Home>Production & Technology>Audio Interface>Handheld Digital Recorder Vs Audio Interface: Which One Works Easiest To Your Computer


Audio Interface
Handheld Digital Recorder Vs Audio Interface: Which One Works Easiest To Your Computer
Modified: January 22, 2024
Looking for the easiest way to connect your computer to an audio device? Compare handheld digital recorders and audio interfaces to find the perfect solution.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to recording audio on your computer, having the right equipment is essential. Two popular options for capturing professional-grade audio are handheld digital recorders and audio interfaces. Both of these devices offer unique features and advantages, but it’s important to understand their differences to determine which one works easiest with your computer.
A handheld digital recorder is a portable device that allows you to record audio directly onto the device itself. It is equipped with built-in microphones and sometimes external inputs for connecting external microphones or instruments. These recorders are commonly used in field recording, interviews, and live music performances. They are designed to provide high-quality audio recordings without the need for a computer connection.
On the other hand, an audio interface is a device that connects your computer to professional audio equipment such as microphones, instruments, and speakers. It acts as a bridge between your computer and the external audio devices, providing high-quality recording and playback capabilities. Audio interfaces are commonly used in home studios, podcasting setups, and music production environments.
In this article, we will compare handheld digital recorders and audio interfaces, specifically focusing on their ease of use with your computer. We will explore the advantages and disadvantages of each option and discuss important factors to consider when choosing between the two. Whether you are a musician, podcaster, or content creator, understanding the differences between these devices will help you make an informed decision to meet your recording needs.
What is a Handheld Digital Recorder?
A handheld digital recorder is a portable recording device that allows you to capture audio in various environments. These devices are equipped with built-in microphones and sometimes offer inputs for connecting external microphones or instruments. Handheld digital recorders are designed to provide high-quality audio recordings without the need for a computer connection.
Handheld digital recorders are commonly used by journalists, field recordists, musicians, and content creators who require a compact and versatile audio recording solution. They are particularly useful when recording interviews, live music performances, lectures, and other audio content on the go.
One of the key advantages of a handheld digital recorder is its portability. These devices are lightweight and easy to carry, making them ideal for capturing audio in different locations. They often come with internal memory or an SD card slot for storage, allowing you to record for extended periods without the need for a computer or external storage device.
Handheld digital recorders also offer a range of features such as adjustable recording levels, built-in metronomes, and easy-to-use controls. Some models even come with advanced features like multi-track recording, time-stamping, and on-board effects for post-processing.
Additionally, many handheld digital recorders have built-in stereo or surround sound microphones. These microphones are specifically designed to capture sound from different directions, providing a more immersive audio experience. They allow you to capture a wide soundstage and create recordings with depth and spatiality.
Some handheld digital recorders also offer the ability to connect external microphones or instruments. These devices feature XLR or 1/4″ inputs, allowing you to connect professional-grade microphones or instruments directly to the recorder. This is particularly useful for musicians and podcasters who want to achieve studio-quality recordings on the go.
In summary, a handheld digital recorder is a portable and versatile device that allows you to capture high-quality audio without the need for a computer. Its portability, range of features, and ability to connect external microphones make it a popular choice for various recording applications.
What is an Audio Interface?
