Home>Production & Technology>Audio Interface>How To Change Buffer Rate For My Audio Interface

Audio Interface
How To Change Buffer Rate For My Audio Interface
Published: February 4, 2024
Learn how to easily change the buffer rate for your audio interface and optimize your recording experience. Enhance the performance of your audio interface with this step-by-step guide.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
An audio interface is a crucial piece of equipment for anyone involved in audio recording and production. It serves as the bridge between your computer and other audio devices, allowing you to capture and process high-quality sound. One important aspect to consider when using an audio interface is the buffer rate, also known as the buffer size or latency.
The buffer rate refers to the amount of time it takes for the computer to process and playback audio. A smaller buffer size results in lower latency, meaning a faster response time between when you play or record audio and when you hear it. Conversely, a larger buffer size may have a higher latency, but it offers more stability and reduces the chances of audio glitches or dropouts.
Understanding how to change the buffer rate for your audio interface is essential for optimizing your recording setup. In this article, we will explore the steps to change the buffer rate on both Windows and Mac operating systems. We will also provide tips on optimizing the buffer rate for recording and troubleshooting any buffer rate issues that may arise.
Understanding Buffer Rate
Before diving into how to change the buffer rate for your audio interface, it’s important to understand what the buffer rate is and how it affects your recording and playback experience.
The buffer rate, also referred to as buffer size or latency, is the amount of time it takes for your computer to process and handle audio data. It is measured in samples and typically represented in milliseconds (ms) or samples per buffer (e.g., 256 samples).
A smaller buffer size results in lower latency, meaning there is less delay between when you play or record audio and when it is heard or recorded. This low latency is crucial for real-time applications such as live performances or monitoring while recording. However, using a smaller buffer size may put more strain on your computer’s resources, potentially leading to audio dropouts or glitches if your system can’t keep up.
On the other hand, a larger buffer size increases the latency but provides more stability, ensuring that your system can handle the audio processing without any interruptions. This is ideal for situations where recording quality is prioritized over immediate feedback, such as when editing audio or mixing multiple tracks.
It’s important to find the right balance between buffer size and performance based on your specific requirements and the capabilities of your computer. This balance will ensure a smooth recording and playback experience while avoiding any performance bottlenecks or audio issues.
Now that we have a better understanding of buffer rate, let’s move on to checking for compatibility with your audio interface.
Checking for Compatibility
Before attempting to change the buffer rate on your audio interface, it’s essential to ensure that your computer and audio interface are compatible and properly connected.
The first step is to check the system requirements of your audio interface. This information can typically be found on the manufacturer’s website or in the user manual. Ensure that your computer meets or exceeds the minimum requirements, including the operating system version, available USB or Thunderbolt ports, and any specific software or driver requirements.
Next, make sure that your audio interface is connected to your computer correctly. Depending on the model, it may connect via USB, Thunderbolt, or another interface. Ensure that the cable is securely plugged in on both ends, and if necessary, try using a different cable or port to rule out any potential connectivity issues.
If you haven’t installed the necessary drivers for your audio interface, it’s crucial to do so before attempting to change the buffer rate. The drivers enable proper communication between your computer and the audio interface, ensuring optimal performance. Check the manufacturer’s website for the latest drivers suitable for your operating system, download them, and follow the installation instructions provided.
Once you have confirmed compatibility and established a stable connection between your computer and audio interface, you can proceed with changing the buffer rate. The next sections will outline the steps for both Windows and Mac operating systems.
Changing Buffer Rate on Windows
If you are using a Windows computer, the process of changing the buffer rate for your audio interface may vary depending on the specific software or driver you are using. However, the general steps outlined below should help you get started:
- Launch the audio interface control panel or the software provided by the manufacturer.
