Home>Production & Technology>Background Music>How To Reduce Volume To Make It Background Music

Background Music
How To Reduce Volume To Make It Background Music
Modified: January 22, 2024
Learn how to reduce the volume of your audio files and transform them into background music. Find step-by-step instructions and tips to create the perfect ambiance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Background music plays a crucial role in various forms of media, including videos, presentations, podcasts, and even websites. It enhances the overall experience and sets the mood for the content. However, there are times when the volume of the background music needs to be reduced to ensure that it doesn’t overpower the primary audio or distract the viewers.
In this article, we will explore different techniques that can be used to reduce the volume of background music effectively. By implementing these techniques, you can strike the right balance between the background music and other audio elements, creating a seamless and engaging experience for your audience.
Before diving into the techniques, it is important to understand the importance of background music and its impact on the overall content. Background music helps create an emotional connection with the audience, evoking certain feelings or enhancing the narrative. It can intensify the suspense, add depth to the storyline, or create a sense of calmness.
However, when the volume of the background music is too high, it can become overpowering and distract the listeners from the main audio or dialogue. This is especially important in videos or presentations where clear communication is essential.
Now, let’s explore the various techniques that can be employed to reduce the volume of background music while preserving its impact and effectiveness.
Understanding the Importance of Background Music
Background music is more than just a filler for the silence. It has the power to transform the entire audiovisual experience, making it more engaging and memorable. Here are a few reasons why background music is important:
- Setting the Mood: Background music can instantly set the tone and mood of the content. Whether it’s a suspenseful scene in a movie or an uplifting message in a presentation, the right choice of music can evoke specific emotions and enhance the overall impact.
- Creating a Memorable Brand Identity: Consistently using background music with a certain style or theme can establish a recognizable brand identity. Think of how the opening jingle of a TV show or the background music in a commercial instantly brings to mind the associated brand. It helps in creating a strong brand association and leaving a lasting impression on the audience.
- Increasing Engagement: Background music adds an extra layer of interest and captivates the attention of the audience. It can heighten the overall sensory experience and make the content more engaging. By holding the listener’s interest, background music can improve comprehension, retention, and overall enjoyment of the content.
- Enhancing Visuals: Background music can complement the visuals and enhance their impact. It can synchronize with the on-screen action or create a contrast to create a more powerful visual experience. It helps in creating a cohesive audiovisual package that captivates the viewers’ attention.
- Transitioning Between Scenes: Background music can smooth out transitions between different scenes or segments of content. It fills the gap between the audio tracks and creates a seamless flow, making the viewing experience more cohesive.
When used effectively, background music can elevate the quality of various forms of media, making them more memorable, emotionally impactful, and engaging. However, it is essential to strike the right balance between the background music and other audio elements in order to ensure that it remains in the background and doesn’t overpower the primary audio or dialogue. In the following sections, we will explore techniques to effectively reduce the volume of background music without compromising its impact.
