Home>Production & Technology>MP3>How To Change Bitrate Of MP3

MP3
How To Change Bitrate Of MP3
Modified: January 22, 2024
Learn how to change the bitrate of your MP3 files with this easy-to-follow tutorial. Optimize your audio quality and file size for a better listening experience.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
MP3, which stands for MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3, is a popular audio file format that compresses audio data to a smaller size without compromising too much on the quality of the sound. One of the key factors that determine the quality and file size of an MP3 file is the bitrate.
Bitrate refers to the amount of data that is processed per unit of time in an audio file. It is measured in kilobits per second (kbps) and determines the level of audio quality and file size. In simple terms, higher bitrates result in better audio quality but larger file sizes, while lower bitrates may compromise the quality but yield smaller file sizes.
In certain cases, you may need to change the bitrate of an MP3 file. Perhaps you want to reduce the file size to save storage space or optimize the file for streaming or online platforms. Conversely, you may want to increase the bitrate to improve the audio quality for a specific purpose like audio mastering or archiving.
In this article, we will explore different methods to change the bitrate of an MP3 file, ranging from using MP3 converters to media player software and command line tools. We will also highlight some considerations when choosing the right bitrate for your needs. So, read on to discover the various options available to modify the bitrate of your MP3 files and make the most out of your audio experience.
Understanding Bitrate
Before delving into the methods of changing the bitrate of an MP3 file, it’s essential to have a solid understanding of what bitrate actually means and how it affects the quality and size of audio files.
Bitrate refers to the amount of data or information transmitted per unit of time in an audio file. It is typically measured in kilobits per second (kbps). The higher the bitrate, the more data is processed per second, resulting in better audio quality but larger file sizes. Conversely, lower bitrates reduce the amount of data processed, resulting in smaller file sizes but potentially compromising the audio quality.
When an audio file is encoded with a higher bitrate, more details and nuances of the sound can be preserved, resulting in a clearer and more accurate representation of the original recording. However, higher bitrates also require more disk space to store the file.
On the other hand, lower bitrates sacrifice some of the audio details and quality to reduce the file size. This can lead to a loss of clarity, noticeable artifacts, and a decrease in the overall fidelity of the sound. Lower bitrates are often used for streaming or online platforms to ensure faster loading times and reduced bandwidth usage.
It is important to note that the bitrate of an MP3 file interacts with other factors such as the source material and the compression algorithm used. While a higher bitrate generally provides better quality, it does not guarantee perfect audio reproduction. The quality also depends on the original recording, the encoding process, and the playback equipment.
In summary, bitrate is a crucial factor in determining the audio quality and file size of an MP3 file. Higher bitrates result in better quality but larger file sizes, while lower bitrates yield smaller file sizes but potentially compromised audio quality. Finding the right balance between audio quality and file size is essential when changing the bitrate of an MP3 file.
Why Change MP3 Bitrate?
There are several reasons why you might want to change the bitrate of an MP3 file. Understanding these reasons will help you determine when and why it is necessary to modify the bitrate of your audio files.
One of the common reasons to change the bitrate of an MP3 file is to reduce its file size. Smaller file sizes are advantageous when you have limited storage space or when you want to optimize the file for online streaming or sharing platforms. By reducing the bitrate, you can compress the audio data and create a smaller file size without a significant loss in audio quality. This can be especially useful when you have a large collection of music and need to save space on your computer, smartphone, or portable music player.
On the other hand, you might want to increase the bitrate to improve the audio quality of an MP3 file. In certain cases, low bitrate MP3 files may sound flat, lack dynamics, and lose some of the finer details in the music. By increasing the bitrate, you can enhance the audio fidelity and capture more nuances in the sound, making it ideal for tasks like audio mastering or when you want to preserve the highest quality possible for archiving purposes.
Additionally, changing the bitrate can also be beneficial when preparing audio files for specific purposes. For example, if you are creating background music for a video project or an advertisement, you may need to adjust the bitrate to match the requirements of the video editing software or platform. By aligning the bitrate of the audio file with the video settings, you can ensure a seamless and synchronized audio-visual experience.
