize their creative visions with precision and artistry. From the early standardization efforts that led to the development of the MIDI protocol to the diverse array of MIDI devices available today, the evolution of MIDI technology has been synonymous with innovation, collaboration, and the democratization of musical expression.
The history of MIDI devices reflects a transformative journey, marked by the unification of disparate musical technologies and the empowerment of artists to explore new sonic frontiers. The introduction of MIDI not only streamlined the integration of electronic musical instruments but also catalyzed a culture of experimentation and sonic exploration, fueling the evolution of music genres and production techniques.
The diverse types of MIDI devices, including MIDI keyboards, pad controllers, interfaces, synthesizers, and drum machines, exemplify the breadth of creative possibilities offered by this technology. These devices serve as conduits for expressive performance, rhythmic composition, sound design, and seamless integration within digital production environments, enriching the musical landscape with their versatility and adaptability.
The functionality of MIDI devices, rooted in the transmission of musical data, control signals, and synchronization information, underscores their pivotal role in facilitating efficient composition, expressive performance, and precise control over musical elements. Whether used in studio recording sessions, live performances, or multimedia productions, MIDI devices provide a cohesive and interconnected ecosystem for realizing musical ideas with finesse and ingenuity.
Furthermore, the benefits of using MIDI devices, spanning from versatility and expressive control to streamlined production workflows and live performance capabilities, underscore their indispensable role in modern music-making. These devices empower musicians and producers to transcend traditional boundaries, unleashing their creativity and shaping captivating sonic experiences that resonate with audiences worldwide.
In essence, MIDI devices stand as pillars of innovation and creativity, offering a dynamic and interconnected framework for musical expression and production. As technology continues to evolve and new creative horizons emerge, MIDI devices remain at the forefront, empowering artists to push the boundaries of sonic artistry and craft immersive musical experiences that captivate and inspire.