Home>Production & Technology>Audio Cable>What Difference Does An Optical Audio Cable Do


Audio Cable
What Difference Does An Optical Audio Cable Do
Modified: January 22, 2024
Discover the difference an optical audio cable can make in your audio setup. Upgrade your sound quality with a reliable and high-performance audio cable.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of audio cables, where the right connection can make all the difference in how you experience sound. When it comes to transmitting audio signals, there are various types of cables available, each with its own unique capabilities. One such cable that has gained popularity in recent years is the optical audio cable.
Also known as TOSLINK or SPDIF, optical audio cables have revolutionized the way we connect our audio devices. Whether you’re a music lover, a movie aficionado, or a gaming enthusiast, understanding the benefits of using an optical audio cable can greatly enhance your audio experience.
In this article, we’ll delve into the ins and outs of optical audio cables, explaining how they transmit signals, the benefits they offer, and the factors to consider when choosing one. Additionally, we’ll provide some helpful tips for setting up an optical audio connection and troubleshooting common issues you may encounter.
So, let’s embark on this audio journey and unlock the secrets of optical audio cables to take your sound experience to a whole new level.
Understanding Optical Audio Cables
Optical audio cables, also known as fiber optic cables or digital audio cables, are designed to transmit digital audio signals. Unlike traditional analog cables, which transmit audio signals through electrical currents, optical cables use pulses of light to carry the audio data.
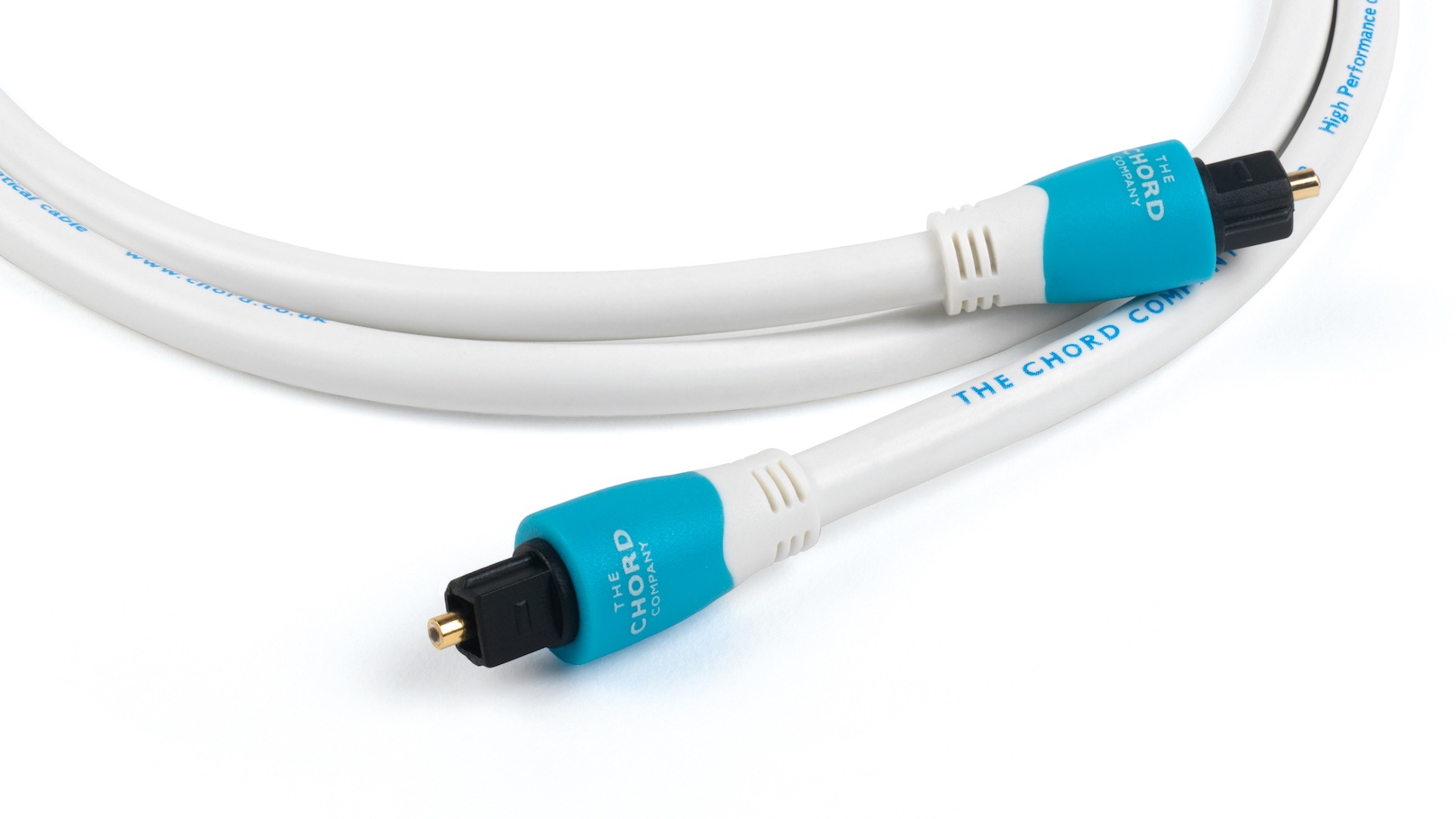
At the core of an optical audio cable is a thin strand of glass or plastic fiber called an optical conductor. This conductor is surrounded by a protective layer to ensure signal integrity. The cable terminates in a connector with a small opening for transmitting and receiving the light signals.