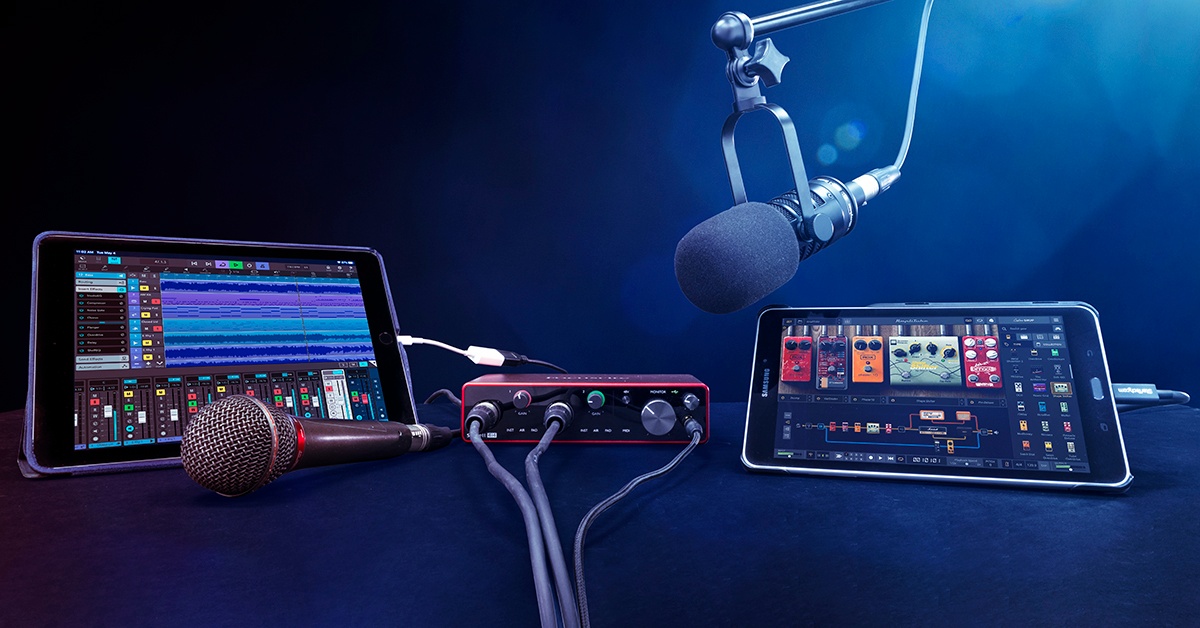
An audio interface is a device that connects your computer to professional audio equipment, such as microphones, instruments, and speakers. It serves as a bridge between your computer and the external audio devices, providing high-quality recording and playback capabilities.
Audio interfaces are essential tools for musicians, podcasters, and content creators who require a dedicated setup for recording and producing audio. These devices offer superior audio quality and greater flexibility compared to built-in computer audio inputs and outputs.
One of the primary functions of an audio interface is to convert analog audio signals into digital signals that can be processed by your computer. This conversion is done using high-quality analog-to-digital converters (ADC) and digital-to-analog converters (DAC) present in the interface. These converters ensure accurate and faithful reproduction of your audio recordings.
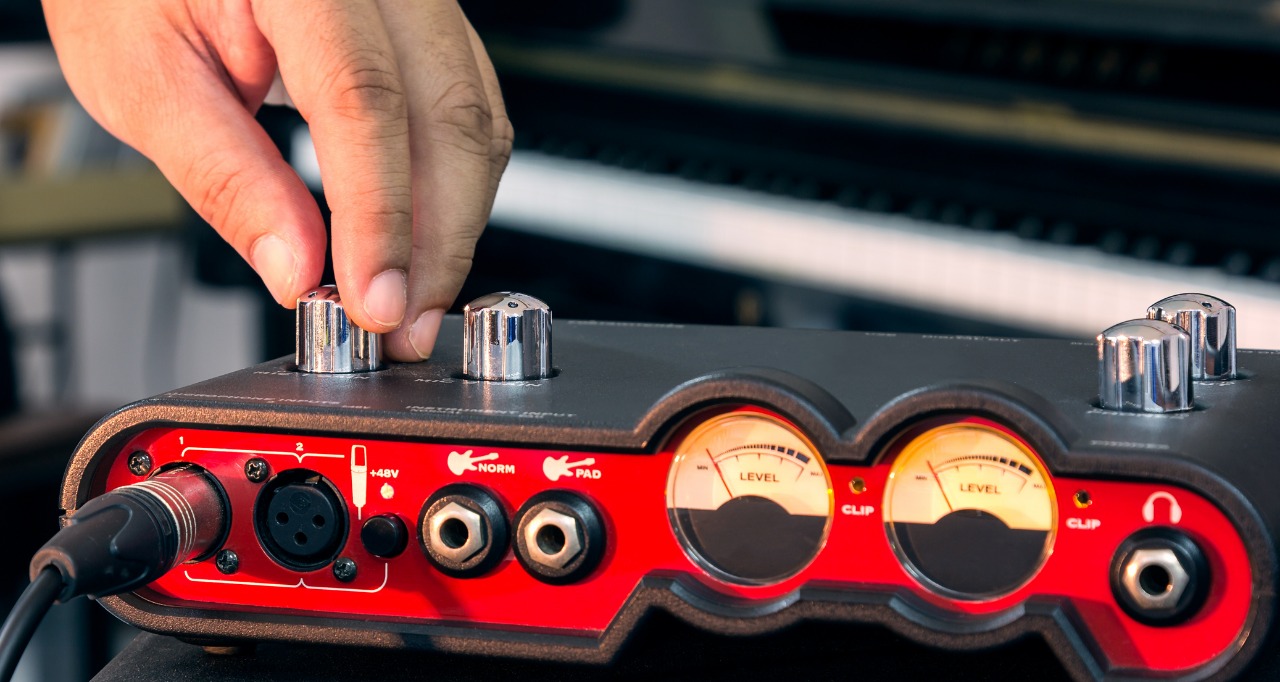
Audio interfaces come in various configurations, offering different input and output options. Commonly, they feature XLR or 1/4″ inputs for connecting microphones or instruments, and line-level inputs for connecting other audio sources. They also provide multiple output options, including headphone outputs for monitoring and line-level outputs for connecting speakers or other audio devices.
