Home>Production & Technology>MIDI>How To Convert MIDI Messages Into Voltages


MIDI
How To Convert MIDI Messages Into Voltages
Modified: February 22, 2024
Learn how to convert MIDI messages into voltages with our comprehensive guide. Explore the possibilities of MIDI control in voltage-based systems.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Have you ever wondered how electronic musical instruments communicate with each other? The answer lies in a fascinating technology called Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MIDI). MIDI has revolutionized the way musicians create and perform music, allowing for seamless connectivity between different devices such as keyboards, synthesizers, and computers. One of the most intriguing aspects of MIDI is its ability to convert musical actions, such as pressing a key or moving a modulation wheel, into digital messages that can be transmitted and interpreted by various musical instruments and software.
In this article, we will delve into the world of MIDI and explore the process of converting MIDI messages into voltages. This conversion is a fundamental aspect of electronic music production and opens up a realm of creative possibilities for musicians and producers. By understanding how MIDI messages can be translated into control voltages, you can harness the power of modular synthesizers, analog gear, and other voltage-controlled instruments to expand your sonic palette and expressiveness.
Join us on this journey as we unravel the inner workings of MIDI, discover the tools and equipment needed for this conversion process, and embark on a step-by-step exploration of transforming digital commands into analog voltages. Whether you're a seasoned electronic musician or a curious enthusiast, this article will provide valuable insights into the intersection of digital and analog realms in the realm of music production. Let's embark on this exciting exploration of MIDI and voltage conversion, where the digital and analog worlds converge to shape the future of music creation.
Understanding MIDI Messages
MIDI, which stands for Musical Instrument Digital Interface, serves as the universal language of electronic musical instruments. It enables devices such as keyboards, synthesizers, drum machines, and computers to communicate with each other, facilitating seamless integration and control within a musical setup. At its core, MIDI operates by transmitting digital messages that represent various musical actions and parameters, allowing for the exchange of performance data and control information.
MIDI messages encompass a diverse range of musical gestures and commands, each serving a specific purpose in the realm of electronic music production. These messages can be broadly categorized into two main types: channel messages and system messages. Channel messages are the most commonly used MIDI messages and are associated with specific channels, allowing for individual control and manipulation of different musical elements within a setup. These messages include note-on and note-off commands, velocity, pitch bend, modulation, and control change messages, each contributing to the expressive and dynamic nature of MIDI-based music production.
In addition to channel messages, MIDI also encompasses system messages, which are global in nature and are not tied to specific channels. System messages facilitate functions such as synchronization, timing, and device configuration, ensuring that different MIDI-enabled devices can operate harmoniously within a musical environment. These messages include timing clock signals, start and stop commands, system exclusive messages for device-specific communication, and more, providing a robust framework for the seamless integration of diverse musical equipment.
Furthermore, MIDI messages are transmitted in a serial fashion, with each message consisting of a status byte followed by one or two data bytes, depending on the message type. This structured format allows for efficient and reliable communication between MIDI devices, ensuring that musical commands and performance data are accurately conveyed and interpreted.
Understanding the intricacies of MIDI messages is crucial for electronic musicians and producers, as it empowers them to harness the full potential of MIDI-enabled instruments and software. By mastering the nuances of MIDI messages, musicians can craft expressive performances, implement intricate control schemes, and unlock the creative possibilities offered by electronic music technology.
In the next section, we will explore the process of converting MIDI messages into voltages, shedding light on the transformative journey from digital commands to analog control signals. This convergence of digital and analog realms is a pivotal aspect of electronic music production, offering a wealth of opportunities for sonic exploration and artistic expression. Let's embark on this enlightening exploration of MIDI and voltage conversion, where the boundaries between the digital and analog worlds blur in the pursuit of musical innovation.
Converting MIDI Messages into Voltages
In the realm of electronic music production, the conversion of MIDI messages into voltages represents a pivotal bridge between the digital and analog domains. This process holds immense significance for musicians and producers, as it enables the translation of digital commands from MIDI-enabled devices into analog control signals that can interface with voltage-controlled instruments and modular synthesizers. By converting MIDI messages into voltages, musicians can harness the expressive capabilities of analog gear, manipulate sound parameters in real-time, and explore the rich sonic textures offered by voltage-controlled synthesis.
