Home>Production & Technology>Audio Interface>How To Hook Up Keyboard To Audio Interface


Audio Interface
How To Hook Up Keyboard To Audio Interface
Modified: February 19, 2024
Learn how to easily connect your keyboard to an audio interface for seamless recording and production. Enhance your audio quality with our step-by-step guide.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Connecting a keyboard to an audio interface can be a game-changer for musicians and producers. It opens up a world of possibilities, allowing you to record and manipulate the sounds of your keyboard with ease. Whether you’re a solo artist, part of a band, or a music producer, having a seamless connection between your keyboard and audio interface will greatly enhance your creative process.
But why do you need to connect your keyboard to an audio interface in the first place? Well, the audio interface acts as a bridge between your keyboard and your computer or recording device. It ensures that the audio signals from your keyboard are captured with the highest quality and are ready for recording, mixing, and editing.
There are various types of audio interfaces available, each offering different features and connectivity options. USB audio interfaces are commonly used and provide a simple and convenient way to connect your keyboard to your computer. On the other hand, more advanced audio interfaces, such as those with MIDI ports, offer additional flexibility for MIDI-based control and integration with software instruments.
In this article, we will cover everything you need to know about connecting a keyboard to an audio interface. We’ll discuss the different types of audio interfaces available and provide a step-by-step guide on how to hook up your keyboard to your audio interface. Additionally, we’ll address common troubleshooting issues you may encounter along the way.
So whether you’re a beginner or an experienced musician, let’s dive in and explore the world of connecting a keyboard to an audio interface.
Why Connect a Keyboard to an Audio Interface?
Connecting your keyboard to an audio interface offers a range of benefits that can greatly enhance your music production and performance capabilities. Here are a few reasons why it’s worth considering:
- High-Quality Sound: An audio interface ensures that the sound from your keyboard is captured with the utmost clarity and fidelity. It converts analog audio signals into digital data, allowing for precise recording and processing.
- Multitrack Recording: By connecting your keyboard to an audio interface, you can record each individual keyboard track separately. This opens up opportunities for more precise mixing and editing during the post-production stage.
- Reduced Latency: Latency refers to the delay between playing a note on your keyboard and hearing the sound. Audio interfaces typically have low latency, resulting in a more responsive and natural playing experience.
- Improved Control and Flexibility: Many audio interfaces come with features like built-in preamps, EQ controls, and gain adjustments. These allow you to shape your keyboard’s sound to your liking and make real-time adjustments during recordings or performances.
- Integration with Virtual Instruments and Software: Connecting your keyboard to an audio interface opens up possibilities for integrating virtual instruments and software plugins. You can use your keyboard to control virtual synthesizers, samplers, and other software-based instruments, expanding your sonic palette.
- External Monitoring: Audio interfaces often have dedicated headphone or monitor outputs, allowing you to connect external speakers or headphones for accurate monitoring of your keyboard’s sound.
Whether you’re recording in a studio or performing live, connecting your keyboard to an audio interface provides a more professional and versatile setup. It ensures that you can capture and manipulate the sounds of your keyboard with precision and versatility, enhancing your overall music production process.
Types of Audio Interfaces for Connecting Keyboards
When it comes to connecting a keyboard to an audio interface, there are different types of interfaces available, each offering unique features and connectivity options. Here are the main types of audio interfaces you can consider:
- USB Audio Interfaces: USB audio interfaces are the most common and user-friendly option for connecting keyboards. They allow you to connect your keyboard directly to your computer via a USB cable. These interfaces typically offer multiple inputs and outputs, allowing you to connect other audio sources as well. USB audio interfaces are compatible with most computers and are generally plug-and-play, making them a convenient choice for beginners and home studios.
- Firewire Audio Interfaces: Firewire interfaces provide a faster data transfer rate compared to USB interfaces, which can be beneficial when recording multiple channels simultaneously. Although Firewire is less common in newer computers, if your computer has a Firewire port, you can still find audio interfaces that support this connection type.
- PCIe Audio Interfaces: PCIe interfaces are designed to be installed directly inside your computer. They offer excellent performance due to the direct connection to the computer’s motherboard. However, they require opening up your computer and installing the interface card, making them less portable and more suitable for dedicated studio setups.
