Home>Production & Technology>MIDI>How To Connect MIDI To Audio Interface
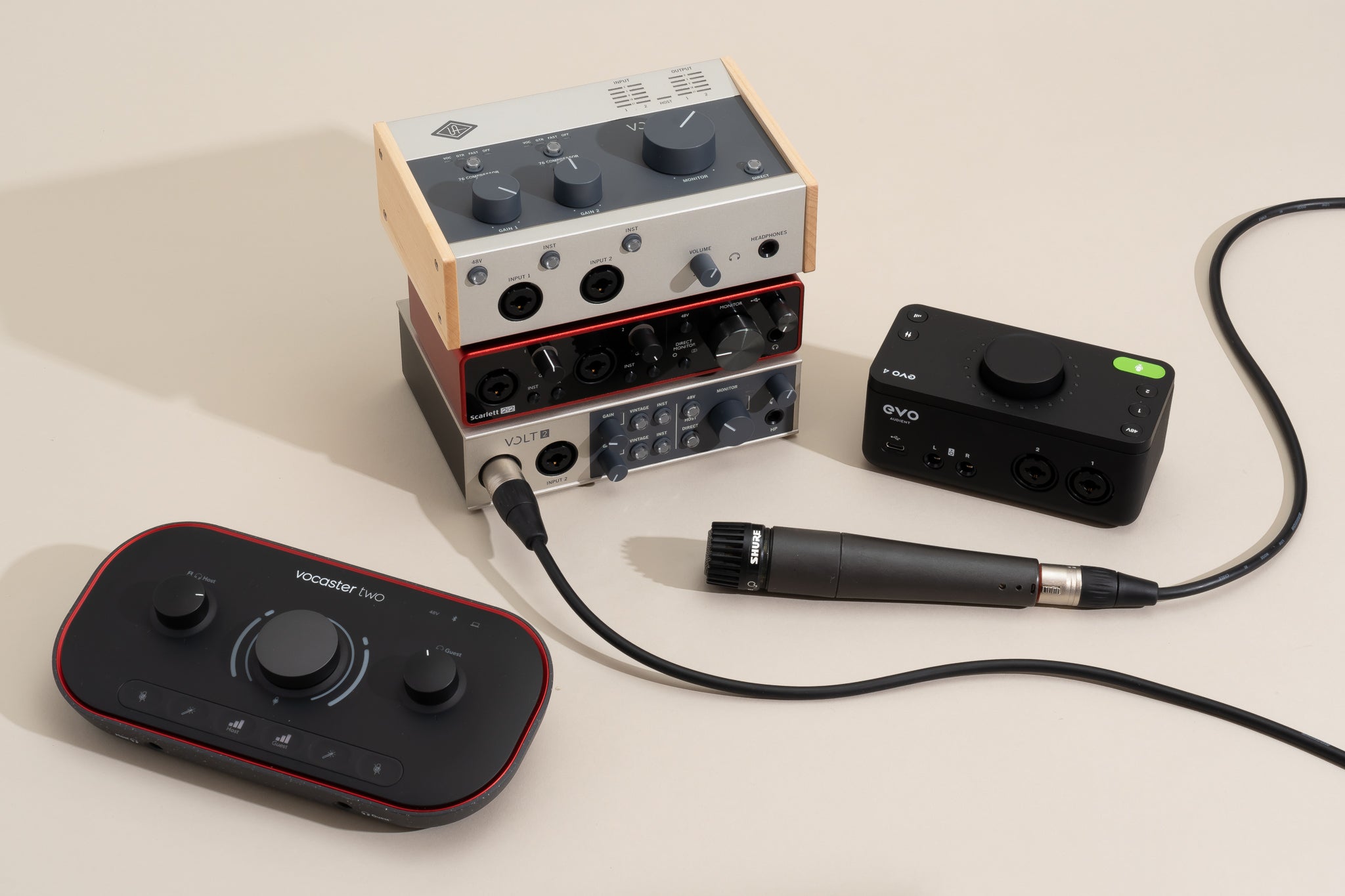


MIDI
How To Connect MIDI To Audio Interface
Modified: February 22, 2024
Learn how to connect MIDI to your audio interface easily and efficiently. Get step-by-step instructions and tips for seamless MIDI integration.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Imagine being able to effortlessly connect your musical instruments and devices to your computer, seamlessly integrating them into your digital music production workflow. This is where MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) and audio interfaces come into play. Whether you're a seasoned music producer or an aspiring musician, understanding how to connect MIDI to an audio interface can significantly enhance your creative capabilities.