Techniques to Reduce Volume
Reducing the volume of background music requires careful consideration and the use of appropriate techniques to maintain the desired impact of the music. Here are several effective techniques that can be employed:
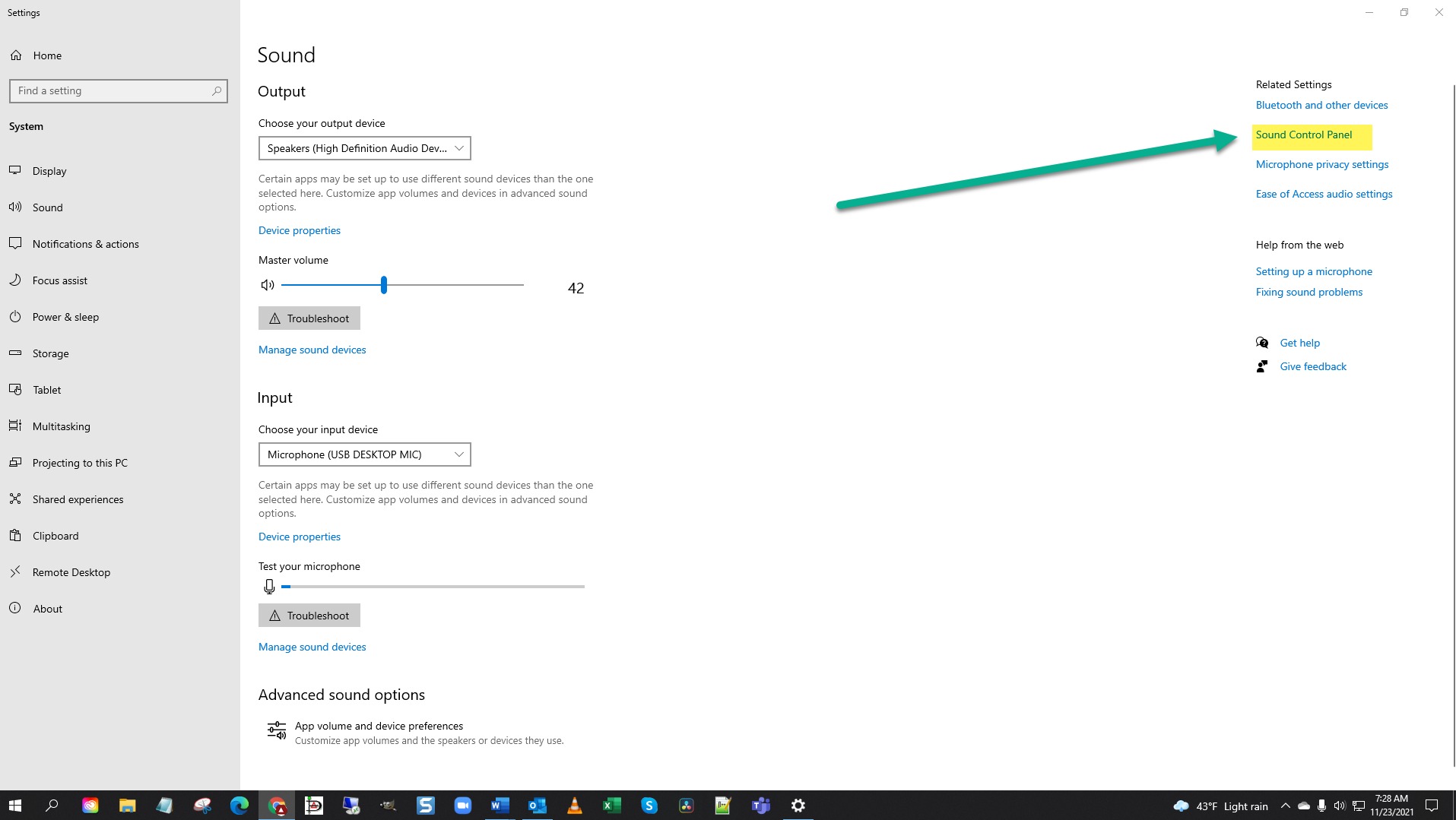
- Adjusting Volume Levels: One of the simplest ways to reduce the volume of background music is by adjusting the volume levels manually. Most audio editing software and media players have volume controls that allow you to decrease the volume of specific tracks. This technique works well when you have individual control over the background music and other audio elements.