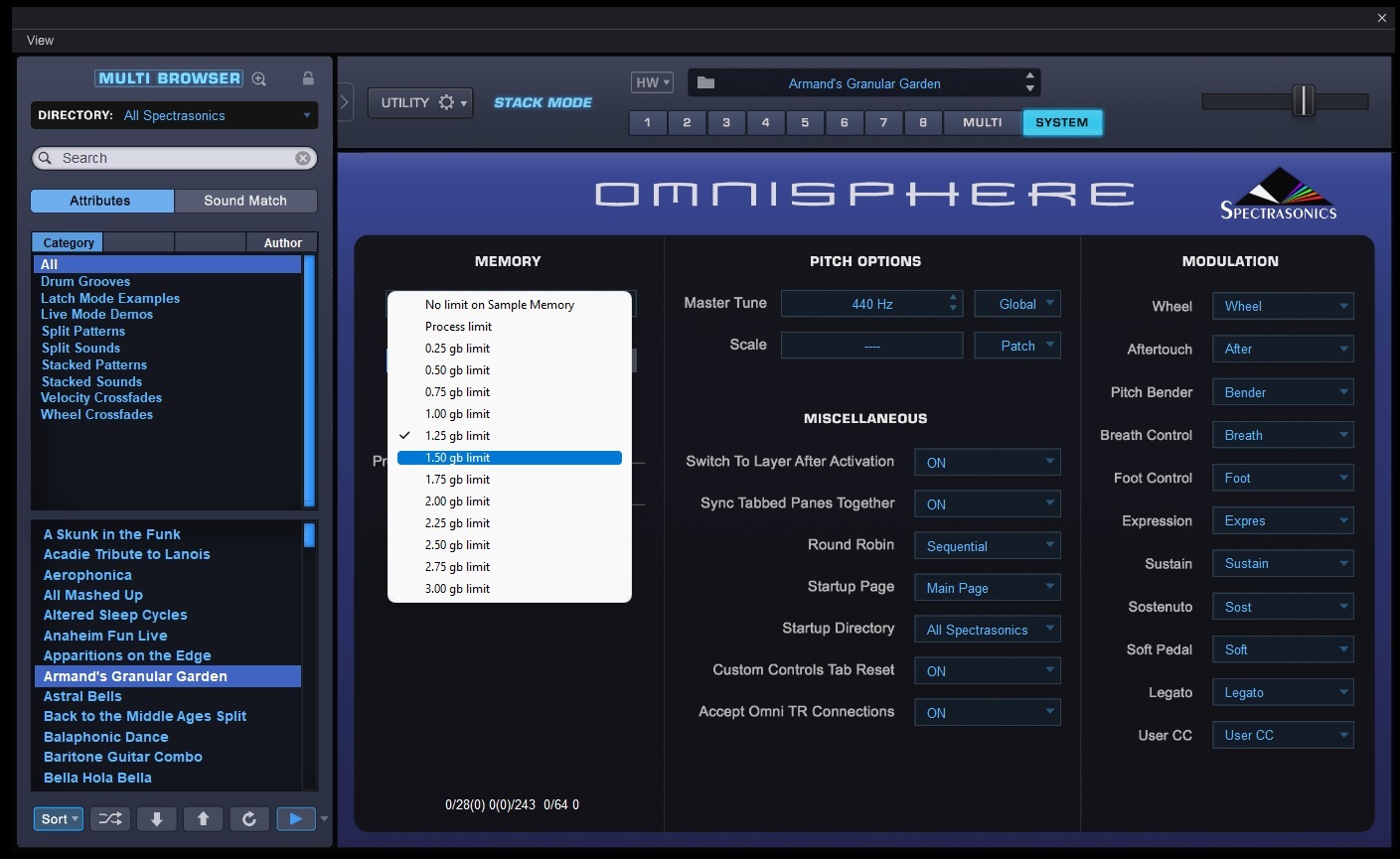
- Navigate to the settings or preferences section and locate the buffer rate or buffer size option.
- Adjust the buffer rate according to your needs. Remember that a smaller buffer size will result in lower latency but may require more CPU power.
- Once you have set the desired buffer rate, click Apply or OK to save the changes.
In some cases, you may need to restart your computer or audio software for the changes to take effect.
Note that the exact steps may differ depending on your audio interface model and the software it uses. It is recommended to consult the user manual or check the manufacturer’s website for specific instructions tailored to your device.
It’s important to experiment with different buffer rates to find the optimal balance between latency and performance for your specific audio recording or playback needs. Keep in mind that setting the buffer rate too low may result in audio glitches or dropouts if your computer cannot handle the processing demands.
Now that we’ve covered changing the buffer rate on Windows, let’s move on to the process on Mac.
Changing Buffer Rate on Mac
If you’re using a Mac computer, the process of changing the buffer rate for your audio interface may vary depending on the software or driver you are using. However, the general steps outlined below should help you get started:
- Launch your audio interface control panel or the software provided by the manufacturer.
- Look for the settings or preferences section and locate the buffer rate or buffer size option.
- Adjust the buffer rate according to your needs. Keep in mind that a smaller buffer size will result in lower latency but may require more processing power.
- Save the changes by clicking Apply or OK, and then close the control panel or software.
Depending on the specific software or driver, you may need to restart your computer or audio software for the changes to take effect.
It’s essential to note that the steps provided above are general guidelines, and the exact process may differ depending on your audio interface model and the software it employs. To get more specific instructions tailored to your device, refer to the user manual or check the manufacturer’s website.
Remember to experiment with different buffer rates to find the optimal balance between latency and performance for your specific recording or playback needs. Setting the buffer rate too low may lead to audio glitches or dropouts if your Mac cannot handle the processing demands.
Now that we’ve covered changing the buffer rate on Mac, let’s move on to optimizing the buffer rate for recording.
