Home>Production & Technology>Sound Effects>How To Remove Sound Effects From Music

Sound Effects
How To Remove Sound Effects From Music
Published: November 9, 2023
Learn how to remove sound effects from music and enhance your listening experience. Follow our step-by-step guide to eliminate unwanted audio effects with ease.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Sound Effects in Music
- Why Remove Sound Effects from Music?
- Different Approaches to Removing Sound Effects
- Method 1: Using Audio Editing Software
- Method 2: Isolating Frequencies
- Method 3: Applying Noise Reduction Techniques
- Method 4: Manual Editing
- Best Practices for Successful Removal
- Conclusion
Introduction
Music is a universal language that has the power to evoke emotions, set the mood, and transport us to different places and times. It is often accompanied by sound effects, which can enhance the overall listening experience. Sound effects are audio elements used to create specific sounds, such as footsteps, door creaks, or gunshots, in music compositions. These effects help create a more immersive and cinematic feel.
However, there may be instances where you want to remove sound effects from music for various reasons. Perhaps you are a musician looking to remix a track and want to isolate the vocals or instrumental parts without the distractions of background noises. Alternatively, you may be a filmmaker or content creator seeking to use a particular piece of music but with the sound effects removed to better suit your project’s needs.
Regardless of the reason, there are multiple approaches to removing sound effects from music, each with its own advantages and limitations. In this article, we will explore various methods for effectively removing sound effects from music and provide some best practices to help you achieve the desired results.
Understanding Sound Effects in Music
Sound effects are widely used in music production to add depth, texture, and realism to a composition. They can range from subtle background noises to prominent and attention-grabbing elements. Some common sound effects used in music include atmospheric sounds, vocal effects, instrumental effects, and percussive elements.
Sound effects can serve several purposes in music. They can create a sense of place or environment, such as the sound of waves crashing on a beach or birds chirping in a forest. They can also enhance the storytelling aspect of a song, such as the sound of thunder during a dramatic moment or the sirens in a police-themed track.
Sound effects are typically added during the production process using various techniques and tools. They can be recorded from real-life sources or generated digitally using software plugins. Sound engineers and producers carefully choose and manipulate these effects to blend them seamlessly into the music, ensuring they enhance the overall composition without overpowering other elements.
It’s important to note that sound effects can vary in complexity and frequency content. Some effects may be more isolated and easier to remove, while others may be intricately embedded within the music. Removing sound effects while maintaining the quality and integrity of the original track can be a challenging task that requires a combination of technical skills and careful listening.
In the following sections, we will explore different approaches to removing sound effects from music, providing you with the knowledge and tools to achieve your desired outcome.
Why Remove Sound Effects from Music?
While sound effects can add depth and atmosphere to a piece of music, there are several reasons why you might want to remove them. Here are a few common scenarios where removing sound effects can be beneficial:
- Remixing and Sampling: If you are a musician or producer working on a remix or sample-based project, you may want to isolate specific elements of a song, such as vocals or instrumentals, without the interference of sound effects. Removing the effects can help you focus on the desired elements and give you more creative freedom in your production.
- Film and Video Projects: Filmmakers, content creators, and video editors often need music tracks for their projects, but they may require the music without the accompanying sound effects. Removing the effects allows them to have more control over the audio in their videos, ensuring the music fits seamlessly with the visuals and doesn’t clash with any existing sound design.
- Improving Clarity: In some cases, sound effects can overpower other elements in a mix, making it difficult to hear certain elements clearly. By removing or reducing the effects, you can improve the clarity and overall balance of the music.
- Customizing Soundtracks: If you’re an aspiring DJ or just enjoy creating custom playlists, removing sound effects can help you create personalized and tailored soundtracks to suit your specific preferences or theme. Whether it’s for a workout session, a party, or a relaxed evening, having the ability to remove unwanted effects gives you more control over the vibe and energy of the music.
It’s important to note that removing sound effects should be done carefully and with consideration for the original artistic intent. It’s always good practice to obtain the necessary permissions and licenses when working with copyrighted material or when modifying someone else’s work.
Now that we understand the motivations behind removing sound effects, let’s explore different approaches and techniques to achieve this effectively.
