Home>Production & Technology>Audio Interface>How To Connect Multiple Headphones To An Audio Interface


Audio Interface
How To Connect Multiple Headphones To An Audio Interface
Modified: March 5, 2024
Learn how to connect multiple headphones to an audio interface for a seamless and optimal audio experience. Explore our step-by-step guide and maximize the functionality of your audio interface.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for AudioLover.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Audio Interfaces
- Types of Audio Interfaces
- Headphone Outputs on Audio Interfaces
- Limitations of Connecting Multiple Headphones to an Audio Interface
- Solutions for Connecting Multiple Headphones
- Method 1: Using a Headphone Distribution Amplifier
- Method 2: Using a Headphone Amplifier with Multiple Outputs
- Method 3: Using a Y-Splitter Cable
- Method 4: Using a Monitor Controller
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to the world of audio interfaces, where sound meets technology! Audio interfaces are essential tools for musicians, producers, and audio enthusiasts looking to record and playback high-quality audio. These devices serve as a bridge between your computer or recording device and your instruments, microphones, and headphones, allowing you to capture and monitor your audio with precision.
In this article, we will delve into the world of audio interfaces and explore how you can connect multiple headphones to these devices. Whether you are a music producer who needs to provide multiple artists with independent monitoring, a band member who wants everyone to listen to the mix simultaneously, or a teacher who requires multiple headphone connections for a classroom setup, we have got you covered!
Understanding the intricacies of audio interfaces is essential to make informed decisions about connecting headphones to these devices. We will explore the various types of audio interfaces available on the market, the different headphone outputs they offer, and the limitations you may encounter when connecting multiple headphones directly.
Fortunately, there are several solutions available to overcome these limitations and ensure that everyone can enjoy their own headphone mix. We will discuss four methods for connecting multiple headphones to an audio interface, including using a headphone distribution amplifier, a headphone amplifier with multiple outputs, a Y-splitter cable, and a monitor controller.
So, whether you are a music producer, a podcaster, or an avid music-lover, read on to discover the best methods for connecting multiple headphones to an audio interface and elevate your listening and recording experience to a whole new level!
Understanding Audio Interfaces
An audio interface is a vital component in any professional audio setup. It acts as the intermediary between your computer or recording device and your musical instruments, microphones, and headphones. Its primary function is to convert analog audio signals into digital data that can be processed and recorded by your computer, and vice versa.
Audio interfaces come in various shapes and sizes, offering different input and output options to suit various recording and playback needs. They typically connect to your computer or recording device via USB, Thunderbolt, or Firewire, providing the necessary connectivity and audio processing capabilities.
These devices are equipped with preamps, which amplify the weak signal from microphones and instruments to a level suitable for recording. They also feature converters that convert the analog audio signals into digital format, ensuring accurate and high-quality recording.
In addition to preamps and converters, audio interfaces often include other features such as headphone outputs, line outputs, MIDI ports, and phantom power for condenser microphones. These features allow you to connect and control various audio devices and peripherals, making the audio interface a versatile centerpiece of your recording setup.
When it comes to selecting an audio interface, it is crucial to consider factors such as the number and type of inputs and outputs, the sample rate and bit depth supported, and the overall build quality. These factors will determine the versatility, audio fidelity, and reliability of the device.
It’s important to note that the quality of your audio interface directly affects the quality of your recordings and playback. Investing in a high-quality audio interface can make a significant difference in the clarity and depth of your recordings, ensuring that your music or audio productions sound professional and polished.
Now that we have a basic understanding of audio interfaces, let’s explore the different types available and how they can accommodate multiple headphones for monitoring and playback.
Types of Audio Interfaces
Audio interfaces come in various types, each designed to fulfill specific recording and playback needs. Let’s take a closer look at the most common types of audio interfaces:
1. USB Audio Interfaces: USB audio interfaces are widely popular due to their ease of use and affordability. They connect to your computer via a USB port and provide a range of input and output options. USB audio interfaces are suitable for home studios, podcasting, and solo musicians who require a simple and portable setup.