- Thunderbolt Audio Interfaces: Thunderbolt interfaces provide a high-speed connection between your keyboard and computer, allowing for low-latency and high-bandwidth audio transfer. They offer advantages for professional recording and mixing studios that require maximum performance and multiple input/output options.
- MIDI and Audio Interfaces: Some audio interfaces come with integrated MIDI ports alongside audio inputs and outputs. This allows you to connect your MIDI-enabled keyboard directly to the interface, providing seamless integration with your computer and software instruments. MIDI and audio interfaces are especially useful for controlling virtual instruments and recording MIDI data simultaneously.
When choosing an audio interface for your keyboard, consider factors such as the number of inputs and outputs you’ll need, the compatibility with your computer, and the specific features required for your music production needs. It’s also important to consider the audio quality and low-latency performance of the interface to ensure optimal recording and playback experiences.
Step-by-Step Guide on Connecting a Keyboard to an Audio Interface
Connecting your keyboard to an audio interface is a relatively straightforward process. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
- Choose the appropriate audio interface: Select an audio interface that meets your specific requirements in terms of input and output options, connectivity, and audio quality. Ensure that it is compatible with your computer and operating system.
- Power off your keyboard and computer: Before connecting any cables, make sure to power off your keyboard and computer. This will help protect the sensitive components and avoid any potential damage during the connection process.
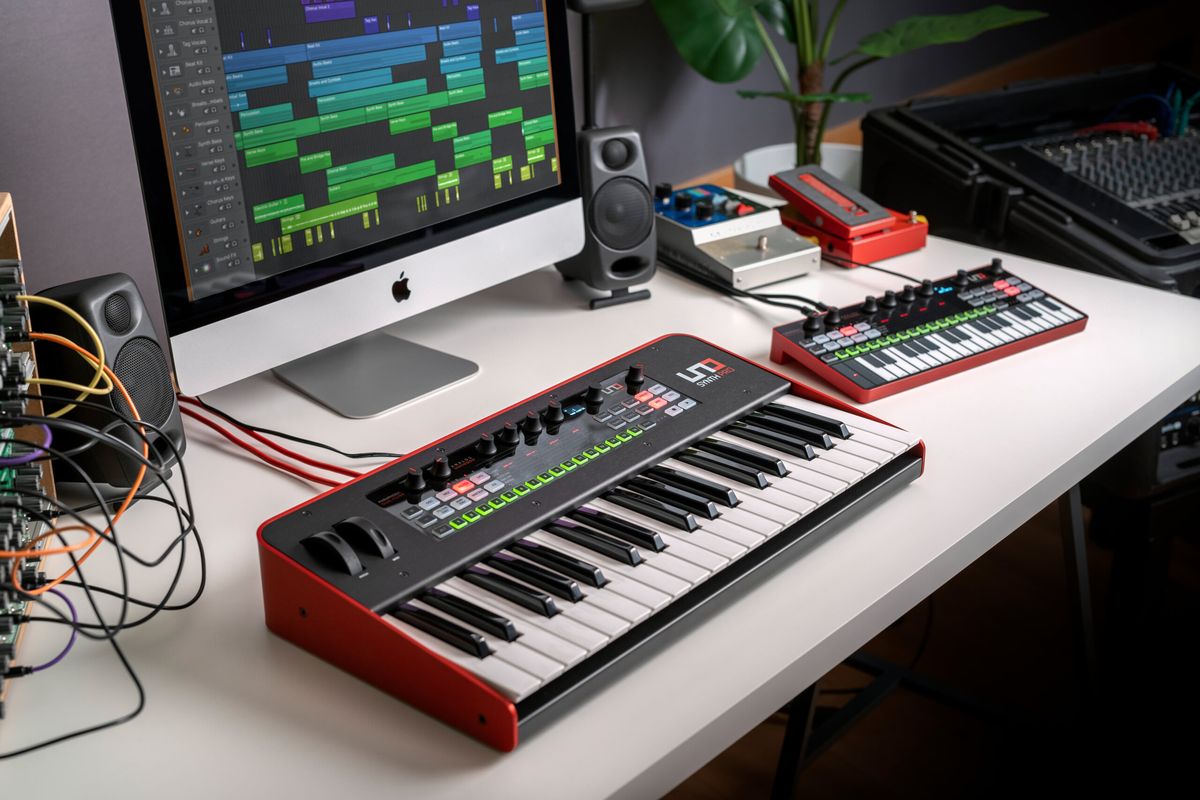
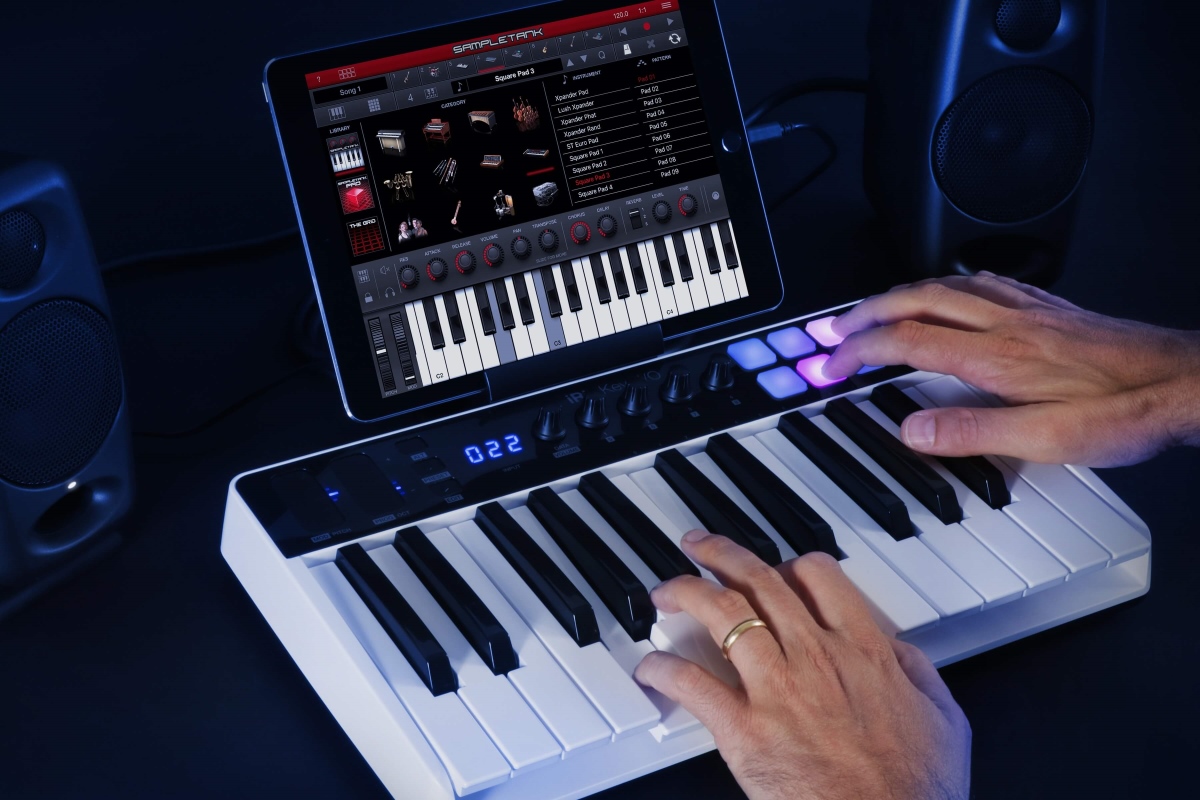
- Connect the keyboard to the audio interface: Use an appropriate cable to connect the output of your keyboard to one of the audio inputs on the audio interface. If your keyboard has different output options, such as 1/4″ TRS or XLR, ensure that the cable matches the corresponding input on the audio interface.
- Connect the audio interface to your computer: Use a USB, Firewire, Thunderbolt, or PCIe cable to connect the audio interface to your computer. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure proper connection and compatibility.
- Install the necessary drivers: Depending on the audio interface, you may need to install specific drivers or software provided by the manufacturer. These drivers enable communication between the interface and your computer’s operating system.
- Configure audio settings: Once the drivers are installed, access your computer’s audio settings or digital audio workstation (DAW) software and set the audio interface as the input and output device. Make sure the sample rate and buffer size are properly adjusted for optimum performance and low latency.
- Test the connection: Turn on your keyboard and computer, and play some notes on your keyboard. Monitor the sound through your audio interface’s headphone or monitor outputs. Ensure that you hear the sound from your keyboard without any distortion or latency issues.