MIDI has been a cornerstone of electronic music production for decades, serving as the universal language that allows electronic musical instruments, computers, and other hardware to communicate. It enables you to control various parameters such as pitch, velocity, and modulation, opening up a world of possibilities for creating and manipulating sounds.
On the other hand, an audio interface acts as the bridge between your musical instruments and your computer, facilitating the conversion of analog audio signals into digital data that can be processed and recorded. It provides high-quality audio inputs and outputs, essential for capturing the nuances of your performances and ensuring pristine sound reproduction.
The marriage of MIDI and audio interfaces empowers you to harness the full potential of your musical instruments in the digital realm. Whether you're recording a live performance, programming intricate sequences, or controlling virtual instruments, this combination offers unparalleled flexibility and control over your music production process.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of connecting MIDI to an audio interface, exploring the fundamental concepts, step-by-step procedures, and troubleshooting tips to ensure a seamless integration. By the end of this journey, you will be equipped with the knowledge and confidence to harness the power of MIDI and audio interfaces, elevating your music production endeavors to new heights.
Understanding MIDI and Audio Interface
MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) serves as a fundamental communication protocol in the realm of music production and performance. It revolutionized the way electronic musical instruments, computers, and other hardware interact, allowing seamless control and synchronization. Unlike audio signals, MIDI does not transmit sound; rather, it conveys a series of instructions and parameters such as note-on and note-off messages, velocity, pitch bend, modulation, and more. This digital representation of musical data enables precise control over various aspects of sound, making it an indispensable tool for musicians, producers, and sound designers.
On the other hand, an audio interface acts as the intermediary device that facilitates the conversion of analog audio signals to digital data and vice versa. It serves as the gateway for connecting microphones, instruments, and other audio sources to your computer, providing high-fidelity audio inputs and outputs. In essence, an audio interface ensures that the nuances of your musical performances are accurately captured and reproduced in the digital domain, maintaining the integrity and quality of the sound throughout the recording and playback process.
When MIDI and audio interfaces are combined, they form a powerful synergy that empowers musicians and producers to seamlessly integrate their hardware instruments with digital audio workstations (DAWs). This integration allows for the recording, playback, and manipulation of MIDI data alongside high-quality audio signals, creating a cohesive environment for music production and performance.
Understanding the intricacies of MIDI and audio interfaces is pivotal for harnessing their full potential. It enables users to leverage the capabilities of MIDI controllers, synthesizers, drum machines, and other MIDI-compatible devices, while ensuring pristine audio capture and playback through the audio interface. By comprehending the roles and functionalities of these essential components, musicians and producers can craft immersive sonic experiences and unlock new dimensions of creativity within their music production endeavors.
Connecting MIDI to Audio Interface
Connecting MIDI devices to an audio interface is a pivotal step in establishing a seamless and efficient music production setup. Whether you're aiming to record MIDI performances, control virtual instruments, or synchronize hardware synthesizers with your digital audio workstation (DAW), the process of connecting MIDI to an audio interface is relatively straightforward. Here's a detailed guide to help you navigate this essential integration:
-
Select the Appropriate Cables: Begin by identifying the necessary cables for connecting your MIDI devices to the audio interface. MIDI devices typically utilize MIDI cables with 5-pin DIN connectors. Ensure that you have the required MIDI cables to establish the physical connection between your MIDI instruments and the audio interface.