2. Thunderbolt Audio Interfaces: Thunderbolt interfaces offer high-speed data transfer and low latency, making them ideal for professional audio production. Thunderbolt technology allows for multichannel recording and playback, making it a preferred choice for demanding recording projects and complex live performances.
3. PCIe Audio Interfaces: PCIe interfaces are internal audio cards that connect directly to your computer’s motherboard via a PCIe slot. These interfaces provide excellent performance and low latency, making them suitable for high-end recording studios and professional audio engineers.
4. Firewire Audio Interfaces: Firewire interfaces, although not as common as they used to be, still offer reliable and fast data transfer for audio recording and playback. They have multiple input and output options and are often favored by musicians and producers who require a stable and dedicated connection.
5. Ethernet Audio Interfaces: Ethernet interfaces utilize Ethernet connectivity to connect to your computer or recording device. They offer high-performance audio streaming capabilities and are commonly used in professional audio networking setups and large-scale studios.
6. Hybrid Audio Interfaces: Hybrid interfaces combine different connection types, such as USB and Thunderbolt, to offer maximum compatibility and flexibility. These interfaces are suitable for users who may need to connect to different devices or switch between setups frequently.
It’s important to consider your specific requirements, budget, and the compatibility with your recording software when choosing an audio interface. Whether you are a home recording enthusiast, a live performer, or a professional audio engineer, there is an audio interface available to meet your needs and provide the necessary connections for multiple headphones.
Headphone Outputs on Audio Interfaces
Headphone outputs on audio interfaces play a crucial role in providing a direct monitoring solution for musicians, producers, and audio enthusiasts. They allow you to connect your headphones to the audio interface and listen to the audio being recorded or played back in real-time.
Most audio interfaces come equipped with at least one dedicated headphone output, although some models may offer multiple headphone outputs to accommodate various monitoring needs. These outputs are typically located on the front panel of the audio interface for easy access.
The headphone outputs on audio interfaces are designed to deliver high-quality audio with low noise and distortion. They provide sufficient power to drive a wide range of headphones, from low-impedance headphones used for casual listening to high-impedance headphones used in professional studio monitoring.
Some audio interfaces offer additional features on their headphone outputs, such as individual volume control, stereo/mono switching, and output routing options. These features allow for personalized monitoring setups and the ability to adjust the headphone mix according to individual preferences.
When connecting headphones to an audio interface’s headphone output, it’s essential to consider the impedance matching. Impedance is the measure of opposition to the flow of electrical current, and different headphones have different impedance ratings. Matching the headphone impedance to the audio interface’s headphone output helps ensure optimal audio performance and prevent potential issues such as low volume or distorted sound.
While the headphone outputs on audio interfaces are convenient for personal monitoring, they have limitations when it comes to connecting multiple headphones directly. Most audio interfaces only have one or two headphone outputs, which may not be sufficient for scenarios where multiple individuals need to monitor the audio simultaneously.
However, there are solutions available to overcome this limitation and connect multiple headphones to an audio interface. In the following sections, we will explore four different methods to achieve this, ranging from headphone distribution amplifiers to monitor controllers.
Limitations of Connecting Multiple Headphones to an Audio Interface
While audio interfaces are powerful tools for recording and monitoring audio, they often have limitations when it comes to connecting multiple headphones directly. Here are some of the main limitations you may encounter:
1. Number of headphone outputs: Most audio interfaces are designed with a single or dual headphone output. This means that if you want to connect more than two headphones, you may need to find alternative solutions.
2. Shared monitoring: When multiple headphones are connected to a single headphone output on an audio interface, the audio being played through the interface is shared among all the connected headphones. This means that everyone hears the same mix, which may not be ideal in situations where individual monitoring is preferred.