- Configure MIDI settings (if applicable): If your audio interface has MIDI ports, you can connect your MIDI-enabled keyboard to the interface using MIDI cables. Configure the MIDI settings in your software or DAW to allow the transmission of MIDI data between your keyboard and computer.
- Start creating music: With your keyboard successfully connected to the audio interface, you are now ready to start creating music. Experiment with different recording techniques, software instruments, and effects to unleash your creativity and take your music production to new heights.
Remember, if you encounter any issues during the connection process or with the audio interface’s functionality, refer to the manufacturer’s documentation or contact their customer support for assistance. Each audio interface may have specific instructions or troubleshooting steps that can help resolve any problems you may encounter.
Troubleshooting Common Issues When Hooking Up a Keyboard to an Audio Interface
While connecting a keyboard to an audio interface is generally a straightforward process, you might encounter some common issues along the way. Here are a few troubleshooting tips to help you resolve potential problems:
- No sound: If you’re not hearing any sound from your keyboard, make sure that you have connected the keyboard’s output to the correct audio input on the interface. Additionally, ensure that the audio interface is properly connected to your computer and that the audio settings are configured correctly.
- Distorted sound: If you’re experiencing distorted sound, it could be due to incorrect input gain settings on your audio interface. Adjust the input gain control to an appropriate level to avoid clipping or distortion. Additionally, make sure that the output level of your keyboard is not too high, as this can also lead to distorted sound.
- Latency issues: If you’re noticing a delay between playing a note on your keyboard and hearing the sound, you may be experiencing latency. To reduce latency, try reducing the buffer size in your audio settings. However, keep in mind that setting the buffer size too low can cause audio dropouts or instabilities. It’s important to find the best balance between low latency and stable performance for your specific setup.
- Driver issues: If you’re using a USB audio interface, ensure that you have installed the necessary drivers provided by the manufacturer. Outdated or incompatible drivers can cause connectivity issues or instability. Check the manufacturer’s website for the latest driver updates and install them accordingly.
- MIDI connectivity: If you’re using MIDI to connect your keyboard to the audio interface, make sure you have connected the MIDI cables to the correct ports. Additionally, check the MIDI settings in your software or DAW to ensure that the MIDI signals are properly being transmitted and received.
- Crackling and popping sounds: If you’re hearing crackling or popping sounds while recording or playing back audio, it could be a sign of buffer underruns or system performance issues. Increase the buffer size in your audio settings to reduce the strain on your computer’s resources. Closing unnecessary background programs can also help improve system performance.
- Audio interface not recognized: If your computer is not recognizing the audio interface, try disconnecting and reconnecting the USB or other connection cables. If the issue persists, try connecting the audio interface to a different USB or Firewire port on your computer. You can also try restarting your computer or reinstalling the audio interface drivers.
If you encounter any persistent issues that you’re unable to resolve, it’s always recommended to consult the manufacturer’s documentation or contact their customer support for further assistance. They can provide specific troubleshooting steps or offer guidance tailored to your specific audio interface model and setup.
Conclusion
Connecting a keyboard to an audio interface opens up a world of possibilities for musicians, producers, and music enthusiasts alike. The ability to capture and manipulate the sound of your keyboard with high-quality and low-latency performance can greatly enhance your music production and performances.
In this article, we explored the reasons why connecting a keyboard to an audio interface is beneficial, such as achieving high-quality sound, enabling multitrack recording, and gaining more control and flexibility in your music production process. We also discussed the different types of audio interfaces available, including USB, Firewire, PCIe, Thunderbolt, and MIDI and audio interfaces.
We provided a step-by-step guide to help you connect your keyboard to an audio interface, emphasizing the importance of choosing the right interface, properly connecting cables, installing drivers, and configuring audio settings. Additionally, we offered troubleshooting tips for common issues you may encounter, such as no sound, distorted sound, latency issues, and driver problems.
Remember, each audio interface may have specific instructions and requirements, so it’s essential to refer to the manufacturer’s documentation for detailed guidance and support.
By following the steps and troubleshooting tips outlined in this article, you can ensure a successful connection between your keyboard and audio interface, paving the way for endless creative possibilities and a seamless music production experience. So go ahead, connect your keyboard to an audio interface, and unlock a new level of musical expression.