The process of transmitting audio signals through an optical cable utilizes a technology called TOSLINK (short for Toshiba Link), which was developed by Toshiba in collaboration with other companies. This technology uses a red LED (light-emitting diode) to emit a beam of light that carries the audio data.
Optical audio cables are capable of transmitting digital audio signals in formats such as PCM (Pulse Code Modulation), Dolby Digital, DTS (Digital Theater System), and more. They can support multiple channels of audio, including stereo, surround sound (5.1 or 7.1), and even higher-end formats like Dolby Atmos.
One of the key advantages of optical audio cables is their ability to transmit digital signals without any interference or loss of quality. Since the signals are transmitted as pulses of light, they are immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) that can degrade the audio quality in traditional analog cables.
Understanding the inner workings of optical audio cables is crucial in appreciating their benefits and making informed decisions when setting up audio connections. In the next section, we will explore how these cables transmit signals and the advantages they offer.
How Does an Optical Audio Cable Transmit Signals?
Optical audio cables utilize a unique method to transmit digital audio signals: light. The process involves converting electrical audio signals into optical signals, which are then transmitted through the cable as pulses of light.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how an optical audio cable transmits signals:
- The audio source, such as a DVD player or game console, generates an electrical audio signal.
- This electrical signal is processed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) to convert it into a digital audio signal.
- The digital audio signal is then passed through an optical transmitter, which converts it into a series of light pulses.
- Inside the optical cable, the light pulses travel through the optical conductor, which is a thin strand of glass or plastic fiber.
- The light pulses reflect off the internal walls of the conductor through a phenomenon called total internal reflection, ensuring they stay confined within the cable.
- On the receiving end, the light pulses reach the optical receiver, which converts them back into electrical audio signals.
- Finally, the electrical audio signals are sent to the audio output device, such as a soundbar or receiver, where they are amplified and played back as sound.
Due to the use of light to transmit audio signals, optical cables offer several advantages. One of the most significant advantages is their ability to transmit audio signals over long distances without degradation or loss of quality. Unlike analog cables that can suffer from signal degradation over long distances, optical cables can transmit signals reliably even over several meters.
Additionally, optical cables are immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) that can negatively impact the audio quality in analog cables. This makes optical cables an ideal choice in environments with high levels of electromagnetic interference, such as near power cables or electronic devices.
Overall, the method of using light to transmit digital audio signals sets optical audio cables apart from other types of audio cables. This unique transmission process ensures high-quality sound and reliable performance, making them a popular choice among audio enthusiasts.
Benefits of Using an Optical Audio Cable
Optical audio cables offer several benefits that make them a preferred choice for many audio enthusiasts. Let’s explore some of the advantages of using an optical audio cable:
- High-Quality Digital Audio: Optical cables transmit digital audio signals with minimal loss of quality. The use of light pulses ensures a clean and accurate transfer of audio data, resulting in a pristine audio experience.
- Immunity to Interference: Unlike analog cables, optical cables are immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). This means that you won’t experience any buzzing, humming, or static caused by nearby electronic devices or power cables, resulting in clear and uninterrupted audio playback.
