Home>Production & Technology>Audio Cable>Where To Plug In Microphone And Audio Cable In


Audio Cable
Where To Plug In Microphone And Audio Cable In
Modified: February 17, 2024
Find out where to plug in your microphone and audio cable for seamless audio connectivity. Improve your audio setup with our easy-to-follow guide.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of audio cables and microphones! These essential components are the backbone of any audio setup, allowing you to capture and transmit sound with clarity and precision. Whether you’re a musician, podcaster, or audio enthusiast, understanding how to properly connect microphones and audio cables is crucial for achieving professional-grade audio quality.
In this article, we will explore the intricacies of microphone and audio cable connections. We’ll discuss the various types of microphones and audio cables available, as well as where to plug them in for optimal performance. So, whether you’re setting up a home recording studio or preparing for a live performance, let’s dive into the world of microphone and audio cable connections!
Before we delve into the technical aspects, it’s important to note that the specific setup and connections may vary depending on your equipment. Always refer to the user manuals and guidelines provided by the manufacturers of your microphones and audio cables for accurate instructions.
Now, let’s start with the basics – microphone connections.
Microphone Connection
When it comes to connecting a microphone, there are a few key factors to consider. The type of microphone, the connection interface, and the power requirements are all important aspects that determine how and where you should plug in your microphone.
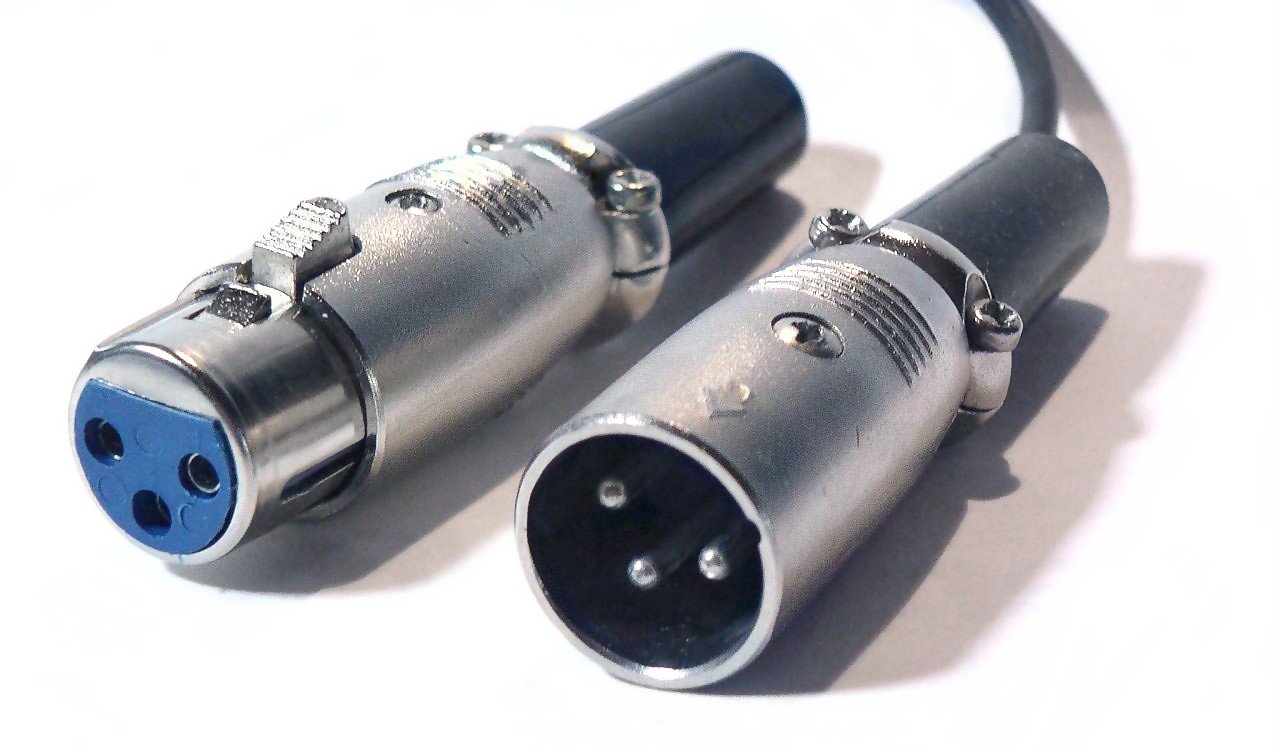
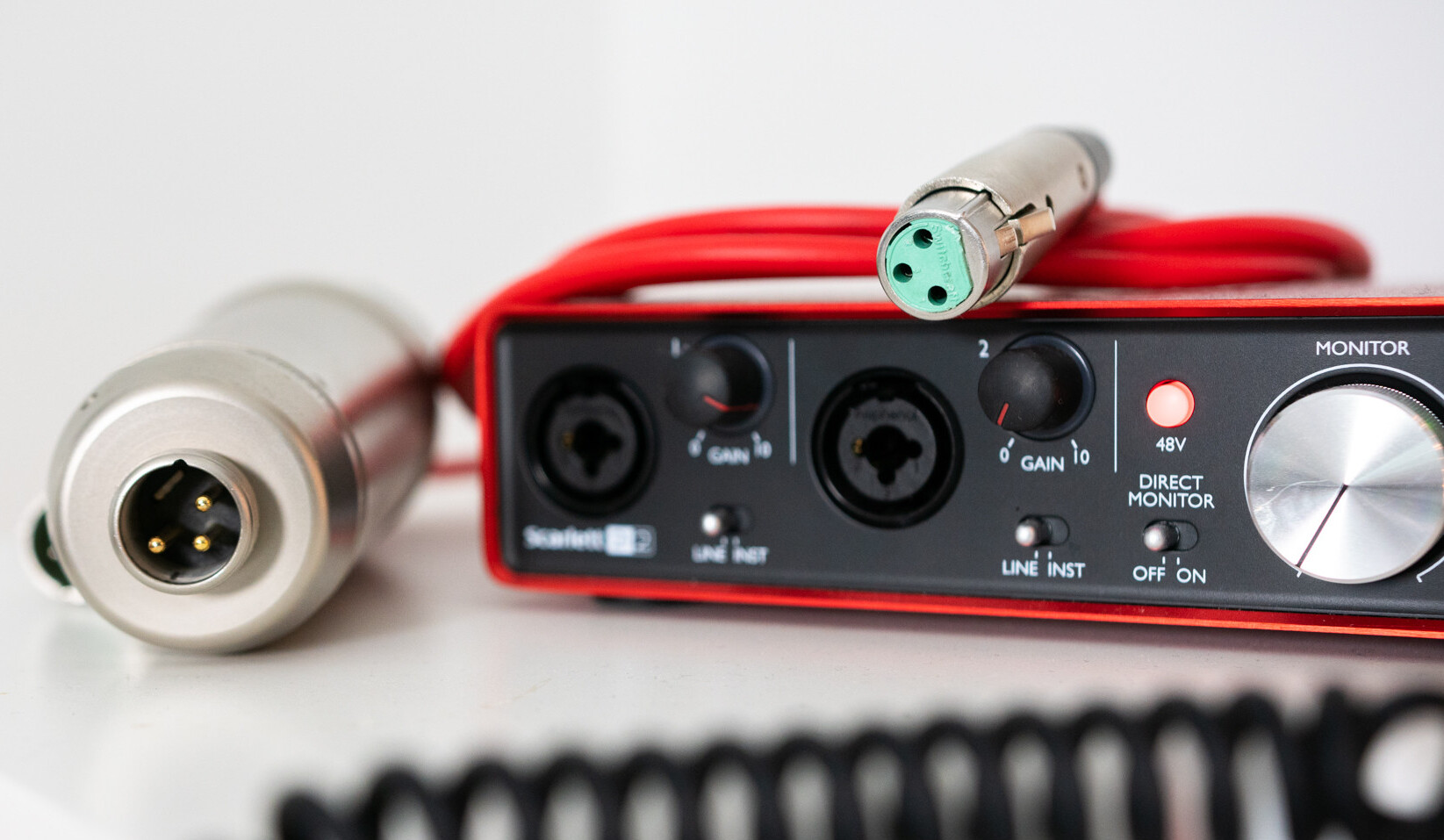
The most common types of microphones are dynamic microphones and condenser microphones. Dynamic microphones are rugged and versatile, making them ideal for live performances and recording in loud environments. They typically have an XLR connection, which is a three-pin connector known for its balanced audio signal.
