Home>Instruments>Synthesizer>How To Use A Multitimbral Software Synthesizer


Synthesizer
How To Use A Multitimbral Software Synthesizer
Modified: March 5, 2024
Learn how to efficiently utilize a multitimbral software synthesizer. Explore the endless possibilities of this versatile instrument. Master the art of synthesizing with our comprehensive guide.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Multitimbral Software Synthesizers
- Setting Up Your Multitimbral Software Synthesizer
- Exploring the User Interface
- Navigating Sound Banks and Presets
- Creating and Editing Sounds
- Layering Multiple Sounds
- Using MIDI Controllers with Multitimbral Software Synthesizers
- Applying Effects and Modulations
- Saving and Exporting Your Creations
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to the world of multitimbral software synthesizers! As a music enthusiast, you know that synthesizers are essential tools for creating electronic music. They allow you to produce a wide range of sounds, from classic analog tones to futuristic digital textures. Multitimbral software synthesizers take things to the next level by allowing you to play and control multiple sounds simultaneously, providing an incredible level of flexibility and creativity.
In this article, we’ll guide you through the ins and outs of using a multitimbral software synthesizer. Whether you are a beginner just starting out or an experienced producer looking to expand your sonic palette, this guide will help you unlock the full potential of these powerful virtual instruments.
First, we’ll begin by explaining what multitimbral software synthesizers are and how they differ from regular synthesizers. Then, we’ll walk you through the initial setup process, including loading the software and connecting it to your DAW (Digital Audio Workstation). Once you’re up and running, we’ll delve into the user interface and show you how to navigate through the various controls and parameters.
Next, we’ll explore the vast library of sound banks and presets that come with the multitimbral software synthesizer. We’ll teach you how to select and load sounds, as well as customize and edit them to suit your musical vision. One of the key features of multitimbral synthesizers is the ability to layer multiple sounds together, so we’ll show you the best techniques for achieving rich and complex textures with your compositions.
If you use MIDI controllers in your music production, we’ve got you covered. We’ll provide tips and tricks for integrating MIDI controllers with your multitimbral software synthesizer, allowing you to control various parameters in real-time and add expressive touches to your performances.
To take your sounds to the next level, we’ll also delve into the world of effects and modulations. You’ll learn how to apply different effects to your sounds and manipulate them dynamically using modulation sources. This will open up endless possibilities for creating unique and vibrant musical landscapes.
Finally, we’ll guide you on how to save and export your creations from the multitimbral software synthesizer. Whether you want to save them as presets for future use or export them as audio files to share with others, we’ll show you the necessary steps to ensure your hard work doesn’t go to waste.
So, get ready to dive into the exciting world of multitimbral software synthesizers and explore new realms of sound creation. Whether you’re a producer, composer, or sound designer, these virtual instruments will revolutionize your music-making process. Let’s begin our journey together!
Understanding Multitimbral Software Synthesizers
To fully harness the power of multitimbral software synthesizers, it’s important to understand what they are and how they differ from regular synthesizers.
A multitimbral software synthesizer is a virtual instrument that allows you to play and control multiple sounds simultaneously. What sets them apart from regular synthesizers is their ability to generate and process multiple audio signals independently, often referred to as “timbres.” This means you can create complex and layered sounds by combining different timbres together.
Each timbre in a multitimbral software synthesizer is essentially a separate synthesizer engine within the larger instrument. This means that you can manipulate the parameters, such as oscillators, filters, envelopes, and effects, individually for each timbre. This level of control opens up a world of sonic possibilities, giving you the ability to create rich and textured compositions.
One of the advantages of using multitimbral software synthesizers is their versatility. They can replicate the sounds of traditional analog synthesizers, complex digital synths, and even acoustic instruments, all within a single instrument. This flexibility allows for creative exploration across a wide range of genres and musical styles.
Another key feature of multitimbral software synthesizers is their integration with your Digital Audio Workstation (DAW). This allows for seamless communication between the synthesizer and your recording software, enabling you to incorporate the sounds created with the synthesizer into your overall production. It also gives you the ability to automate parameters, control the synthesizer with MIDI controllers, and synchronize it with other elements of your composition.