- Long Cable Runs: Optical cables can transmit signals over long distances without any loss in audio quality. This makes them ideal for setting up audio systems in large rooms or home theaters where the audio source and output devices are far apart.
- No Ground Loop Issues: Ground loops can cause annoying hum or buzzing sounds in audio systems. Since optical cables use light transmission, they do not rely on electrical grounding, eliminating the possibility of ground loop issues and the associated audio interference.
- Support for Surround Sound Formats: Optical cables have the bandwidth capacity to transmit multi-channel audio formats, including Dolby Digital, DTS, and even advanced formats like Dolby Atmos. This makes them suitable for connecting devices such as game consoles, Blu-ray players, and AV receivers that support immersive surround sound experiences.
- Ease of Use: Optical cables are easy to connect and disconnect, as they use a standardized TOSLINK connector. This makes it a hassle-free process to set up or reconfigure your audio system, without the need for specialized adapters or converters.
- Durability: Optical cables are typically more durable than analog cables, as they are not susceptible to wear and tear caused by electrical currents. The use of fiber optic technology ensures longevity and consistent performance over time.
With their high audio quality, immunity to interference, and support for surround sound formats, optical audio cables offer a superior audio experience for music, movies, and gaming. Their ease of use and durability further add to their appeal, making them an excellent choice for any audio setup.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Optical Audio Cable