In addition to the input and output options, audio interfaces often include built-in preamps. Preamps are essential for amplifying the low-level signals from microphones or instruments, providing proper gain staging and signal optimization. Having high-quality preamps in your audio interface ensures that your recordings have optimal clarity and dynamic range.
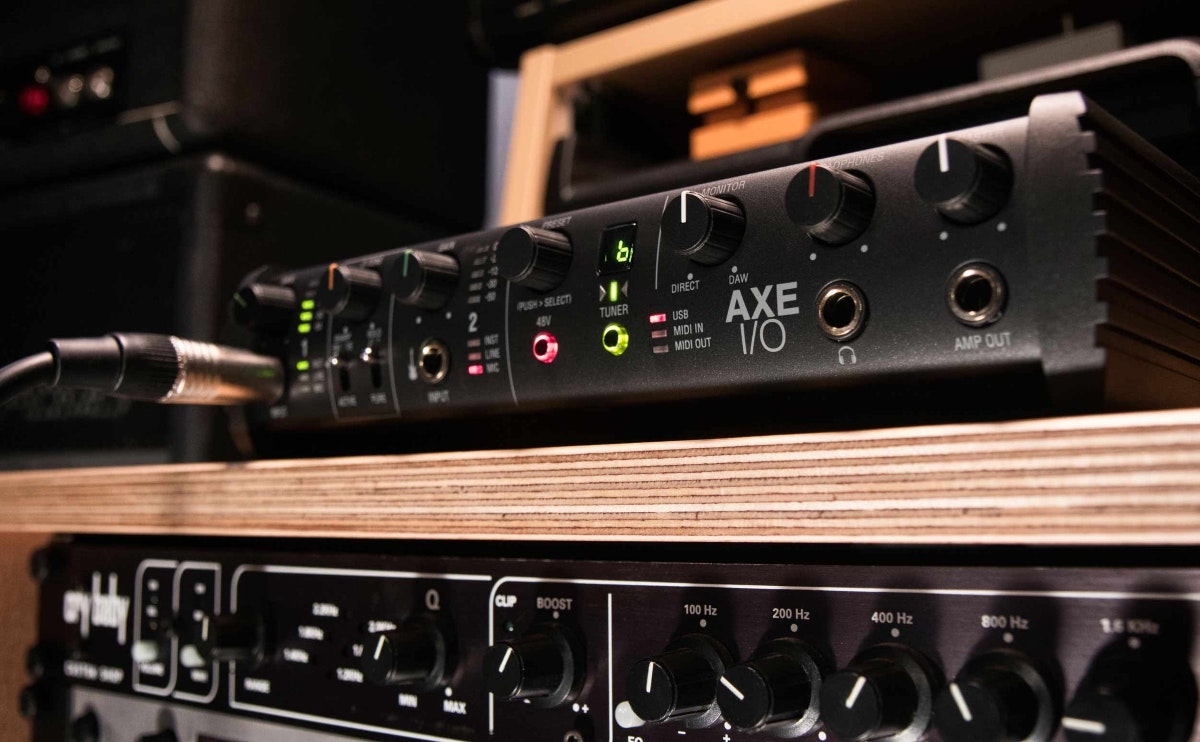
Audio interfaces are typically connected to your computer via USB, Thunderbolt, or PCIe connections. USB is the most common and versatile option, allowing for easy plug-and-play connectivity with both Mac and PC systems. Thunderbolt and PCIe connections offer faster data transfer speeds, making them ideal for professional-level audio production and low-latency performance.
