Home>Production & Technology>Audio Interface>How To Choose Audio Interface In Logic

Audio Interface
How To Choose Audio Interface In Logic
Modified: March 11, 2024
Learn how to choose the perfect audio interface for Logic Pro. Discover the best features and specs to enhance your music production. Find the ideal Audio Interface for your needs.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of audio interfaces! If you’re an aspiring musician, producer, or audio enthusiast, finding the right audio interface is crucial for recording and producing high-quality sound. Whether you’re a Logic Pro user or considering using Logic as your digital audio workstation (DAW), it’s essential to choose an audio interface that is compatible and optimized for use with the software.
An audio interface is a device that connects your instruments, microphones, and other audio sources to your computer. It serves as the bridge between the analog and digital realms, converting analog audio signals into digital information that can be processed and manipulated within your DAW. The audio interface also plays a vital role in delivering excellent audio quality and minimizing latency during recording and playback.
Logic Pro, developed by Apple, is a popular and powerful DAW used by musicians, producers, and sound engineers around the world. It offers a wide range of features and tools for recording, editing, mixing, and mastering audio projects. To fully harness the capabilities of Logic, you’ll need an audio interface that meets its requirements and can handle the demands of your creative process.
Choosing the right audio interface involves considering several factors, such as inputs and outputs, connection type, sample rate and bit depth, latency, audio quality, and your budget. Each of these aspects plays a crucial role in determining the compatibility and functionality of the interface with Logic.
In this article, we’ll explore the key factors you should consider when choosing an audio interface for Logic. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced producer, this guide will help you make an informed decision that suits your specific needs and enhances your music production experience.
Understanding Audio Interfaces
Before diving into the details of choosing an audio interface for Logic, it’s important to have a clear understanding of what an audio interface is and how it functions.
An audio interface is an external device that connects to your computer and allows you to record and playback audio. It acts as a translator between the analog world of audio signals (such as microphones and instruments) and the digital realm of your computer’s software. It converts analog audio signals into digital data that your computer can recognize and manipulate.
Audio interfaces come in various shapes and sizes, with different features and capabilities. They typically offer a range of inputs and outputs, allowing you to connect microphones, instruments, studio monitors, headphones, and other audio equipment. The inputs capture the audio signals, while the outputs send the processed audio back out to your headphones or speakers.
Audio interfaces also come equipped with built-in preamps, which amplify weak analog signals from microphones and instruments to a level that is suitable for recording and processing. High-quality preamps are crucial for capturing clear and accurate audio recordings. Some interfaces also offer additional features such as phantom power for condenser microphones, MIDI connectivity, and digital inputs/outputs.
When choosing an audio interface, it’s important to consider the number and type of inputs and outputs that you’ll need. For example, if you primarily record vocals and acoustic instruments, a simple interface with two XLR inputs may be sufficient. However, if you work with a full band or need to connect multiple synthesizers or outboard gear, you may require an interface with more inputs and outputs.
In terms of connectivity, audio interfaces typically connect to your computer via USB, Thunderbolt, or FireWire. USB is the most common and widely supported option, while Thunderbolt offers faster data transfer speeds, making it ideal for large-scale projects with high track counts and complex processing. FireWire is less common these days but is still found on some older interfaces.
Now that you have a basic understanding of audio interfaces, let’s explore how to choose an interface that is specifically optimized for use with Logic.
Compatibility with Logic
When it comes to choosing an audio interface for Logic, compatibility is a critical factor to consider. Logic Pro has specific requirements and recommendations for audio interfaces, and it’s essential to ensure that the interface you choose is compatible and optimized for use with the software.
First and foremost, check the system requirements of the version of Logic Pro you are using or planning to use. These requirements will list the compatible operating systems and hardware specifications. Make sure that the audio interface you are considering is supported on your operating system and meets or exceeds the recommended specifications.
Next, consider whether the audio interface has specific drivers or software that are designed to work seamlessly with Logic Pro. Some manufacturers provide dedicated drivers that enhance the performance and functionality of the audio interface when used with Logic. These drivers can help minimize latency and ensure stable operation of the interface within the software.