When it comes to choosing an optical audio cable, there are several factors to consider to ensure you select the right cable for your needs. Let’s take a look at some key factors to keep in mind:
- Length: Determine the length of cable you require based on the distance between your audio source and output device. It’s important to choose a cable that is long enough to reach without excessive slack, as excessive bending or coiling can impact signal quality.
- Construction: Look for optical cables with a sturdy construction, including a durable outer jacket and strain relief at the connectors. This ensures longevity and prevents the cable from easily bending or breaking during use.
- Bandwidth: Consider the bandwidth capacity of the cable. Most standard optical cables can handle common audio formats such as PCM, Dolby Digital, and DTS. However, if you plan to connect higher-end audio equipment that supports formats like Dolby Atmos, make sure the cable is rated for the required bandwidth.
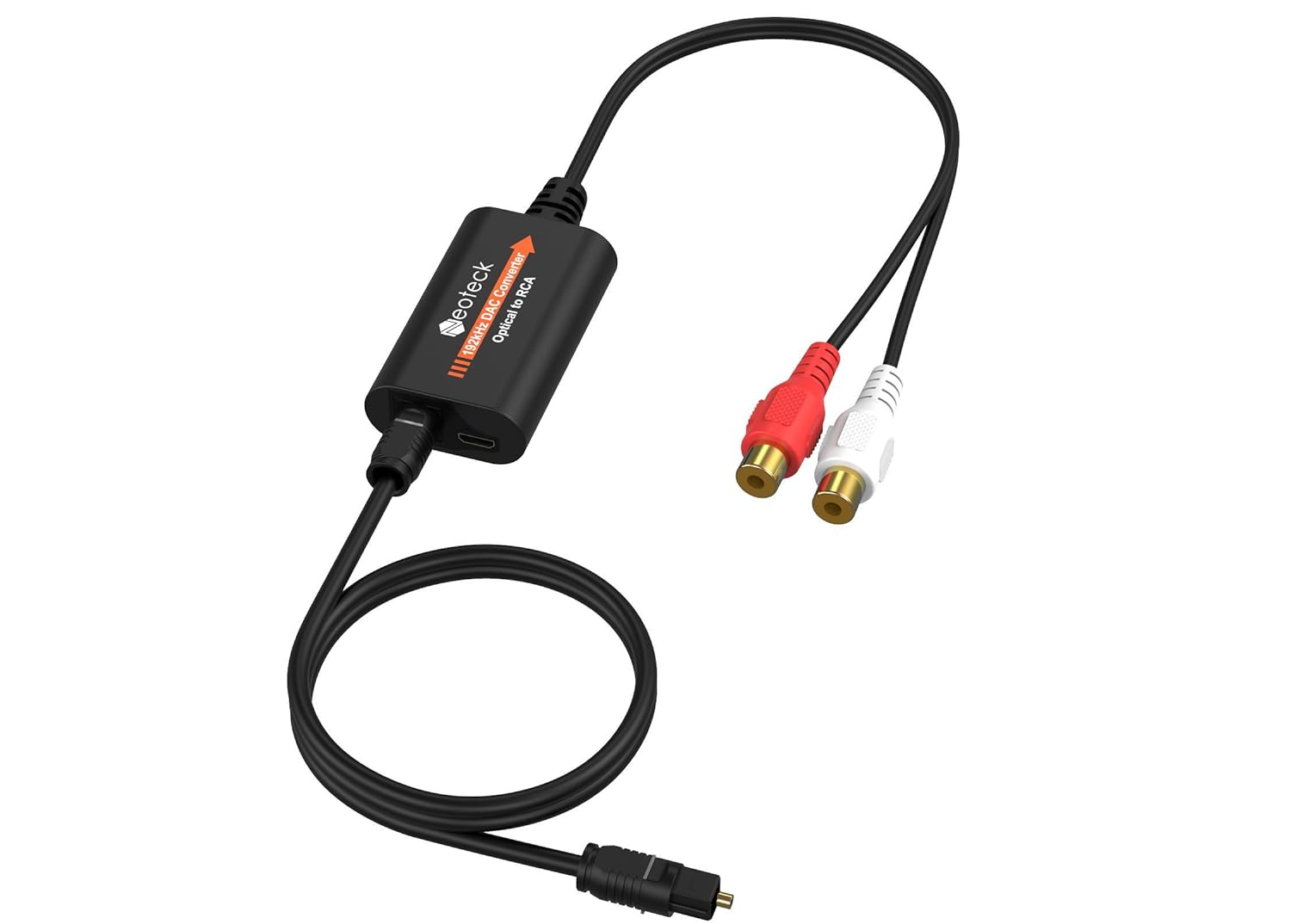
- Connectors: Check that the cable has compatible connectors for your audio devices. The most common connector for optical cables is the TOSLINK connector, but there are variations such as mini-TOSLINK and 3.5mm optical connectors. Ensure that the cable’s connectors match the ports on your devices for a proper connection.
- Price: Consider your budget when choosing an optical audio cable. While there are budget-friendly options available, investing in a higher-quality cable can provide better signal transmission and durability, resulting in improved audio performance over time.
