Home>Instruments>Guitar>How To Mic An Acoustic Guitar


Guitar
How To Mic An Acoustic Guitar
Published: February 13, 2024
Learn how to properly mic an acoustic guitar for optimal sound quality. Discover essential tips and techniques for capturing the rich tones of your guitar.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to capturing the rich, resonant tones of an acoustic guitar, using a microphone can make all the difference. Whether you're recording in a studio, performing on stage, or simply jamming at home, knowing how to properly mic an acoustic guitar can significantly enhance the sound quality and overall musical experience.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the art of miking an acoustic guitar, exploring various types of microphones suitable for this purpose, optimal placement techniques, and valuable tips for achieving the best possible sound. Whether you're a seasoned musician or just starting out, understanding the nuances of miking an acoustic guitar can elevate your playing to new heights.
By the end of this article, you will have a solid grasp of the different microphone options available, how to position them for optimal sound capture, and essential tips to ensure that your acoustic guitar sounds its best in any setting. So, let's embark on this sonic journey and unlock the secrets to effectively mic an acoustic guitar.
Types of Microphones for Acoustic Guitars
When it comes to selecting a microphone for miking an acoustic guitar, there are several types to consider, each with its own unique characteristics and sonic qualities. Understanding the differences between these microphone options can help you make an informed decision based on your specific recording or performance needs.
1. Condenser Microphones: Condenser microphones are a popular choice for miking acoustic guitars due to their ability to capture the instrument’s nuances with exceptional clarity. These microphones are known for their sensitivity and wide frequency response, making them well-suited for capturing the intricate details of acoustic guitar playing. They are available in both large-diaphragm and small-diaphragm variations, each offering distinct sonic characteristics.
2. Dynamic Microphones: While dynamic microphones are often associated with live performances and instrument amplification, they can also be used to mic acoustic guitars. Dynamic mics are rugged and versatile, making them a reliable choice for capturing the robust sound of an acoustic guitar, particularly in live settings where feedback rejection is crucial.
3. Ribbon Microphones: Ribbon microphones are revered for their warm, vintage sound and smooth frequency response. Although they are less commonly used for miking acoustic guitars, they can impart a unique sonic coloration that complements certain playing styles and genres.
4. Soundboard Transducer Pickups: In addition to traditional microphones, soundboard transducer pickups offer an alternative approach to capturing the sound of an acoustic guitar. These pickups are designed to be mounted on the guitar’s soundboard, directly capturing the instrument’s vibrations and translating them into electrical signals. While they may not provide the same tonal character as microphones, they offer a practical solution for amplified acoustic guitar sound reinforcement.
Each type of microphone brings its own sonic characteristics to the table, and the choice ultimately depends on the desired sound, the recording environment, and the specific nuances of the acoustic guitar being miked. Experimenting with different microphone types can lead to exciting sonic discoveries and help you find the perfect match for your acoustic guitar sound.
Placement Techniques
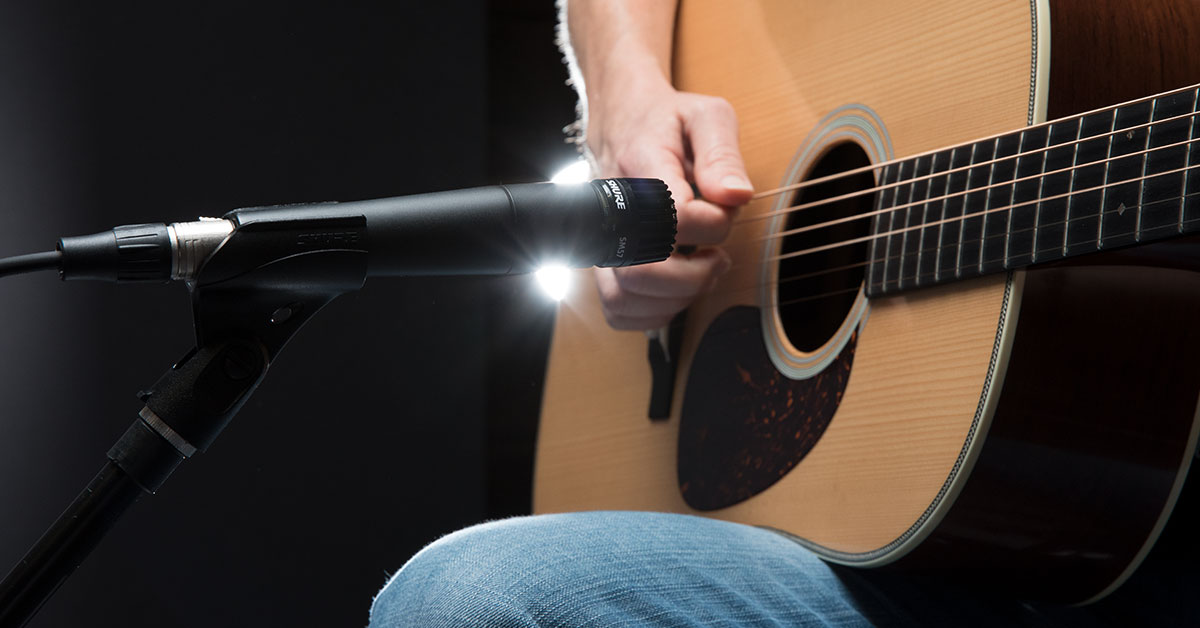
Proper microphone placement is essential for capturing the full tonal spectrum and natural resonance of an acoustic guitar. Whether you’re aiming to achieve a balanced representation of the instrument’s sound or looking to emphasize specific tonal qualities, the placement of the microphone relative to the guitar is a critical factor. Here are some tried-and-true placement techniques to consider:
- On-Axis vs. Off-Axis Placement: Placing the microphone directly in front of the guitar’s soundhole (on-axis) can result in a balanced representation of the instrument’s sound, capturing both low and high frequencies. However, this position may also accentuate low-end frequencies, so adjusting the angle slightly off-axis can help achieve a more balanced tonal capture.