Another aspect of compatibility to consider is whether the audio interface offers integration with Logic’s Control Surface feature. Control Surface allows you to control various aspects of Logic using physical controls on your audio interface. This can greatly enhance your workflow and efficiency during recording and mixing sessions.
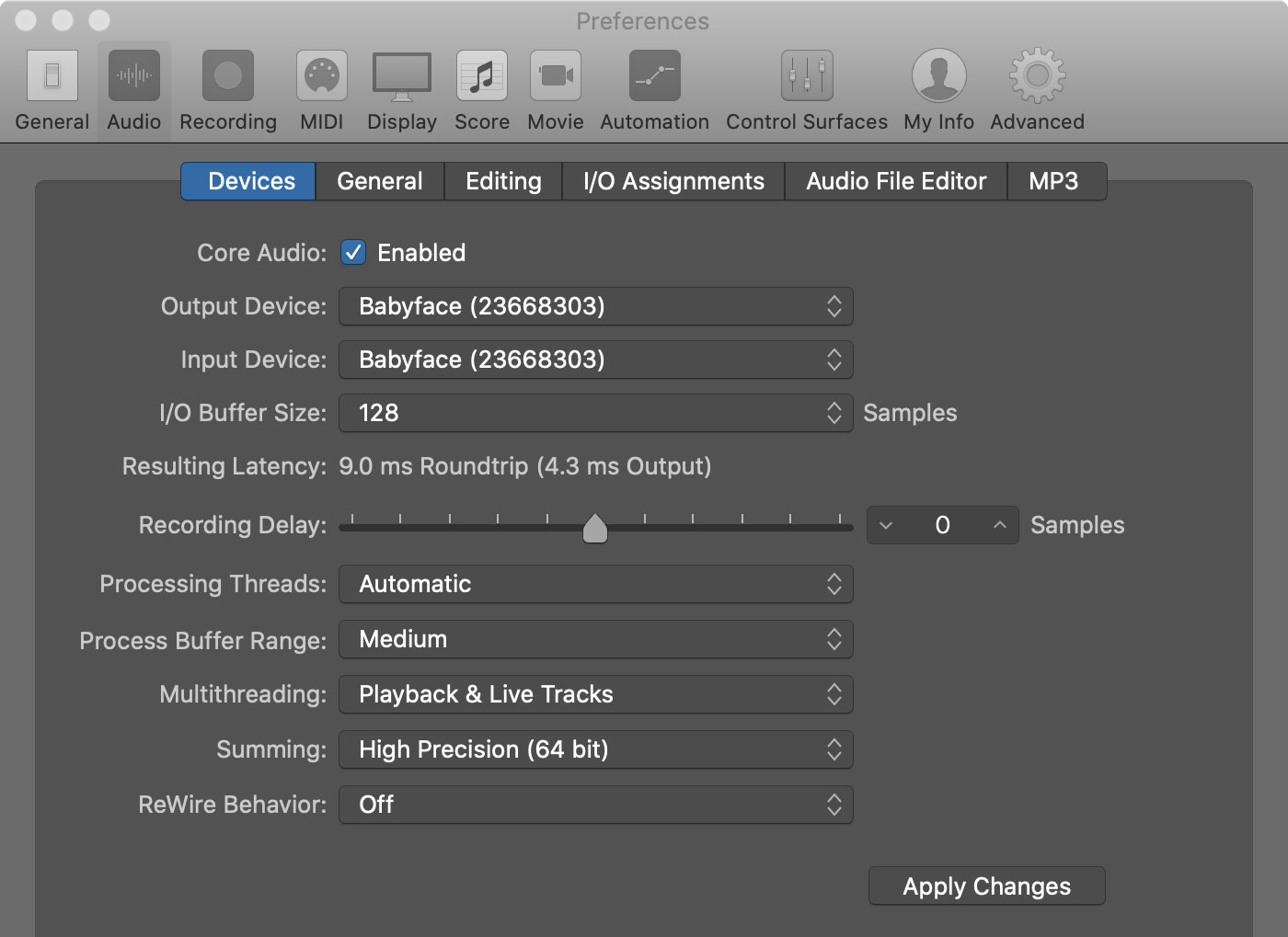
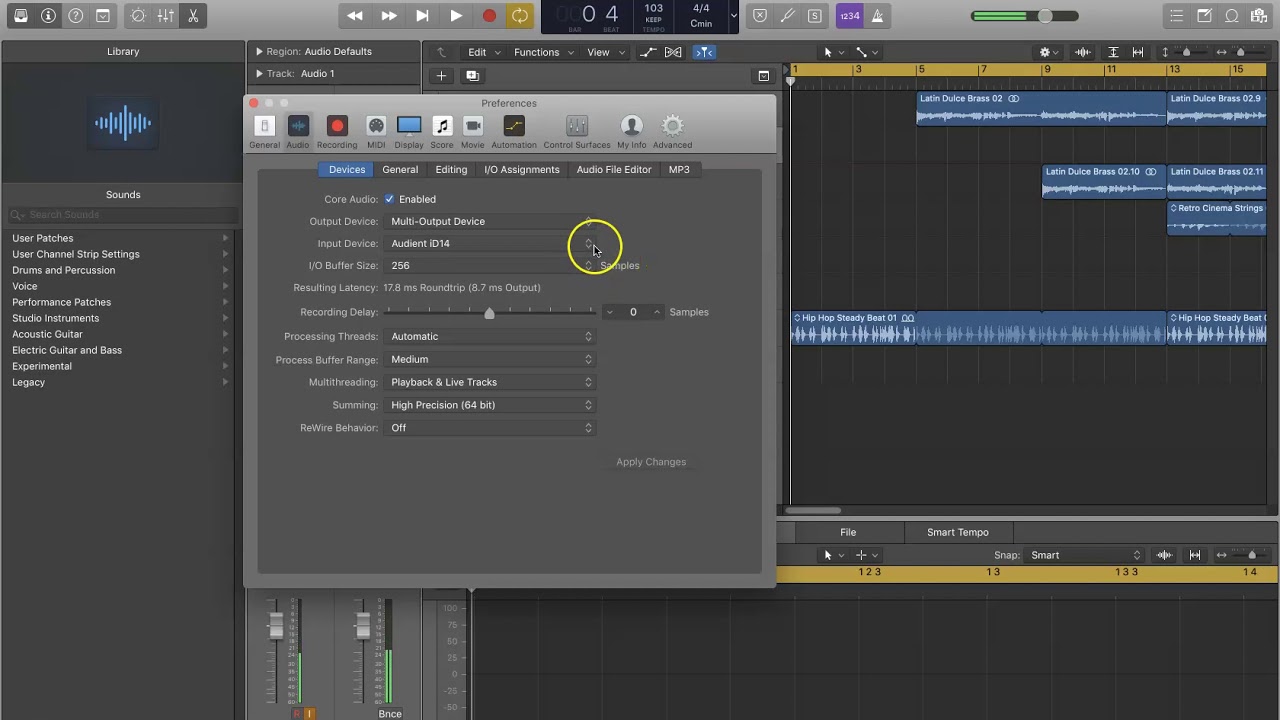
Moreover, it is worth checking if the audio interface supports Core Audio, which is the audio framework used by macOS. A Core Audio-compliant interface ensures smooth communication between Logic and the interface, allowing for low-latency operation and optimal audio performance.
Lastly, consider the overall reputation and track record of the audio interface’s compatibility with Logic. Research user reviews, forums, and manufacturer documentation to get insights into other users’ experiences with the interface and its compatibility with Logic. Reliable and well-established brands often have a proven track record of compatibility and support for popular DAWs like Logic Pro.
By ensuring compatibility between your audio interface and Logic Pro, you can have a seamless and hassle-free experience while recording, producing, and mixing your music.
