Home>Production & Technology>Music Theory>How To Study For Testing Out Of Music Theory 1


Music Theory
How To Study For Testing Out Of Music Theory 1
Published: January 29, 2024
Learn how to effectively prepare for and pass the Music Theory 1 test by following these expert study tips. Enhance your understanding of music theory and save time with our comprehensive study guide.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding the Testing Out Process
- Assessing Your Current Knowledge
- Reviewing Musical Fundamentals
- Studying Key Signatures and Scales
- Mastering Rhythmic Notation
- Learning Basic Chord Progressions
- Analyzing Melodic Structure
- Exploring Harmonic Functions
- Practicing Sight-Reading Skills
- Developing Aural Skills
- Taking Practice Tests
- Final Tips and Strategies
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to the world of music theory! If you have a passion for music and a desire to deepen your understanding of its inner workings, studying music theory is an excellent way to do so. Music theory provides the foundation for composition, performance, and analysis, allowing you to better appreciate and communicate musical ideas.
Whether you are a student preparing for a music theory exam, a musician seeking to expand your knowledge, or simply someone with a keen interest in the subject, this article will guide you through the process of studying music theory effectively.
Testing out of Music Theory 1 can be a great option for those who already have a solid understanding of the basic concepts. It allows you to skip the introductory course and move on to more advanced topics. However, preparing for the test can be challenging, as it requires a comprehensive review of foundational musical elements.
In this article, we will explore the various steps you can take to study for testing out of Music Theory 1. From assessing your current knowledge to practicing sight-reading skills and developing aural abilities, we will cover all the essential strategies to help you succeed. So, let’s dive in and begin your journey towards mastering music theory!
Understanding the Testing Out Process
Before diving into your music theory studies, it’s crucial to understand the testing out process. Different institutions may have varying requirements and procedures, so be sure to consult your school’s guidelines or speak with your music theory instructor to get specific details.
In general, testing out of Music Theory 1 involves taking an exam that assesses your knowledge and understanding of the foundational concepts covered in the course. This exam may consist of written or online components, such as multiple-choice questions, short answers, or even practical elements like sight-reading or ear training.
One important aspect to consider is the scoring and passing criteria. Each institution may have different standards, such as a minimum score required for passing or proficiency level needed in each topic area. Familiarize yourself with these requirements to gauge the level of preparation necessary.
Keep in mind that testing out of a course doesn’t necessarily mean you can skip all subsequent music theory courses. It typically allows you to move on to the next level, such as Music Theory 2, provided that you’ve demonstrated a sufficient understanding of the foundational material.
An advantage of testing out is the flexibility it offers. By successfully bypassing Music Theory 1, you can save time and resources, allowing you to focus on more advanced coursework or explore other areas of musical study.
However, it’s important to note that testing out may not be appropriate for everyone. If you have limited or no prior knowledge of music theory, it may be more beneficial to start with the introductory course to build a strong foundation. Consult with your instructor or academic advisor to determine the best path for your learning journey.
Now that you have a clear understanding of the testing out process, let’s move on to the next step: assessing your current knowledge.
Assessing Your Current Knowledge
Before you begin studying for the Music Theory 1 test, it’s important to assess your current knowledge of music theory. This step will help you identify areas of strength and weakness, allowing you to focus your study efforts where they are most needed.
Start by reviewing any previous music theory coursework or materials you have covered. Recall the concepts, terminology, and techniques you have learned. Make a list of topics and subtopics, and rate your familiarity and understanding on a scale of 1-10 for each.
Additionally, consider any practical experience you have had with music. Have you played an instrument or received formal music training? This background knowledge can be advantageous in grasping certain concepts and applying them in practice.
Next, take advantage of various online resources and practice tests specifically designed for music theory assessment. These assessments range from basic to advanced levels and cover a wide range of topics. Completing these tests will give you a more accurate gauge of your current proficiency in different areas of music theory.
Don’t be discouraged if you struggle with certain concepts or find gaps in your understanding. This assessment is meant to be a starting point for your study journey, and it’s natural to have areas for improvement. Recognizing your weaknesses will help you tailor your study plan to address those specific areas.