While multitimbral software synthesizers offer tremendous creative freedom, they can also be complex and overwhelming. Understanding the terminology and different components of the synthesizer’s user interface is crucial. Key components include oscillators (sound generators), filters (tone modifiers), envelopes (modifiers over time), and effects (sonic enhancements).
By familiarizing yourself with these elements, you will be able to navigate the interface and shape your sounds with precision. With time and practice, you’ll develop a keen sense of how to leverage the full potential of multitimbral software synthesizers to achieve your desired musical vision.
Now that we have a better understanding of what multitimbral software synthesizers are and how they work, let’s move on to the next section, where we’ll guide you through the process of setting up your multitimbral software synthesizer.
Setting Up Your Multitimbral Software Synthesizer
Before you can start using your multitimbral software synthesizer, you’ll need to go through the setup process. This will involve installing the software and making the necessary connections to integrate it with your Digital Audio Workstation (DAW).
The first step is to download and install the multitimbral software synthesizer from the manufacturer’s website. Follow the installation instructions provided to ensure a successful setup. Once the software is installed, open your DAW and navigate to the plugin manager. Locate the multitimbral software synthesizer and enable it as a plugin in your DAW. This will allow you to access and control the synthesizer within your DAW’s interface.
Next, you’ll need to create a MIDI track in your DAW and assign the MIDI output to the multitimbral software synthesizer. This will establish the communication between your DAW and the synthesizer. Ensure that the MIDI input settings in the multitimbral software synthesizer are correctly configured to receive MIDI signals from your DAW.
Additionally, if you plan to use an external MIDI controller to play the multitimbral software synthesizer, connect the controller to your computer via USB or MIDI cables. Configure the MIDI input settings in both your DAW and the multitimbral software synthesizer to recognize the MIDI controller and map its controls to the appropriate parameters in the synthesizer.
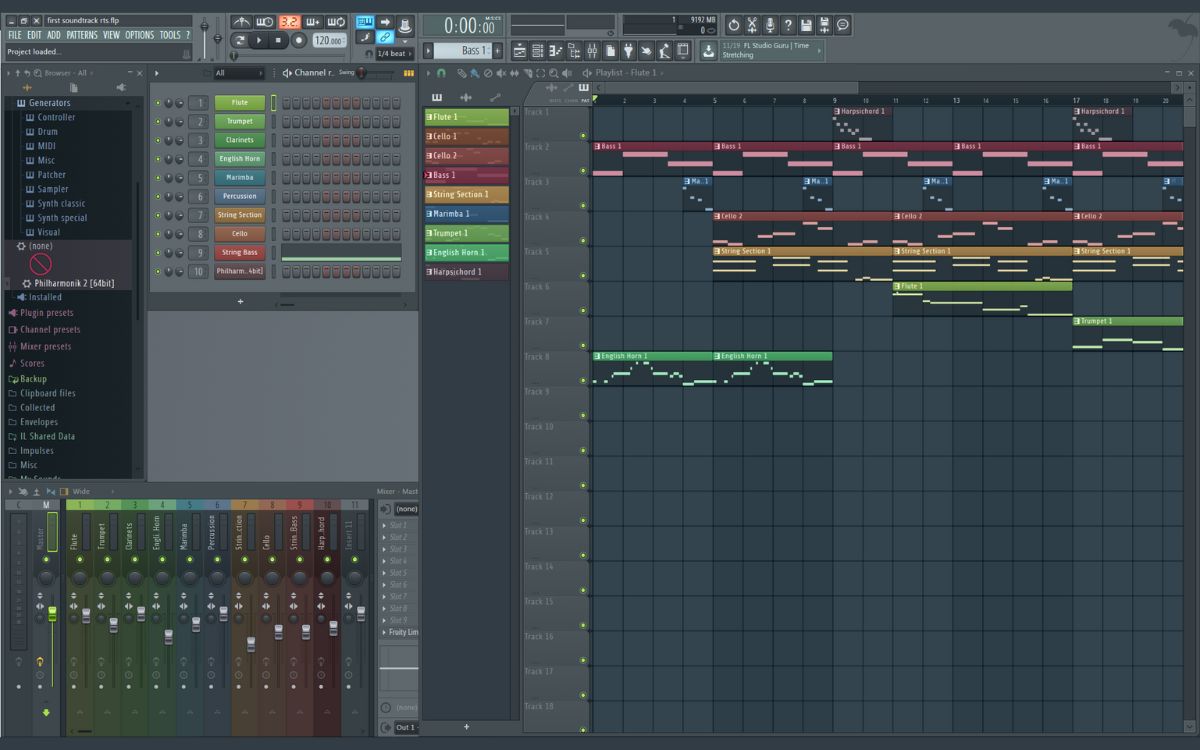
Once the setup is complete, you’re ready to start exploring and creating with your multitimbral software synthesizer. Load the synthesizer onto a track in your DAW, and you’ll be greeted with a user interface that consists of various knobs, sliders, and buttons to control the different parameters of the synthesizer.