Inputs and Outputs
When choosing an audio interface for Logic, one of the key factors to consider is the number and type of inputs and outputs it offers. The inputs allow you to connect your microphones and instruments, while the outputs send the processed audio to your headphones or speakers.
The number of inputs and outputs you need depends on your specific recording and production needs. If you primarily work with solo recordings or small ensembles, an interface with two or four inputs may be sufficient. However, if you often record full bands, podcasts, or live performances, you’ll need an interface with multiple XLR or combination inputs to accommodate all the sources simultaneously.
Consider the types of inputs and outputs that are essential for your workflow. Most audio interfaces offer a combination of XLR, ¼-inch TRS, and sometimes RCA inputs. XLR inputs are commonly used for microphones, while TRS inputs can accommodate instruments and line-level signals. Having a combination of both gives you versatility in working with different audio sources.
It’s also worth considering if the audio interface offers dedicated headphone outputs. This allows you to monitor your recordings and mixes without the need for additional headphone amplifiers or splitters. If you often collaborate with others or need to provide separate headphone mixes, look for an interface with multiple headphone outputs and independent volume controls.
In addition to inputs and outputs, some audio interfaces offer digital connections like ADAT or S/PDIF. These digital connections allow for expansion of the interface’s capabilities by connecting additional external preamps or digital devices. If you anticipate the need for expanding your recording setup in the future, having digital connectivity options can be advantageous.
Consider your future needs and growth potential when deciding on the number and type of inputs and outputs. It’s always better to have more I/O options than you currently require, as it allows for greater flexibility and expandability as your recording needs evolve.
By carefully assessing your recording requirements and selecting an audio interface with the appropriate inputs and outputs, you can ensure that your workflow in Logic is optimized, and you have the necessary connections to capture and monitor your audio sources effectively.
Connection Type
When choosing an audio interface for Logic, one important consideration is the connection type that the interface uses to communicate with your computer. The connection type determines the data transfer speed, latency, and overall stability of the audio interface.
USB is the most common and widely supported connection type for audio interfaces. USB 2.0 offers sufficient data transfer speeds for most recording and playback needs. However, if you’re working with a large number of tracks or complex projects that require high track counts and low latency, consider using an audio interface with USB 3.0 or USB-C connectivity.
Thunderbolt is another connection type worth considering, especially if you require lightning-fast data transfer speeds and ultra-low latency. Thunderbolt interfaces are designed for high-bandwidth audio recording and can handle large track counts and demanding processing tasks without compromising performance. However, it’s important to ensure that your computer has a Thunderbolt port to connect the interface.
FireWire, once a popular connection option, has become less common in recent years. It offers decent data transfer speeds and is suitable for smaller recording setups. If you have an older interface with FireWire connectivity or want to connect multiple chainable devices, it may still be a viable option. However, compatibility with newer computers may be limited.
Additionally, some audio interfaces offer Ethernet or AVB (Audio Video Bridging) connectivity. These interfaces use standard Ethernet cables to transmit audio data, allowing for long cable runs and easy integration in studio or live sound environments. They are suitable for professional applications and may require specialized network switches or protocol support.
It’s crucial to ensure that your chosen connection type is compatible with your computer’s available ports. Many audio interfaces are cross-platform compatible, meaning they can work with both Mac and Windows systems, but double-check the manufacturer’s website or documentation to confirm.
Consider the specific demands of your projects and your future expansion plans when choosing a connection type. If you anticipate working with larger track counts, multiple peripherals, or demanding plugins, opting for a faster and more robust connection type will ensure smooth operation and reduce potential latency issues.
Ultimately, the connection type of your audio interface affects the speed and reliability of data transfer between the interface and your computer. By selecting the appropriate connection type for your needs, you can ensure optimal performance and stability when working with Logic.
Sample Rate and Bit Depth
When choosing an audio interface for Logic, it’s important to consider the sample rate and bit depth capabilities of the interface. These two parameters determine the audio quality and resolution of your recordings.
