Home>Production & Technology>Audio Interface>Can You Keep Phantom Power Turned On When You Shut Off Your Audio Interface


Audio Interface
Can You Keep Phantom Power Turned On When You Shut Off Your Audio Interface
Modified: February 17, 2024
Discover if it's safe to keep phantom power on when turning off your audio interface. Find out how it affects your equipment and performance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of audio interfaces, where the quality of sound is paramount. Whether you are a musician, podcaster, or audio engineer, having a reliable audio interface is essential to capture and process your audio signals. One important aspect of audio interfaces that often confuses beginners is the concept of phantom power.
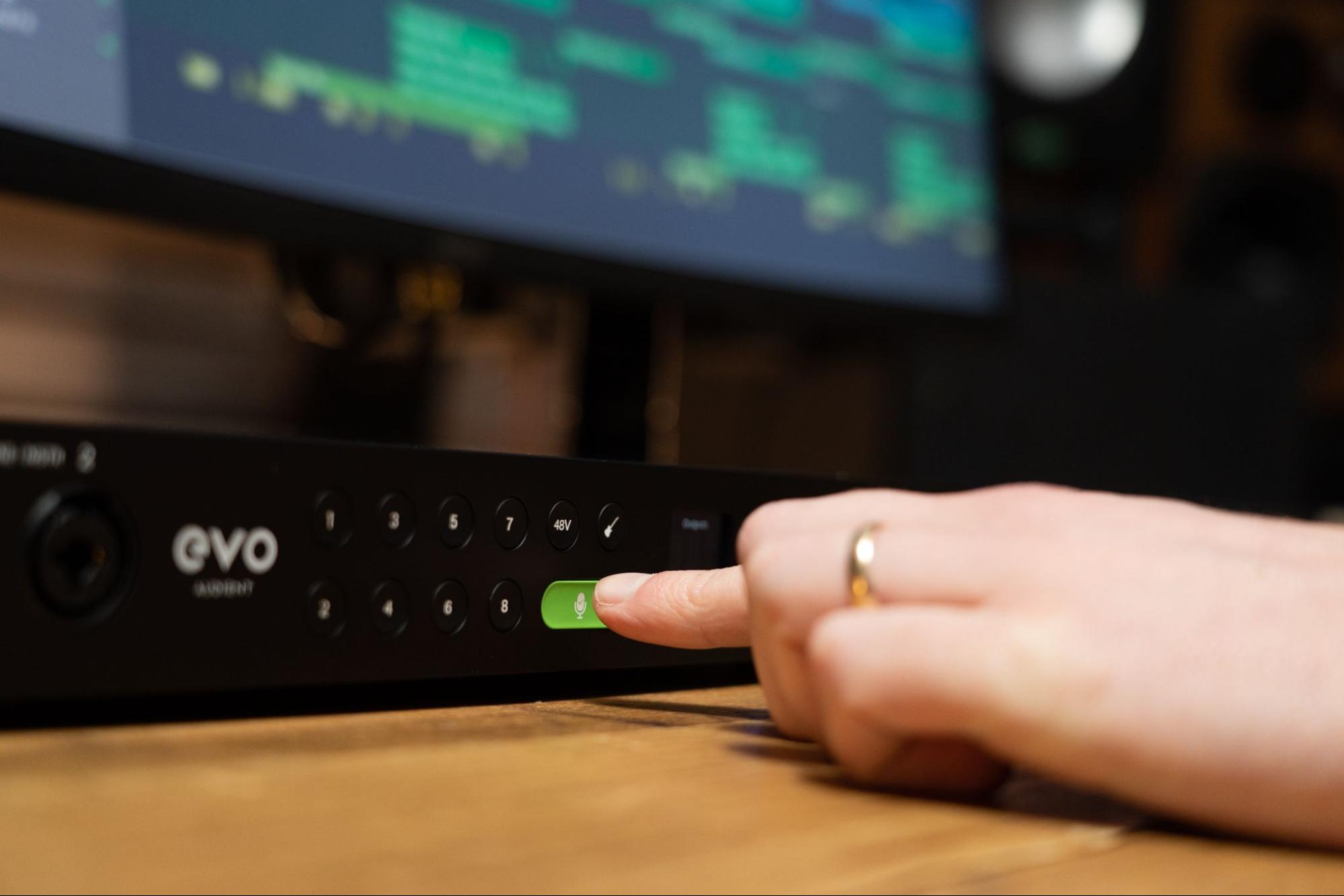
Phantom power is a feature found on many audio interfaces that provides the necessary voltage to power condenser microphones. These microphones require external power to operate, and phantom power supplies that power through the microphone cable itself.
But what happens when you turn off your audio interface? Can you keep the phantom power turned on, or should you always switch it off? In this article, we will explore the pros and cons of keeping phantom power turned on, as well as the factors you should consider when making this decision.