Consider seeking guidance from a music theory instructor or tutor. They can provide valuable feedback and additional resources to supplement your self-assessment. They may also suggest specific study materials or exercises to help you strengthen your knowledge and skills.
Remember, the goal of assessing your current knowledge is to set a baseline and identify your strengths and weaknesses. It will provide valuable insights to guide your study plan and ensure you focus on the areas that require the most attention. With a clear understanding of your starting point, you can now move on to the next step: reviewing musical fundamentals.
Reviewing Musical Fundamentals
As you embark on your journey to test out of Music Theory 1, it’s essential to review the fundamental concepts of music. These concepts serve as the building blocks of music theory and provide the groundwork for understanding more complex topics.
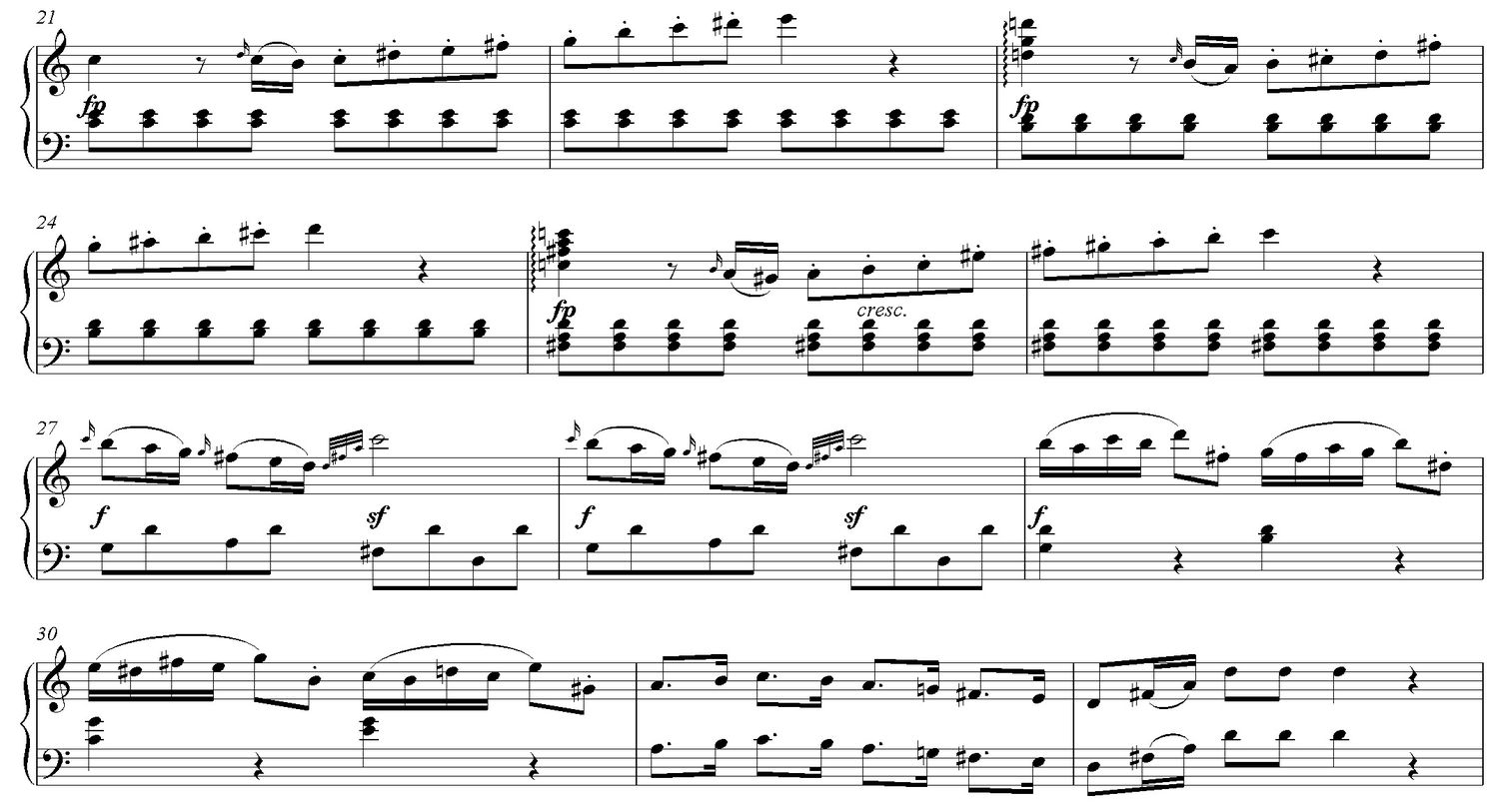
Start by revisiting the basics of notation. Familiarize yourself with the different symbols used in sheet music, such as clefs, noteheads, stems, and rests. Review the durations of notes and rests, as well as the concept of time signatures.