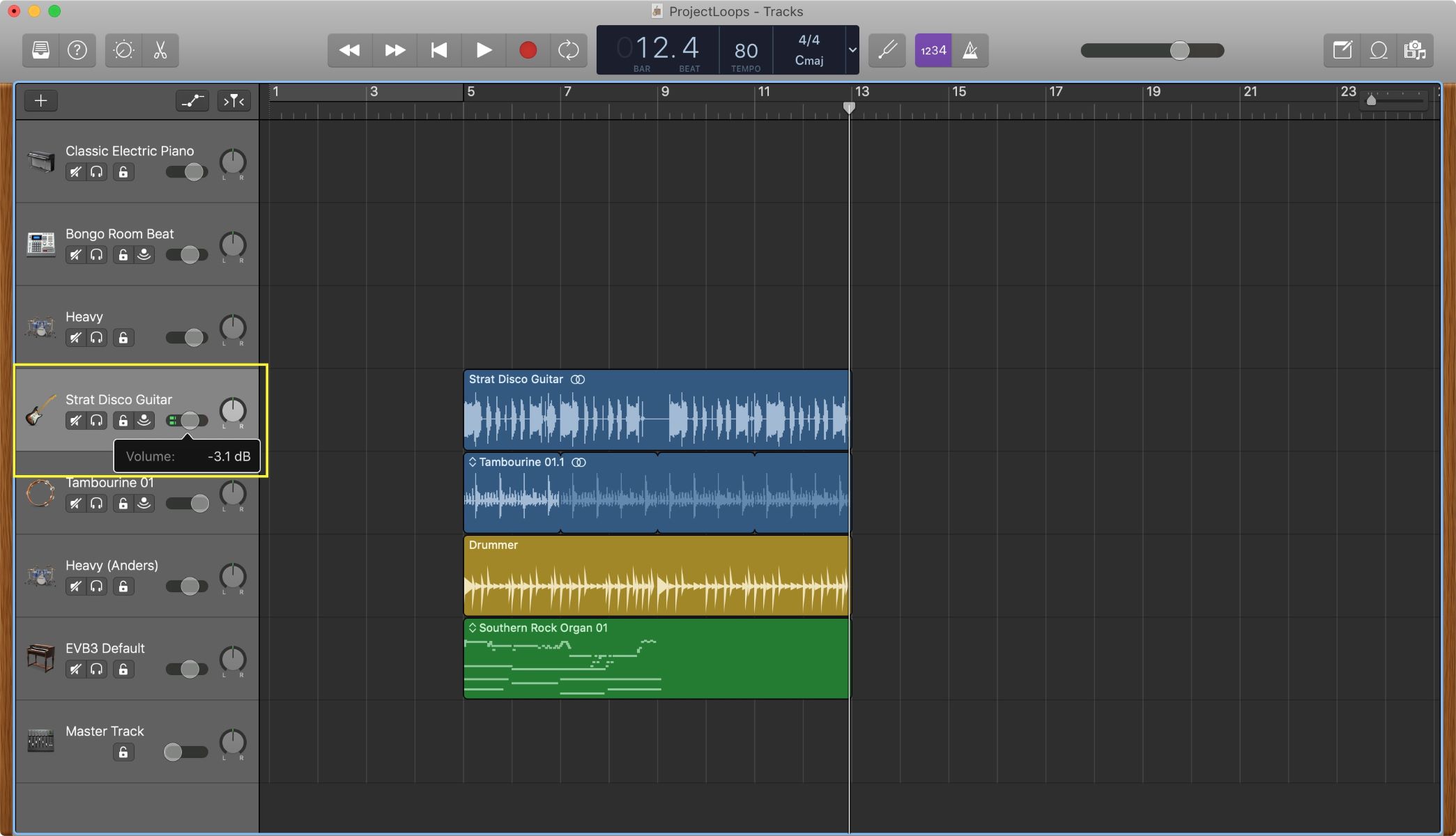
- Using Audio Editing Software: Audio editing software such as Audacity, Adobe Audition, or GarageBand provide advanced tools and features to manipulate and fine-tune audio tracks. With these tools, you can precisely control the volume of background music, apply fades, and make other adjustments to ensure it remains in the background while preserving its impact.
- Applying Audio Effects: Many audio editing software also offer a range of audio effects that can be used to alter the volume and characteristics of the background music. For example, you can use the “Ducking” effect, which automatically lowers the volume of the background music when the primary audio or dialogue is playing. This technique ensures that the background music doesn’t overpower the main audio.
- Utilizing Equalization: Equalization (EQ) allows you to adjust the frequency balance of the background music. By reducing specific frequencies that clash with the primary audio, you can create more space and separation between the two elements. This helps in reducing the dominance of background music without completely eliminating it.