Furthermore, adjusting the bitrate can also impact the streaming experience for online platforms. Lower bitrates are often preferred for streaming because they require less bandwidth, ensuring a smooth and uninterrupted playback experience even for users with slower internet connections. By reducing the bitrate, you can optimize your MP3 files for streaming platforms and improve the accessibility of your audio content.
In a nutshell, changing the bitrate of an MP3 file allows you to strike a balance between file size and audio quality, cater to specific requirements, and optimize your audio files for various purposes. Whether you need to reduce file sizes, enhance audio quality, sync with video projects, or optimize for streaming platforms, modifying the bitrate gives you the flexibility to adapt your MP3 files to your specific needs.
Method 1: Using an MP3 Converter
One of the easiest and most accessible ways to change the bitrate of an MP3 file is by using an MP3 converter. There are various online tools and software available that allow you to convert and customize the bitrate of your audio files effortlessly.
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to change the bitrate using an MP3 converter:
1. Search for a reliable MP3 converter: Look for a reputable online MP3 converter or download and install a trusted software on your computer. Ensure that the converter supports bitrate customization and offers the desired output format.
2. Upload or select the MP3 file: In the MP3 converter interface, either upload the MP3 file you want to modify by browsing through your local storage or choose the file from a directory.
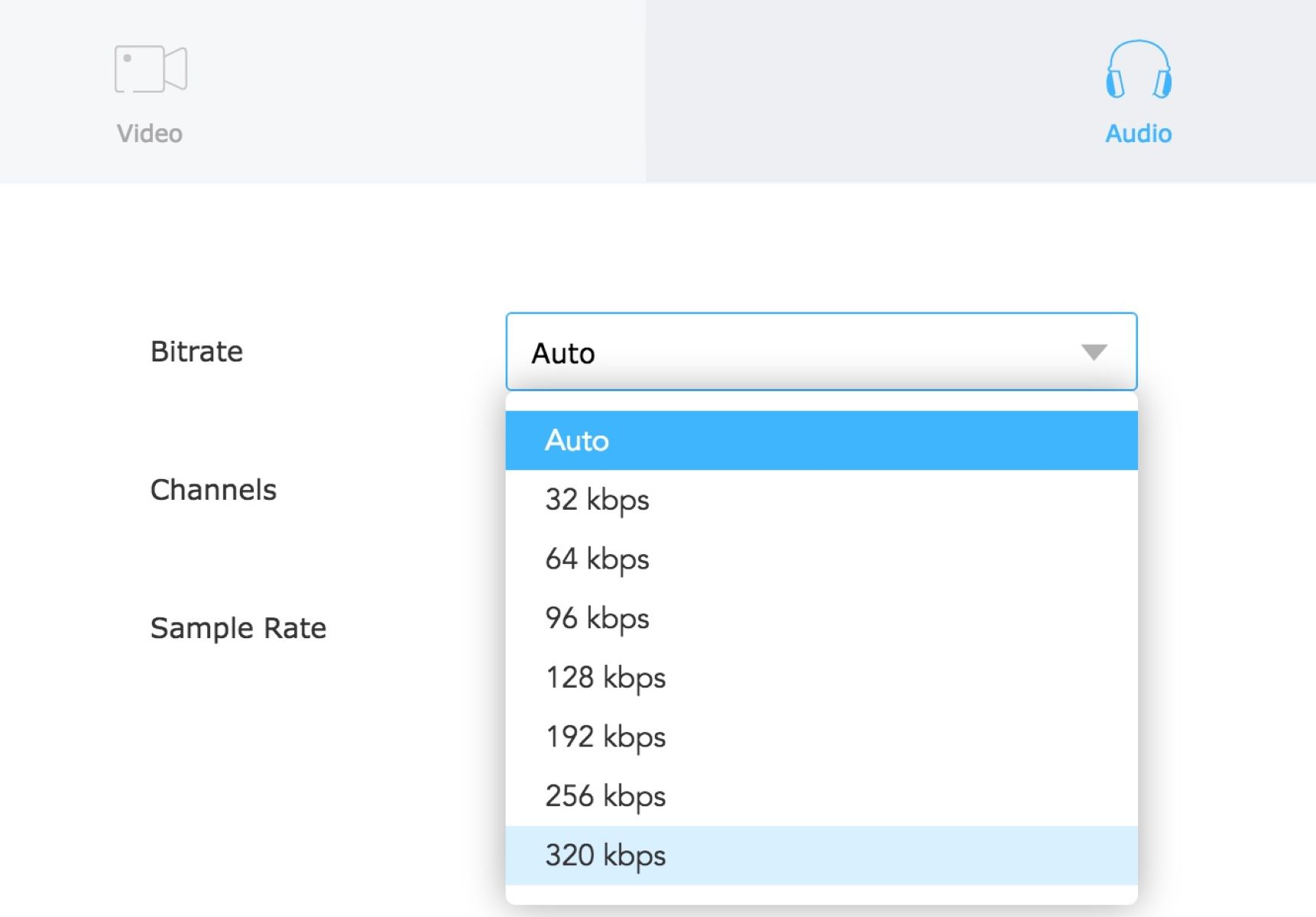
3. Choose the desired bitrate: Once the file is uploaded, you will have the option to select the output bitrate. Typically, you can choose from a range of available options, such as 128kbps, 192kbps, or 320kbps. Select the desired bitrate that suits your requirements.
4. Convert the file: After selecting the bitrate, initiate the conversion process. Depending on the size of the file and your internet connection, the conversion may take a few moments. The converter tool will process the file and create a new MP3 file with the adjusted bitrate.
5. Download the converted file: Once the conversion is complete, you will be provided with a download link or prompt to save the modified MP3 file to your computer. Click on the download option and save the file in your desired location.
It is important to note that when using an MP3 converter, the output quality can be influenced by the compression algorithm used in the conversion process. Some converters offer better audio quality retention than others, so it’s advisable to choose a converter with a good reputation and positive user reviews.