Next, brush up on your understanding of pitch and the musical staff. Recall how different pitches are represented on the staff using treble and bass clefs. Practice identifying notes on the staff and associating them with their corresponding pitches on an instrument or in your singing voice.
Understanding intervals is another fundamental concept to review. Refresh your knowledge of the various types of intervals, such as unison, octave, major, and minor intervals. Practice identifying intervals by sight and sound.
Harmony is another crucial aspect to revisit. Review the basic chord types, such as major, minor, augmented, and diminished chords. Understand how chord progressions are built and the function of different chords within a key.
Additionally, delve into the essentials of scales and key signatures. Study the major and minor scales, their construction, and the relationship between scales and key signatures. Practice identifying key signatures and understanding their impact on the overall tonality of a piece of music.
Finally, familiarize yourself with common musical terms and symbols. Refresh your knowledge of dynamic markings, tempo indications, articulations, and other expressive markings used in music notation.
Engage with various learning resources, such as textbooks, online tutorials, and interactive exercises, to reinforce your understanding of these fundamental concepts. Working through examples and exercises will help solidify your knowledge and ensure you are well-prepared for the testing out exam.
Remember, reviewing musical fundamentals is essential in establishing a strong foundation to build upon. By refreshing your knowledge of notation, pitch, intervals, harmony, scales, and key signatures, you will have a solid grasp of the basic concepts necessary for success in Music Theory 1. With these fundamentals in place, you can now move forward to the next step: studying key signatures and scales.
Studying Key Signatures and Scales
Key signatures and scales are essential elements of music theory. Understanding key signatures helps us identify the tonality of a piece, while scales provide the framework for melodies and harmonies. In this section, we will explore effective strategies for studying key signatures and scales.
Begin by reviewing the concept of key signatures. Familiarize yourself with the circle of fifths and how it relates to the order of sharps and flats. Practice writing out the major and minor key signatures, both in terms of sharps and flats. Pay attention to the patterns and relationships between the keys.
Next, delve into the different types of scales. Study the major scale, its construction, and the sequence of whole and half steps. Practice playing and writing out major scales in different keys. Understand the concept of relative minor scales and how they relate to their corresponding major scales.
Explore the various modes, such as the Dorian, Mixolydian, and Lydian modes. Learn their unique characteristics and how they differ from the major scale. Practice identifying and playing these modes.
Take time to study and apply the concept of minor scales. Understand the construction of the natural, melodic, and harmonic minor scales, as well as their differences. Practice playing and writing out minor scales in different keys.
Consider using mnemonic devices or memory aids to help you remember key signatures and scales. For example, using the phrase “Father Charles Goes Down And Ends Battle” to remember the order of sharps (F#, C#, G#, D#, A#, E#, B#) can be useful. Mnemonic devices like these can assist in memorization and recall.
Utilize interactive resources and apps that provide visual and auditory feedback for practicing key signatures and scales. These tools can provide an engaging and interactive learning experience, making it easier to memorize and internalize the patterns and structures of different keys.
Practice applying key signatures and scales to musical examples. Work through exercises that require identifying key signatures, writing out scales, and applying them in melodic and harmonic contexts. This practical application will strengthen your understanding and help you develop fluency with key signatures and scales.
Remember to take a systematic approach to studying key signatures and scales. Start with the basics, such as major scales and key signatures, before moving on to minor scales and more advanced concepts. Regular practice and consistent exposure to key signatures and scales will lead to mastery over time.