Different Approaches to Removing Sound Effects
When it comes to removing sound effects from music, there are various approaches you can take. The effectiveness of each method depends on the complexity and integration of the effects within the audio. Here are four common approaches:
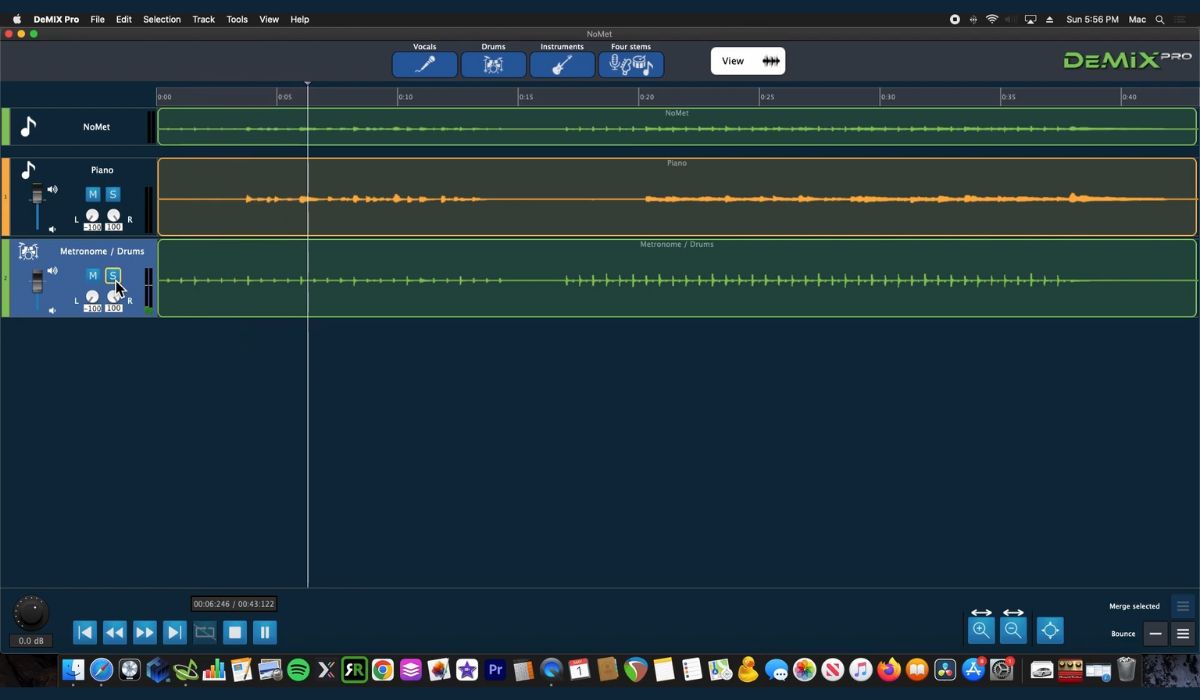
- Using Audio Editing Software: Audio editing software such as Adobe Audition, Pro Tools, or Audacity provides tools and features that allow you to isolate and remove specific frequencies or sections of a music track. This method involves analyzing the audio visually, identifying the sound effects, and applying filters or edits to remove them. It offers precise control and flexibility but may require some technical expertise.
- Isolating Frequencies: Sound effects often occupy specific frequency ranges. By using an equalizer or spectral editing tool, you can identify and reduce the frequencies associated with the effects while preserving the desired elements of the music. This method requires a good understanding of frequency ranges and may involve some trial and error to achieve the desired result.
- Applying Noise Reduction Techniques: Noise reduction plugins and tools can be effective in reducing unwanted sound effects. These tools analyze the audio and identify noise or repetitive patterns to suppress them. They can be particularly useful in attenuating background noises or hisses, but may not be as effective for more complex or integrated sound effects.
- Manual Editing: In some cases, manually editing the audio waveform is necessary to remove sound effects. This method involves carefully listening to the track, identifying the specific parts with sound effects, and using audio editing software to silence or remove those sections. Manual editing can be time-consuming, but it offers precise control over the removal process.
It’s important to note that not all sound effects can be completely removed without affecting the quality of the music. In some cases, there may be remnants of the effects or noticeable artifacts after removal. Experimenting with different methods and combining multiple techniques can often yield better results.
In the next sections, we will dive deeper into each of these methods, providing step-by-step instructions and tips for successful sound effects removal.
Method 1: Using Audio Editing Software
One of the most common and effective methods for removing sound effects from music is using audio editing software. With the help of specialized tools and features, you can isolate and remove specific frequencies or sections of a track that contain the unwanted effects. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use audio editing software to remove sound effects:
- Choose the right software: There are several audio editing software options available, both free and paid. Popular choices include Adobe Audition, Pro Tools, and Audacity. Make sure to choose a software that you are comfortable with and offers the necessary tools for isolating and editing audio.