Using an MP3 converter provides a simple and efficient method to change the bitrate of your audio files. It allows you to customize the bitrate to meet your specific needs and preferences, whether you want to reduce the file size or enhance the audio quality. Experiment with different bitrates to find the ideal balance between file size and audio fidelity for your MP3 files.
Method 2: Using a Media Player Software
Another convenient way to change the bitrate of an MP3 file is by using a media player software that offers encoding or transcoding capabilities. Many popular media players provide the option to convert and customize the bitrate of audio files, allowing you to modify your MP3 files without the need for additional software.
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to change the bitrate using a media player software:
1. Install a media player with encoding capabilities: Choose a media player software that supports encoding or transcoding functionality. Some popular options include VLC Media Player, iTunes, and Foobar2000. Download and install the media player on your computer.
2. Open the media player and import the MP3 file: Launch the media player software and import the MP3 file you want to modify. Most media players allow you to import files by dragging and dropping them into the player interface or using the “Open File” or “Import” option from the menu.
3. Access the conversion or transcoding settings: Once the MP3 file is imported, look for the settings or preferences section of the media player that allows you to adjust the encoding or transcoding options. The location and terminology may vary depending on the media player software.
4. Choose the desired bitrate: In the settings or preferences section, locate the bitrate or quality settings for the audio output. Select the desired bitrate, ensuring it meets your requirements in terms of file size and audio quality. Some media players offer a range of bitrate options, while others allow you to manually enter the desired bitrate.
5. Start the conversion process: After selecting the bitrate, initiate the conversion process by either clicking on a “Convert” or “Start” button or following the prompts provided by the media player. The software will convert the MP3 file to the specified bitrate in the output format.
6. Save the converted file: Once the conversion is complete, the media player will typically ask you to choose a location to save the converted MP3 file. Select your desired location and save the file.