By dedicating time and effort to studying key signatures and scales, you will gain a solid foundation in music theory and be well-prepared for the testing out exam. With this knowledge in hand, you are ready to tackle the next essential topic: mastering rhythmic notation.
Mastering Rhythmic Notation
Rhythm is the backbone of music, and understanding rhythmic notation is crucial for any musician or music theorist. In this section, we will discuss strategies to help you master rhythmic notation and develop a strong sense of rhythm.
Start by reviewing the basic elements of rhythmic notation. Familiarize yourself with note durations, such as whole notes, half notes, quarter notes, eighth notes, and sixteenth notes. Understand how these notes relate to each other in terms of duration.
Practice counting rhythms out loud using syllables or numbers. For example, using “ta” or “1 and” for quarter notes and eighth notes respectively. This vocalization technique helps internalize the rhythmic patterns and improves your ability to accurately notate and perform rhythms.
Next, explore different time signatures. Understand the concept of beats per measure and how note values are divided within a measure. Practice identifying and notating rhythms in different time signatures, such as 4/4, 3/4, 6/8, and 5/8.
Study rests and their corresponding durations. Rests represent moments of silence within music. Practice notating and counting rhythms that include rests, paying attention to their placement and duration.
Work on sight-reading exercises to improve your ability to read and perform rhythms on the spot. Start with simple rhythms and gradually increase the complexity as you become more comfortable. Utilize sheet music and online resources that provide rhythm exercises specifically designed for practice.
Engage in rhythmic dictation exercises, where you hear a rhythm and must notate it accurately. This exercise sharpens your listening skills and helps you develop a strong connection between hearing rhythms and writing them down.
Experiment with different rhythms and explore their contrasting effects on music. Practice creating rhythmic variations of melodies or musical passages to enhance your understanding of rhythmic possibilities and their impact on musical expression.
Take advantage of technology and utilize metronome apps or rhythm training apps that provide visual and auditory cues. These tools can help you develop a solid sense of pulse and improve your ability to play rhythms accurately.
Collaborate with other musicians or join a music ensemble to further enhance your rhythmic skills. Playing music with others not only improves your rhythmic precision but also allows you to experience how rhythm interacts with other musical elements in a performance setting.
Remember, mastering rhythmic notation takes time and practice. Be patient with yourself and maintain consistency in your study. Regular practice of rhythmic exercises and continual exposure to different rhythms will greatly enhance your rhythmic abilities and prepare you for success in the testing out exam.
With a solid foundation in rhythmic notation, you are well-prepared to dive into the next topic: learning basic chord progressions.
Learning Basic Chord Progressions
Chord progressions are fundamental to understanding the harmony and structure of music. They provide the foundation for melodies and serve as the backbone of many songs. In this section, we will explore strategies to help you learn and understand basic chord progressions.
Start by familiarizing yourself with the basic chords in a given key. In major keys, these chords are typically the I, IV, and V chords. In minor keys, they are often the i, iv, and V chords. Practice playing these chords on your instrument or keyboard to develop a solid understanding of their sound and fingering.
Study the concept of roman numeral analysis, which assigns roman numerals to each chord in a progression based on its position within the key. This analysis helps you identify the function of each chord and understand the relationships between chords in a progression.
Practice identifying common chord progressions in different musical genres. For example, the I-IV-V progression is commonly found in rock and blues music, while the vi-IV-V progression is popular in pop music. Engage with different musical styles to expand your repertoire of chord progressions.
Experiment with different inversions and voicings of chords to add variation and color to your chord progressions. Understand how inversions affect the overall sound and movement of the progression. Practice playing these inversions to develop muscle memory and increase your familiarity with different chord shapes.
Utilize resources such as chord charts, chord progression books, and online tutorials to discover new chord progressions and explore their applications in various musical contexts. These resources provide a wealth of knowledge and inspiration for practicing and incorporating different chord progressions into your musical repertoire.
Train your ear to recognize chord progressions by listening to music and trying to identify the chords being played. Engaging with recordings and transcribing chord progressions will enhance your ability to hear and understand the relationships between chords.
