Home>Production & Technology>MIDI>How To Connect MIDI


MIDI
How To Connect MIDI
Modified: February 22, 2024
Learn how to connect MIDI devices and use MIDI technology to enhance your music production. Find step-by-step guidance and tips for working with MIDI.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
MIDI, which stands for Musical Instrument Digital Interface, is a powerful and versatile technology that has revolutionized the way musicians create, record, and perform music. Whether you're a professional musician, a hobbyist, or someone who simply loves music, understanding how to connect MIDI devices and use MIDI software can open up a world of creative possibilities.
In today's digital age, MIDI has become an integral part of music production and performance. It allows electronic musical instruments, computers, and other devices to communicate, enabling seamless integration and control over a wide range of musical elements. From keyboards and synthesizers to drum machines and digital audio workstations (DAWs), MIDI provides a standardized protocol for transmitting musical data, such as note information, control signals, and synchronization cues.
The beauty of MIDI lies in its flexibility and universality. It transcends the limitations of traditional audio recording by enabling precise editing, automation, and manipulation of musical elements. With MIDI, you can effortlessly change the tempo, key, and instrumentation of a musical piece, opening up endless creative avenues for experimentation and innovation.
Furthermore, MIDI is not just limited to musical instruments. It can also be used to control lighting systems, stage effects, and other multimedia elements, making it an indispensable tool for live performances, theater productions, and multimedia installations.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of MIDI, exploring how to connect MIDI devices, set up MIDI software, and troubleshoot common issues. Whether you're a beginner looking to dip your toes into the world of MIDI or a seasoned musician seeking to expand your technical prowess, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to harness the full potential of MIDI technology. So, let's embark on this enlightening journey into the realm of MIDI and unlock the boundless possibilities it offers.
Understanding MIDI
MIDI, an acronym for Musical Instrument Digital Interface, is a versatile and powerful technology that has revolutionized the landscape of music creation and performance. At its core, MIDI serves as a communication protocol that enables electronic musical instruments, computers, and other devices to interact and exchange musical information. Unlike traditional audio recording, which captures sound in a fixed format, MIDI records musical data in a digital format, allowing for unparalleled flexibility and control.
One of the key aspects that sets MIDI apart is its ability to transmit a wide range of musical information, including note data, control signals, and synchronization cues. This means that MIDI can convey not only the notes being played on a keyboard or other MIDI instrument but also the nuances of how those notes are played, such as velocity, pitch bend, and modulation. Additionally, MIDI allows for the seamless integration of various musical elements, enabling musicians to layer different sounds, alter tempos, and manipulate musical parameters with ease.
Furthermore, MIDI is not limited to a specific type of musical instrument or device. It is a universal standard that can be implemented across a diverse array of equipment, ranging from keyboards and synthesizers to drum machines, digital audio workstations (DAWs), and even lighting systems. This universality makes MIDI a unifying language for musical expression, fostering interoperability and collaboration among different musical tools and technologies.
In the realm of music production, MIDI serves as a foundational building block for creating and arranging musical compositions. It allows musicians and producers to capture musical ideas in a non-destructive manner, providing the flexibility to edit and refine musical performances with precision. Moreover, MIDI data can be easily manipulated and edited within a DAW, enabling tasks such as quantizing notes, adjusting timing, and experimenting with different instrument sounds.
Another remarkable aspect of MIDI is its role in live performances and stage productions. By leveraging MIDI, musicians can control various aspects of their performance, from triggering backing tracks and samples to synchronizing lighting and visual effects. This level of control empowers artists to deliver captivating and immersive live experiences, blurring the lines between music and multimedia artistry.
In essence, MIDI represents a paradigm shift in the way music is created, performed, and experienced. Its adaptability, precision, and universality have cemented its position as an indispensable tool for musicians, producers, and performers alike. As we continue to explore the intricacies of MIDI, we will uncover the methods for connecting MIDI devices, setting up MIDI software, and troubleshooting common issues, further unraveling the potential of this transformative technology.