Using a media player software to change the bitrate of your MP3 files provides a seamless and integrated method. It eliminates the need for external converters and allows you to modify the bitrate while taking advantage of the media player’s features and user interface.
Remember to consider the capabilities and options provided by the media player software you choose. Some players offer more advanced settings, giving you greater control over the encoding process and allowing for higher quality output. Experiment with different media players and settings to find the most suitable option for your needs.
By utilizing a media player software with encoding capabilities, you can easily change the bitrate of your MP3 files and customize them according to your specific requirements.
Method 3: Using a Command Line Tool
For tech-savvy individuals or those comfortable with command line interfaces, using a command line tool is an efficient way to change the bitrate of MP3 files. Command line tools offer more control and flexibility over the encoding process, allowing you to customize the settings according to your specific needs.
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to change the bitrate using a command line tool:
1. Install the command line tool: Choose a reliable command line tool for encoding MP3 files. Popular options include FFmpeg and LAME. Download and install the tool on your computer, ensuring that it supports bitrate customization.
2. Open the command line interface: Open the command prompt or terminal on your computer. This may vary depending on your operating system. For Windows, press Win + R, type “cmd” and hit Enter. For Mac, go to Applications -> Utilities -> Terminal.
3. Navigate to the directory with the MP3 file: Use the “cd” command to navigate to the directory that contains the MP3 file you want to modify. For example, if the file is located in the “Music” folder on your desktop, you would use the command “cd Desktop/Music”.
4. Execute the command to change the bitrate: In the command line interface, enter the appropriate command to change the bitrate of the MP3 file. This will depend on the command line tool you are using. For example, using FFmpeg, the command might look like this: “ffmpeg -i input.mp3 -b:a 192k output.mp3”. This command specifies the input file (“input.mp3”), the desired bitrate (“192k”), and the output file (“output.mp3”). Adjust the bitrate value as needed.
5. Run the command and wait for the conversion to complete: After entering the command, press Enter to execute it. The command line tool will process the MP3 file, converting it to the specified bitrate. The time required for the conversion will depend on the size of the file and the speed of your computer.
6. Locate the converted file: Once the conversion is complete, navigate to the directory specified in the command line to find the converted MP3 file. You can then move or rename the file as needed.
Using a command line tool provides a powerful and customizable method to change the bitrate of your MP3 files. It allows for more precise control over the encoding process and offers advanced options for manipulating audio files.
Keep in mind that command line tools may have a steeper learning curve compared to other methods, and familiarity with command line interfaces is required. However, once you become acquainted with the tools and commands, you’ll have greater flexibility and control over the bitrate customization process.
Experiment with different command line tools and options to find the most suitable and efficient solution for your specific needs. By utilizing a command line tool, you can modify the bitrate of your MP3 files with precision and tailor them to your desired audio quality and file size.
Comparison of Different Bitrates
When changing the bitrate of an MP3 file, it’s important to understand the impact it has on the audio quality and file size. Different bitrates offer varying levels of audio fidelity and compression, which can affect the listening experience and the storage requirements.
Here is a comparison of different bitrates and their corresponding qualities:
1. Low Bitrate (64kbps-96kbps): MP3 files encoded at low bitrates are commonly used for streaming and online platforms. While they provide smaller file sizes, they tend to sacrifice audio quality. Low bitrate MP3 files may sound compressed, with reduced dynamic range and noticeable loss of detail. However, they are suitable for casual listening or situations where conserving bandwidth and storage space is crucial.
2. Medium Bitrate (128kbps-192kbps): This range offers a better compromise between file size and audio quality. Most online music stores and streaming services provide music in the medium bitrate range. At these bitrates, the sound quality is generally acceptable for average listening purposes. The audio is relatively clear and retains a good amount of detail, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
3. High Bitrate (256kbps-320kbps): High bitrate MP3 files offer excellent audio quality and are ideal for those who prioritize fidelity. At these bitrates, the audio retains more of the original recording’s nuances, resulting in a more immersive listening experience. High bitrate files are often used by audiophiles, DJs, and audio professionals to ensure the highest level of audio fidelity, but they occupy larger file sizes.