Play along with backing tracks or use a loop pedal to practice playing chord progressions in different keys and styles. This allows you to develop a sense of timing and reinforces your ability to transition smoothly between chords.
Apply your knowledge of chord progressions by accompanying yourself or others while singing or playing melodies. This practical application will deepen your understanding of how chords and melodies work together to create music.
Collaborate with other musicians to explore different chord progressions and create new musical arrangements. Engaging in group settings allows you to experience the dynamic interplay of chords within the context of a larger musical ensemble.
Remember, learning basic chord progressions is key to understanding the harmonic structure of music. By developing a solid foundation in chord progressions, you will be equipped with the tools to create, analyze, and appreciate music in a more profound way. With this knowledge, you can confidently move on to the next topic: analyzing melodic structure.
Analyzing Melodic Structure
Understanding the structure of melodies is crucial for analyzing and appreciating music. Melodies are the heart of a composition, carrying the listener through various musical phrases and creating emotional depth. In this section, we will explore strategies for analyzing melodic structure.
Start by listening actively to melodies in different genres and styles of music. Pay close attention to the contour, or shape, of the melody. Is it ascending, descending, or a combination of both? Understanding the overall contour of a melody provides valuable insights into its expressive qualities.
Identify and analyze the characteristics of melodic phrases. A phrase is a musical idea or segment that often ends with a cadence or a resting point. Pay attention to the length and symmetry of phrases, as well as any melodic motifs or patterns that are repeated throughout the melody.
Study the use of intervals within the melody. Identify any significant leaps or intervals that create tension or interest. Analyze the melodic intervals in relation to the underlying harmony to understand how they contribute to the overall musical expression.
Examine the rhythmic aspect of the melody. Observe the rhythm of individual notes and the relationship between different rhythmic values. Analyzing the rhythmic structure of a melody helps to understand its energy, drive, and syncopation.
Explore the use of ornamentation and embellishments within the melody. Look for trills, turns, slides, and other decorative elements that enhance the expressiveness of the melody. Consider how these embellishments contribute to the overall character and mood of the piece.
Utilize sheet music or notation software to visualize and study melodies. Analyze the melodic structure by following the movement of the notes on the staff. Identify the key signatures, scales, and intervals used within the melody to gain a deeper understanding of its musical framework.
Consider the relationship between the melody and the underlying harmony. Analyze how the melody interacts with chord progressions, identifying chord tones and non-chord tones. Understanding the melodic interaction with harmony provides insights into the overall tonal structure of the piece.
Practice transcribing melodies by ear. Listen to recordings and try to notate the melody accurately. This exercise sharpens your listening skills and deepens your understanding of melodic structure.
Collaborate with other musicians to analyze and interpret melodies. Discuss different interpretations and perspectives on the melodic structure, allowing you to gain a broader understanding of the possibilities within a melody.
Remember, analyzing melodic structure requires active listening, observation, and understanding of musical elements. By analyzing contour, phrases, intervals, rhythms, ornamentation, and the interaction with harmony, you will develop a deeper appreciation for the artistry and craftsmanship of melodies. With this knowledge, you can progress to the next topic: exploring harmonic functions.
Exploring Harmonic Functions
Harmonic functions play a vital role in music, providing the framework for the movement and progression of chords. Understanding harmonic functions allows us to analyze and appreciate the underlying harmony of a piece. In this section, we will explore strategies for exploring and understanding harmonic functions.
Start by familiarizing yourself with the concept of tonal centers and keys. Understand how a piece is centered around a particular tonic, which serves as the home chord and provides a sense of resolution. Practice identifying the tonic chord in different keys and recognizing its importance within a piece.
Study the different types of harmonic functions. The three primary functions are tonic, dominant, and subdominant. The tonic function creates a sense of stability and resolution. The dominant function creates tension and leads back to the tonic. The subdominant function provides a sense of departure from the tonic and prepares for the return to it.
Analyze chord progressions in different musical genres and styles. Pay attention to the patterns and relationships between chords. Identify how different functions (tonic, dominant, subdominant) are used to create movement and emotional tension within the progression.