- Employing Compression Techniques: Compression is a widely used audio processing technique that helps in controlling the dynamic range of the background music. By compressing the volume peaks and boosting the soft sections, you can create a more balanced and controlled sound. This technique helps in reducing the overall volume of the background music without sacrificing its impact.
- Mixing Audio Layers: When working with multiple audio layers, such as voiceovers, dialogue, and background music, careful mixing is essential. By adjusting the volume levels and panning of each layer, you can create a cohesive blend where the background music complements the primary audio without overpowering it. This technique requires a bit of experimentation and fine-tuning to achieve the desired balance.
It is important to remember that every situation is unique, and the technique used to reduce the volume of background music may vary. Experimentation and careful listening are key in finding the right balance between the background music and other audio elements. By employing these techniques, you can ensure that the background music remains in the background, providing a seamless and enhanced audiovisual experience for your audience.
Adjusting Volume Levels
One of the simplest and most straightforward techniques to reduce the volume of background music is by manually adjusting the volume levels. This technique works well when you have individual control over the background music and other audio elements.
Most audio editing software, media players, and mixing consoles provide volume controls that allow you to decrease the volume of specific tracks. By lowering the volume of the background music, you can ensure that it remains in the background and doesn’t overpower the primary audio or dialogue.
To adjust the volume levels, follow these steps:
- Identify the volume control: Locate the volume control for the background music track. It may be a physical knob on the mixing console or a software slider in audio editing software or media players.
- Gradually decrease the volume: Start by gradually reducing the volume of the background music. Listen carefully to the overall balance between the background music and other audio elements. Make small adjustments until you achieve the desired balance where the background music remains audible but not overpowering.
- Test with other audio elements: Play the primary audio or dialogue along with the background music to ensure that the volume levels are adjusted correctly. Pay attention to how well the primary audio is heard and understood in relation to the background music. If necessary, make further adjustments to fine-tune the balance.
- Preview and adjust as needed: After adjusting the volume levels, play through the content to listen to the overall effect. If any section stands out as too loud or too soft, go back and make additional adjustments to ensure a consistent and balanced audio mix throughout.
Adjusting volume levels is a simple but effective technique to reduce the volume of background music. It allows you to have precise control over the audio mix and maintain a harmonious balance between the background music and other audio elements. Experiment with different volume settings to find the optimal balance that enhances the overall audiovisual experience without overpowering the primary audio or dialogue.
Using Audio Editing Software
Audio editing software provides advanced tools and features that empower you to manipulate and fine-tune audio tracks with precision. By using audio editing software such as Audacity, Adobe Audition, or GarageBand, you can effectively reduce the volume of background music while maintaining its impact.
Here’s how you can use audio editing software to reduce the volume of background music:
- Import the audio file: Open the audio editing software and import the audio file containing the background music.
- Select the background music track: Identify the specific track or section of the audio file that contains the background music.
- Access volume controls: Look for volume controls or level adjustments within the software that allow you to change the volume of the selected track. These controls may be represented as sliders, knobs, or numerical input fields.
- Lower the volume: Gradually decrease the volume level of the background music track. Pay attention to the changes in volume and their effect on the overall audio mix.
- Listen and adjust: After lowering the volume, listen to the modified audio and assess whether the background music remains in the background and doesn’t overpower the primary audio. Make further adjustments as necessary.
- Preview and export: Play through the entire audio file to ensure that the changes made to the background music track are consistent throughout. Once you are satisfied with the results, export or save the modified audio file.
Using audio editing software gives you precise control over the volume of the background music. It allows you to make fine adjustments, apply fades, and ensure that the background music enhances the overall audiovisual experience without overshadowing the main audio or dialogue.
Each software may have its own specific interface and tools, so it is essential to familiarize yourself with the features and capabilities of the audio editing software you choose to utilize. Experiment with different settings and techniques to find the right balance and achieve the desired volume reduction for the background music.
Applying Audio Effects
Applying audio effects is an effective technique to reduce the volume of background music while preserving its impact. Many audio editing software provide a range of effects that can be used to alter the volume and characteristics of the background music, ensuring it remains in the background without overpowering the primary audio or dialogue.