3. Volume control: With a limited number of headphone outputs, controlling the volume for each individual becomes challenging. Adjusting the volume on one headphone affects the volume for all connected headphones, making it difficult to cater to different listening preferences.
4. Sound quality and power limitations: Depending on the specific audio interface, connecting multiple headphones directly can impact the overall sound quality and the available power for each headphone. It’s important to ensure that the audio interface is capable of driving multiple headphones simultaneously without compromising the audio performance.
5. Cable clutter: Connecting multiple headphones directly to an audio interface can result in cable clutter and a messy workspace. This can make it difficult to manage and can potentially lead to cable tangling or accidental disconnections.
To overcome these limitations, alternative solutions are available that allow for connecting multiple headphones to an audio interface. These solutions enable independent monitoring with individual volume control and ensure optimal sound quality for each listener. In the following sections, we will explore four methods to achieve this, providing you with the flexibility and convenience you need when connecting multiple headphones to your audio interface.
Solutions for Connecting Multiple Headphones
While the limitations of connecting multiple headphones directly to an audio interface may pose challenges, there are several effective solutions available. These solutions allow for independent monitoring, individual volume control, and ensure optimal sound quality for each listener. Here are four common methods for connecting multiple headphones to an audio interface:
1. Method 1: Using a Headphone Distribution Amplifier: A headphone distribution amplifier, also known as a headphone amp, is a device that takes a single audio signal and splits it into multiple outputs, each with its own dedicated headphone jack. It amplifies the audio signal to ensure that each connected headphone receives sufficient power and maintains high-quality sound. A headphone distribution amplifier is an excellent option for scenarios where multiple listeners need independent monitoring with separate volume control.
2. Method 2: Using a Headphone Amplifier with Multiple Outputs: Similar to a headphone distribution amplifier, a headphone amplifier with multiple outputs provides the flexibility to connect several headphones simultaneously. These amplifiers have multiple built-in headphone jacks, along with individual volume controls for each output. They are an ideal solution when you want to monitor audio with different headphone mixes or cater to specific preferences of each listener.
3. Method 3: Using a Y-Splitter Cable: A Y-splitter cable, as the name suggests, is a cable that splits a single headphone output into two separate outputs. It allows you to connect two headphones to a single headphone output on the audio interface. While this method doesn’t provide independent monitoring or individual volume control, it can be a quick and simple solution for occasional use or situations where only two listeners are involved.
4. Method 4: Using a Monitor Controller: A monitor controller is a device that allows for precise control of audio signals between multiple sources, such as audio interfaces, computers, and speakers. Some monitor controllers also feature multiple headphone outputs, enabling independent monitoring for multiple listeners. They often provide additional functionality, such as volume control, source selection, and even talkback capabilities, making them a versatile and comprehensive solution for managing multiple headphones and audio sources.
By utilizing one of these methods, you can overcome the limitations of connecting multiple headphones directly to an audio interface and achieve the desired monitoring setup. Whether you opt for a headphone distribution amplifier, a headphone amplifier with multiple outputs, a Y-splitter cable, or a monitor controller, each method offers its own advantages and allows for flexible, personalized monitoring setups.
Method 1: Using a Headphone Distribution Amplifier
A headphone distribution amplifier, also known as a headphone amp, is a dedicated device designed to split a single audio signal into multiple outputs. This method is particularly useful when you need to connect more than two headphones to your audio interface, providing independent monitoring for each listener.
Headphone distribution amplifiers come in various configurations, ranging from simple models with a few outputs to more advanced units with multiple channels and additional features. They typically connect to the headphone output of your audio interface and offer multiple headphone jacks, each with its own volume control.
By using a headphone distribution amplifier, you can ensure that each listener receives an optimal audio signal with sufficient power. The amplifier amplifies the audio signal coming from the audio interface, compensating for any potential loss in quality or volume caused by splitting the signal.