At the heart of this conversion process lies the concept of control voltage (CV), which serves as a fundamental currency in the world of analog synthesis. Control voltages are analog signals that dictate various parameters of sound generation and manipulation, including pitch, amplitude, timbre, and modulation. By converting MIDI messages into control voltages, electronic musicians can leverage the flexibility and tactile nature of analog control, infusing their performances and productions with a hands-on, organic feel.
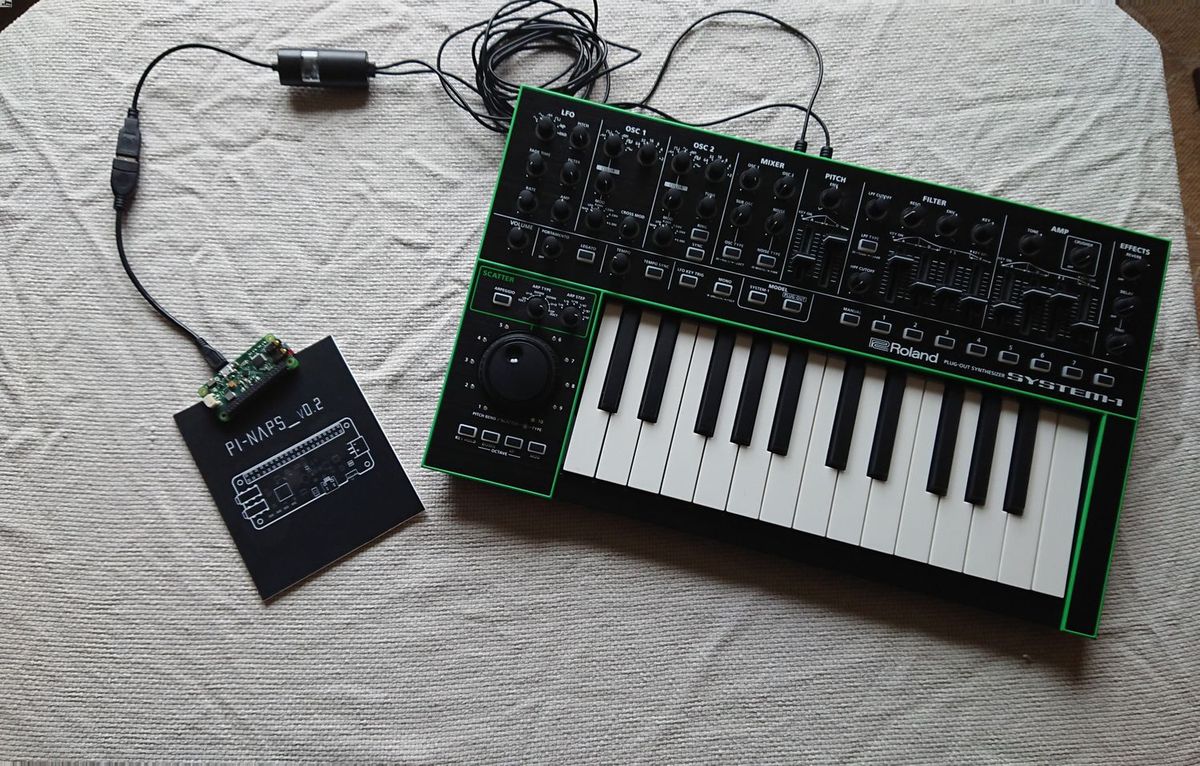
The conversion of MIDI messages into voltages can be achieved through the use of dedicated MIDI to CV converters or modules, which are designed to interpret MIDI data and generate corresponding control voltages. These converters typically offer a range of outputs for different types of control signals, allowing for precise manipulation of parameters such as pitch, gate signals for note triggering, modulation sources, and more. Additionally, some MIDI to CV converters feature advanced functionalities such as velocity sensitivity, polyphonic output, and extensive parameter mapping, providing a versatile toolkit for shaping and sculpting musical elements.