It’s worth noting that the perceived differences between different bitrates also depend on the quality of the source audio. A low bitrate file converted to a higher bitrate will not magically enhance the audio quality; it can only retain the quality present in the original source.
When choosing a bitrate, it’s important to consider the purpose of the file. For example, if you plan to stream music, a medium bitrate may be sufficient to balance audio quality and bandwidth requirements. However, for critical listening or professional applications, a higher bitrate is recommended to ensure the best possible sound reproduction.
Ultimately, the choice of bitrate depends on personal preference and the specific requirements of your use case. It’s advisable to experiment with different bitrates and compare the resulting audio quality and file sizes to find the optimal balance that meets your needs.
Tips for Choosing the Right Bitrate
Choosing the right bitrate for your MP3 files is crucial to strike the perfect balance between audio quality and file size. Consider the following tips to help you make an informed decision when selecting the bitrate:
1. Purpose of the audio: Determine the intended use of the audio file. If it’s for casual listening or background music, a lower bitrate may suffice. However, if it’s for critical listening or professional purposes, a higher bitrate will ensure better audio fidelity.
2. Storage limitations: Evaluate the available storage space on your device. If storage is limited, opting for a lower bitrate can help conserve space. Keep in mind that reducing the bitrate too much may compromise the audio quality.
3. Bandwidth considerations: If the audio files will be streamed or uploaded to online platforms, consider the bandwidth requirements. Lower bitrates are suitable for streaming as they minimize buffering time and reduce bandwidth usage.
4. Audience preferences: Understand the preferences of your target audience. If your audience values high-quality audio, consider offering higher bitrate options. However, if they prioritize convenience and faster downloads, lower bitrates may be more suitable.
5. Source quality: Consider the quality of the original audio source. If the source material is already of lower quality or highly compressed, converting it to a higher bitrate may not result in significant improvements. In such cases, a medium bitrate may be adequate.
6. Auditory sensitivity: Take into account your personal sensitivity to audio quality. Some individuals may be more discerning and able to notice subtle differences in audio quality, while others may not. Adjust the bitrate based on your own ability to perceive audio nuances.
7. Test and compare: Experiment with different bitrates and listen to the resulting audio files. Compare the quality and file sizes to identify the optimal bitrate for your specific needs. Trust your ears and choose the bitrate that provides the best balance between quality and file size.
Remember, there is no one-size-fits-all approach to selecting the bitrate. The right bitrate will depend on your specific requirements, preferences, and constraints. By considering these tips and conducting thorough testing, you can choose the most appropriate bitrate for your MP3 files and achieve the desired audio quality and file size.
Conclusion
Changing the bitrate of an MP3 file allows you to customize the audio quality and file size to better suit your needs. Whether you want to reduce file sizes for storage optimization or enhance audio quality for critical listening, there are several methods available to modify the bitrate.
Using an MP3 converter, media player software, or command line tools provides convenient ways to adjust the bitrate. Each method offers its own advantages, so choose the one that aligns with your comfort level and requirements.
When selecting the bitrate, consider factors such as the purpose of the audio, storage limitations, bandwidth considerations, audience preferences, source quality, auditory sensitivity, and testing results. By taking these factors into account, you can find the right balance between audio quality and file size.
Remember, the bitrate is just one aspect of audio quality, and the overall quality also depends on other factors like the original recording, encoding process, and playback equipment. It’s essential to strike a balance between file size and audio fidelity while considering the specific needs of your use case.
So, whether you’re compressing audio files for limited storage or aiming for the best possible sound reproduction, changing the bitrate of your MP3 files empowers you to tailor your audio experience to your preferences.
Take advantage of the various methods available, explore different bitrates, and find the perfect balance that meets your requirements. With the ability to customize the bitrate, you can optimize your MP3 files for a range of purposes, from leisurely listening to professional projects, and enjoy a personalized audio experience.