Depending on the specific multitimbral software synthesizer you’re using, the user interface may be organized into sections such as oscillators, filters, envelopes, effects, and modulation. Familiarize yourself with the layout and functionality of each section to effectively manipulate the timbres and shape your sounds.
It’s also worth noting that multitimbral software synthesizers often come with a wide range of included presets and sound banks. These provide a good starting point for your exploration and can be an excellent source of inspiration. Spend some time browsing through the available sounds to get a sense of the capabilities of your multitimbral software synthesizer.
With the software installed, the connections established, and a basic understanding of the user interface, you’re now ready to unleash your creativity and dive into the world of multitimbral sound design. In the next section, we’ll take a closer look at the various components of the user interface and guide you through navigating and manipulating the sounds on your multitimbral software synthesizer.
Exploring the User Interface
Now that your multitimbral software synthesizer is set up, it’s time to familiarize yourself with its user interface. Understanding the various controls and parameters will allow you to navigate and manipulate the sounds with ease.
When you open your multitimbral software synthesizer, you’ll typically be presented with a graphical representation of the synthesizer’s user interface. This interface will display different sections and modules that you can interact with to shape your sounds.
One of the key sections you’ll find in most multitimbral software synthesizers is the oscillator section. This is where you can control the primary sound source of your synthesizer. You’ll typically find options for selecting different waveform types, adjusting the pitch, and controlling the modulation of the oscillators.
Another important section is the filter section. This allows you to shape the timbre of your sounds by controlling the frequency response. You can adjust parameters such as cutoff frequency, resonance, and filter type to achieve the desired tonal characteristics.
The envelope section is where you’ll find controls for shaping the trajectory of your sound over time. Envelopes typically consist of parameters like attack, decay, sustain, and release. Adjusting these parameters will affect how the sound evolves from the moment it’s triggered until it fades out.
Most multitimbral software synthesizers also provide an effects section. This allows you to add various types of audio enhancements to your sounds, such as reverb, delay, chorus, and distortion. These effects can significantly alter the character and spatial quality of your sounds, adding depth and richness.
Modulation is another essential aspect of multitimbral software synthesizers. This section enables you to modulate different parameters of your sound over time or based on specific input sources. Common modulation sources include LFOs (Low-Frequency Oscillators), which can add vibrato or create rhythmic effects, and modulation envelopes, which can shape parameters dynamically.
As you explore the user interface, take note of any additional sections or modules that may be specific to your multitimbral software synthesizer. Some synthesizers may have advanced features like arpeggiators, step sequencers, or wavetable editors, which provide even more creative possibilities.
Once you become familiar with the layout and functionality of the user interface, it’s time to start experimenting. Begin by tweaking the various parameters and controls to understand how they affect the sound. Try combining different waveforms, adjusting filter settings, and adding modulation to bring movement and complexity to your sounds.
Remember that multitimbral software synthesizers often come with a wide range of presets and sound banks. These can be a great starting point for your exploration, allowing you to dive into different genres and styles. Load up presets and dissect them to understand how they were created, and use them as a foundation for your own unique sound design.