Connecting MIDI Devices
Connecting MIDI devices is a fundamental step in harnessing the power of MIDI technology. Whether you're assembling a home studio setup or preparing for a live performance, establishing seamless connections between MIDI instruments, controllers, and computers is essential for unleashing the full potential of MIDI.
Physical Connections
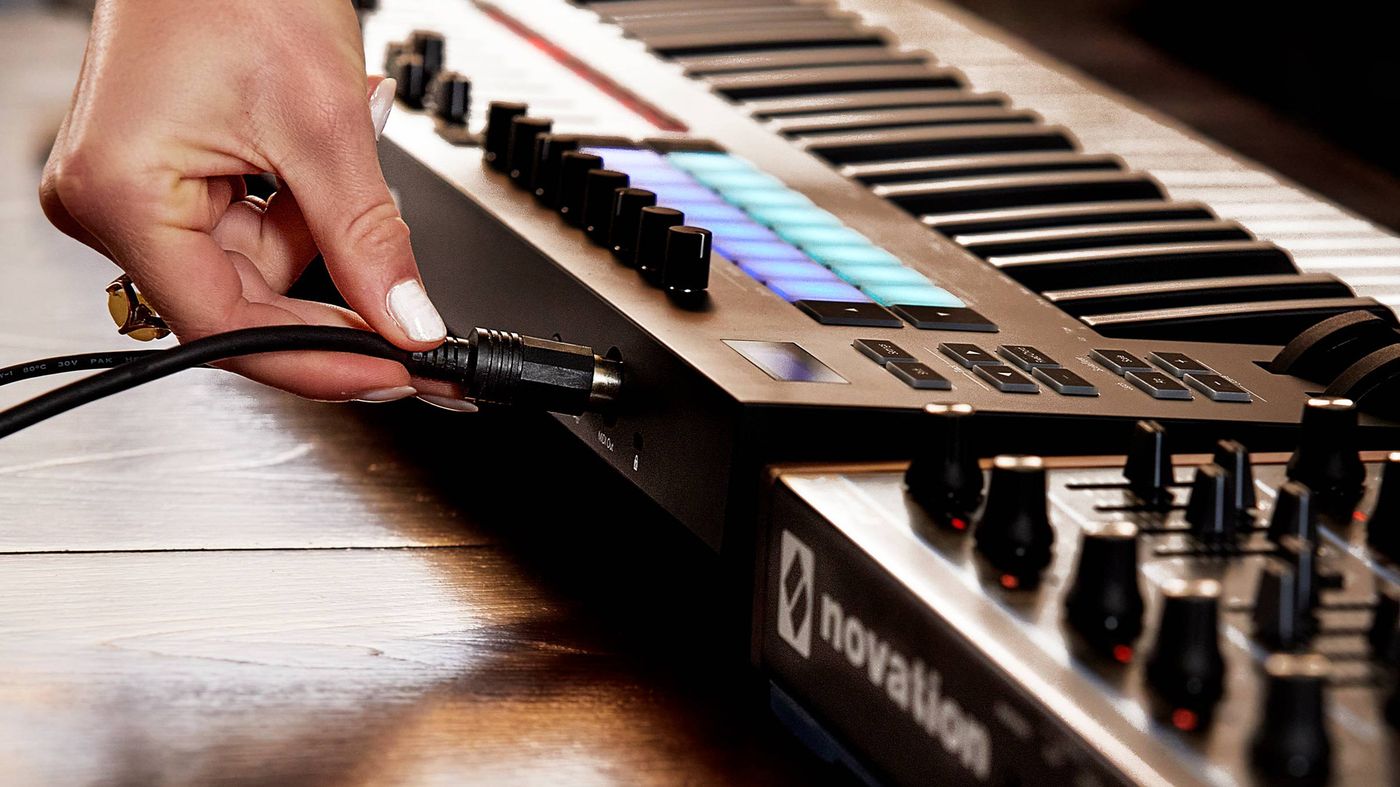