- Brand Reputation: Opt for reputable brands that are known for producing high-quality audio cables. Brands with a good reputation typically ensure better build quality, reliable performance, and customer support.
- Customer Reviews: Read customer reviews and ratings to get insights into the real-world performance and reliability of the cable. This can help you make an informed decision based on the experiences of other users.
By considering these factors, you can select an optical audio cable that meets your specific requirements, ensuring a seamless and high-quality audio connection between your devices.
Setting Up an Optical Audio Connection
Setting up an optical audio connection is a straightforward process that involves a few simple steps. Follow these guidelines to ensure a proper and efficient setup:
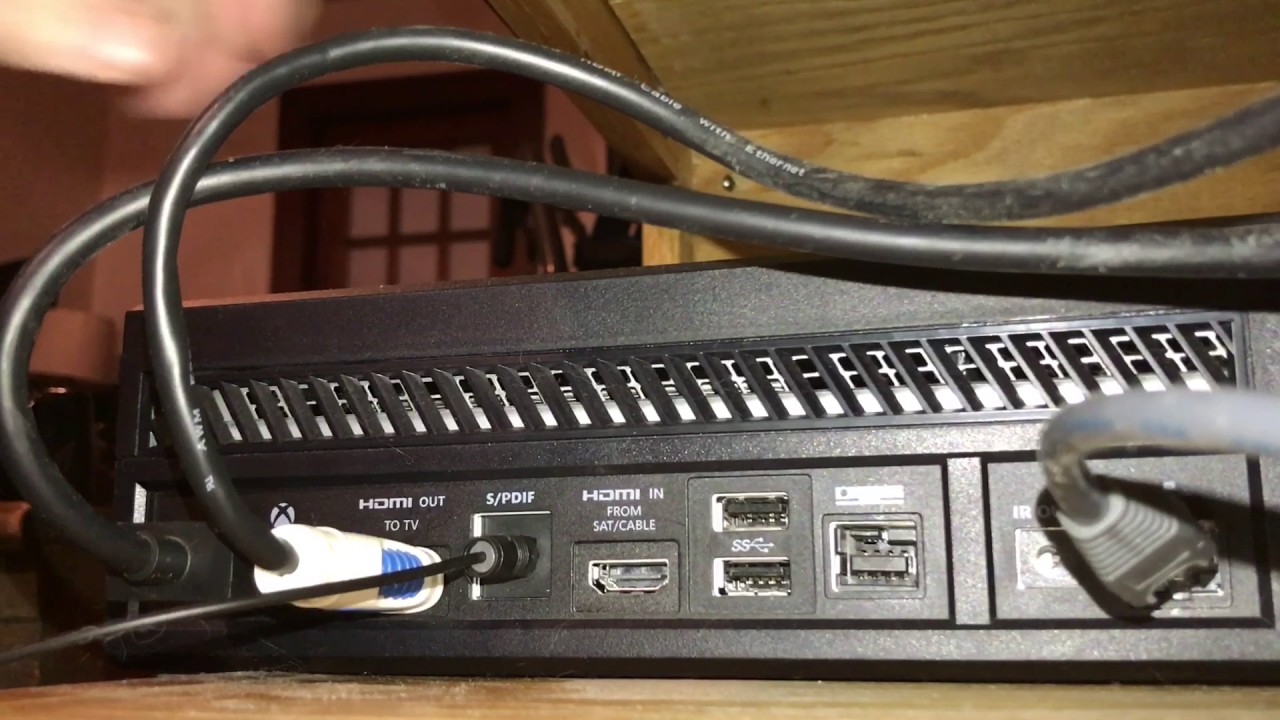
- Check Compatibility: Make sure that both your audio source (such as a Blu-ray player or game console) and your audio output device (such as a soundbar or AV receiver) have optical audio ports. These ports are typically labeled as “optical,” “TOSLINK,” or “SPDIF.”
- Choose the Right Cable: Select an optical audio cable that matches the length required to connect your devices. Ensure that the cable has the appropriate TOSLINK connectors on both ends.
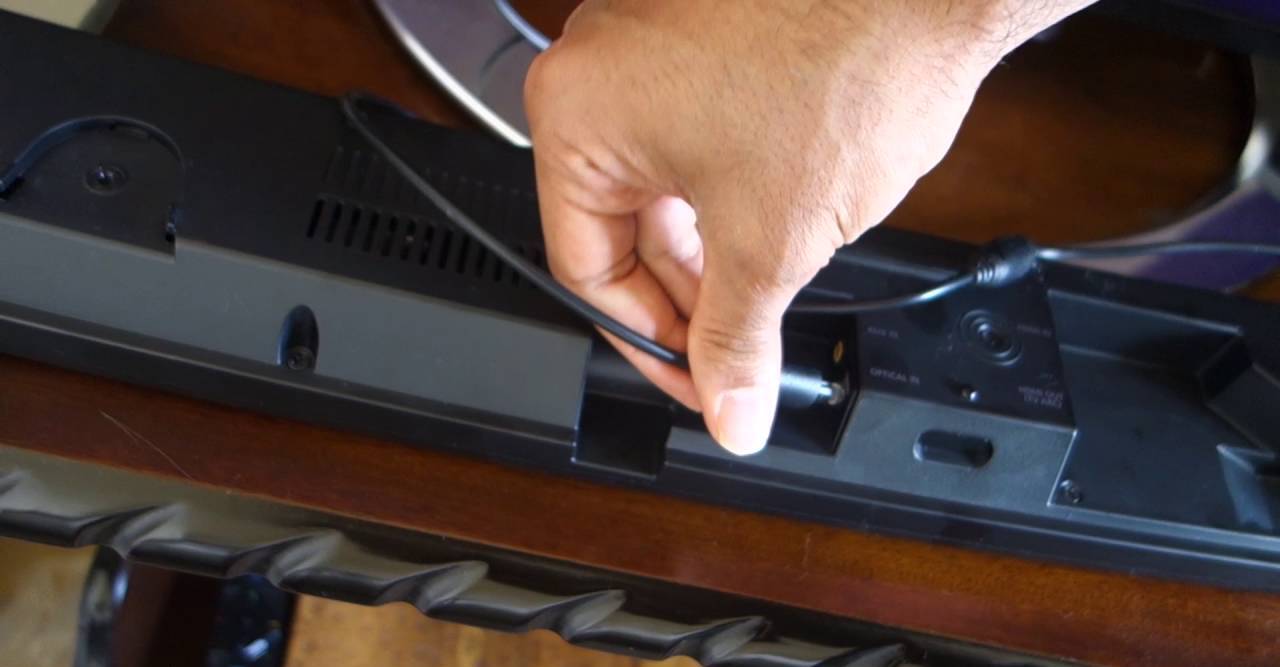
- Plug in the Cable: Insert one end of the optical audio cable into the optical audio output port on your audio source device. Make sure it is firmly inserted for a secure connection.