As you spend more time exploring the user interface and experimenting with different settings, you’ll develop a deeper understanding of your multitimbral software synthesizer and the countless possibilities it offers for sound creation. In the next section, we’ll dive into the process of navigating and selecting sounds from the available sound banks and presets.
Navigating Sound Banks and Presets
One of the exciting aspects of using a multitimbral software synthesizer is the vast library of sound banks and presets that come with it. These pre-designed sounds can serve as a starting point for your compositions or provide instant inspiration. Navigating and selecting the right sounds from these libraries is an essential skill for any sound designer or music producer.
When you open your multitimbral software synthesizer, you’ll typically have access to a sound browser or preset manager. This feature allows you to search and browse through the available sound banks and presets based on various criteria such as genre, instrument, or mood.
Start by exploring the different sound banks and categories available in your multitimbral software synthesizer. These categories can be organized by instrument type, sound character, or even specific genres. Take your time to navigate through each category and get an overview of the sounds available to you.
When you find a category that interests you, delve deeper by browsing through the individual presets. Presets are pre-designed sound settings created by sound designers or the manufacturers themselves. They offer a wide range of sounds, from basic acoustic timbres to complex synthesized textures and effects.
As you navigate through the presets, take note of any that catch your attention. You can listen to the presets directly within the multitimbral software synthesizer to get a sense of their sonic characteristics. Some synthesizers may even allow you to preview the sounds in the context of your composition.
Once you’ve found a preset that you like, load it into the multitimbral software synthesizer. This will instantly apply the preset’s sound settings to the corresponding timbre. You can then begin modifying the preset to suit your musical needs by adjusting the parameters of the oscillators, filters, envelopes, and effects within the synthesizer’s user interface.
In addition to the built-in sound banks and presets, many multitimbral software synthesizers allow for the creation and saving of your own custom sounds. This gives you the freedom to explore and experiment with sound design, tailoring the instrument to your unique style and musical vision.
When saving your own sounds, consider using descriptive names and organize them into your own custom sound banks. This will make it easier for you to locate and recall your creations in the future. Managing your sounds effectively will save you valuable time and allow you to focus more on the creative aspects of your music production.
Remember that sound selection is a highly personal process. What works for one song or genre may not necessarily work for another. Always trust your ears and experiment with different sounds to find the one that best fits your composition.
With the ability to navigate sound banks and presets, you now have a wealth of sonic possibilities at your fingertips. In the next section, we’ll explore how to create and edit your own sounds within a multitimbral software synthesizer.
Creating and Editing Sounds
While presets offer a great starting point, the true power of a multitimbral software synthesizer lies in the ability to create and customize your own sounds. This allows you to craft unique timbres that perfectly fit your musical vision. Let’s explore the process of creating and editing sounds within a multitimbral software synthesizer.
Start by selecting an empty timbre or initializing a new sound in your multitimbral software synthesizer. This will provide a blank canvas for you to work with.
Begin shaping the sound by adjusting the parameters in the oscillators section. Experiment with different waveform types, detuning options, and pitch controls to create the fundamental tone of your sound. A combination of multiple oscillators can add depth and richness to your sound.
Next, move on to the filter section. Here, you can fine-tune the tonal characteristics of your sound by adjusting the cutoff frequency, resonance, and filter type. Play around with these parameters to sculpt the sound according to your preferences.
For dynamic control, navigate to the envelopes section. Envelopes determine how your sound changes over time, from the initial attack to the decay, sustain, and release phases. Adjust the envelope parameters to shape the sound’s volume, cutoff, or other relevant parameters based on your desired effect.
Explore the modulation options available in your multitimbral software synthesizer. Modulation sources like LFOs (Low-Frequency Oscillators) and modulation envelopes can add movement and variations to your sound. Experiment with assigning these modulators to parameters like pitch, volume, or filter cutoff to introduce dynamic changes to your sound.
Don’t forget the effects section, where you can add the finishing touches to your sound. Apply reverb, delay, chorus, or other effects to create a sense of space and depth. Experiment with different effect settings to find the perfect combination for your sound.