-
Locate the MIDI Ports on the Audio Interface: Most audio interfaces feature MIDI input and output ports, allowing seamless integration with external MIDI devices. These ports are commonly labeled as MIDI In and MIDI Out, providing the necessary interfaces for bi-directional MIDI communication.
-
Connect the MIDI Devices to the Audio Interface: With the MIDI cables in hand, proceed to connect the MIDI Out port of your MIDI device to the MIDI In port of the audio interface. This establishes the transmission of MIDI data from your instrument to the audio interface, enabling it to be processed and utilized within your DAW.
-
Configure MIDI Settings: Once the physical connections are established, it's essential to configure the MIDI settings within your DAW to recognize the connected MIDI devices via the audio interface. Access the MIDI settings or preferences in your DAW and ensure that the MIDI input and output ports correspond to the ports on the audio interface where your MIDI devices are connected.
-
Test the MIDI Connection: To verify the successful connection, trigger MIDI events such as playing notes on a MIDI keyboard or sending MIDI sequences from an external MIDI controller. Monitor the input indicators within your DAW to confirm that MIDI data is being received from the connected devices via the audio interface.
By following these steps, you can seamlessly connect your MIDI devices to an audio interface, unlocking a world of creative possibilities within your music production environment. Whether you're capturing expressive MIDI performances, controlling virtual instruments, or integrating hardware synthesizers, the integration of MIDI and audio interfaces forms the backbone of a versatile and dynamic music production setup.
Setting up MIDI in DAW
Setting up MIDI within your digital audio workstation (DAW) is a pivotal aspect of leveraging the capabilities of MIDI devices connected to your audio interface. This process enables you to seamlessly integrate MIDI controllers, synthesizers, drum machines, and other MIDI-compatible instruments into your music production workflow. Here's a comprehensive guide to effectively configure MIDI settings in your DAW:
Accessing MIDI Preferences
Begin by accessing the MIDI preferences or settings within your DAW. This can typically be found within the software's preferences or settings menu. Once you've located the MIDI settings, you'll be presented with options to configure MIDI input and output ports, as well as other relevant parameters.
Selecting MIDI Input and Output Ports
Within the MIDI preferences, identify the MIDI input and output ports associated with your audio interface. The input port corresponds to the MIDI data received from your connected MIDI devices, while the output port facilitates the transmission of MIDI data from your DAW to external MIDI instruments or hardware modules.
Configuring MIDI Channels and Assignments
Depending on your specific MIDI setup, you may need to configure MIDI channels and assignments within your DAW. MIDI channels allow for the simultaneous control and playback of multiple MIDI devices, each operating on its designated channel. Ensure that the MIDI channels align with the settings on your MIDI devices to establish seamless communication.
Enabling MIDI Thru and Input Monitoring
Many DAWs offer features such as MIDI Thru and input monitoring, which are essential for real-time MIDI performance and recording. MIDI Thru enables the direct forwarding of MIDI data from the input port to the output port, facilitating the control of external MIDI instruments. Input monitoring allows you to monitor the MIDI input signal, ensuring that your performances are accurately captured during recording.
Mapping MIDI Controllers and Devices
If you're utilizing MIDI controllers such as keyboards, drum pads, or control surfaces, it's crucial to map these devices within your DAW. This involves assigning MIDI control parameters, such as knobs, sliders, and buttons, to specific functions within your music production software, allowing for intuitive and expressive control over various aspects of your production.
By meticulously configuring MIDI settings within your DAW, you can seamlessly integrate MIDI devices connected to your audio interface, unlocking a world of creative possibilities within your music production environment. Whether you're recording expressive MIDI performances, controlling virtual instruments, or synchronizing hardware synthesizers, the effective setup of MIDI in your DAW forms the foundation of a versatile and dynamic music production setup.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with careful setup, encountering technical hiccups when connecting MIDI to an audio interface is not uncommon. Understanding and addressing common issues can ensure a seamless music production experience. Here are some prevalent problems and their troubleshooting methods:
1. MIDI Signal Not Detected
- Issue: Your DAW fails to recognize MIDI input from connected devices.