Examine the use of chord inversions and voice leading within harmonic functions. Understanding the role of inversions and the smooth voice leading between chords can enhance the overall harmonic flow of a piece. Practice recognizing inversions and analyzing their impact on the progression.
Explore common harmonic progressions, such as the I-IV-V or ii-V-I progressions. These progressions are prevalent in various styles of music and provide a solid foundation for understanding harmonic functions. Practice playing and analyzing these progressions in different keys.
Utilize Roman numeral analysis to analyze and notate chord progressions. Assign roman numerals to each chord based on its function within the key. This analysis helps identify the harmonic relationships and the overall structure of a piece.
Experiment with chord substitutions and extensions to expand your understanding of harmonic possibilities. Explore how altered chords, borrowed chords, or extended harmonies can create unique and colorful harmonic progressions. Analyze the impact of these substitutions on the overall mood and tension of the music.
Listen actively to music and focus on the harmonic functions within the piece. Pay attention to the resolutions, tensions, and progressions that define the harmonic landscape. Analyze how the harmonic choices impact the emotional impact and overall character of the music.
Collaborate with other musicians to analyze and discuss harmonic functions within music. Engage in conversations about different harmonic approaches and interpretations, broadening your perspective and understanding of the subject.
Remember, exploring harmonic functions requires a combination of analysis, active listening, and practical application. By understanding tonal centers, recognizing harmonic functions, analyzing chord progressions, and exploring different harmonic possibilities, you will deepen your understanding and appreciation of the harmonic language in music. With this knowledge, you can confidently move on to the next topic: practicing sight-reading skills.
Practicing Sight-Reading Skills
Sight-reading is a valuable skill for any musician, enabling you to play music on the spot without prior rehearsal. Developing strong sight-reading skills allows you to quickly digest and perform written music accurately. In this section, we will explore strategies to improve your sight-reading abilities.
Select music of appropriate difficulty for sight-reading practice. Start with simple and familiar pieces, gradually progressing to more complex and unfamiliar ones. Choose a variety of genres and styles to expose yourself to different musical challenges.
Set aside dedicated practice time for sight-reading. Treat it as a separate skill to focus on, rather than solely relying on rehearsal or performance situations. Aim for regular practice sessions to build familiarity and confidence in reading music notation.
Begin by scanning the music before starting to play. Take note of the key signature, time signature, tempo markings, and any other important musical indicators. This initial scan helps prepare your mind for what to expect in terms of key, rhythm, and overall structure.
Focus on rhythm accuracy. Develop a strong mental metronome to assist in keeping a steady pulse while reading. Practice counting rhythm out loud or silently to improve your sense of time and ensure accurate rhythm execution as you sight-read.
Work on recognizing patterns and common musical phrases. By training your brain to identify frequently occurring musical elements, you’ll be able to anticipate and interpret them more efficiently, making sight-reading smoother and more intuitive.
Practice sight-singing in addition to instrumental sight-reading. This exercises your ability to read and interpret melodies without relying on a physical instrument. Singing allows you to internalize the melodic contour, phrasing, and intervals, which can translate to improved instrumental sight-reading skills.
Strive for fluency and continuity when sight-reading. Minimize pauses or hesitations as you encounter unfamiliar passages. Rather than stopping to correct mistakes, focus on maintaining a steady flow by adjusting your reading speed and keeping the overall musical intent intact.
Study music theory concepts and harmonic progressions to aid your sight-reading comprehension. Having a solid understanding of theory helps you recognize chord progressions, key modulations, and other musical elements as you read through a piece of music.
Utilize sight-reading exercises and resources available online or in music books. These materials are specifically designed to hone your sight-reading skills. Incorporate sight-reading exercises into your practice routine to challenge yourself with new musical material on a regular basis.
Record and review your sight-reading sessions. By capturing your sight-reading performances, you can assess your accuracy, identify areas for improvement, and track your progress over time. This self-evaluation will help you identify strengths and weaknesses in your sight-reading and fine-tune your practice approach.
Remember to approach sight-reading practice with patience and persistence. It is a skill that develops over time and requires consistent effort. With regular practice and exposure to various musical pieces, your sight-reading abilities will improve, boosting your confidence and versatility as a musician.