As you delve deeper into sound creation, make use of your ears and trust your intuition. Experiment with different parameter settings, push the boundaries, and embrace happy accidents. Taking risks and exploring uncharted territories will lead you to exciting and innovative sounds.
Once you’ve created a sound that you’re satisfied with, consider saving it as a new preset or adding it to your custom sound bank. This will allow you to easily access it in future compositions.
Remember that sound creation is a continual learning process, and practice will help you refine your skills. Tweak existing sounds, explore the various sections and components of your multitimbral software synthesizer, and experiment with different combinations to continually evolve your sound design abilities.
In the next section, we’ll explore another powerful feature of multitimbral software synthesizers: layering multiple sounds together to create rich and complex textures.
Layering Multiple Sounds
A key advantage of multitimbral software synthesizers is the ability to layer multiple sounds together, resulting in rich and complex textures. Layering allows you to combine different timbres and create unique sonic combinations that enhance your compositions. Let’s explore how to effectively layer multiple sounds within a multitimbral software synthesizer.
Start by selecting the timbres you want to layer. Each timbre can be thought of as an individual sound source within the multitimbral software synthesizer. Choose sounds that complement each other and create a cohesive sonic palette.
Once you have your desired timbres, assign each timbre to its own MIDI channel within the multitimbral software synthesizer. This will ensure that each sound is triggered independently and can be processed separately.
Experiment with different timbral combinations to find the right balance. Layering timbres with different characteristics, such as a lush pad with a gritty bass sound, can create an intriguing contrast that adds depth and complexity to your composition.
Adjust the volume levels and panning positions of each timbre to create a balanced and spacious mix. You can use the mixer section within the multitimbral software synthesizer to control these parameters. By panning the sounds across the stereo field, you can achieve a wider and more immersive soundstage.
Consider applying different effects and processing to each layer to further enhance their individual characteristics. For example, you can add reverb or delay to a pad layer to create a sense of space, while adding distortion or modulation effects to a lead layer for added intensity and movement.
Experiment with different modulation techniques to create evolving and dynamic layered sounds. Applying modulation to each layer can introduce subtle variations in pitch, volume, or timbre over time, resulting in a more organic and evolving sound.
Take advantage of the multitimbral software synthesizer’s capabilities to assign different MIDI controllers to control specific parameters of each layer. This allows for expressive real-time control over each sound, adding a human touch and allowing you to shape the performance dynamically.
Remember to use your ears and trust your instincts when layering sounds. Listen carefully to the combinations and make adjustments as needed. Layering can be a trial-and-error process, but with practice, you’ll develop an understanding of how different timbral combinations work together.
By layering multiple sounds within a multitimbral software synthesizer, you can create unique and complex textures that elevate your compositions. The possibilities are endless, so don’t be afraid to push the boundaries and explore different combinations to find your signature layered sound.
In the next section, we’ll explore how to make the most out of using MIDI controllers with multitimbral software synthesizers, unlocking even more expressive possibilities for your sound design and performance.
Using MIDI Controllers with Multitimbral Software Synthesizers
MIDI controllers provide a hands-on approach to control and manipulate the parameters of multitimbral software synthesizers. They offer a more expressive and dynamic way to interact with your sounds, allowing you to infuse your performances with personal touches. Let’s explore how to effectively utilize MIDI controllers with multitimbral software synthesizers.
Connect your MIDI controller to your computer via USB or MIDI cables. Ensure that both the MIDI controller and the multitimbral software synthesizer are recognized and configured correctly. This usually involves assigning MIDI channels for each timbre or sound layer within the synthesizer.
Once your MIDI controller is connected and configured, familiarize yourself with the different controls and assignments available on the controller. These can include keys, pads, knobs, sliders, and wheels, each with its own unique functionality.
Assign specific parameters of the multitimbral software synthesizer to the controls on your MIDI controller. This can be achieved through MIDI mapping or MIDI learn functions within the synthesizer or your DAW. Map parameters such as cutoff frequency, resonance, envelope settings, or effects parameters to the appropriate controls on your MIDI controller.
Experiment with assigning different parameters to different controls to suit your playing style and musical needs. Consider mapping performance-oriented controls such as pitch bend, mod wheel, or aftertouch to bring extra expression and character to your sound design and performances.