Here’s how you can apply audio effects to reduce the volume of background music:
- Open the audio editing software: Launch your preferred audio editing software, such as Audacity, Adobe Audition, or GarageBand.
- Import the audio file: Import the audio file that includes the background music.
- Select the background music track: Identify and select the specific track or section of the audio file that contains the background music.
- Access the effects panel: Locate the effects panel within the audio editing software. This panel typically contains a list of available audio effects.
- Browse and apply the desired effect: Look for effects such as “Ducking” or “Volume Reduction.” Apply the effect to the background music track to lower its volume during sections where the primary audio or dialogue is playing. Adjust the parameters of the effect, such as the attenuation level or duration, to achieve the desired volume reduction.
- Preview and fine-tune: Listen to the modified audio and assess whether the background music appropriately takes a lower volume when the primary audio or dialogue is present. Make any necessary adjustments to the effect settings to achieve a seamless and balanced audio mix.
- Preview and export: Play through the entire audio file to ensure that the effect is consistently applied throughout. Once satisfied with the results, export or save the modified audio file.
Applying audio effects like “Ducking” or “Volume Reduction” can automatically lower the volume of the background music when the primary audio or dialogue is playing. This technique maintains the impact and effectiveness of the background music while ensuring it remains in the background and maintains a complementary role in the overall audio mix.
Remember to experiment with different effect settings to achieve the optimal balance between the background music and other audio elements. Each audio editing software may offer different effects and parameters, so explore the capabilities of the software you are using to find the most suitable effect for your specific needs.
Utilizing Equalization
Equalization, or EQ, is a powerful technique that can be used to adjust the frequency balance of audio tracks. By utilizing equalization, you can reduce the volume of specific frequencies in the background music to create a more balanced audio mix without completely eliminating the music.
Here’s how you can utilize equalization to reduce the volume of background music:
- Open the audio editing software: Launch your chosen audio editing software, such as Audacity, Adobe Audition, or GarageBand.
- Import the audio file: Import the audio file containing the background music.
- Select the background music track: Identify and select the specific track or section of the audio file that contains the background music.
- Access the equalization controls: Look for the equalization or EQ controls within the audio editing software. These controls may be in the form of sliders or graphic equalizers that allow you to adjust the volume of specific frequency bands.
- Reduce specific frequencies: Identify the frequencies in the background music that clash or interfere with the primary audio or dialogue. Use the equalization controls to reduce the volume of those specific frequencies. This will create more space and separation between the background music and the primary audio.
- Listen and adjust: After making the equalization adjustments, listen to the modified audio and assess the overall balance between the background music and the primary audio. Make any necessary adjustments by fine-tuning the equalization settings.
- Preview and export: Play through the entire audio file to ensure a consistent and balanced audio mix. Once satisfied with the results, export or save the modified audio file.
Utilizing equalization allows you to control the frequency balance of the background music and reduce the volume of specific frequencies that may clash with the primary audio. This technique helps create more clarity and separation between the background music and other audio elements, ensuring a more balanced and cohesive audio mix.
Experiment with different equalization settings and frequencies to find the optimal balance for your specific audio content. Keep in mind that excessive equalization adjustments may alter the overall tonal characteristics of the background music, so it’s important to strike a balance that preserves the intended impact of the music while reducing its volume appropriately.
Employing Compression Techniques
Compression is a widely used audio processing technique that can be employed to control the dynamic range of audio tracks. By utilizing compression, you can effectively reduce the volume of the background music without sacrificing its impact and overall intelligibility.
Here’s how you can employ compression techniques to reduce the volume of background music:
- Open the audio editing software: Launch your preferred audio editing software, such as Audacity, Adobe Audition, or GarageBand.
- Import the audio file: Import the audio file that includes the background music.
- Select the background music track: Identify and select the specific track or section of the audio file that contains the background music.
- Access the compression controls: Look for the compression controls or plugins within the audio editing software. These controls may include settings such as threshold, ratio, attack, and release.