To connect a dynamic microphone, locate the XLR input on your audio interface, mixer, or preamp. The XLR cable has three pins that correspond to the three holes in the XLR input. Simply align the pins with the holes and gently push the XLR connector in until it clicks into place. Ensure a snug fit to avoid any unwanted noise or disconnections during your recording or performance.
Condenser microphones, on the other hand, are known for their sensitivity and accuracy, making them popular among studio recording artists and podcasters. They often require phantom power to operate, which is a low-voltage electrical current that powers the microphone. Phantom power is usually provided by audio interfaces, mixers, or preamps that have a dedicated switch or button for enabling it.
To connect a condenser microphone, first, make sure the phantom power is turned off. Then, locate the XLR input and connect the microphone using the same method described for dynamic microphones. Once the microphone is securely connected, you can switch on the phantom power to provide the necessary voltage for the microphone to function.
Some microphones, such as USB microphones, have a built-in analog-to-digital converter, allowing them to be connected directly to your computer via a USB port. These microphones eliminate the need for additional audio interfaces or mixers and are generally easier to set up.
Now that we’ve covered microphone connections, let’s move on to audio cable connections.
Audio Cable Connection
Audio cables are essential for connecting various audio devices such as microphones, instruments, mixers, speakers, and audio interfaces. Understanding the different types of audio cables and their connection options is crucial for achieving optimal audio performance.
One of the most commonly used audio cables is the XLR cable. As mentioned earlier, XLR cables are often used for connecting microphones with XLR outputs. However, they can also be used for other audio devices such as mixers and audio interfaces. XLR cables come in various lengths, typically ranging from 3 to 25 feet.
To connect an XLR cable, simply plug one end of the cable into the XLR output of your audio device, and the other end into the corresponding XLR input of your destination device. Ensure a snug fit to avoid any loose connections that may cause audio distortion or disruptions.
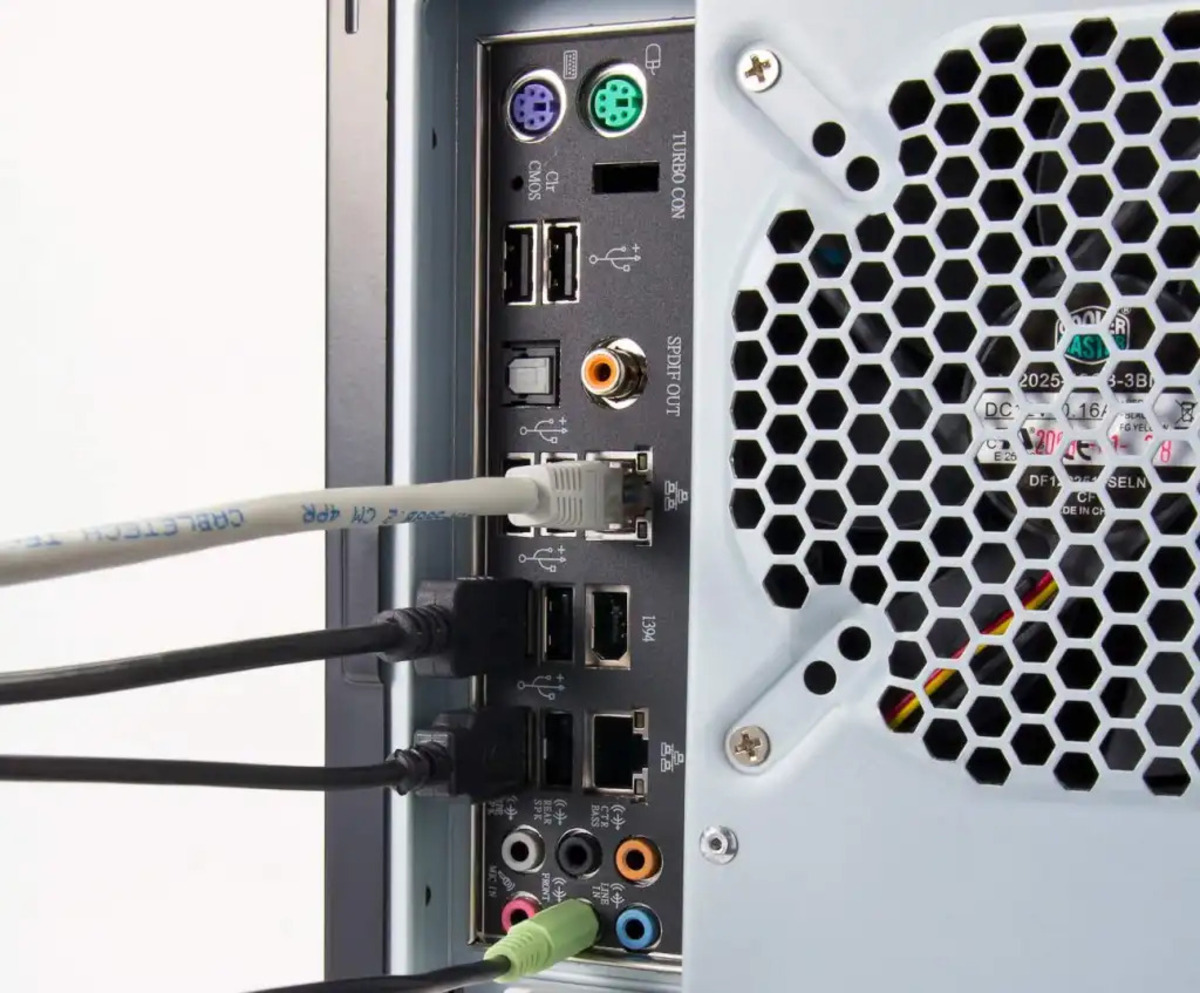
Another popular type of audio cable is the quarter-inch (6.35mm) TRS (Tip-Ring-Sleeve) cable. This cable is commonly used for connecting instruments, headphones, and speakers. The TRS cable has two rings on its connector, allowing for stereo or balanced audio transmission.
To connect a TRS cable, insert one end of the cable into the output or input jack of your audio device, and the other end into the corresponding jack of your destination device. Make sure the connector is aligned with the jack and gently push it in until it is firmly connected.