One of the key advantages of using a headphone distribution amplifier is the ability to provide independent monitoring. Each listener can adjust their own volume level to suit their preferences, allowing for a personalized monitoring experience. This is especially important in scenarios where different musicians or artists require different balances in their headphone mix.
Another advantage of headphone distribution amplifiers is their versatility. They often have multiple input options, allowing you to connect different audio sources to the amplifier. This means that you can use them not only with an audio interface, but also with mixing consoles, studio monitors, and other professional audio devices.
When selecting a headphone distribution amplifier, consider factors such as the number of outputs, build quality, and additional features like stereo/mono switching, durable headphone jacks, and overall audio fidelity. It’s also essential to ensure compatibility with your audio interface and the impedance requirements of your headphones.
Overall, using a headphone distribution amplifier provides a reliable and efficient solution for connecting multiple headphones to your audio interface. With separate volume control for each listener and the ability to maintain audio quality, this method is ideal for studio recording sessions, band practices, or any situation where independent monitoring is required.
Method 2: Using a Headphone Amplifier with Multiple Outputs
If you are looking for a solution that provides both flexibility and control when connecting multiple headphones to your audio interface, a headphone amplifier with multiple outputs is an excellent option. This method allows each listener to have their own dedicated headphone output with individual volume control.
A headphone amplifier with multiple outputs works similarly to a headphone distribution amplifier, but with the added advantage of individual volume control for each output. It takes the audio signal from your audio interface and amplifies it to provide sufficient power to multiple headphones simultaneously.
These headphone amplifiers often feature several built-in headphone jacks, allowing you to connect multiple headphones directly. Each output has its own volume control knob, giving the listener the freedom to adjust their headphone volume to their preference without affecting the others.
This method is particularly useful in recording or mixing sessions where different individuals require their own customized mix. Musicians can have their headphones connected to the respective outputs and adjust the volume as needed, enabling them to focus on their specific parts without compromising on the overall listening experience.