- Import the music track: Open the audio editing software and import the music track that contains the sound effects you want to remove. Most software allows you to simply drag and drop the file into the workspace.
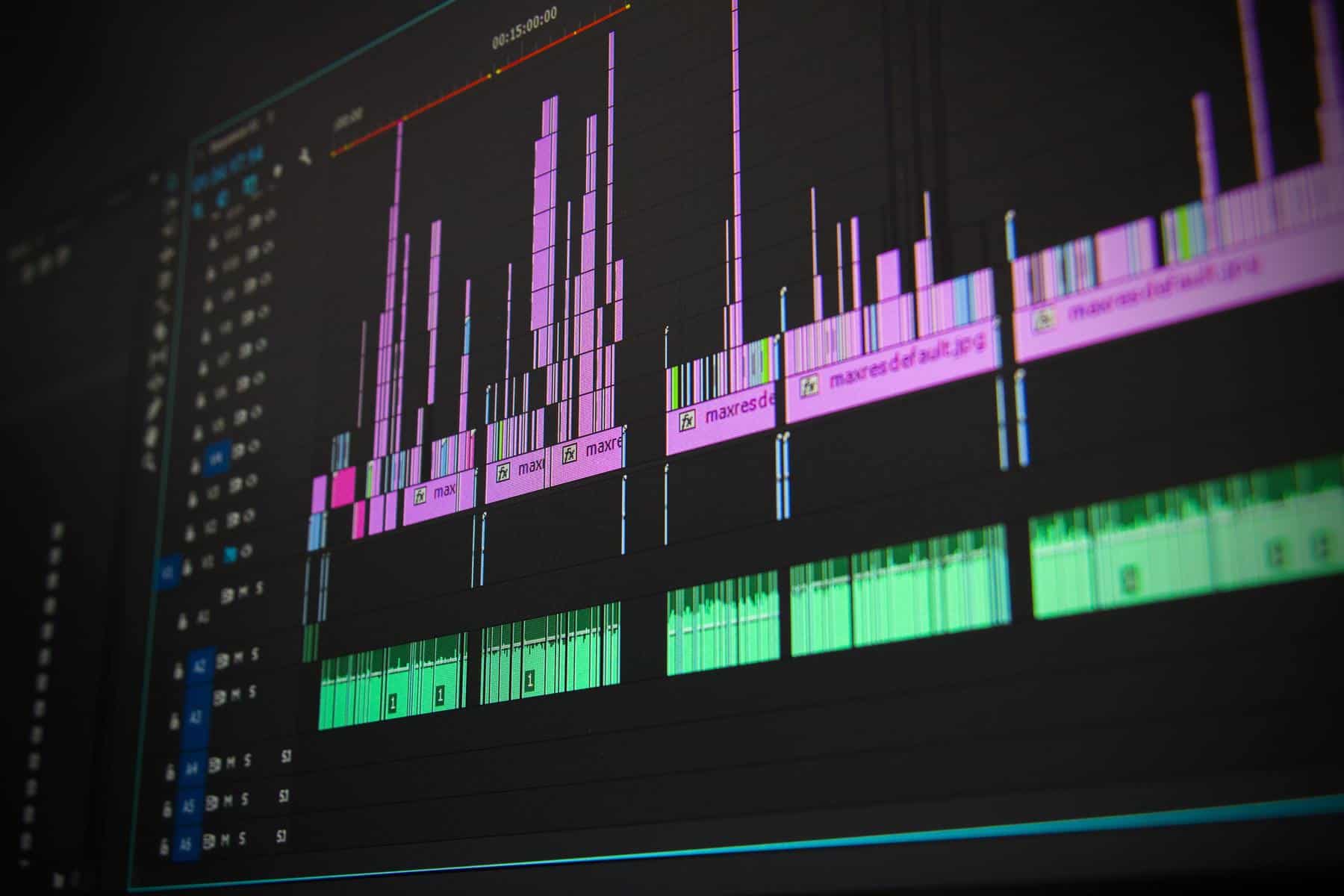
- Visualize the audio: Use the waveform or spectral view to analyze the audio visually. Look for sections where the sound effects are prominent or distinguishable from the rest of the music.
- Select the affected sections: Using the selection tools provided by the software, carefully select the sections of the track that contain the sound effects you want to remove. Be precise in your selection to minimize any unintended impact on the surrounding audio.