Now that you have some strategies to enhance your sight-reading skills, you can confidently move on to the next topic: developing aural skills.
Developing Aural Skills
Aural skills, also known as ear training, are vital for any musician. Developing strong aural skills allows you to identify and understand musical elements by ear, enhancing your ability to improvise, transcribe, and communicate with other musicians. In this section, we will explore strategies to help you develop your aural skills.
Start by practicing active listening. Engage with a wide variety of music, focusing on different musical elements such as melody, harmony, rhythm, and timbre. Train your ear to discern these elements and understand how they contribute to the overall musical composition.
Work on interval recognition. Practice identifying and naming intervals by ear. Begin with simple intervals, such as perfect fifths or major thirds, and gradually progress to more challenging intervals. Use mnemonic devices or songs to help memorize the distinct sounds of each interval.
Train your ability to recognize and sing or play back melodies by ear. Start with simple melodies and gradually work your way up to more complex ones. Focus on accuracy, pitch, and rhythm as you reproduce the melody. This exercise develops your aural memory and strengthens your ability to internalize and replicate music without the aid of notation or instruments.
Practice chord recognition by ear. Train yourself to identify the quality and function of different chords within a progression. Start with simple major and minor chords, and then progress to more complex chords such as augmented or diminished chords. This skill is particularly valuable for improvisation and harmonizing with other musicians.
Work on rhythmic dictation exercises. Listen to rhythmic patterns and transcribe them accurately. Pay attention to the duration of notes and rests, as well as any syncopations or complex rhythms. This practice will sharpen your rhythmic perception and improve your ability to notate rhythms accurately.
Engage in sight-singing exercises to improve your ability to sing pitch accurately without the aid of an instrument. Practice sight-singing melodies, intervals, and different musical phrases. Focus on correct pitch, rhythm, and musical expression to develop your overall aural skills.
Utilize online resources and mobile apps specifically designed for aural skills development. These resources often provide exercises, quizzes, and interactive tools to help you train your ear. Take advantage of these resources to practice aural skills regularly.
Work with a partner or join a music ensemble to engage in aural skills exercises together. Practice singing or playing back melodies, harmonizing, and improvising collectively. Collaborating with others reinforces your ability to listen and respond to music in real-time.
Take advantage of transcribing music by ear. Choose songs or instrumental solos and work on transcribing them note by note. This exercise challenges your aural skills and unveils the inner workings of the music, enabling you to appreciate the intricacies of different musical styles and techniques.
Remember, developing aural skills takes time, consistency, and active engagement with music. Regular practice and exposure to a wide range of musical material will enhance your ability to identify, replicate, and understand music by ear. With well-developed aural skills, you will become a more versatile and expressive musician.
Now that you have some strategies to develop your aural skills, you can confidently move on to the next topic: taking practice tests.
Taking Practice Tests
Taking practice tests is an effective way to gauge your knowledge and readiness for the Music Theory 1 exam. Practice tests provide an opportunity to familiarize yourself with the format and types of questions you may encounter, helping you identify areas that need further study. In this section, we will explore the benefits of taking practice tests and strategies to make the most of them.
Practice tests help you simulate the actual exam environment, allowing you to become comfortable with the testing process. By experiencing timed conditions and the pressure of test-taking, you can better manage your time, reduce anxiety, and build confidence before the real exam.
Time yourself while taking practice tests to get a realistic idea of how you perform under timed conditions. This helps you understand which sections or types of questions require more focus and practice, enabling you to allocate your study time effectively.
Review your answers and explanations after taking each practice test. Identify any patterns of mistakes or areas for improvement. Focus on understanding the correct answers and explanations for any questions you answered incorrectly.
Keep track of your progress by recording your scores and monitoring your improvement over time. This allows you to track your strengths and weaknesses and adjust your study plan accordingly. Celebrate small victories and use low-scoring areas as motivation for targeted improvement.
Utilize practice tests from various sources to expose yourself to different question styles and difficulty levels. Online resources, textbooks, and study guides can provide a range of practice questions and sample exams. Variety in practice tests helps to broaden your understanding and prepares you for a wider range of challenges.