Headphone amplifiers with multiple outputs come in various configurations, accommodating different numbers of headphones. Some models offer two or four outputs, while others provide even more channels, catering to larger group environments such as educational institutions or music production studios.
When selecting a headphone amplifier with multiple outputs, consider factors such as audio fidelity, impedance compatibility with your headphones, build quality, and additional features such as stereo/mono switching or additional input options for flexible connectivity. It’s also important to ensure that the amplifier is compatible with your audio interface and can deliver sufficient power to drive multiple headphones simultaneously.
Overall, using a headphone amplifier with multiple outputs offers a versatile, customizable, and user-friendly solution for connecting multiple headphones to your audio interface. With individual volume control for each listener, this method is perfect for collaborative recording sessions, band practices, or any scenario where personalized monitoring is essential.
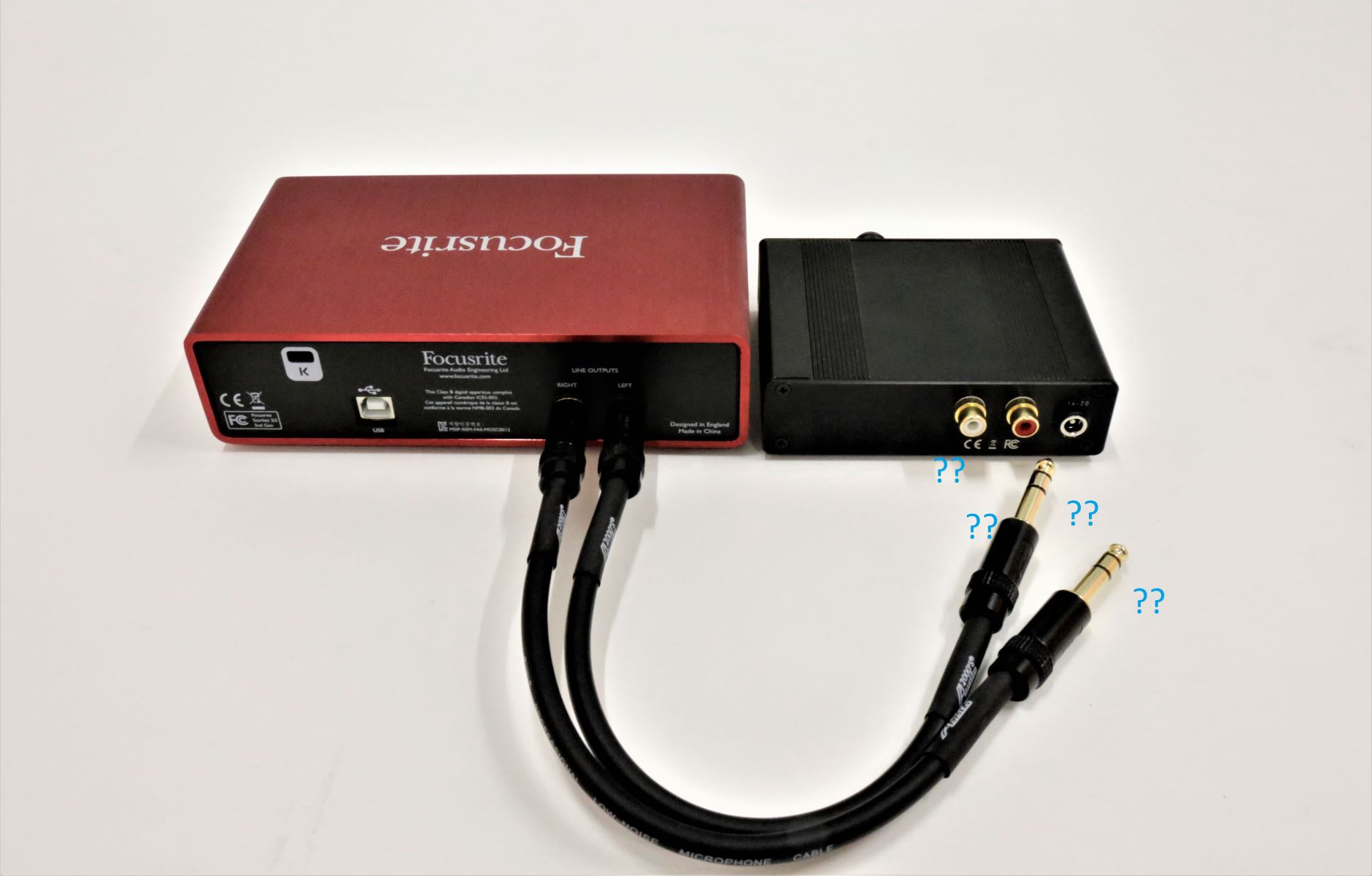
Method 3: Using a Y-Splitter Cable
If you need a quick and simple solution for connecting two headphones to your audio interface, using a Y-splitter cable can be a convenient option. This method allows you to split the audio signal from a single headphone output into two separate outputs, enabling two listeners to monitor simultaneously.
A Y-splitter cable consists of a single 1/4″ or 3.5mm stereo jack on one end and two 1/4″ or 3.5mm stereo jacks on the other end. It typically connects to the headphone output of your audio interface, splitting the audio signal into two separate outputs. Each output can then be connected to a pair of headphones, allowing two listeners to monitor the audio simultaneously.
While using a Y-splitter cable is a straightforward solution, it’s important to note its limitations. Since the audio signal is simply split without any amplification or control, both listeners will hear the same mix at the same volume. This means that individual volume control or independent monitoring is not possible with this method.
A Y-splitter cable is best suited for situations where only two listeners are involved, and the sharing of the same mix is acceptable. It can be useful for casual listening, practicing with a friend, or situations where the need for separate mixes or volume control is not necessary.