Another advantage of using an audio interface is the ability to use professional audio software for recording, editing, and mixing. These interfaces are compatible with digital audio workstations (DAWs) such as Pro Tools, Ableton Live, Logic Pro, and many others. They offer additional control features, such as gain control knobs, headphone monitoring, and direct monitoring, which allow for precise adjustment and real-time monitoring of your audio recordings.
In summary, an audio interface is a vital component of a professional audio setup, connecting your computer to external audio equipment and providing high-quality recording and playback capabilities. Its analog-to-digital conversion, input/output options, preamps, and compatibility with DAWs make it an essential tool for achieving professional-grade audio recordings and productions.
Comparison of Handheld Digital Recorder and Audio Interface
Handheld digital recorders and audio interfaces are both valuable tools for recording audio, but they serve different purposes and offer distinct advantages. Let’s compare these devices to help you determine which one works easiest with your computer.
Portability: Handheld digital recorders are designed for on-the-go recording. They are compact, lightweight, and often include built-in microphones. This portability allows you to capture audio in various environments without the need for a computer. Audio interfaces, on the other hand, are usually used in home studios or fixed setups. They require a computer connection and are not as portable as handheld recorders.
Input Options: Handheld digital recorders typically have built-in microphones and sometimes offer external microphone or instrument inputs. This versatility allows you to capture audio in different ways. Audio interfaces, on the other hand, provide a wide range of input options, including XLR and 1/4″ inputs for connecting microphones and instruments. They also offer line-level inputs for connecting other audio sources.
Audio Quality: Both handheld digital recorders and audio interfaces can produce high-quality audio recordings. Handheld recorders often have built-in stereo or surround sound microphones designed for capturing immersive audio. However, audio interfaces usually offer better sound quality due to their dedicated preamps, analog-to-digital converters, and compatibility with professional-grade microphones and instruments.
Computer Integration: Handheld digital recorders do not require a computer connection for recording. They usually have internal memory or an SD card slot for storage. Some recorders may offer USB connectivity for transferring files to a computer. In contrast, audio interfaces are designed to work with computers and require a connection via USB, Thunderbolt, or PCIe. They allow for real-time monitoring, recording, and playback within digital audio workstation (DAW) software.
Software Compatibility: Handheld digital recorders often come with their own software for basic editing and transferring files. Audio interfaces, on the other hand, are compatible with professional-level DAW software such as Pro Tools, Ableton Live, and Logic Pro. This compatibility provides more advanced recording, editing, and mixing capabilities.
Flexibility and Expandability: Handheld digital recorders are versatile and can be used in a wide range of recording scenarios. They are self-contained units that can capture audio anytime, anywhere. However, their functionality is limited to what the device offers. Audio interfaces offer greater flexibility and expandability, as they can be connected to a variety of external audio devices such as microphones, instruments, and studio monitors.
Overall, the choice between a handheld digital recorder and an audio interface depends on your specific recording needs and workflow. If you require portability and the ability to record anywhere without a computer, a handheld digital recorder may be the ideal choice. However, if you are primarily recording in a home studio or prefer the flexibility and advanced capabilities of professional audio software, an audio interface would be the better option.
Ease of Use with Your Computer
When it comes to ease of use with your computer, there are some key differences between handheld digital recorders and audio interfaces. Let’s explore how these devices integrate with your computer and which one offers a more user-friendly experience.
Handheld Digital Recorder: One of the major advantages of handheld digital recorders is their simplicity and autonomy. These devices can be operated independently, without the need for a computer connection. They typically have built-in memory or an SD card slot for storing your recordings. This makes them incredibly easy to use, especially for on-the-go recording or when you don’t want to deal with the complexities of computer-based recording setups.
Transferring files from a handheld digital recorder to your computer is usually straightforward. Many recorders can be connected via USB, allowing you to easily transfer the recorded files to your computer for further editing or storage. Some models may also come with software that simplifies the file transfer process.
Audio Interface: Audio interfaces, on the other hand, rely on a computer connection to function. They are designed to seamlessly integrate with your computer’s operating system and digital audio workstation (DAW) software. While this adds an extra step in terms of setup and configuration, it offers a wide range of features and flexibility for recording, editing, and mixing audio.
