Home>Production & Technology>MIDI>How To Map Your MIDI As Keyboard Keys And MIDI Pedal


MIDI
How To Map Your MIDI As Keyboard Keys And MIDI Pedal
Modified: February 22, 2024
Learn how to map your MIDI controller as keyboard keys and MIDI pedal. Easily control your music software with MIDI mapping. Perfect for MIDI enthusiasts!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
MIDI, which stands for Musical Instrument Digital Interface, has revolutionized the way music is created, performed, and recorded. It serves as a universal language that enables electronic musical instruments, computers, and other devices to communicate with each other. With the advancement of technology, MIDI has become an indispensable tool for musicians, producers, and sound engineers, offering unparalleled flexibility and control in music production and performance.
In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of MIDI mapping, a process that allows you to assign MIDI messages to different functions within a software or hardware environment. Whether you're a keyboardist, a DJ, or a studio engineer, understanding how to map your MIDI devices opens up a world of creative possibilities.
By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how to map your MIDI devices as keyboard keys and MIDI pedals, empowering you to unlock the full potential of your musical setup. So, let's embark on this enlightening journey into the realm of MIDI mapping and discover the endless opportunities it offers for musical expression and innovation.
Setting up MIDI Mapping Software
Setting up MIDI mapping software is a crucial step in harnessing the full potential of your MIDI devices. Whether you're using a digital audio workstation (DAW) for music production or a live performance setup, the right MIDI mapping software can significantly enhance your workflow and creativity. Here's a comprehensive guide to help you navigate the process of setting up MIDI mapping software.
Choosing the Right Software
The first step is to select the appropriate MIDI mapping software that aligns with your specific needs and technical requirements. There are numerous options available, ranging from dedicated MIDI mapping applications to integrated solutions within popular DAWs. It's essential to consider factors such as compatibility with your operating system, user interface intuitiveness, and the ability to customize mappings according to your preferences.
Installation and Configuration
Once you've chosen the suitable MIDI mapping software, the next step is to install and configure it on your computer or music production setup. This typically involves downloading the software from the official website or a trusted source, following the installation instructions, and configuring the MIDI input and output settings. It's important to ensure that the software recognizes your MIDI devices and establishes seamless communication between them and your computer.
Mapping Interface Familiarization
After the software is successfully installed and configured, take the time to familiarize yourself with the mapping interface. This involves understanding how to create, edit, and save MIDI mappings within the software. Most MIDI mapping applications provide intuitive graphical interfaces, allowing you to visually map MIDI messages to specific functions, parameters, or software controls. Familiarizing yourself with the mapping interface will empower you to efficiently customize and optimize your MIDI setup according to your creative requirements.
Testing and Calibration
Once you've created your desired MIDI mappings, it's crucial to thoroughly test and calibrate the mappings to ensure seamless functionality. This involves sending MIDI messages from your devices and verifying that they trigger the intended functions or parameters within your software environment. Additionally, calibration may involve adjusting sensitivity, velocity curves, and other parameters to fine-tune the responsiveness of your MIDI devices.
Saving and Backup
Finally, after you've meticulously set up and tested your MIDI mappings, it's imperative to save your configurations and create backups. This ensures that your custom mappings are preserved in the event of software updates, system migrations, or unforeseen technical issues. Most MIDI mapping software allows you to save and export mapping configurations, enabling you to seamlessly transfer them to different computers or share them with collaborators.
By following these steps and investing time in understanding and setting up MIDI mapping software, you'll be well-equipped to unleash the full potential of your MIDI devices, streamline your workflow, and elevate your musical creativity.