Before we dive into the details, let’s take a closer look at what exactly phantom power is and why it is important in the audio world.
What is Phantom Power?
In the world of audio, phantom power refers to the DC voltage that is applied to the microphone’s XLR connector to power condenser microphones. Condenser microphones, unlike dynamic microphones, require an external power source to function properly.
Phantom power is typically provided at +48 volts, although some audio interfaces may offer different voltage options. This power is sent through the same audio cable that carries the audio signal, allowing condenser microphones to operate without the need for an external power supply.
When phantom power is turned on, the audio interface sends the necessary voltage to the microphone, ensuring that it has enough power to capture sound accurately. This is especially important for condenser microphones, which are known for their sensitivity and ability to capture nuances in audio.
It’s worth noting that not all microphones require phantom power. Dynamic microphones, which are more commonly used for live performances and broadcasting, do not need external power and can be used without phantom power turned on.
Now that we have an understanding of what phantom power is and its purpose, let’s investigate whether it is safe to keep phantom power turned on even when you shut off your audio interface.
Is it Safe to Keep Phantom Power Turned On?
One of the most common questions among audio interface users is whether it is safe to keep phantom power turned on when the audio interface is shut off. The short answer is that it is generally safe, but there are some factors to consider.
Firstly, most audio interfaces are designed to handle the continuous supply of phantom power even when they are powered off. The phantom power circuitry is often separate from the main power supply, allowing it to function independently. This means that you can leave phantom power turned on without worrying about damaging the equipment.
However, it’s important to note that this may not always be the case with every audio interface. It is always a good idea to consult the user manual or contact the manufacturer to ensure that your specific audio interface is designed to handle phantom power being left on when the device is turned off.
Additionally, leaving phantom power turned on can consume a small amount of power even when the audio interface is inactive. While this may not be a significant concern for most users, it is worth considering if you are looking to minimize power consumption or if you are using a portable audio interface that relies on battery power.
Furthermore, if you have multiple devices connected to the audio interface, such as microphones, it’s crucial to ensure that all the connected devices are compatible with phantom power. Some microphones, especially ribbon microphones, are not designed to handle the application of phantom power and may get damaged if connected to a phantom-powered interface. Always check the specifications of your microphone to ensure compatibility.
Ultimately, the decision of whether to keep phantom power turned on or off when the audio interface is shut off depends on your specific needs and preferences. Let’s explore some of the factors you should consider before making your decision.
Factors to Consider
Before deciding whether to keep phantom power turned on or off when your audio interface is shut off, there are several factors you should take into consideration:
- Compatibility: As mentioned earlier, it’s crucial to ensure that all of your connected devices, particularly microphones, are compatible with phantom power. Check the specifications of your microphone to verify whether it can safely handle phantom power. If you have any doubts, it’s best to consult the manufacturer or avoid leaving phantom power turned on.
- Power Consumption: Leaving phantom power turned on when your audio interface is shut off may result in a small but continuous power consumption. If you are concerned about energy efficiency or are using a battery-powered audio interface, you may prefer to turn off phantom power to conserve power.
- Equipment Lifespan: Although most audio interfaces are designed to handle phantom power being left on, some users prefer to turn it off as an extra precaution to extend the lifespan of their equipment. If you want to minimize wear and tear on your audio interface, you may choose to turn off phantom power when not in use.
- Noise Reduction: In some cases, leaving phantom power turned on when the audio interface is shut off may result in increased background noise or interference. This can occur due to the continuous power supply and associated electronic components. If you notice any unwanted noise, it may be worth experimenting with turning off phantom power to see if it improves the audio quality.
- Workflow and Convenience: Keeping phantom power turned on can be more convenient for certain workflows. If you frequently use condenser microphones and want them ready to go at a moment’s notice, leaving phantom power turned on can save you time and effort. However, if you have a strict routine and prefer to power up your equipment manually, you may choose to turn off phantom power when not in use.
Considering these factors will help you make an informed decision about whether to keep phantom power turned on or off when your audio interface is shut off. It’s important to find the balance that suits your specific needs while ensuring the safety and optimal performance of your audio equipment.
Benefits of Keeping Phantom Power Turned On
Keeping phantom power turned on, even when your audio interface is shut off, can offer several benefits depending on your specific needs and workflow:
- Convenience: One of the significant advantages of leaving phantom power turned on is the convenience it provides. When phantom power is already activated, you can simply connect your condenser microphone and start recording without any additional steps. This can be especially beneficial for individuals who work in fast-paced environments or need to quickly capture spontaneous moments.
- Reduced Setup Time: If you frequently use condenser microphones for your recordings or live performances, keeping phantom power on eliminates the need to remember to turn it on every time you want to use your audio interface. This can help streamline your workflow and reduce setup time, allowing you to focus more on your creative process.