- Distance from the Guitar: The distance between the microphone and the guitar significantly influences the captured sound. Placing the microphone closer to the guitar emphasizes the instrument’s intimacy and detail, while moving it farther away can introduce more room ambience and airiness to the sound.
- Multiple Microphone Setup: Using multiple microphones to capture the acoustic guitar from different angles can provide a more comprehensive sonic picture. Pairing a close-miked condenser with a room microphone, for example, can offer a blend of direct sound and ambient richness, allowing for greater flexibility during the mixing process.
- Experiment with Height and Angle: Varying the height and angle of the microphone can yield different tonal characteristics. Positioning the microphone at different heights above the guitar’s body or angling it towards the fretboard or soundhole can alter the balance of frequencies and the overall timbre of the captured sound.
- Consider the Room Acoustics: The acoustic properties of the recording space should also be taken into account when placing the microphone. Rooms with natural reverb and resonance can contribute to the overall sound, so experimenting with microphone placement to capture the room’s acoustic characteristics can add depth and dimension to the recording.
Ultimately, the optimal microphone placement depends on the desired sonic outcome, the specific tonal qualities of the acoustic guitar, and the sonic characteristics of the recording environment. It’s important to experiment with different placement techniques to discover the best approach for capturing the unique sound of your acoustic guitar.
Tips for Achieving the Best Sound
When it comes to miking an acoustic guitar, attention to detail and thoughtful execution can make a significant difference in the quality of the captured sound. Here are some valuable tips to help you achieve the best possible sonic results when miking an acoustic guitar:
- Experiment with Microphone Positions: Don’t hesitate to try different microphone placements to find the sweet spot that best captures the tonal characteristics of your acoustic guitar. Small adjustments in angle and distance can yield noticeable sonic variations.
- Use High-Quality Cables and Preamps: Investing in high-quality microphone cables and preamps can contribute to a cleaner, more transparent signal chain, preserving the nuances of the acoustic guitar’s sound from the microphone to the recording device.
- Monitor the Sound During Recording: Utilize headphones or studio monitors to actively monitor the miked sound of the acoustic guitar as you adjust microphone placement and settings. This real-time feedback can guide you toward the optimal capture of the instrument’s sound.
- Consider the Polar Pattern: If using a condenser microphone, be mindful of its polar pattern. Cardioid, omnidirectional, and figure-8 patterns offer distinct sonic capture characteristics, so select the polar pattern that aligns with your sonic goals.
- Minimize Background Noise: When recording, ensure that the environment is as quiet as possible to minimize unwanted background noise. Acoustic guitar recordings benefit from a clean, noise-free background, allowing the instrument’s natural resonance to shine through.
- Embrace Post-Processing Techniques: After capturing the acoustic guitar sound, consider employing subtle post-processing techniques such as EQ, compression, and reverb to enhance the recorded sound and address any tonal nuances that may benefit from refinement.
- Account for Player Movement: If the acoustic guitar will be played while being miked, anticipate the player’s movements and adjust the microphone placement accordingly to maintain a consistent and balanced capture of the instrument’s sound.
By incorporating these tips into your approach to miking an acoustic guitar, you can elevate the sonic quality of your recordings or live performances, ensuring that the natural beauty and expressive nuances of the instrument are faithfully preserved.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of miking an acoustic guitar is a journey that combines technical knowledge with a keen ear for capturing the instrument’s natural beauty. Whether you’re a recording engineer, a performing musician, or an avid enthusiast of acoustic guitar music, understanding the nuances of microphone types, placement techniques, and sound capture tips can significantly enhance the sonic results of your endeavors.
By exploring the various types of microphones suitable for miking acoustic guitars, such as condenser microphones, dynamic microphones, ribbon microphones, and soundboard transducer pickups, you gain insight into the sonic characteristics and applications of each option. This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions based on your specific recording or performance needs, ultimately shaping the tonal quality of the captured acoustic guitar sound.
Delving into the intricacies of microphone placement techniques reveals the importance of on-axis and off-axis positioning, distance from the guitar, multiple microphone setups, and the influence of height, angle, and room acoustics. These techniques offer a palette of sonic possibilities, allowing you to tailor the captured sound to align with your artistic vision and the unique qualities of the acoustic guitar being miked.
Furthermore, embracing valuable tips for achieving the best sound, including experimenting with microphone positions, utilizing high-quality cables and preamps, actively monitoring the sound during recording, considering polar patterns, minimizing background noise, and employing post-processing techniques, equips you with the tools to refine and elevate the sonic character of your acoustic guitar recordings and performances.
As you continue to explore the realm of miking acoustic guitars, remember that the journey is as much about technical proficiency as it is about artistic expression. Each acoustic guitar possesses its own voice, and by mastering the art of miking, you can ensure that its unique timbre and emotive qualities are faithfully conveyed to your audience or listeners, creating an immersive and captivating musical experience.
So, whether you’re embarking on a recording session, preparing for a live performance, or simply seeking to capture the essence of your acoustic guitar playing, the knowledge and techniques shared in this guide serve as valuable tools to help you unlock the full sonic potential of the instrument and bring your musical visions to life.