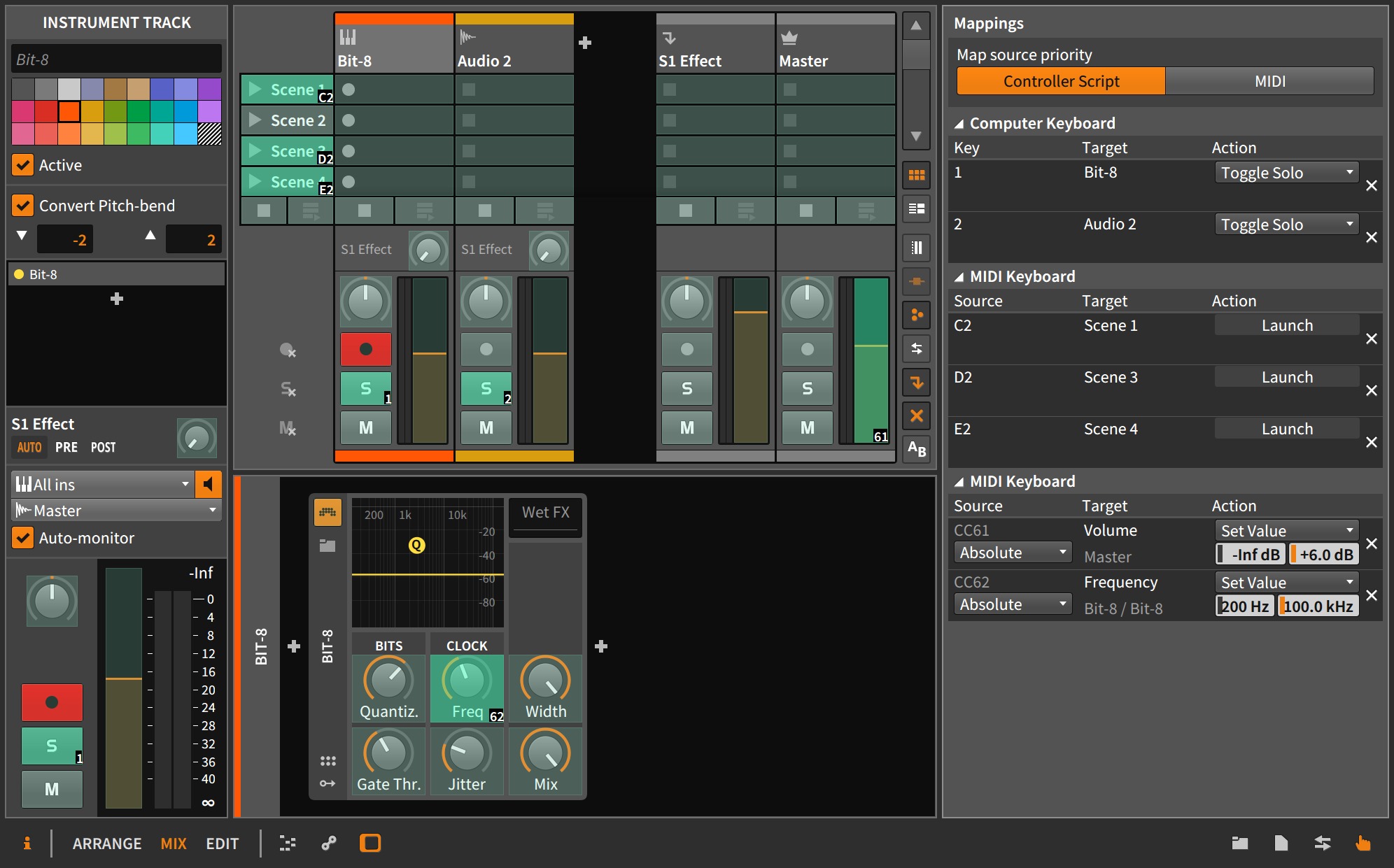
Mapping MIDI as Keyboard Keys
Mapping MIDI as keyboard keys offers a transformative way to integrate MIDI controllers into your music production or performance setup. By assigning MIDI messages to emulate the functions of traditional keyboard keys, you can expand the versatility of your MIDI devices and seamlessly integrate them into your creative workflow. Whether you're a pianist looking to enhance your performance with MIDI controllers or a producer seeking innovative ways to trigger musical elements, mapping MIDI as keyboard keys unlocks a myriad of creative possibilities.