The sample rate refers to the number of samples taken per second to capture the audio signal. A higher sample rate allows for more accurate representation of the original audio, especially for high-frequency content. The standard sample rate used in most audio interfaces is 44.1kHz, which provides excellent audio quality for most musical applications. However, if you work in the professional audio field or need to preserve the highest level of detail, you may want to consider an interface that supports higher sample rates like 48kHz, 96kHz, or even 192kHz.
Bit depth, on the other hand, determines the dynamic range and precision of the audio signal. It refers to the number of bits used to represent each sample. The most common bit depth used in audio interfaces is 24-bit, which provides ample headroom and dynamic range for capturing and processing audio. It allows for a greater range between the quietest and loudest parts of a recording, resulting in less noise and improved audio fidelity. Some interfaces also offer 16-bit mode, which is suitable for basic recording needs or compatibility with older equipment, but may sacrifice some dynamic range.
When selecting an audio interface, it’s essential to choose one that supports the sample rate and bit depth that matches your desired level of audio quality. Keep in mind that higher sample rates and bit depths may require more computing power and storage space.
Additionally, consider the compatibility of the sample rate and bit depth settings with Logic Pro. Logic supports a wide range of sample rates and bit depths, but it’s important to ensure that the audio interface you choose can work seamlessly with the software at your desired settings.
Ultimately, selecting an audio interface with the appropriate sample rate and bit depth capabilities ensures that your recordings and mixes have the highest possible audio quality and resolution. It allows for greater sonic detail, improved dynamic range, and an overall more professional sound.
Latency
Latency is a crucial factor to consider when choosing an audio interface for Logic. It refers to the delay or lag between the moment you input an audio signal (e.g., play a note on a MIDI keyboard or sing into a microphone) and the moment you hear the processed audio through your speakers or headphones.
Low latency is crucial, especially for recording and monitoring purposes, as it allows you to play and record in real-time with minimal delay. High latency can be problematic, as it can make it difficult to play instruments or sing in time with the music, causing a noticeable disruption in your workflow and performance.
Latency is measured in milliseconds (ms), and it’s a combination of various factors, including the hardware buffer size, processing power of your computer, and the efficiency of the drivers of the audio interface. A smaller hardware buffer size generally leads to lower latency, but it can put a higher strain on your computer’s processing power.
When choosing an audio interface, look for one that offers low-latency performance. Some interfaces have dedicated circuitry and optimized drivers that minimize round-trip latency, allowing for real-time monitoring without any noticeable delay.
It’s also worth considering the type of audio project you’ll be working on. If you primarily record and mix with virtual instruments and plugins, look for an interface with excellent DSP (Digital Signal Processing) capabilities. This can offload some of the processing tasks from your computer’s CPU, resulting in lower latency during playback and recording.
Finally, it’s important to note that the latency you experience may also be affected by the performance of your computer and the efficiency of your DAW. Make sure your computer meets the recommended specifications for running Logic Pro smoothly and optimize your software settings to minimize latency as much as possible.
Overall, low latency is critical for a seamless recording and monitoring experience in Logic. By selecting an audio interface with low-latency performance and optimizing your computer and software settings, you can ensure that your workflow remains efficient and uninterrupted.
Audio Quality
When it comes to audio production, the quality of your recordings is essential. The audio interface you choose plays a significant role in capturing and reproducing high-quality sound. To ensure the best audio quality in your Logic projects, there are several factors to consider.
The first factor is the quality of the preamps in the audio interface. Preamps are responsible for amplifying the incoming audio signals from microphones and instruments. High-quality preamps can deliver clean, transparent, and detailed recordings, while lower-quality preamps may introduce noise, distortion, or coloration to the audio signal. Look for an audio interface that is known for having high-quality preamps to ensure accurate and faithful sound reproduction.
The analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) in the audio interface also affect the audio quality. ADCs convert the analog audio signals into digital data. Higher-quality converters provide better accuracy and resolution, resulting in more detailed and dynamic recordings. Look for an interface that uses high-grade ADCs for optimal audio quality.
Additionally, consider the overall build quality and components used in the audio interface. Quality components and robust construction can help minimize signal interference, electrical noise, and other undesirable artifacts that can degrade audio quality. Look for interfaces made by reputable manufacturers known for their attention to detail and quality craftsmanship.