Furthermore, the process of converting MIDI messages into voltages opens up a world of creative possibilities for integrating MIDI-based instruments and software with analog synthesizers, sequencers, and other voltage-controlled devices. This integration empowers musicians to craft intricate patch configurations, explore unconventional sound design techniques, and blur the boundaries between digital precision and analog warmth. The synergy between MIDI and voltage-controlled instruments offers a dynamic playground for sonic experimentation, enabling artists to sculpt evolving textures, intricate melodies, and expressive timbral shifts in real-time.
In essence, the conversion of MIDI messages into voltages represents a transformative journey from the realm of digital commands to the realm of analog control, where musical expression transcends the binary confines of digital data and embraces the fluidity of voltage-based modulation. This convergence of digital and analog technologies paves the way for innovative musical explorations, inviting musicians to navigate the interconnected landscapes of MIDI and voltage control with boundless creativity and sonic ingenuity.
Tools and Equipment Needed
To embark on the journey of converting MIDI messages into voltages, a specific set of tools and equipment is essential to facilitate this transformative process. The seamless integration of MIDI-based instruments and software with voltage-controlled devices and analog synthesizers requires specialized hardware and modules designed to interpret digital commands and generate corresponding control voltages. Here's a detailed overview of the tools and equipment needed to embark on this captivating exploration of MIDI and voltage conversion:
-
MIDI to CV Converter Module: At the core of the conversion process lies the MIDI to CV converter module, a fundamental component that serves as the bridge between the digital realm of MIDI and the analog domain of control voltages. This module is designed to receive MIDI data from input sources such as keyboards, sequencers, or DAWs, and translate this information into a variety of control signals. It typically features multiple outputs for pitch, gate, velocity, modulation, and other parameters, offering a comprehensive toolkit for shaping and manipulating control voltages.
-
Analog Synthesizer or Voltage-Controlled Instrument: In order to fully harness the converted control voltages, an analog synthesizer or voltage-controlled instrument is essential. This serves as the canvas upon which the translated MIDI messages manifest as tangible sonic expressions. Whether it's a modular synthesizer, analog monosynth, or voltage-controlled effects unit, having a capable analog device allows for the exploration of rich timbral textures, expressive modulation, and hands-on control over sound parameters.
-
MIDI Controller or Sequencer: To initiate the generation of MIDI messages that will undergo the conversion process, a MIDI controller or sequencer becomes a vital tool. This could be a MIDI keyboard, pad controller, or hardware sequencer, serving as the interface through which musical gestures and commands are translated into MIDI data. The versatility and expressive capabilities of the MIDI controller contribute to the dynamic nature of MIDI-based performances and productions.
-
Patch Cables and Interconnectivity: A robust collection of patch cables and interconnectivity accessories is indispensable for establishing the necessary connections between MIDI devices, MIDI to CV converter modules, and voltage-controlled instruments. These cables facilitate the transmission of MIDI data and control voltages, enabling seamless integration and communication within a modular or hybrid setup.
-
Power Supply and Mounting Hardware: As the setup expands to incorporate MIDI to CV converter modules and analog synthesizers, ensuring a reliable power supply and suitable mounting hardware becomes crucial. This includes power distribution solutions for modular systems, as well as mounting brackets, stands, or enclosures to accommodate the various components within a cohesive and ergonomic configuration.
By assembling this comprehensive array of tools and equipment, musicians and producers can embark on a captivating journey of converting MIDI messages into voltages, unlocking the boundless creative potential offered by the convergence of digital and analog technologies. With the right tools at their disposal, artists can sculpt immersive sonic landscapes, sculpt expressive performances, and push the boundaries of musical innovation through the seamless integration of MIDI and voltage control.
Step-by-Step Process
Embarking on the process of converting MIDI messages into voltages involves a series of deliberate steps aimed at establishing a seamless connection between digital commands and analog control signals. This transformative journey unfolds through a structured and methodical approach, allowing musicians and producers to navigate the intersection of MIDI and voltage control with precision and creativity. Here is a comprehensive step-by-step guide to the process of converting MIDI messages into voltages:
-
Assemble the Setup: Begin by assembling the necessary tools and equipment, including a MIDI to CV converter module, an analog synthesizer or voltage-controlled instrument, a MIDI controller or sequencer, patch cables, and power supply/mounting hardware. Ensure that all components are interconnected and powered up, creating a cohesive environment for the conversion process to unfold.