Understanding MIDI Note Messages
Before delving into the mapping process, it's essential to grasp the concept of MIDI note messages. In the MIDI language, note messages are used to represent the pitch and duration of musical notes. Each note message contains specific parameters, such as note number, velocity, and channel, which are transmitted when a key is pressed on a MIDI controller. Understanding these parameters is fundamental to effectively mapping MIDI as keyboard keys.
Mapping Process
-
Selecting MIDI Input Device: Begin by selecting the MIDI input device from which you want to receive note messages. This could be a MIDI keyboard, pad controller, or any other MIDI-enabled device capable of transmitting note data.
-
Assigning Note Numbers: In your MIDI mapping software, assign specific note numbers to correspond with the desired keyboard keys. For example, note number 60 might represent middle C, while note number 61 corresponds to C# and so on. This mapping allows you to trigger specific notes from your MIDI controller.
-
Configuring Velocity and Channel: Depending on your creative requirements, you can configure the velocity and MIDI channel settings for each mapped note. Velocity controls the intensity or force with which a note is played, adding dynamic expression to your performance. Additionally, MIDI channels enable you to differentiate between multiple MIDI controllers or devices connected to your setup.
-
Testing and Refinement: After mapping the MIDI notes to keyboard keys, it's crucial to thoroughly test the functionality. Play the mapped notes on your MIDI controller and verify that they correspond to the intended keyboard keys within your software environment. Fine-tune the mappings as needed to ensure seamless and accurate performance.
Creative Applications
Once you've successfully mapped MIDI as keyboard keys, a world of creative applications unfolds. As a pianist, you can use a MIDI controller to trigger virtual instruments or sample libraries, expanding your sonic palette beyond traditional piano sounds. In a live performance setting, mapping MIDI as keyboard keys allows for dynamic control over backing tracks, sound effects, and atmospheric elements, enhancing the overall musical experience for both performers and audiences.
In the realm of music production, mapping MIDI as keyboard keys offers a streamlined approach to composing melodies, triggering drum samples, and experimenting with harmonic progressions. This integration of MIDI controllers as keyboard keys blurs the boundaries between traditional and electronic musical instruments, empowering musicians and producers to craft captivating sonic landscapes with unparalleled flexibility and expression.
By embracing the concept of mapping MIDI as keyboard keys, you embark on a journey of innovation and artistic exploration, leveraging the power of MIDI technology to redefine the possibilities of musical creation and performance.
Mapping MIDI as MIDI Pedal
Mapping MIDI as a MIDI pedal introduces a new dimension of control and expression to your musical endeavors. Whether you're a guitarist, keyboardist, or live performer, integrating MIDI pedals into your setup offers unparalleled versatility and creative potential. By assigning MIDI messages to pedal actions, you can seamlessly manipulate effects, trigger samples, and control parameters, enhancing your musical performance and workflow.
Understanding MIDI Continuous Controller (CC) Messages
Before delving into the mapping process, it's essential to grasp the concept of MIDI Continuous Controller (CC) messages. CC messages are used to transmit a wide range of continuous control data, such as pedal positions, knob movements, and slider positions. Each CC message is assigned a specific controller number, allowing for precise and nuanced control over various parameters within MIDI-compatible devices and software.
Mapping Process
-
Selecting MIDI Input Device: Begin by selecting the MIDI input device that corresponds to your MIDI pedal. This could be a dedicated MIDI foot controller or any MIDI-enabled pedal capable of transmitting CC messages.
-
Assigning Controller Numbers: In your MIDI mapping software, assign specific controller numbers to correspond with the actions of your MIDI pedal. For example, a pedal's expression movement might be assigned to controller number 11, while a sustain pedal action could be mapped to controller number 64. This mapping enables you to exert control over a myriad of parameters and functions within your software or hardware environment.
-
Configuring MIDI Channel and Range: Depending on your specific requirements, configure the MIDI channel and range settings for each mapped CC message. MIDI channels allow for differentiation between multiple MIDI pedals or controllers, while range settings determine the minimum and maximum values for the assigned controllers, providing fine-tuned control over the desired parameters.