For digital audio transmission, such as connecting audio interfaces to computers or other digital devices, the USB cable is the standard choice. USB cables offer fast and reliable data transfer, enabling high-quality audio recording and playback.
To connect a USB cable, plug one end into the USB output of your audio interface or digital device, and the other end into a USB port on your computer or another compatible device. USB cables are typically plug-and-play, meaning they are automatically recognized by your computer or device without the need for additional drivers.
It’s worth noting that there are many other types of audio cables available, such as RCA, TRRS, and optical cables, which are commonly used for specific audio connections. Always consult the user manuals of your devices to determine the appropriate cable type and connection method.
With your microphones and audio cables properly connected, you’re now ready to embark on your audio journey with confidence and clarity.
Conclusion
Understanding and mastering the art of connecting microphones and audio cables is essential for anyone looking to achieve professional-grade audio quality. Whether you’re a musician, podcaster, or audio enthusiast, knowing where to plug in your microphones and audio cables will enable you to capture and transmit sound with clarity and precision.
When it comes to microphone connections, it’s important to consider the type of microphone you’re using, the connection interface it requires, and any power requirements. Dynamic microphones typically use XLR cables and can be plugged into the XLR input of your audio interface, mixer, or preamp. Condenser microphones often require phantom power and are connected in the same way as dynamic microphones, with the addition of enabling the phantom power switch. USB microphones have a built-in analog-to-digital converter and can be directly connected to your computer via a USB port.
Audio cable connections play a vital role in transmitting audio signals between various devices. XLR cables are commonly used for microphones, while TRS cables are suitable for instruments, headphones, and speakers. USB cables are ideal for digital audio transmission between audio interfaces and computers. Remember to select the appropriate cable type and ensure a secure connection for optimal audio performance.
It’s important to consult the user manuals and guidelines provided by your microphone and audio cable manufacturers to ensure accurate and proper connections. Every setup may have slight variations, so following the manufacturer’s instructions is crucial.
By understanding how to connect microphones and audio cables, you’ll have the foundation to create professional-quality recordings, perform live with confidence, or simply enjoy high-fidelity audio in your home setup. So, let your creativity flow, and explore the possibilities that the world of audio has to offer!