-
Configure MIDI Input: Connect the MIDI output of the MIDI controller or sequencer to the MIDI input of the MIDI to CV converter module. This establishes the pathway through which MIDI messages generated by the controller or sequencer will be transmitted to the converter module for interpretation and conversion into control voltages.
-
Assign MIDI Channels and Parameters: Configure the MIDI controller or sequencer to transmit specific MIDI messages, such as note-on/off commands, modulation data, pitch bend information, and other performance parameters. Assign MIDI channels and control assignments as needed, ensuring that the transmitted MIDI data aligns with the intended sonic expressions and control signals.
-
Interpret MIDI Data: The MIDI to CV converter module interprets the incoming MIDI data and translates it into corresponding control voltages. Depending on the capabilities of the converter module, this may involve generating control signals for pitch, gate triggers, velocity sensitivity, modulation sources, and other parameters based on the received MIDI messages.
-
Connect Control Voltages to Analog Instrument: Route the generated control voltages from the MIDI to CV converter module to the inputs of the analog synthesizer or voltage-controlled instrument. This establishes the direct link between the translated MIDI messages and the analog domain, allowing for real-time manipulation of sound parameters and expressive control over the analog device.
-
Experiment and Refine: Once the control voltages are interfaced with the analog synthesizer or instrument, engage in experimentation and refinement to explore the sonic possibilities offered by the converted MIDI messages. Manipulate the control voltages to modulate pitch, trigger note events, introduce expressive nuances, and sculpt dynamic timbral variations, leveraging the tactile nature of analog control to shape the musical output.
-
Integrate with Modular System (Optional): If working within a modular synthesizer environment, further integrate the converted control voltages with additional modules to expand the sonic palette and introduce complex modulation routings. This step allows for intricate patch configurations and the creation of evolving, organic soundscapes within a modular synthesis framework.
By following this step-by-step process, musicians and producers can seamlessly convert MIDI messages into voltages, bridging the realms of digital precision and analog expressiveness. This transformative journey empowers artists to sculpt immersive sonic experiences, craft expressive performances, and push the boundaries of musical innovation through the convergence of MIDI and voltage control.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the process of converting MIDI messages into voltages represents a transformative gateway to the seamless integration of digital and analog technologies in the realm of electronic music production. By unraveling the inner workings of MIDI and delving into the intricacies of control voltages, musicians and producers gain access to a rich tapestry of sonic possibilities, expressive control, and innovative sound design techniques.
The journey from digital commands to analog control signals embodies a convergence of art and technology, where the tactile nature of voltage control intersects with the precision of MIDI communication. This convergence empowers artists to sculpt immersive sonic landscapes, craft expressive performances, and push the boundaries of musical innovation through the seamless integration of MIDI and voltage control.
By understanding the nuances of MIDI messages and the transformative capabilities of control voltages, musicians can harness the expressive potential of analog gear, modular synthesizers, and voltage-controlled instruments. This opens up a world of creative possibilities, enabling artists to explore rich timbral textures, dynamic modulation, and hands-on control over sound parameters, fostering a deeper connection between the performer and the musical instrument.
Furthermore, the synergy between MIDI and voltage control invites artists to navigate interconnected landscapes of digital precision and analog warmth, blurring the boundaries between traditional and modern approaches to music production. The transformative journey of converting MIDI messages into voltages serves as a testament to the evolving nature of electronic music technology, where the fusion of digital and analog realms paves the way for innovative sonic explorations and artistic expressions.
In essence, the process of converting MIDI messages into voltages transcends the realm of technical conversion, embodying a creative odyssey that empowers musicians to shape sound with unparalleled depth and expressiveness. As the digital and analog worlds converge, a new frontier of musical innovation emerges, inviting artists to embark on a captivating exploration of MIDI and voltage control, where the boundaries between technology and artistry fade, and the language of music transcends the binary confines of digital data to embrace the fluidity of voltage-based modulation.