Setting up an audio interface involves connecting it to your computer via USB, Thunderbolt, or PCIe, depending on the interface’s connectivity options and your computer’s ports. Once connected, you may need to install drivers or software provided by the interface manufacturer. These drivers ensure that your computer recognizes and communicates with the audio interface effectively.
Audio interfaces typically come with control panels or software that allow you to adjust settings, monitor input and output levels, and select input sources. Within your DAW software, you can record, edit, and mix audio tracks with precision and control. While using an audio interface may require a bit more technical knowledge and setup than a handheld digital recorder, it offers a more professional and feature-rich recording experience.
In terms of ease of use, handheld digital recorders are generally more user-friendly, especially for those who prefer a simple and quick recording setup without the need for computer integration. On the other hand, audio interfaces provide a more comprehensive and customizable recording experience, allowing for greater control and flexibility.
Ultimately, the choice between a handheld digital recorder and an audio interface in terms of ease of use depends on your recording needs, technical proficiency, and preference for standalone recording or computer-based workflows.
Factors to Consider When Choosing between a Handheld Digital Recorder and Audio Interface
When deciding between a handheld digital recorder and an audio interface, there are several important factors to consider. Understanding these factors will help you make an informed decision based on your specific recording needs and preferences.
Portability: If portability is a priority for you and you need a device that can be used in various locations without the need for a computer, a handheld digital recorder might be the better choice. These portable devices allow you to record audio on the go, making them ideal for field recording, interviews, and live performances.
Audio Quality: Consider the level of audio quality you require for your recordings. While both handheld digital recorders and audio interfaces can produce high-quality audio, audio interfaces generally offer better sound quality due to the use of dedicated preamps and higher quality analog-to-digital converters. If achieving professional-grade audio is essential for your projects, an audio interface may be the preferred option.
Recording Flexibility: Evaluate your recording needs and the flexibility required for your projects. Handheld digital recorders are generally more versatile in terms of capturing different types of audio, thanks to their built-in microphones and sometimes external inputs. On the other hand, audio interfaces offer more flexibility in terms of connecting external microphones, instruments, and studio monitors, allowing for a more customizable recording setup.
Computer Integration: Consider how important it is for your recording setup to integrate with your computer. If you prefer a standalone device that can be used independently without a computer connection, a handheld digital recorder is the way to go. However, if you require advanced recording, editing, and mixing capabilities with the use of professional audio software, an audio interface will be necessary.
Budget: Assess your budget for purchasing equipment. Handheld digital recorders generally come at a lower price point compared to audio interfaces. If you are on a tight budget or if you prioritize affordability, a handheld digital recorder may be a more cost-effective choice.
Future Expansion: Consider your long-term recording goals. If you anticipate expanding your recording setup and desire the ability to connect external microphones, instruments, and studio monitors, an audio interface provides more room for future growth and advancements in your recording projects.
By carefully considering these factors and how they align with your specific recording needs and preferences, you can make an informed decision about whether a handheld digital recorder or an audio interface is the right choice for you.
Conclusion
Choosing between a handheld digital recorder and an audio interface ultimately depends on your specific recording needs and workflow. Both devices offer distinct advantages that cater to different scenarios.
If portability and simplicity are your top priorities, a handheld digital recorder is a great choice. These devices are compact, lightweight, and designed for on-the-go recording. They offer built-in microphones, external inputs for connecting additional audio sources, and often have memory storage for recording without the need for a computer. Handheld digital recorders are ideal for field recording, interviews, and live performances where mobility is crucial.
On the other hand, if you prioritize audio quality, recording flexibility, and advanced recording capabilities, an audio interface is the more suitable option. Audio interfaces provide superior sound quality due to dedicated preamps and high-quality converters. They offer a wide range of input and output options, allowing for connections with professional microphones, instruments, and studio monitors. With seamless integration into your computer’s operating system and compatibility with digital audio workstation software, audio interfaces provide a comprehensive recording, editing, and mixing experience.
Consider other factors such as budget, future expansion plans, and the level of computer integration you desire when making your decision. Handheld digital recorders tend to be more affordable and require minimal technical setup, while audio interfaces offer room for growth and the ability to connect external hardware.
In conclusion, both handheld digital recorders and audio interfaces serve different recording purposes and offer unique advantages. Assess your specific needs, prioritize what matters most to you in terms of portability, audio quality, flexibility, and integration, and make an informed decision that aligns with your recording goals. Choosing the right tool will ensure that you achieve the best results and a seamless recording experience.