- Set compression parameters: Adjust the compression settings to control the dynamic range of the background music. Lower the threshold to capture more of the softer sections and apply more compression to the louder parts. Adjust the ratio to determine the amount of volume reduction applied. Fine-tune the attack and release parameters to ensure a smooth and natural sounding compression.
- Listen and adjust: After applying compression, listen to the modified audio and assess the overall balance between the background music and the primary audio. Make any necessary adjustments to the compression settings to achieve the desired volume reduction and maintain the appropriate impact of the background music.
- Preview and export: Play through the entire audio file to ensure a consistent and balanced audio mix. Once satisfied with the results, export or save the modified audio file.
Employing compression techniques allows you to control the dynamic range of the background music, reducing the volume of louder sections while maintaining clarity and impact. By compressing the volume peaks and boosting the softer sections, you can create a more balanced and controlled sound in the mix.
Experiment with different compression settings to find the optimal balance between the background music and other audio elements. Keep in mind that excessive compression may result in a loss of natural dynamics, so it’s crucial to strike a balance that reduces the volume appropriately while preserving the overall impact and emotion of the background music.
Mixing Audio Layers
When working with multiple audio layers, such as voiceovers, dialogue, and background music, careful mixing is essential to achieve a well-balanced audio mix. By adjusting the volume levels and panning of each layer, you can ensure that the background music remains in the background and complements the primary audio without overpowering it.
Here’s how you can mix audio layers to reduce the volume of the background music:
- Open the audio editing software: Launch your preferred audio editing software, such as Audacity, Adobe Audition, or GarageBand.
- Import the audio files: Import the audio files containing the primary audio, dialogue, and background music.
- Separate the audio tracks: Place the primary audio, dialogue, and background music each on separate audio tracks within the software.
- Adjust the primary audio and dialogue levels: Listen to the primary audio and dialogue and adjust their respective volume levels to ensure they are clear and intelligible.
- Lower the volume of the background music: After adjusting the primary audio and dialogue levels, reduce the volume of the background music track. Gradually lower the volume until it sits at a level where it supports the content without drawing too much attention.
- Experiment with panning: Use panning techniques to further separate the background music from the primary audio and dialogue. Adjust the panning settings to position the background music slightly to the sides, creating a sense of width in the audio mix.
- Listen and adjust: Play through the entire audio mix and carefully listen to the balance between the different audio layers. Make any necessary adjustments to volume levels and panning to achieve a cohesive and balanced audio mix.
- Preview and export: Play through the entire audio file to ensure a consistent and harmonious audio mix. Once satisfied with the results, export or save the final mixed audio file.
Mixing audio layers allows you to control the volume and spatial placement of each element within the audio mix. By adjusting the levels and panning, you can ensure that the background music enhances the primary audio without overpowering it.
Experiment with different volume levels and panning positions to find the optimal balance and spatial placement for your specific content. Careful mixing will contribute to a more immersive and enjoyable audiovisual experience, where the background music seamlessly integrates with the primary audio and dialogue.
Conclusion
Reducing the volume of background music is essential to maintain a balanced audio mix and prevent it from overpowering the primary audio or dialogue. By employing various techniques such as adjusting volume levels, using audio editing software, applying audio effects, utilizing equalization, employing compression techniques, and mixing audio layers, you can achieve a harmonious blend where the background music enhances the overall audiovisual experience without overshadowing other elements.
Background music plays a crucial role in setting the mood, creating brand identity, increasing engagement, enhancing visuals, and transitioning between scenes. However, it is important to strike the right balance, ensuring that the background music remains in the background, supporting the content without becoming a distraction.
When reducing the volume of background music, careful consideration and experimentation are key. Each technique offers its own approach and benefits, allowing you to customize the volume reduction process to suit your specific needs. It’s important to carefully listen to the mix, making adjustments as necessary to maintain a cohesive and balanced audio experience for your audience.
Remember, the ultimate goal is to create an immersive audio experience where the background music adds depth, emotion, and engagement to your content without overpowering the primary audio or dialogue. By implementing these techniques and finding the right balance, you can ensure that your background music becomes an effective and impactful supporting element in your audiovisual projects.