Home>Production & Technology>MIDI>How To Assign Instruments To MIDI Channel In FL Studio

MIDI
How To Assign Instruments To MIDI Channel In FL Studio
Modified: February 22, 2024
Learn how to assign instruments to MIDI channels in FL Studio to optimize your music production workflow. Discover essential MIDI tips and techniques.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
MIDI, which stands for Musical Instrument Digital Interface, is a powerful tool that has revolutionized the way music is created and produced. It allows musicians and producers to control various aspects of their music electronically, from notes and rhythms to instrument sounds and effects. One of the key elements of working with MIDI is the ability to assign different instruments to specific MIDI channels. This process enables the creation of rich, layered compositions and gives producers the flexibility to manipulate individual elements of a musical piece.
Understanding how to assign instruments to MIDI channels is crucial for anyone working with MIDI-based music production software, such as FL Studio. Whether you are a seasoned music producer or just starting out, mastering this aspect of MIDI functionality can significantly enhance your creative process and the quality of your music.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of MIDI channels and explore the methods for assigning instruments to these channels within FL Studio. By the end of this guide, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how MIDI channels work and the practical steps to optimize your music production workflow in FL Studio. Let's embark on this journey to unlock the full potential of MIDI channels and elevate your music production capabilities.
Understanding MIDI Channels
MIDI channels play a pivotal role in the realm of digital music production, serving as the pathways through which musical data is transmitted and received. In essence, MIDI channels act as virtual conduits that allow for the independent control and manipulation of different musical elements within a composition. Each MIDI channel is capable of carrying discrete streams of MIDI data, encompassing information related to note pitches, velocities, durations, and control parameters.
In the context of MIDI, channels are often likened to individual lanes on a multi-lane highway, where each lane represents a distinct pathway for transmitting musical information. This segregation enables the simultaneous handling of diverse musical components, such as melody lines, bass patterns, chord progressions, and percussive elements, without these elements interfering with one another.
MIDI channels are typically designated by numbers, with the standard MIDI specification accommodating 16 channels (ranging from 1 to 16). This numerical assignment facilitates the segregation and organization of musical data, allowing for precise control and manipulation of individual components within a composition. Furthermore, MIDI channels are not inherently tied to specific instruments or sounds; rather, they serve as versatile conduits for transmitting MIDI data to compatible devices and software.
In practical terms, MIDI channels enable producers to orchestrate complex musical arrangements by assigning different instruments or sound generators to distinct channels. This allocation empowers producers to independently manipulate the musical characteristics of each instrument, including parameters such as volume, panning, and timbre, thereby sculpting a cohesive and harmonious sonic landscape.
Understanding MIDI channels is fundamental to harnessing the full potential of MIDI-based music production. It provides producers with the means to exercise precise control over the various musical elements within a composition, fostering a creative environment where intricate arrangements can be meticulously crafted and refined. As we delve deeper into the realm of MIDI channels, we will explore the practical methodologies for assigning instruments to these channels within the FL Studio environment, further unlocking the boundless possibilities of MIDI-based music production.
Assigning Instruments to MIDI Channels in FL Studio
In FL Studio, the process of assigning instruments to MIDI channels is integral to crafting intricate and dynamic musical compositions. This pivotal functionality empowers producers to allocate specific instruments or sound generators to individual MIDI channels, thereby facilitating precise control and manipulation of each musical element within a composition. By mastering the art of assigning instruments to MIDI channels in FL Studio, producers can unleash the full potential of their creative vision and elevate the sonic richness of their musical productions.
Step 1: Selecting the Instrument
The first step in assigning instruments to MIDI channels in FL Studio involves selecting the desired instrument or sound generator for integration into the composition. FL Studio offers a diverse array of virtual instruments, synthesizers, and sample-based sound libraries, providing producers with a vast palette of sonic possibilities. Whether it's a classic piano, a pulsating synthesizer lead, or a thunderous drum kit, FL Studio equips producers with an extensive collection of high-quality instruments to suit their musical preferences and artistic aspirations.