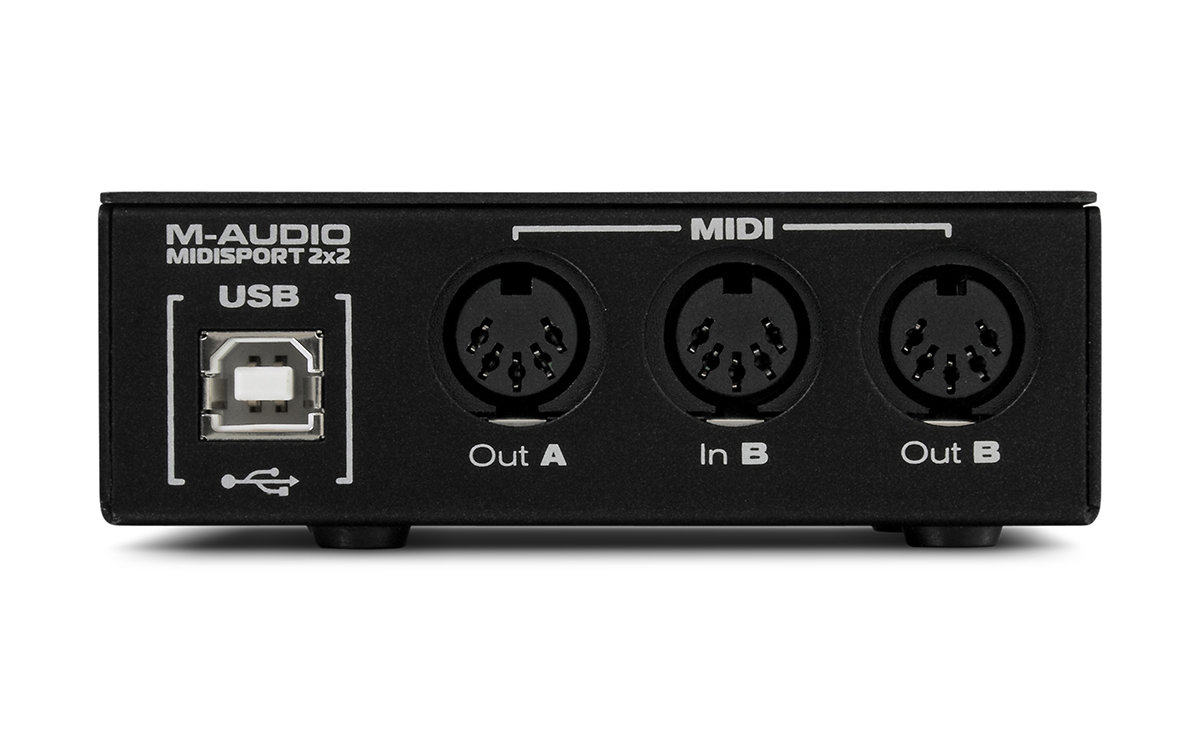
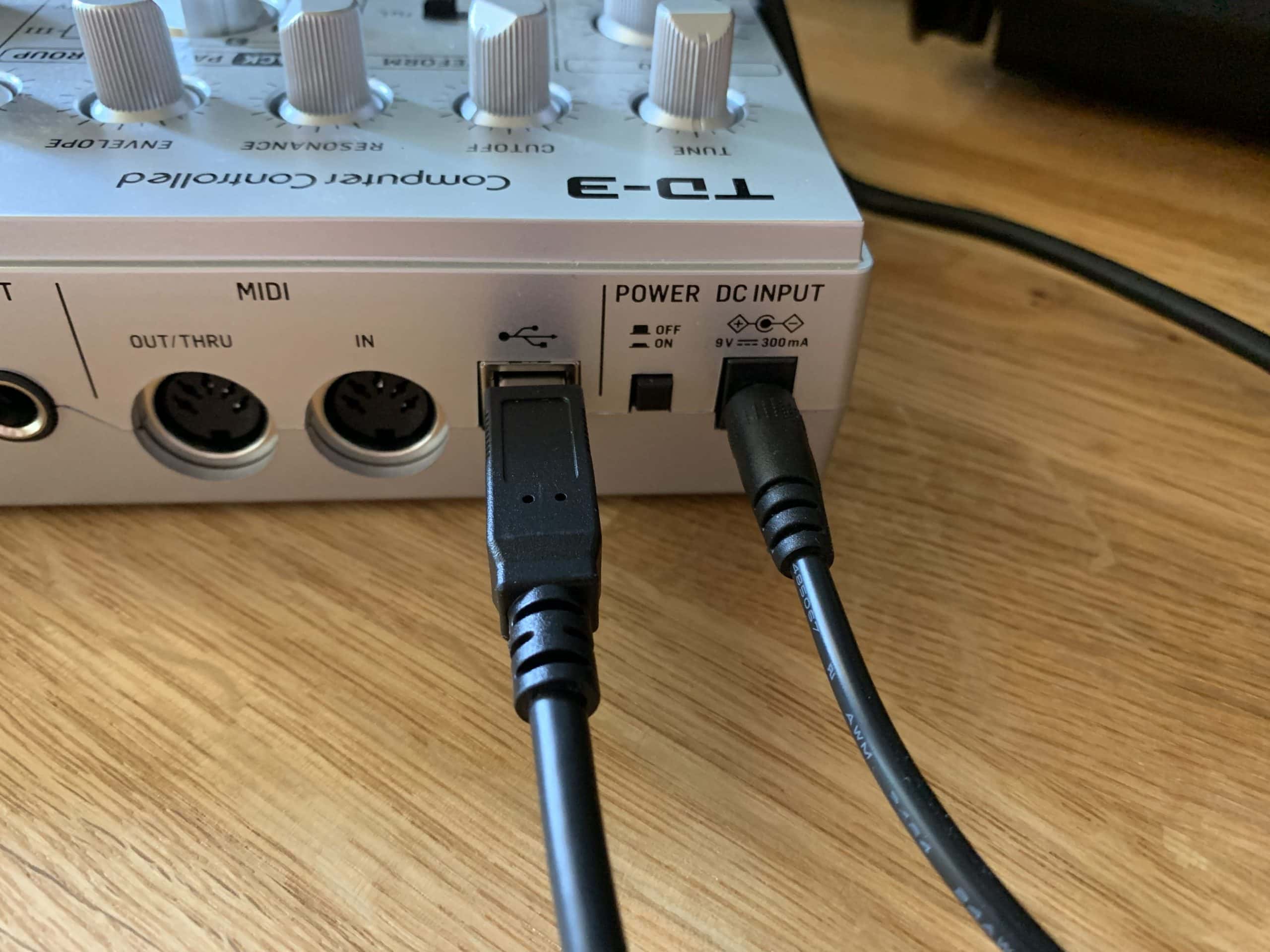
The first step in connecting MIDI devices involves establishing physical connections. MIDI devices typically feature MIDI ports, which are labeled as "MIDI In" and "MIDI Out." To initiate a connection, a MIDI cable is used to link the "MIDI Out" port of one device to the "MIDI In" port of another. This creates a daisy-chain configuration, allowing multiple MIDI devices to communicate with each other.
MIDI Interfaces
In scenarios where MIDI devices need to be connected to a computer, a MIDI interface comes into play. A MIDI interface serves as a bridge between MIDI devices and the computer, enabling seamless communication. Modern MIDI interfaces often connect to the computer via USB and provide multiple MIDI ports for accommodating various devices.