You can also make use of MIDI controller features like velocity sensitivity to control parameters based on how hard you strike the keys or pads. This can be especially useful for controlling things like volume, filter cutoff, or envelope dynamics based on the intensity of your playing.
Explore the possibilities of MIDI controller mappings in layers. By assigning different parameters to different MIDI channels or zones on your controller, you can control multiple timbres or sounds simultaneously, further expanding your sonic capabilities.
Take advantage of MIDI controller presets or memory banks to save and recall different mappings for various performance situations. This allows you to switch between different setups effortlessly, whether you’re in the studio or performing on stage.
Keep in mind that MIDI controller integration with multitimbral software synthesizers can vary depending on the specific synthesizer and controller you use. Some multitimbral software synthesizers may have dedicated support or templates for popular MIDI controllers, making the setup process and mapping more streamlined.
Experiment with different playing techniques and gestures on your MIDI controller to discover unique ways to interact and shape your sounds. Whether it’s using the pitch bend to create expressive bends and glides or using the pads to trigger rhythmic patterns, explore the full potential of your MIDI controller to bring life to your soundscapes.
Using MIDI controllers with multitimbral software synthesizers adds a new level of creativity and expression to your music production. By mapping and manipulating parameters in real-time, you’ll be able to infuse your compositions with your unique musical voice.
In the next section, we’ll delve into applying effects and modulations to further enhance and shape your sounds within a multitimbral software synthesizer.
Applying Effects and Modulations
Add extra depth, dimension, and movement to your sounds within a multitimbral software synthesizer by applying effects and modulations. Effects and modulations allow you to create sonic variations, textures, and transformations that add a unique touch to your compositions. Let’s explore how to effectively use effects and modulations within a multitimbral software synthesizer.
Effects are audio processors that can be applied to your sounds to enhance or modify them. Common effects include reverb, delay, chorus, flanger, distortion, and more. Experiment with different effects to achieve the desired sonic aesthetic for your sounds.
Begin by selecting the effect you want to apply to a specific timbre or layer within your multitimbral software synthesizer. Adjust the effect parameters to your liking. For example, with reverb, you may control parameters such as decay time, room size, or wet/dry mix. With distortion, you can adjust the gain, tone, and saturation settings.
Consider using multiple effects in combination to achieve more complex and intricate sound textures. For instance, combining reverb with delay can create a sense of spaciousness and depth, while adding chorus can add a rich, modulated quality to your sounds.
Modulation within a multitimbral software synthesizer allows you to introduce dynamic changes to specific parameters of your sound over time or based on various modulation sources. Common modulation sources include LFOs (Low-Frequency Oscillators) and modulation envelopes.
Assigning modulation sources to parameters can create rhythmic patterns, vibrato, tremolo, or other time-based effects. For example, assigning an LFO to control the filter cutoff frequency can create a sweeping or pulsating effect as the LFO’s waveform modulates the cutoff value.
Explore the different modulation options within your multitimbral software synthesizer. Experiment with various modulation sources and destinations to discover unique and expressive ways to shape your sounds. Modulation can add movement, dynamics, and interest to otherwise static timbres.
Take advantage of the depth and flexibility offered by modulations. Adjust the intensity, speed, and depth of the modulation sources to achieve the desired effect. Fine-tune the settings until the modulation becomes an integral part of the sound design, enhancing the overall sonic tapestry.
Consider using MIDI controllers to modulate parameters in real-time. For example, mapping a mod wheel or expression pedal to control the depth or speed of a modulation can allow for dynamic, hands-on control over the effect, adding an extra layer of expressiveness to your performances.
Combining effects and modulations can lead to even more complex and sonically rich sounds. Experiment with different effects and modulation combinations to push the boundaries of your sound design and discover new sonic possibilities.
As you work with effects and modulations, always trust your ears and let your creativity guide you. Test different settings, automate parameters, and be open to happy accidents that may unveil unexpected and inspiring results.
In the next section, we’ll explore how to save and export your creations from the multitimbral software synthesizer so you can preserve and share your musical ideas with others.