- Troubleshooting:
- Check the MIDI connections: Ensure that the MIDI cables are securely connected to the appropriate ports on both the MIDI devices and the audio interface.
- Verify MIDI settings: Access the MIDI preferences in your DAW to confirm that the correct MIDI input ports are selected and enabled.
2. Latency and Timing Issues
- Issue: Delay in MIDI response or erratic timing during playback.
- Troubleshooting:
- Adjust buffer settings: In your audio interface settings or DAW preferences, optimize the buffer size to minimize latency without overburdening your system.
- Enable low-latency mode: Many audio interfaces offer a low-latency mode, which prioritizes real-time performance and reduces delay during MIDI playback and recording.
3. MIDI Channel Configuration
- Issue: MIDI devices are not responding as expected on specific channels.
- Troubleshooting:
- Verify MIDI channel assignments: Ensure that the MIDI channels on your devices align with the corresponding channels set within your DAW's MIDI preferences.
- Test different channels: Experiment with different MIDI channels to identify and resolve any channel-specific issues.
4. Audio Interface Driver Problems
- Issue: Unstable performance or erratic behavior of the audio interface.
- Troubleshooting:
- Update drivers: Visit the manufacturer's website to download and install the latest drivers for your audio interface, ensuring compatibility with your operating system and DAW.
- Check system resources: Insufficient system resources, such as CPU or RAM, can impact the performance of the audio interface. Close unnecessary applications and processes to alleviate resource strain.
5. MIDI Feedback and Looping
- Issue: Unwanted MIDI feedback or looping causing erratic behavior.
- Troubleshooting:
- Check MIDI Thru settings: Ensure that MIDI Thru functionality is appropriately configured to prevent unintended MIDI feedback loops.
- Isolate MIDI connections: If using multiple MIDI devices, disconnect and reintroduce them one at a time to identify and address potential feedback issues.
By proactively addressing these common issues and implementing the suggested troubleshooting methods, you can optimize the connectivity between MIDI devices and your audio interface, ensuring a seamless and frustration-free music production experience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the integration of MIDI with an audio interface is a transformative enabler for musicians and producers, offering a seamless bridge between analog musical instruments and the digital realm. By understanding the fundamental concepts of MIDI and audio interfaces, users can harness the full potential of these technologies to elevate their music production endeavors.
The process of connecting MIDI devices to an audio interface opens up a myriad of creative possibilities, from capturing expressive performances to controlling virtual instruments and hardware synthesizers. The physical connection, complemented by meticulous configuration within a digital audio workstation (DAW), forms the cornerstone of a versatile and dynamic music production setup.
Furthermore, the effective setup of MIDI within a DAW empowers users to seamlessly integrate MIDI controllers, synthesizers, drum machines, and other MIDI-compatible instruments, fostering a cohesive environment for music creation and performance. This integration not only streamlines the production process but also enhances the expressive capabilities of musicians, allowing for intuitive and nuanced control over their musical compositions.
Despite the potential for technical challenges, proactive troubleshooting methods can mitigate common issues, ensuring a smooth and uninterrupted music production experience. By addressing concerns such as MIDI signal detection, latency, channel configuration, audio interface stability, and MIDI feedback, users can optimize the connectivity between MIDI devices and their audio interface, fostering a frustration-free creative environment.
In essence, the synergy between MIDI and audio interfaces empowers musicians and producers to transcend traditional boundaries, seamlessly blending the analog and digital domains to craft immersive sonic experiences. Whether in the studio or on stage, the integration of MIDI with an audio interface unlocks a world of creative potential, enabling artists to realize their musical visions with precision and artistry. As technology continues to evolve, the symbiotic relationship between MIDI and audio interfaces will undoubtedly shape the future of music production, offering limitless opportunities for creative expression and sonic innovation.