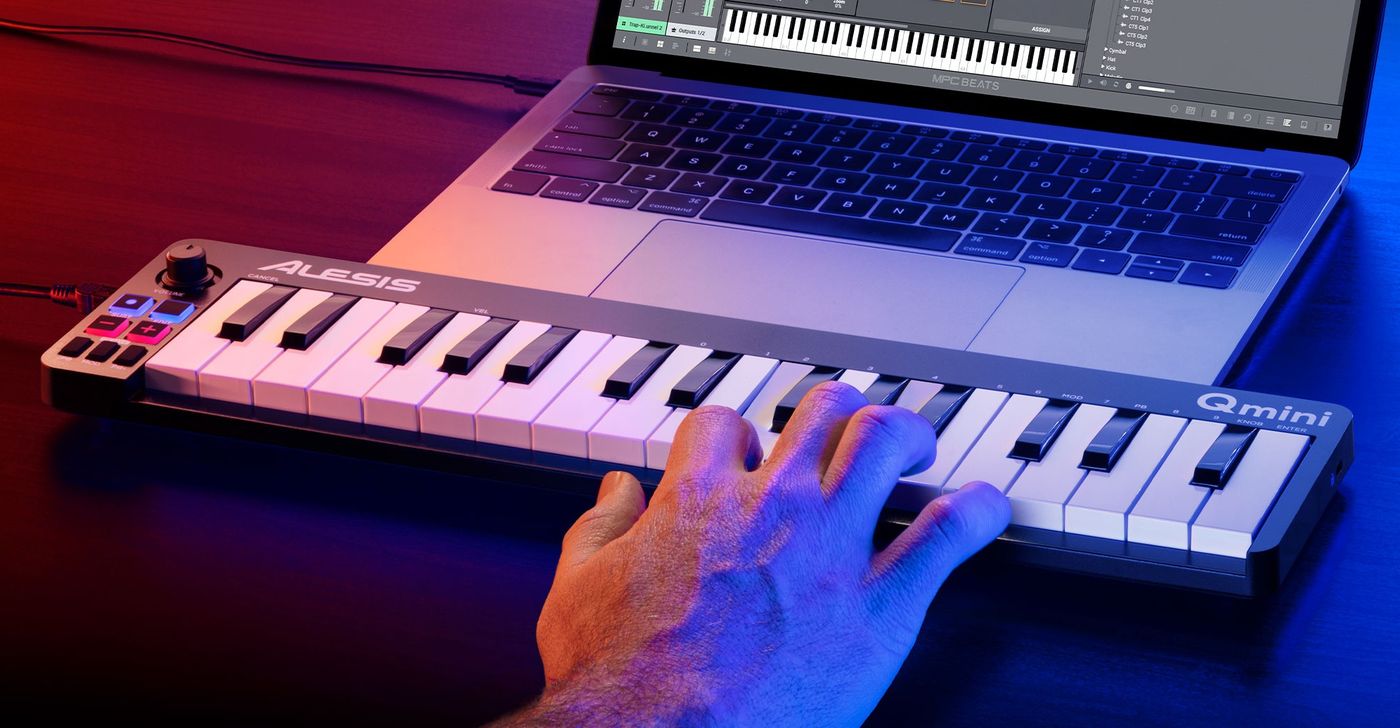
USB MIDI Controllers
For musicians utilizing USB MIDI controllers, the connection process is simplified, as these controllers can be directly plugged into the USB ports of computers or compatible devices. This plug-and-play functionality makes USB MIDI controllers a convenient option for music production and live performances, eliminating the need for traditional MIDI cables and interfaces.
Software Configuration
Once the physical connections are established, configuring MIDI settings within music production software or digital audio workstations (DAWs) is the next crucial step. This involves specifying MIDI input and output sources within the software to ensure that MIDI data can be transmitted between devices accurately.
Wireless MIDI Solutions
In addition to traditional wired connections, wireless MIDI solutions have gained popularity, offering the flexibility of transmitting MIDI data without the constraints of physical cables. Wireless MIDI adapters and Bluetooth MIDI controllers enable musicians to connect and control their devices wirelessly, opening up new possibilities for stage performances and studio setups.
MIDI Network Protocols
For advanced setups involving multiple MIDI devices and computers, MIDI network protocols such as RTP-MIDI can be utilized to establish MIDI communication over Ethernet or Wi-Fi networks. This approach facilitates the integration of diverse MIDI-enabled devices within a networked environment, paving the way for expansive and interconnected musical setups.