Analyze the results of your practice tests to identify topics or areas where you struggled the most. Allocate additional study time to these specific areas to reinforce your knowledge and understanding. Focus on targeted learning and practice to refine your skills and solidify your understanding.
Simulate the testing environment as closely as possible when taking practice tests. Find a quiet place free from distractions, and use pencil and paper or a computer-based platform to answer the questions. This creates a more realistic test-taking experience and helps simulate the mental focus required during the actual exam.
Seek feedback from instructors, tutors, or study partners to gain different perspectives on your progress. They can offer insights and tips based on their expertise and experience, helping you identify blind spots or areas that require further attention.
Set aside dedicated time to review and reflect on each practice test. Use this time to reinforce your understanding of the material and identify any lingering gaps in your knowledge. Reviewing and reflecting on your practice tests ensures that you are continually learning and growing throughout your study process.
Remember, practice tests are valuable tools for assessing your knowledge, identifying areas for improvement, and gaining confidence before the Music Theory 1 exam. By incorporating practice tests into your study routine and leveraging the insights gained from them, you can increase your chances of performing well and achieving success on the actual exam.
Now that you have strategies for taking practice tests, you are ready to move on to the final topic: tips and strategies for the Music Theory 1 exam.
Final Tips and Strategies
As you prepare for the Music Theory 1 exam, here are some final tips and strategies to help you perform at your best:
- Create a study schedule: Develop a study schedule that allows for regular practice and review. Consistency is key to retaining information and building strong foundations in music theory.
- Break it down: Break down the material into manageable chunks. Focus on understanding one concept before moving on to the next. This approach prevents overwhelm and promotes deep comprehension.
- Practice regularly: Practice daily, even if it’s just for a short period of time. Consistent practice reinforces your knowledge and builds fluency in music theory concepts.
- Teach someone else: Teach the material to someone else. Explaining concepts to others helps solidify your understanding and reveals any gaps in your knowledge.
- Use mnemonic devices: Utilize mnemonic devices, such as acronyms or catchy phrases, to remember key concepts, formulas, or sequences of information.
- Engage in active learning: Actively engage with the material by practicing, applying, and analyzing concepts. Passive reading or memorization alone may not lead to a deep understanding of music theory.
- Don’t neglect practical application: Apply music theory concepts by playing an instrument, composing, or improvising. Practical application enhances your understanding and connection to the material.
- Seek help if needed: If you’re struggling with specific topics or feel overwhelmed, seek help from a music theory instructor, tutor, or fellow musicians. They can offer guidance, explanations, and resources to aid your understanding.
- Stay organized: Keep your study materials, notes, and resources organized for easy reference. This helps you efficiently review and locate information when needed.
- Take care of yourself: Prioritize self-care, including adequate sleep, nutrition, and exercise. Taking care of your physical and mental well-being enhances your focus, memory, and overall learning ability.
Remember, everyone learns at their own pace. Be patient with yourself and celebrate your progress along the way. With dedication, consistent practice, and a positive mindset, you can successfully test out of Music Theory 1 and continue your musical journey with a strong foundation in music theory.
Good luck!
Conclusion
Congratulations on embarking on your journey to test out of Music Theory 1! By employing the strategies and tips outlined in this article, you have equipped yourself with the tools and knowledge to succeed.
Through understanding the testing out process, assessing your current knowledge, reviewing musical fundamentals, studying key signatures and scales, mastering rhythmic notation, learning basic chord progressions, analyzing melodic structure, exploring harmonic functions, practicing sight-reading skills, developing aural skills, taking practice tests, and utilizing final tips and strategies, you have prepared yourself for the Music Theory 1 exam.
Remember that studying music theory is a continuous process, and a passion for learning will guide you as you delve deeper into the subject. Music theory serves as the backbone of musical understanding and communication, empowering you to express yourself and connect with others through music.
As you embark on your exam journey, take the time to appreciate the beauty and intricacies of music theory. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your skills, broaden your musical horizons, and deepen your understanding of the rich world of music.
So, go forth with confidence, practice diligently, and embrace the joy of studying music theory. May your dedication and hard work pay off as you test out of Music Theory 1 and continue your musical pursuits!