Step 2: Channel Routing
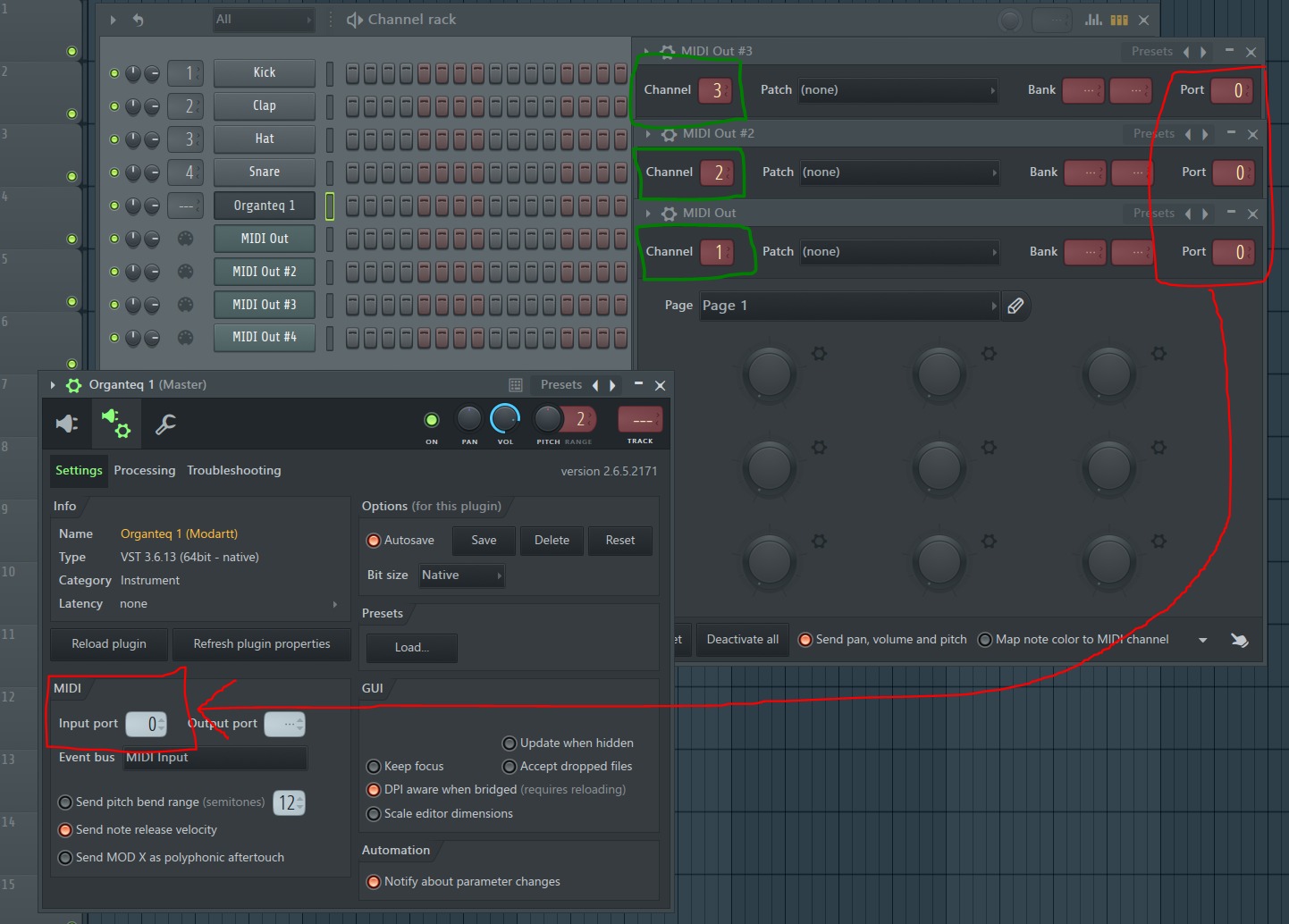
Once the instrument has been selected, the next crucial phase entails routing the instrument to a specific MIDI channel within FL Studio. This process involves establishing a direct connection between the chosen instrument and a designated MIDI channel, thereby enabling seamless communication and control between the two entities. FL Studio simplifies this routing process through an intuitive interface, allowing producers to swiftly and efficiently assign instruments to their preferred MIDI channels with precision and ease.
Step 3: MIDI Channel Configuration
With the instrument successfully routed to a MIDI channel, producers can delve into the realm of MIDI channel configuration within FL Studio. This pivotal stage empowers producers to fine-tune the parameters and attributes of the assigned instrument, encompassing elements such as volume, panning, and MIDI data modulation. By customizing these settings at the MIDI channel level, producers can sculpt the sonic characteristics of the instrument, imbuing it with a distinct identity and seamlessly integrating it into the broader musical composition.
Step 4: Layering and Stacking
FL Studio's versatile MIDI channel functionality extends beyond individual instrument assignments, offering producers the flexibility to layer and stack multiple instruments within a single MIDI channel. This capability enables the creation of rich, layered textures and harmonious amalgamations of musical elements, fostering a sonic tapestry that is both nuanced and immersive. By harnessing the power of layered MIDI channels, producers can orchestrate complex musical arrangements with depth and intricacy, elevating the expressive potential of their compositions.
Step 5: Real-time Control and Automation
An inherent advantage of assigning instruments to MIDI channels in FL Studio is the ability to exert real-time control and automation over the assigned instruments. Producers can leverage FL Studio's comprehensive automation features to dynamically modulate various parameters of the assigned instruments, such as filter cutoff frequencies, envelope settings, and effect parameters. This real-time manipulation empowers producers to infuse their compositions with expressive nuances and dynamic fluctuations, breathing life into their musical creations.
Mastering the art of assigning instruments to MIDI channels in FL Studio is a transformative endeavor that empowers producers to sculpt intricate and evocative musical compositions. By navigating the nuanced terrain of MIDI channel assignments, producers can harness the full potential of FL Studio as a versatile and expressive platform for music production. This mastery unlocks a realm of creative possibilities, enabling producers to craft compelling sonic narratives and immersive musical experiences that resonate with audiences on a profound level.