By mastering the art of connecting MIDI devices, musicians and producers can seamlessly integrate their gear, unleash their creativity, and unlock the boundless potential of MIDI technology. Whether it's creating intricate musical compositions, orchestrating captivating live performances, or exploring innovative soundscapes, the art of connecting MIDI devices lays the foundation for a world of musical possibilities.
Setting up MIDI Software
Setting up MIDI software is a pivotal aspect of leveraging the full potential of MIDI technology. Whether you're embarking on a music production journey or preparing for a live performance, configuring MIDI software enables seamless integration of MIDI devices and unlocks a myriad of creative possibilities.
Choosing the Right Software
The first step in setting up MIDI software involves selecting the appropriate digital audio workstation (DAW) or music production software. There is a diverse range of options available, each offering unique features and workflows tailored to different musical styles and production requirements. From industry-standard DAWs such as Ableton Live, Logic Pro, and Pro Tools to versatile software instruments and MIDI controllers, the choice of software plays a crucial role in shaping the music creation process.
MIDI Device Integration
Once the software is selected, the next step is to integrate MIDI devices within the software environment. This involves configuring MIDI input and output settings to ensure seamless communication between MIDI instruments, controllers, and the software itself. Most modern DAWs provide intuitive interfaces for managing MIDI devices, allowing users to map MIDI controllers, assign MIDI channels, and customize MIDI routing to suit their specific workflow and creative preferences.
Instrument and Controller Mapping
Mapping MIDI instruments and controllers within the software is a key aspect of setting up MIDI software. This process involves assigning MIDI input from external devices to control virtual instruments, effects parameters, and software-based synthesizers. By mapping MIDI controllers to software parameters, musicians can harness the expressive capabilities of their physical instruments to manipulate and shape digital sound sources, adding a layer of tactile control to the music production process.
MIDI Recording and Editing
Configuring MIDI recording and editing settings is essential for capturing musical performances with precision. MIDI recording allows musicians to capture note data, dynamics, and articulations, providing a non-destructive and flexible approach to recording musical ideas. Additionally, MIDI editing tools within the software enable users to quantize notes, adjust timing, and fine-tune musical performances, empowering them to sculpt and refine their compositions with meticulous detail.
Virtual Instrument Integration
Many MIDI software solutions offer a vast array of virtual instruments, sample libraries, and software-based synthesizers that can be seamlessly integrated into the production environment. Setting up MIDI software involves loading and configuring virtual instruments to expand the sonic palette, enabling musicians to access a diverse range of sounds and textures to enrich their compositions.
Automation and Control
Configuring MIDI software for automation and control functions enhances the creative possibilities within a production. By utilizing MIDI automation, musicians can dynamically control parameters such as volume, panning, and effects settings over time, adding depth and expression to their musical arrangements. This level of control empowers artists to craft nuanced and evolving sonic landscapes, elevating the emotional impact of their music.
Collaborative Workflows
In the realm of collaborative music production, setting up MIDI software to facilitate seamless project sharing and collaboration is paramount. Many DAWs offer collaborative features that enable multiple users to work on the same project simultaneously, exchange MIDI data, and synchronize their creative efforts. This collaborative aspect of MIDI software sets the stage for collective creativity and shared musical experiences, fostering a sense of unity and synergy among artists and producers.
Performance Setup
For live performance scenarios, configuring MIDI software to accommodate performance setups is crucial. This involves creating performance templates, mapping MIDI controllers for real-time manipulation, and optimizing the software environment for stability and low-latency operation. By tailoring MIDI software for live performance, musicians can deliver captivating and immersive experiences, blurring the lines between studio production and live expression.
In essence, setting up MIDI software is a multifaceted process that encompasses a wide range of technical and creative considerations. By mastering the art of configuring MIDI software, musicians, producers, and performers can harness the full potential of MIDI technology, shaping their musical vision with precision, expressiveness, and boundless creativity.