- Preservation of Audio Settings: By keeping phantom power turned on, you can maintain the settings you have carefully configured for your condenser microphones. Certain microphones require specific settings to capture the desired sound accurately. Turning off phantom power would require you to readjust those settings each time you power on your audio interface.
- Instrument and Vocal Response: Some musicians and audio engineers argue that leaving phantom power on can enhance the response and performance of condenser microphones. With phantom power continuously applied, the microphones remain “awake” and ready to capture the nuances of instruments and vocals. This can result in a more detailed and dynamic recording, particularly in situations where subtle nuances are crucial.
It’s important to note that the benefits of keeping phantom power turned on may vary depending on your specific setup and requirements. While these advantages can enhance convenience and workflow efficiency, it’s essential to weigh them against other factors, such as power consumption and equipment longevity, to make an informed decision.
Risks of Keeping Phantom Power Turned On
While there are benefits to keeping phantom power turned on, there are also potential risks that you should consider before making your decision:
- Power Consumption: Leaving phantom power turned on continuously can lead to power consumption, even when your audio interface is not in use. This continuous power usage can be a concern if you prioritize energy efficiency or if you are using a battery-powered audio interface.
- Equipment Longevity: Although most audio interfaces are designed to handle phantom power being left on, some users may choose to turn it off to minimize wear and tear on the equipment. The continuous power supply can potentially contribute to the aging of internal components, which could shorten the lifespan of your audio interface.
- Background Noise and Interference: In certain situations, leaving phantom power turned on when the audio interface is shut off may result in increased background noise or interference. The continuous power supply and associated electronic components can introduce noise into the audio signal, affecting the overall sound quality. If you notice any unwanted noise, it may be worth experimenting with turning off phantom power to mitigate this issue.
- Misuse with Incompatible Devices: It is crucial to ensure that all the devices connected to your audio interface, especially microphones, are compatible with phantom power. Using microphones that are not designed to handle phantom power can potentially damage the microphone or the audio interface itself. Always check the specifications of your microphone and consult the manufacturer if you have any doubts.
Considering these potential risks will help you make an informed decision about whether to keep phantom power turned on or off when your audio interface is shut off. It’s important to strike a balance between the benefits and risks, considering your specific needs, equipment, and workflow.
Best Practices for Phantom Power Usage
To ensure the safe and efficient use of phantom power with your audio interface, consider these best practices:
- Read the Documentation: Always refer to the user manual or documentation provided by the manufacturer of your audio interface. It will provide specific guidance on phantom power usage, including whether it is safe to leave it turned on when the device is shut off.
- Check Microphone Compatibility: Before connecting a microphone to your audio interface, verify that it is designed to work with phantom power. Some microphones, such as ribbon microphones, are not compatible and can be damaged if used with phantom power enabled.
- Power On/Off Sequence: If you decide to turn off phantom power, it is generally recommended to power off the audio interface before disconnecting or connecting any microphones. This helps prevent any potential damage to the audio interface or the microphones being used.
- Monitor for Noise: When using phantom power, monitor the audio signal for any unwanted noise or interference. If you notice any issues, such as buzzing or humming, try disabling phantom power or troubleshooting the audio chain to identify the source of the problem.
- Conservation of Power: If power consumption is a concern, consider turning off phantom power when it is not in use or when you are using dynamic microphones that do not require phantom power.
- Regular Maintenance: Periodically check the cables and connectors used with your audio interface to ensure proper connections and prevent any potential issues with phantom power supply. Cleaning the connectors and cables can also help maintain good electrical contact.
- Consult with Professionals: If you have any doubts or concerns about using phantom power with your specific audio setup, do not hesitate to consult with professionals, such as audio engineers or technical support from the manufacturer. They can provide guidance tailored to your unique situation.
By following these best practices, you can ensure the proper and safe utilization of phantom power with your audio interface, enhancing the overall performance and longevity of your equipment.
Conclusion
Deciding whether to keep phantom power turned on or off when you shut off your audio interface is a personal choice that depends on various factors. While leaving phantom power on can provide convenience, reduced setup time, and preserve audio settings, there are also potential risks to consider, such as power consumption, equipment longevity, and background noise. It’s crucial to weigh these factors and make an informed decision based on your specific needs and preferences.
To ensure the safe and optimal use of phantom power, always consult the user manual or documentation provided by the manufacturer of your audio interface. Confirm the compatibility of your microphones and follow the recommended power on/off sequence. Regularly monitor for any unwanted noise or interference, and maintain your cables and connectors for good electrical contact.
Ultimately, the best practice for using phantom power is to find the balance that suits your workflow, while prioritizing the safety and performance of your audio equipment. Whether you choose to keep phantom power turned on or prefer to turn it off when your audio interface is shut off, being aware of the benefits, risks, and best practices will help you make an informed decision and optimize your audio recording experience.