- Apply filters or edits: Once you have selected the affected sections, apply filters or edits to remove or reduce the sound effects. This can include using equalizers, noise reduction tools, or volume adjustments. Experiment with different settings and techniques to achieve the best results.
- Preview and fine-tune: After applying the filters or edits, listen to the modified track and make any necessary adjustments. Fine-tune the settings until you achieve the desired outcome.
- Export the cleaned track: Once you are satisfied with the removal of the sound effects, export the cleaned track to your desired audio file format. Make sure to save a backup of the original file before making any modifications.
Remember that the effectiveness of this method depends on the complexity and integration of the sound effects. Some effects may be easier to remove, while others may require more advanced techniques or a combination of methods.
In the next section, we will explore another approach for removing sound effects: isolating frequencies.
Method 2: Isolating Frequencies
Another approach to removing sound effects from music is by isolating frequencies. This method involves identifying the specific frequency ranges occupied by the sound effects and applying techniques to reduce or eliminate those frequencies while preserving the desired elements of the music. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to isolate frequencies to remove sound effects:
- Select the right audio editing software: Choose an audio editing software that provides a comprehensive equalizer or spectral editing tool. Options like Adobe Audition, Izotope RX, and FabFilter Pro-Q are commonly used for this purpose.
- Import the music track: Open the software and import the music track you want to work on. Ensure that the software displays the spectrogram or frequency analysis of the audio.
- Analyze the frequency content: Study the spectrogram or frequency analysis to identify the specific frequency range where the sound effects are present. Look for visual cues, such as spikes or bands, that indicate the presence of the effects.
- Apply a spectral editing tool: Once you have identified the frequency range, use the spectral editing tool in your software to select and manipulate only the frequencies within that range. This allows you to isolate the sound effects while leaving the rest of the audio untouched.
- Reduce or remove the selected frequencies: Apply a reduction or removal process to the selected frequency range. This can be done by using an equalizer to reduce the specific frequencies or by applying spectral editing techniques that allow you to erase or attenuate the selected range.
- Preview and adjust: After applying the frequency isolation and reduction, listen to the modified track and make any necessary adjustments. Fine-tune the settings to ensure that the sound effects are sufficiently removed without negatively impacting the desired elements.
- Export the cleaned track: Once you are satisfied with the removal of the sound effects, export the cleaned track to your desired audio file format. It is always a good practice to save a backup of the original file before making any modifications.
Keep in mind that isolating frequencies can be a precise and time-consuming process. It requires a good understanding of frequency ranges and may involve some trial and error to achieve the desired result. Additionally, some sound effects may be intricately intertwined with the desired audio, making complete removal challenging.
In the next section, we will explore another method for removing sound effects: applying noise reduction techniques.
Method 3: Applying Noise Reduction Techniques
Noise reduction techniques can be effective in removing unwanted sound effects from music. These techniques utilize specialized plugins or tools that analyze the audio and identify noise or repetitive patterns to suppress them. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to apply noise reduction techniques to remove sound effects:
- Select an appropriate noise reduction plugin: Choose an audio editing software or plugin that provides noise reduction capabilities. Options like iZotope RX, Waves NS1, and Cedar DNS are commonly used for this purpose.
- Import the music track: Open the software or plugin and import the music track you want to work on. Ensure that the track is loaded into the software’s workspace.
- Analyze the audio: Use the software’s analysis tools to identify the noise or sound effects you want to remove. Most plugins offer visual representations of the audio that help identify problem areas.
- Apply the noise reduction process: Once you’ve identified the sound effects, apply the noise reduction process or plugin. This could involve adjusting threshold settings, selecting specific frequency ranges, or using algorithms designed for noise reduction.
- Preview and adjust: After applying the noise reduction process, listen to the modified track and make any necessary adjustments. Fine-tune the settings to ensure that the sound effects are adequately removed without negatively affecting the desired elements of the music.
- Export the cleaned track: Once you are satisfied with the removal of the sound effects, export the cleaned track to your desired audio file format. Always keep a backup of the original file before making any modifications.
Noise reduction techniques can be effective in attenuating or eliminating unwanted sound effects, especially background noises or repetitive patterns. However, the success of this method depends on the complexity and integration of the effects within the audio. Some effects may still leave behind remnants or artifacts after the noise reduction process.
In the next section, we will explore a manual editing approach for removing sound effects.