Troubleshooting MIDI Connections
Troubleshooting MIDI connections is an essential skill for musicians and producers, ensuring that MIDI devices communicate seamlessly and reliably. While MIDI technology offers unparalleled flexibility and control, occasional technical hiccups may arise, requiring troubleshooting to diagnose and resolve connectivity issues.
Check Physical Connections
The first step in troubleshooting MIDI connections involves inspecting the physical connections between MIDI devices. Ensure that MIDI cables are securely plugged into the correct MIDI input and output ports, as loose or incorrect connections can lead to data transmission errors. Additionally, examining the condition of MIDI cables for any signs of damage or wear is crucial, as faulty cables can impede proper signal transmission.
MIDI Interface Configuration
For setups involving MIDI interfaces and computer connectivity, verifying the configuration of the MIDI interface is paramount. This includes checking the device settings within the computer's operating system and ensuring that the MIDI interface is recognized and operational. In some cases, updating the drivers for the MIDI interface may be necessary to address compatibility issues and ensure seamless communication with the computer.
MIDI Channel and Device Settings
When encountering MIDI communication issues, inspecting MIDI channel settings and device configurations is essential. Ensure that MIDI devices are set to transmit and receive data on the correct MIDI channels, as mismatched channel assignments can result in data being sent to the wrong destinations or not being received at all. Additionally, confirming that MIDI devices are set to the appropriate MIDI mode, such as "Omni" or "Poly," can help resolve compatibility issues between different MIDI instruments and controllers.
Software MIDI Routing
In the context of software-based MIDI setups, troubleshooting MIDI connections often involves examining the MIDI routing within digital audio workstations (DAWs) and music production software. Verify that MIDI input and output assignments are correctly configured within the software, allowing MIDI data to flow between devices without impediments. Addressing any routing errors or conflicts within the software environment can rectify issues related to MIDI signal transmission and device control.
Latency and Timing Issues
In scenarios where MIDI data transmission exhibits latency or timing discrepancies, troubleshooting the MIDI connections may involve adjusting buffer settings within the audio interface or MIDI software. Optimizing buffer sizes and latency settings can mitigate timing irregularities and ensure that MIDI events are captured and processed with minimal delay, enhancing the responsiveness of MIDI devices during performance and recording sessions.
MIDI Thru and Chain Configurations
For setups involving multiple MIDI devices daisy-chained together, diagnosing MIDI Thru and chain configurations is crucial. Verify that MIDI Thru functionality is enabled on the appropriate devices, allowing MIDI data to pass through the chain without signal degradation. Additionally, inspecting the order of devices in the MIDI chain and addressing any issues related to signal routing and device prioritization can resolve communication issues within complex MIDI setups.
Firmware and Software Updates
Keeping MIDI devices and software up to date with the latest firmware and software updates can address compatibility issues and performance optimizations. Manufacturers often release firmware updates to address MIDI-related issues and enhance the functionality of MIDI devices. Similarly, updating music production software and DAWs to the latest versions can introduce bug fixes and improvements related to MIDI communication and device integration.
Testing and Isolation
In cases where troubleshooting MIDI connections proves challenging, employing a systematic approach to testing and isolation can help identify the root cause of connectivity issues. This may involve testing MIDI devices individually to isolate faulty components, swapping MIDI cables to rule out cable-related issues, and systematically introducing devices into the MIDI chain to pinpoint potential sources of communication disruptions.
Community Support and Resources
Seeking assistance from online forums, user communities, and technical support resources can provide valuable insights and troubleshooting tips for resolving MIDI connectivity issues. Engaging with fellow musicians and professionals who have encountered similar MIDI challenges can offer practical solutions and guidance in addressing complex connectivity issues, leveraging the collective knowledge and experiences of the MIDI community.
By mastering the art of troubleshooting MIDI connections, musicians, producers, and performers can overcome technical hurdles and ensure that their MIDI setups operate seamlessly and reliably. With a methodical approach to diagnosing and resolving connectivity issues, MIDI technology can continue to serve as a powerful and dependable tool for unleashing creative expression and musical innovation.