Another aspect to consider is the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the audio interface. SNR measures the level of unwanted noise in the audio signal relative to the desired signal. A higher SNR indicates a cleaner and more accurate audio signal. Look for interfaces that have a high SNR to ensure your recordings and mixes have minimal noise and maximum clarity.
Lastly, consider whether the audio interface supports higher sample rates and bit depths, as mentioned in the previous section. Higher sample rates and bit depths can contribute to better overall audio quality by capturing more details and dynamic range in your recordings.
Keep in mind that the quality of your audio chain is only as strong as its weakest link. While the audio interface plays a significant role, other factors such as microphone choice, acoustic treatment, and proper gain staging also impact the final audio quality. Consider your entire recording and production setup holistically to ensure the best possible sound.
By selecting an audio interface with high-quality preamps, converters, and components, you can ensure that your Logic projects have excellent audio quality from start to finish.
Budget Considerations
When it comes to choosing an audio interface for Logic, your budget will inevitably be a significant factor to consider. Audio interfaces come in a wide range of price points, and determining your budget can help narrow down your options and find the best interface within your price range.
It’s important to strike a balance between your budget and the features and quality you require. While it can be tempting to opt for a budget-friendly interface, keep in mind that the quality of the preamps, converters, and components may be compromised in cheaper models. This can affect the overall audio quality of your recordings.
Consider your specific needs and requirements. If you’re a hobbyist or a beginner who is just starting out, investing in a more affordable audio interface can be a sensible choice. Look for interfaces that offer a good balance of features and quality for the price.
On the other hand, if you’re a professional or an advanced user who relies on quality and high-end features, you may need to allocate a higher budget to invest in a higher-grade audio interface. These interfaces often offer better preamps, converters, and overall build quality, which can result in superior audio quality.
While setting your budget, it’s essential to consider any additional equipment or accessories you may need. Factor in the cost of cables, microphones, headphones, and other studio essentials that are necessary for a complete recording setup. It’s important to have a realistic budget that accounts for all the components required for your specific needs.
Additionally, consider the long-term value of the audio interface. Will it meet your needs for the foreseeable future, or will you likely need to upgrade in a few years? Investing in a higher-quality interface now may save you money in the long run by avoiding the need for premature upgrades.
Lastly, be sure to do your research and read reviews from other users to understand the overall reputation and performance of the audio interface within your budget range. It’s helpful to compare features, specifications, and user experiences to make an informed decision.
Remember, while budget is a significant consideration, it’s crucial not to compromise too much on quality or features, as this can impact the audio quality and functionality of your recording and production process.
By carefully assessing your budget and considering the features and quality necessary for your specific needs, you can find an audio interface that offers the best value for your money.
Conclusion
Choosing the right audio interface for Logic is a crucial step in ensuring high-quality recordings and a seamless production workflow. By considering factors such as compatibility, inputs and outputs, connection type, sample rate and bit depth, latency, audio quality, and budget, you can find an interface that suits your specific needs and enhances your music production experience.
Understanding the compatibility requirements of Logic and selecting an interface optimized for use with the software is fundamental. Ensuring the interface has the right inputs and outputs for your recording needs allows you to connect your microphones and instruments effectively. The connection type determines the data transfer speed and stability, while sample rate and bit depth impact the audio quality and resolution of your recordings. Low latency ensures real-time monitoring and seamless performance, while high-quality audio components contribute to excellent sound reproduction. Lastly, considering your budget and finding the right balance between price and quality is essential in making an informed decision.
By carefully considering these factors and conducting thorough research, you can choose an audio interface that integrates beautifully with Logic, supports your recording setup, and delivers exceptional audio quality. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced producer, investing in a reliable and compatible audio interface will enhance your music production process and elevate the overall quality of your projects.
Remember, the audio interface is the essential link between your musical creativity and the digital realm. Choose wisely, and embark on a sonic journey with Logic and your chosen audio interface.