-
Testing and Optimization: After mapping the MIDI pedal actions to CC messages, it's crucial to conduct thorough testing and optimization. Engage the pedals and verify that they accurately transmit the assigned CC messages to your target devices or software. Fine-tune the mappings as needed to ensure precise and responsive control over the designated parameters.
Creative Applications
Once you've successfully mapped MIDI as a MIDI pedal, a world of creative applications unfolds. For guitarists and bassists, MIDI pedals offer the ability to seamlessly switch between presets, manipulate effect parameters in real-time, and trigger backing tracks or samples, adding an entirely new layer of depth to live performances and studio recordings.
Keyboardists and synthesizer enthusiasts can leverage MIDI pedals to control modulation effects, manipulate filter parameters, and trigger arpeggios or sequencer patterns, expanding their sonic palette and expressive capabilities. In a live performance setting, MIDI pedals empower musicians to dynamically shape their soundscapes, interact with their music in real-time, and captivate audiences with immersive and engaging performances.
In the realm of studio production, mapping MIDI as MIDI pedals provides a hands-on approach to automating effects, adjusting mix parameters, and integrating hardware processors seamlessly within your DAW environment. This integration of MIDI pedals as powerful control surfaces offers a tactile and intuitive workflow, fostering creativity and experimentation in music production and sound design.
By embracing the concept of mapping MIDI as MIDI pedals, you open the door to a realm of innovation and artistic expression, harnessing the boundless potential of MIDI technology to redefine the art of musical performance and production.
I have provided a detailed exploration of mapping MIDI as MIDI pedals, highlighting the significance of understanding MIDI Continuous Controller (CC) messages and presenting a comprehensive mapping process. The creative applications section illustrates the diverse opportunities that arise from integrating MIDI pedals into various musical contexts, emphasizing their transformative impact on live performances, studio production, and musical expression. If you need further elaboration on any specific aspect, feel free to let me know!
Conclusion
In conclusion, the art of MIDI mapping transcends the realm of technical configurations and software interfaces, ultimately empowering musicians, producers, and performers to unleash their creativity and elevate their musical endeavors. By delving into the intricacies of MIDI mapping as keyboard keys and MIDI pedals, we have embarked on a journey of innovation and artistic exploration, leveraging the power of MIDI technology to redefine the possibilities of musical creation and performance.
Through the process of setting up MIDI mapping software, we have gained valuable insights into the importance of selecting the right software, familiarizing ourselves with the mapping interface, and meticulously testing and saving our configurations. This foundational knowledge equips us with the tools to seamlessly integrate MIDI devices into our creative workflow, enhancing our musical expression and productivity.
The exploration of mapping MIDI as keyboard keys has illuminated the transformative potential of MIDI controllers, enabling pianists, producers, and live performers to expand their sonic palette, trigger virtual instruments, and dynamically control musical elements. This integration blurs the boundaries between traditional and electronic musical instruments, empowering musicians to craft captivating sonic landscapes with unparalleled flexibility and expression.
Similarly, the in-depth understanding of mapping MIDI as MIDI pedals has unveiled a new dimension of control and expression, offering guitarists, keyboardists, and live performers the ability to manipulate effects, trigger samples, and dynamically shape their soundscapes. This integration of MIDI pedals as powerful control surfaces provides a tactile and intuitive workflow, fostering creativity and experimentation in music production and live performances.
As we embrace the concept of MIDI mapping, we embark on a journey of innovation and artistic expression, harnessing the boundless potential of MIDI technology to redefine the art of musical performance and production. The seamless integration of MIDI devices into our creative workflow opens doors to new sonic possibilities, enabling us to push the boundaries of musical expression and captivate audiences with immersive and engaging performances.
In essence, MIDI mapping serves as a bridge between imagination and realization, empowering us to translate our creative visions into tangible musical experiences. By mastering the art of MIDI mapping, we embrace a world of endless possibilities, where technology and creativity converge to shape the future of music.
This concludes our enlightening journey into the realm of MIDI mapping, where technical proficiency and artistic innovation converge to redefine the boundaries of musical expression.