Optimizing Buffer Rate for Recording
When it comes to recording audio, finding the right buffer rate can significantly impact the quality and performance of your recordings. Here are some tips to help optimize the buffer rate for recording:
- Balance between latency and performance: Determine the lowest buffer rate that still provides acceptable latency without causing audio glitches or dropouts. Keep in mind that lower buffer rates may require more processing power, so find the balance that works best for your system.
- Consider your recording needs: The buffer rate you choose should align with the type of recording you are doing. For live performances or real-time monitoring, a lower buffer rate with minimal latency is crucial. However, if you’re editing or mixing, a higher buffer rate that prioritizes stability over real-time feedback may be more appropriate.
- Monitor system performance: Keep an eye on your computer’s performance while recording. If you notice audio glitches or dropouts, it may be an indication that your buffer rate is too low and stressing your system. In such cases, gradually increase the buffer size until the issues are resolved.
- Upgrade hardware if needed: If your computer is consistently struggling to handle lower buffer rates and you require real-time recording or monitoring, consider upgrading your computer’s hardware, such as increasing RAM or using a faster processor. This can help improve performance and stability.
- Test and adjust as necessary: It’s essential to experiment with different buffer rates and monitor the results. Make test recordings with varying buffer rates and listen back for any distortion, latency, or audio artifacts. By testing and adjusting as necessary, you can find the optimal buffer rate that suits your recording needs.
Ultimately, optimizing the buffer rate for recording involves finding a balance between latency, performance, and stability. By understanding your specific recording requirements and experimenting with different buffer rates, you can ensure smooth and high-quality recordings.
Now let’s move on to troubleshooting any buffer rate issues that may arise.
Troubleshooting Buffer Rate Issues
While changing the buffer rate can improve your audio recording and playback experience, it’s not uncommon to encounter issues along the way. Here are some common buffer rate issues and troubleshooting steps:
- Audio dropouts or glitches: If you are experiencing audio dropouts or glitches, it may be an indication that your buffer rate is too low for your system to handle. Try increasing the buffer size gradually until the issues subside. Keep in mind that increasing the buffer size will increase the latency.
- Increased latency: If you find that your latency is too high, meaning there’s a noticeable delay between playing or recording audio and hearing it, you may need to decrease the buffer rate. However, be cautious not to set it too low, as it can cause stability issues.
- Insufficient processing power: If you notice that changing the buffer rate significantly impacts your computer’s performance, it may be an indication that your system doesn’t have enough processing power. Consider upgrading your hardware or closing unnecessary applications to free up resources.
- Incompatibility with specific software/drivers: Different audio software or drivers may have compatibility issues when changing the buffer rate. If you encounter any compatibility problems or unexpected behavior, check for software updates or consult the manufacturer’s support resources for guidance.
- Conflicting audio settings: Sometimes, other audio settings or plugins can conflict with the buffer rate settings. Try temporarily disabling any unnecessary audio effects or plugins and see if it resolves the issues. Additionally, ensure that your audio software is configured correctly with the appropriate sample rate settings.
If you continue to experience buffer rate issues after troubleshooting, it may be helpful to seek assistance from the manufacturer’s technical support or online audio recording communities. They can provide specific guidance and troubleshooting tips based on your audio interface and specific setup.
Remember, finding the optimal buffer rate requires a bit of trial and error, as every system and recording setup is unique. With patience and persistence, you can overcome buffer rate issues and achieve the desired performance and stability in your audio recordings.
Now let’s conclude our discussion.
Conclusion
Understanding and optimizing the buffer rate for your audio interface is crucial for achieving high-quality audio recordings and smooth playback. By adjusting the buffer rate to find the right balance between latency and performance, you can enhance your overall recording experience.
In this article, we explored the concept of buffer rate and its impact on audio processing. We discussed the importance of checking for compatibility between your computer and audio interface and provided general steps for changing the buffer rate on both Windows and Mac operating systems.
We also covered tips for optimizing the buffer rate specifically for recording, such as finding the right balance between latency and performance, considering your recording needs, monitoring system performance, and potentially upgrading hardware if needed.
Furthermore, we discussed common buffer rate issues and provided troubleshooting steps to help resolve them, including dealing with audio dropouts or glitches, addressing increased latency, resolving insufficient processing power, handling compatibility issues, and addressing conflicting audio settings.
Ultimately, finding the optimal buffer rate for your audio interface may require some experimentation and adjustment based on your unique recording setup and requirements. It’s important to stay patient, test different buffer rates, and monitor the results to achieve the desired recording and playback performance.
By following the guidelines and recommendations outlined in this article, you will be well-equipped to change and optimize the buffer rate for your audio interface, improving your overall audio production workflow.
Remember to consult the user manual or seek assistance from the manufacturer’s support if you encounter any specific issues or need further guidance tailored to your audio interface model or software.
Now, armed with this knowledge, go ahead and confidently optimize the buffer rate for your audio interface and enjoy smooth, high-quality audio recordings!