Saving and Exporting Your Creations
Once you’ve created and fine-tuned your sounds within a multitimbral software synthesizer, it’s important to save and export your creations so that you can preserve them for future use or share them with others. Let’s explore how to effectively save and export your creations from a multitimbral software synthesizer.
Most multitimbral software synthesizers offer the ability to save your custom sounds as presets. Saving your sounds as presets allows you to quickly recall and use them in future compositions. When saving a preset, give it a descriptive name that reflects the character or intended use of the sound.
In addition to saving presets, many multitimbral software synthesizers allow you to organize your sounds into sound banks or folders. This helps keep your sounds organized and easily accessible. Consider creating custom sound banks based on sound characteristics, genres, or specific projects to streamline your workflow.
If you want to export your creations as audio files, you can utilize the recording capabilities of your Digital Audio Workstation (DAW). Route the audio output of your multitimbral software synthesizer to an audio track in your DAW, and then record the audio as you play or sequence your sounds. This allows you to capture your creations as audio files that can be further edited or mixed within your DAW.
When exporting your audio, consider saving the files in a high-quality format such as WAV or FLAC to preserve the quality of your sounds. Pay attention to the export settings in your DAW, ensuring that the sample rate, bit depth, and file format are suitable for your desired end use.
If you want to share your sounds with others, consider creating a sound library or sample pack. This can be a collection of presets, MIDI files, audio loops, or even standalone project files that include the presets and configuration for your multitimbral software synthesizer. Package the files in a organized and user-friendly manner, and share them through online platforms or with your collaborators and fellow musicians.
Before finalizing and exporting your creations, it’s always a good idea to check your settings and make sure everything sounds as intended. Do a thorough listen and make any necessary adjustments to the levels, effects, or modulation settings to ensure the best possible representation of your sound.
Remember to back up your creations regularly. It’s wise to create backup copies of your sound banks, presets, and associated project files, either on external hard drives, cloud storage, or another reliable backup solution. This helps protect your creations from accidental loss or hardware failures.
By saving and exporting your creations from the multitimbral software synthesizer, you can build a library of custom sounds that reflect your unique style and musical vision. Whether using them in your own compositions or sharing them with others, these saved creations serve as a valuable resource for your creative endeavors.
As we conclude this guide, we hope that it has empowered you to effectively utilize multitimbral software synthesizers and explore the vast world of sound design and music production. Remember to continue experimenting, exploring new techniques, and unleashing your creativity through the power of multitimbral software synthesizers.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve reached the end of our comprehensive guide on using multitimbral software synthesizers. We’ve covered a lot of ground, from understanding the fundamentals of multitimbral synthesis to exploring sound banks, creating and editing sounds, layering multiple sounds, using MIDI controllers, applying effects and modulations, and saving and exporting your creations.
With the knowledge and skills you’ve gained, you now have the tools to unlock the full potential of multitimbral software synthesizers and elevate your music production. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced producer, these versatile virtual instruments offer endless possibilities for sound creation and exploration across a wide range of musical styles.
Remember, practice makes perfect. As you delve deeper into multitimbral synthesis, continue to experiment, explore new techniques, and trust your instincts. Develop your unique sound signature by combining different timbres, layering sounds, and applying creative effects and modulations. The more you explore and push the boundaries of your multitimbral software synthesizer, the more you’ll discover your own musical voice.
Take advantage of the included presets and sound banks as a starting point but don’t be afraid to venture into sound design territory. Customize and shape your sounds to fit your artistic vision. Trust your ears, follow your intuition, and let your creativity guide you.
Lastly, always remember to save and backup your creations. Whether you’re saving presets, organizing sound banks, or exporting audio files, ensure that your hard work is safeguarded. This way, you can revisit and share your creations with others, allowing you to collaborate, inspire, and contribute to the vibrant world of music production.
We hope this guide has provided you with the knowledge and inspiration to fully utilize multitimbral software synthesizers and unlock new sonic horizons. Embrace the endless possibilities, hone your skills, and enjoy the journey of creating unique and captivating sounds that will enrich your music for years to come.