- Connect to the Output Device: Take the other end of the cable and plug it into the optical audio input port on your audio output device. Again, ensure a secure connection.
- Configure Audio Settings: On your audio source device, access the audio settings menu and select the optical audio output as your desired audio output option. This step may vary depending on the specific device, so consult the user manual if needed.
- Power On the Devices: Turn on both the audio source device and the audio output device (e.g., TV, soundbar, receiver) and make sure they are set to the appropriate input source.
- Test the Connection: Play audio from your source device to ensure that the optical audio connection is working correctly. Check for audio output from your output device and adjust the volume as needed.
- Secure and Organize the Cable: Bundle any excess cable length neatly, using cable ties or Velcro straps, to avoid tangling or tripping hazards. Keep the cable away from other power cables or sources of interference to minimize audio interference.
Follow these steps, and you’ll have an optical audio connection established between your devices, providing you with high-quality digital audio for an enhanced audio experience.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Optical Audio Cables
While optical audio cables offer reliable and high-quality audio transmission, occasional issues may arise. Here are some common problems you may encounter with optical audio cables and possible solutions:
- No Sound: If you’re not getting any sound, ensure that both the audio source and output devices are properly connected to the optical audio cable. Check that the cable is securely inserted into the ports. Also, verify that the audio settings on your devices are configured correctly, selecting the optical audio output as the desired option.
- Audio Dropouts: If the audio intermittently cuts out or experiences dropouts, inspect the optical cable for any physical damage or loose connections. Confirm that the cable is not bent or kinked sharply, as this can affect signal transmission. Try using a different optical cable to rule out a faulty cable as the cause of the issue.
- Interference or Distorted Sound: If you notice static, buzzing, or distorted sound, ensure that the optical cable is not near any power cables or sources of electromagnetic interference (EMI). Keep the cable away from electronic devices like routers, Wi-Fi equipment, or microwaves, as these can introduce noise. Consider using an optical cable with a robust shielding design to minimize the impact of external interferences.
- One Channel Not Working: If you experience audio only in one channel (e.g., left or right), check the connections on both ends of the optical cable. Make sure the connectors are fully inserted and do not have any debris or obstructions. Try swapping the cable ends or testing with a different optical cable to identify if the issue lies with the cable or the audio device.
- Optical Port Damage: If the optical port on your audio device becomes damaged or fails to work, consult the user manual for alternative audio connection options. This may involve using different audio ports or employing a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) to convert the optical signal to an analog format.
- Incompatible Devices: Occasionally, certain audio devices may not be compatible with each other, resulting in no audio or limited functionality. Ensure that both your audio source and output devices support the same digital audio format. If necessary, consult the manufacturer’s guidelines or seek technical support to verify compatibility.
If you encounter persistent issues with your optical audio connection, it may be helpful to update the firmware or drivers of your audio devices. Additionally, consulting technical support from the device manufacturer or seeking professional assistance can provide further troubleshooting guidance.
By troubleshooting these common issues, you can overcome audio interruptions and enjoy a seamless and uninterrupted audio experience with your optical audio cable setup.
Conclusion
Optical audio cables have revolutionized the way we connect our audio devices, providing a reliable and high-quality digital audio transmission. Through the use of light pulses, these cables offer several advantages, including immunity to interference, support for surround sound formats, and ease of use.
When selecting an optical audio cable, consider factors such as cable length, construction quality, compatibility with connectors, and your budget. Opt for reputable brands known for their reliability and customer satisfaction.
Setting up an optical audio connection is a simple process involving connecting the cable to the audio source and output device, configuring audio settings, and testing the connection for proper sound output.
In the event of issues, troubleshooting common problems such as no sound, audio dropouts, or interference can help restore optimal audio performance. Checking connections, cable integrity, and minimizing sources of EMI are key steps to resolve these issues.
Overall, optical audio cables provide a superior audio experience, delivering high-quality digital audio without interference. By understanding their benefits, selecting the right cable, and troubleshooting common issues, you can enjoy a seamless and immersive audio experience in your home entertainment setup.