Method 4: Manual Editing
Manual editing is another approach to remove sound effects from music. This method involves carefully listening to the audio, identifying the sections with the unwanted effects, and using audio editing software to manually silence or remove those sections. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use manual editing to remove sound effects:
- Select an audio editing software: Choose an audio editing software that provides the necessary tools for precise editing. Programs like Adobe Audition, Pro Tools, or Audacity are popular choices.
- Import the music track: Open the software and import the music track that contains the sound effects you want to remove. Ensure that the track is loaded and ready for editing.
- Listen and identify the affected sections: Carefully listen to the audio and identify the sections where the sound effects occur. You can visually mark these sections using markers or by noting down the timestamps.
- Use the editing tools: Utilize the editing tools in the software to select and silence or remove the affected sections. This can be done by cutting out the sections, muting them, or using fade-in/fade-out effects to smooth the transitions.
- Preview and adjust: After making the edits, listen to the modified track and make any necessary adjustments. Ensure that the sound effects are effectively removed without affecting the quality of the remaining audio.
- Export the cleaned track: Once you are satisfied with the removal of the sound effects, export the cleaned track to your desired audio file format. Save a backup of the original file before making any modifications.
Manual editing offers precise control over the removal process, allowing you to specifically target the sections with sound effects. However, it can be a time-consuming process, especially for longer or more complex audio tracks. Careful attention must be given to ensure seamless transitions and maintain the overall integrity of the music.
In the next section, we will discuss some best practices that can help you achieve successful sound effects removal.
Best Practices for Successful Removal
Removing sound effects from music can be a challenging task, but by following some best practices, you can increase your chances of achieving successful results. Here are some tips to keep in mind:
- Start with high-quality source files: Begin with high-quality audio files to maintain the integrity of the music during the removal process. A clean and uncompressed source file will provide a better starting point for removing the sound effects.
- Work in a controlled environment: Minimize external noise or distractions when editing the audio. A quiet environment allows you to focus on the subtle details and make accurate decisions during the removal process.
- Listen critically: Train your ears to identify the specific sound effects you want to remove. Pay attention to details like frequency ranges, timing, and consistency to help in selecting and isolating the effects accurately.
- Use a combination of techniques: Experiment with different approaches, such as using audio editing software, isolating frequencies, applying noise reduction techniques, and manual editing. Combining these techniques can often yield better results for complex sound effects.
- Work in layers: Make a copy of the original track and work on a separate layer when applying edits or modifications. This allows you to easily compare the modified version with the original and make adjustments without losing the original audio.
- Keep backups: Always keep backups of the original audio file before making any modifications. This ensures that you can revert back to the original if needed or revisit the removal process with a fresh perspective.
- Listen to the final result: After removing the sound effects, listen to the modified track in its entirety. Ensure that the desired elements of the music are preserved, and there are no noticeable artifacts or unnatural sound alterations.
Remember, the success of removing sound effects varies depending on the complexity and integration within the audio. Be patient, take your time, and be prepared to make adjustments as necessary to achieve the desired outcome.
With these best practices in mind, you are well-equipped to embark on your sound effects removal journey.
Conclusion
Sound effects can add depth, atmosphere, and storytelling elements to music compositions. However, there are situations where you may want to remove sound effects from music. Whether you are a musician, filmmaker, or content creator, the ability to remove or reduce unwanted effects provides greater control and customization over the audio.
In this article, we explored different approaches to removing sound effects from music. We discussed using audio editing software to isolate and remove specific frequencies, applying noise reduction techniques to suppress unwanted effects, and manually editing the audio to silence or remove affected sections. Each method has its advantages and limitations, and the effectiveness may vary depending on the complexity and integration of the sound effects within the music.
We also emphasized the importance of best practices when attempting to remove sound effects. Starting with high-quality source files, working in a controlled environment, critically listening to the audio, and using a combination of techniques can greatly enhance your chances of achieving successful results.
It’s important to remember that complete removal of sound effects may not always be possible without affecting the overall quality of the music. Therefore, it’s crucial to strike a balance between removing unwanted effects and preserving the desired elements of the composition.
As you embark on your journey of removing sound effects from music, don’t be afraid to experiment, learn from your experiences, and refine your techniques. With time and practice, you will develop the skills and discernment necessary to achieve your desired outcomes.
So, whether you’re a musician looking to remix a track, a filmmaker in need of a specific piece of music without sound effects, or simply a music enthusiast seeking a more personalized listening experience, the ability to remove sound effects from music opens up a world of possibilities for creative expression and customization.