When choosing a Y-splitter cable, make sure to select a cable with sturdy construction and good shielding to minimize interference. It’s also important to ensure that the cable matches the connectors of your audio interface and headphones, whether they are 1/4″ or 3.5mm stereo jacks.
It’s important to note that using a Y-splitter cable to connect more than two headphones is not recommended, as it can lead to decreased volume and potential audio quality degradation.
In summary, if you only need to connect two headphones to your audio interface and are comfortable with sharing the same audio mix, using a Y-splitter cable offers a simple and cost-effective solution. However, for scenarios that require individual volume control or accommodate more than two listeners, alternative methods such as a headphone distribution amplifier or a headphone amplifier with multiple outputs would be more suitable.
Method 4: Using a Monitor Controller
If you’re looking for a comprehensive solution for connecting multiple headphones to your audio interface, using a monitor controller is an excellent choice. A monitor controller not only provides multiple headphone outputs but also offers additional functionality and control over your audio sources and monitoring setup.
A monitor controller acts as a central hub for managing audio signals between multiple sources, such as audio interfaces, computers, and speakers. Many monitor controllers come equipped with multiple headphone outputs, allowing you to connect multiple headphones directly and provide independent monitoring for each listener.
One of the key advantages of using a monitor controller is the control it offers over your monitoring setup. These devices typically include features such as volume control, source selection, and input switching, allowing you to easily adjust the audio levels and select between different audio sources. This level of control is especially beneficial in recording studios or professional audio environments where flexibility and precision are crucial.
Monitor controllers often offer options for individual volume control for each headphone output. This means that each listener can adjust their own headphone volume level independently, providing a personalized monitoring experience and accommodating different listening preferences.
In addition to headphone outputs, monitor controllers may have other useful features such as talkback functionality, integrated cue mixes, or even built-in headphone amplifiers. These additional features make them highly versatile and suitable for a wide range of professional audio applications.
When choosing a monitor controller, consider factors such as the number of headphone outputs, the quality of the built-in amplifiers, the overall build quality, and compatibility with your audio interface and headphones. Also, look for features that align with your specific requirements, such as talkback functionality for communication during recording sessions or multiple input options for flexible connectivity.
Using a monitor controller as a solution for connecting multiple headphones to your audio interface offers the benefits of independent monitoring, individual volume control, and enhanced control over your entire monitoring setup. It’s an ideal choice for professional studios, production environments, or any situation where precise monitoring and flexibility are essential.
Conclusion
Connecting multiple headphones to your audio interface opens up a world of possibilities for collaborative recording sessions, band practices, and professional audio environments. While audio interfaces may have limitations when it comes to directly connecting multiple headphones, several effective solutions are available to overcome these challenges.
We explored four methods for connecting multiple headphones to an audio interface: using a headphone distribution amplifier, a headphone amplifier with multiple outputs, a Y-splitter cable, and a monitor controller. Each method offers its own advantages and caters to different needs and preferences.
If you require independent monitoring with individual volume control, a headphone distribution amplifier or a headphone amplifier with multiple outputs is an excellent choice. These devices ensure that each listener can personalize their monitoring experience and maintain optimal sound quality.
On the other hand, if you only need to connect two headphones and sharing the same audio mix is acceptable, a Y-splitter cable provides a quick and straightforward solution. However, it’s important to note that this method does not offer individual volume control or independent monitoring.
For a comprehensive and versatile solution, a monitor controller is an ideal option. In addition to multiple headphone outputs, a monitor controller provides additional control over your audio sources and monitoring setup, allowing for precise adjustments and flexibility in professional audio environments.
When selecting your method, consider factors such as the number of headphones you need to connect, the level of control you require, compatibility with your audio interface, and the quality of the audio signal and power delivery.
In conclusion, with the right method and equipment, connecting multiple headphones to your audio interface becomes a seamless and enjoyable experience. Whether you’re a musician, producer, or audio enthusiast, leveraging these solutions will enhance your monitoring capabilities and elevate your recording and playback experience to new heights.