Tips for Organizing MIDI Channels
Organizing MIDI channels is a fundamental aspect of efficient music production, enabling producers to streamline their workflow and maintain a structured environment for creative exploration. Within the realm of FL Studio, where intricate compositions and complex arrangements abound, effective organization of MIDI channels is paramount. Here are some invaluable tips to optimize the organization of MIDI channels in FL Studio:
1. Naming and Labeling
Assigning clear and descriptive names to MIDI channels is a simple yet powerful strategy for enhancing organization. By labeling MIDI channels according to the instruments or musical elements they represent, producers can swiftly identify and navigate through the myriad components of their compositions. This practice fosters clarity and coherence, allowing producers to maintain a lucid overview of their musical arrangements.
2. Color Coding
Leveraging FL Studio's color coding functionality to visually differentiate MIDI channels can significantly expedite the navigation and management of musical elements. By assigning distinct colors to individual MIDI channels based on instrument families or musical sections, producers can intuitively discern and manipulate various components within their compositions. This visual categorization enhances efficiency and minimizes the cognitive load associated with complex arrangements.
3. Grouping and Busing
Grouping related MIDI channels and routing them to dedicated buses can streamline the processing and manipulation of musical elements. By consolidating similar instruments or musical sections into cohesive groups, producers can apply collective processing, such as equalization and compression, with precision and efficiency. This approach fosters a cohesive sonic balance and facilitates targeted adjustments across entire musical sections.
4. Utilizing Channel Racks
FL Studio's Channel Rack feature serves as a versatile hub for organizing and managing MIDI channels, offering a centralized interface for seamless navigation and editing. Producers can leverage the Channel Rack to arrange, group, and manipulate MIDI channels with ease, fostering a structured and accessible framework for composing and producing music.
5. Creating Templates
Developing customized templates that encompass predefined MIDI channel configurations tailored to specific musical genres or production workflows can expedite the creative process. By establishing templates with pre-routed MIDI channels, instrument settings, and effects chains, producers can eliminate repetitive setup tasks and focus on the artistic expression, thereby enhancing productivity and consistency in music production.
6. Streamlining Unused Channels
Regularly auditing and decluttering unused MIDI channels can optimize the workspace and enhance overall efficiency. By purging redundant or inactive MIDI channels, producers can declutter the interface and streamline the visualization of essential musical components, fostering a focused and uncluttered environment for creative exploration.
7. Documentation and Annotations
Maintaining comprehensive documentation or annotations regarding MIDI channel configurations, instrument settings, and production notes can serve as invaluable references for future projects. Producers can document unique routing configurations, instrument layering approaches, and creative insights, facilitating knowledge retention and fostering a repository of best practices for informed decision-making in subsequent productions.
By implementing these tips, producers can elevate their organization and management of MIDI channels within FL Studio, fostering an environment conducive to creative exploration and efficient music production. These strategies empower producers to navigate the intricate landscape of MIDI-based compositions with clarity, coherence, and precision, thereby unlocking the full potential of their artistic vision.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the art of assigning instruments to MIDI channels in FL Studio is a transformative endeavor that empowers producers to sculpt intricate and evocative musical compositions. The intricate functionality of MIDI channels serves as the cornerstone of nuanced music production, enabling producers to orchestrate complex arrangements with precision and creativity. By delving into the realm of MIDI channels and understanding the practical methodologies for assigning instruments within FL Studio, producers can unlock a realm of creative possibilities and elevate their music production capabilities.
The journey through MIDI channels in FL Studio unveils a landscape of boundless potential, where producers can harness the power of digital orchestration to craft compelling sonic narratives and immersive musical experiences. From selecting instruments to channel routing, MIDI channel configuration, layering, and real-time control, the process of assigning instruments to MIDI channels is a symphony of creative expression and technical finesse. It embodies the fusion of artistry and technology, empowering producers to breathe life into their musical visions and captivate audiences with captivating compositions.
Furthermore, the tips for organizing MIDI channels in FL Studio offer invaluable insights into streamlining workflow efficiency and maintaining structured environments for creative exploration. From naming and labeling to color coding, grouping and busing, utilizing channel racks, creating templates, streamlining unused channels, and documentation, these strategies provide producers with a roadmap to optimize their organization and management of MIDI channels, fostering an environment conducive to creative exploration and efficient music production.
Ultimately, the mastery of MIDI channels in FL Studio transcends technical proficiency, encapsulating the essence of musical storytelling and artistic innovation. It empowers producers to navigate the intricate terrain of digital composition with clarity, coherence, and precision, thereby unlocking the full potential of their creative vision. As producers embark on their journey through MIDI channels, they embark on a voyage of sonic discovery, where every note, every rhythm, and every texture converges to form a symphony of boundless creativity and expressive depth.
In essence, the mastery of MIDI channels in FL Studio is a gateway to a realm where imagination knows no bounds, and the language of music resonates with profound emotion and ingenuity. It is a testament to the enduring fusion of technology and artistry, where the digital canvas becomes a playground for boundless creativity and sonic innovation. As producers navigate the intricate landscape of MIDI channels, they embark on a transformative odyssey, where every musical element converges to form a tapestry of immersive and evocative compositions.